| Citation: |
Ting Zhi, Tao Tao, Xiaoyan Liu, Junjun Xue, Jin Wang, Zhikuo Tao, Yi Li, Zili Xie, Bin Liu. Low-threshold lasing in a plasmonic laser using nanoplate InGaN/GaN[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(12): 122803. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/12/122803
T Zhi, T Tao, X Y Liu, J J Xue, J Wang, Z K Tao, Y Li, Z L Xie, B Liu, Low-threshold lasing in a plasmonic laser using nanoplate InGaN/GaN[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(12): 122803. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/12/122803.
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
Low-threshold lasing in a plasmonic laser using nanoplate InGaN/GaN
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/12/122803
More Information-
Abstract
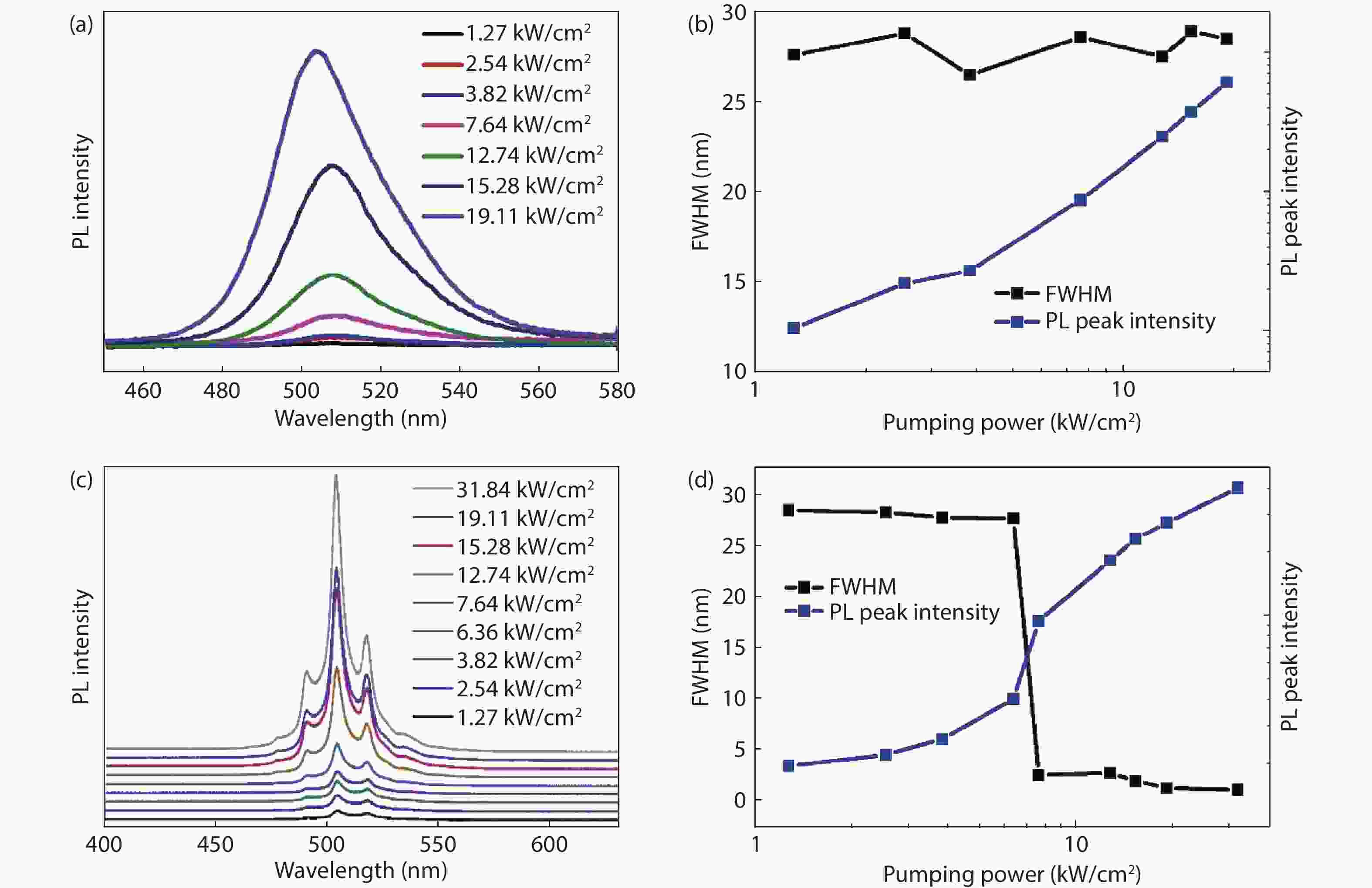
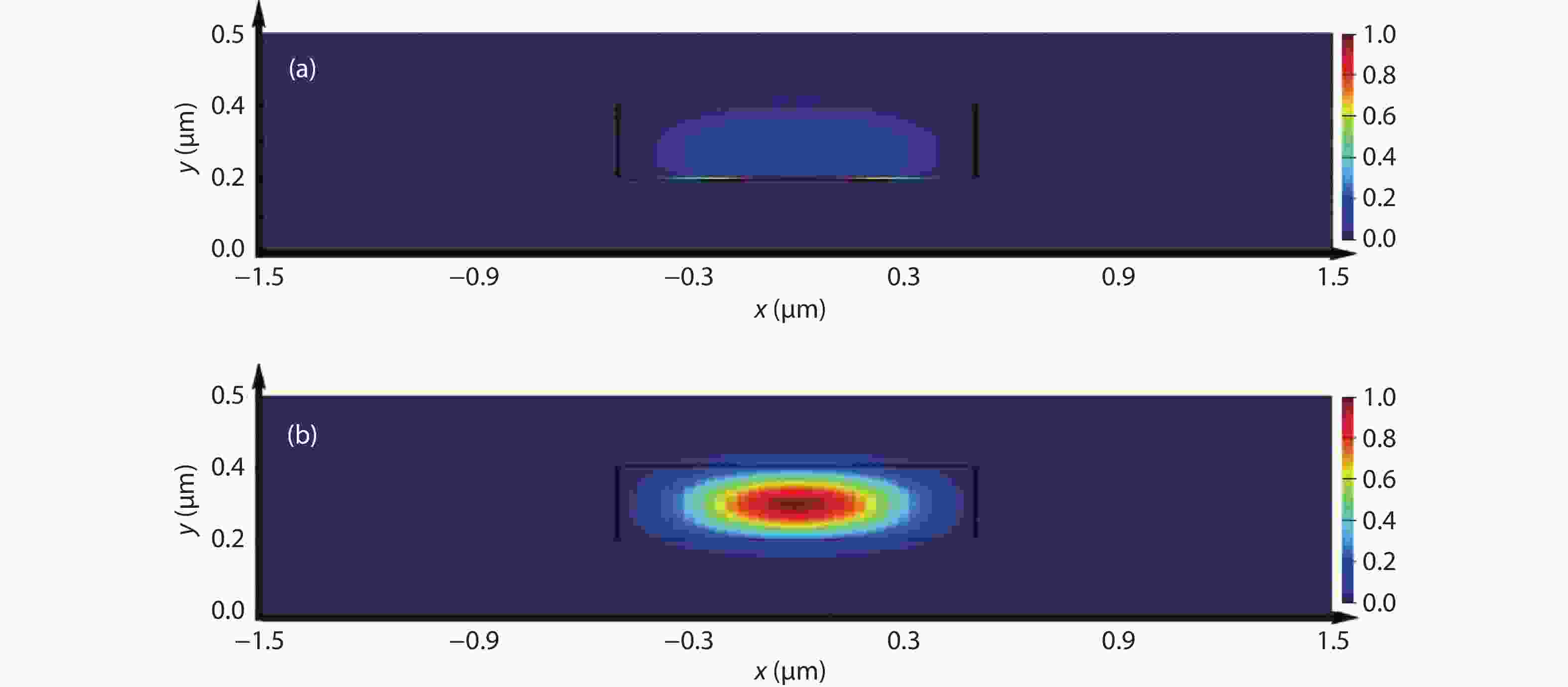
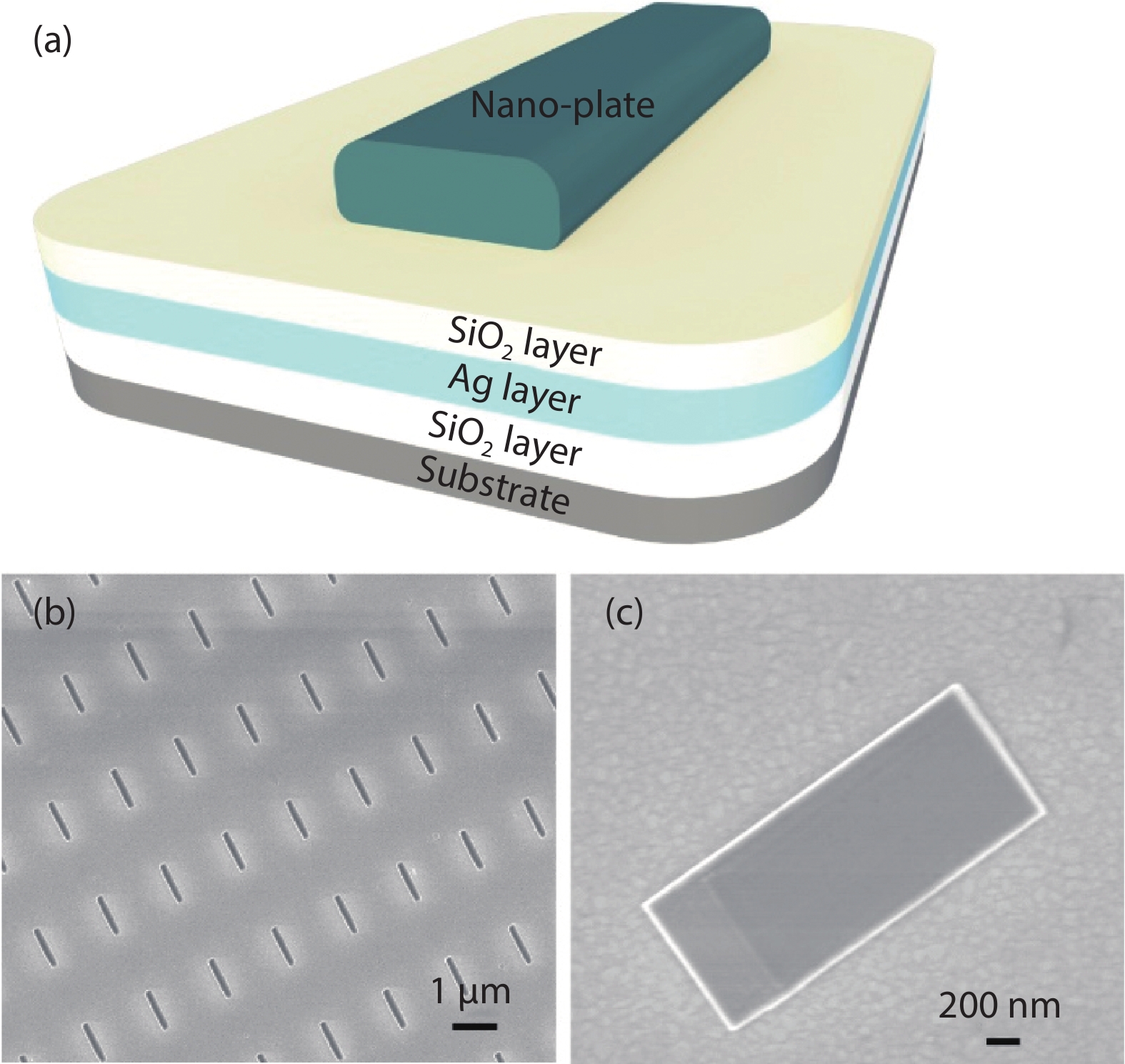
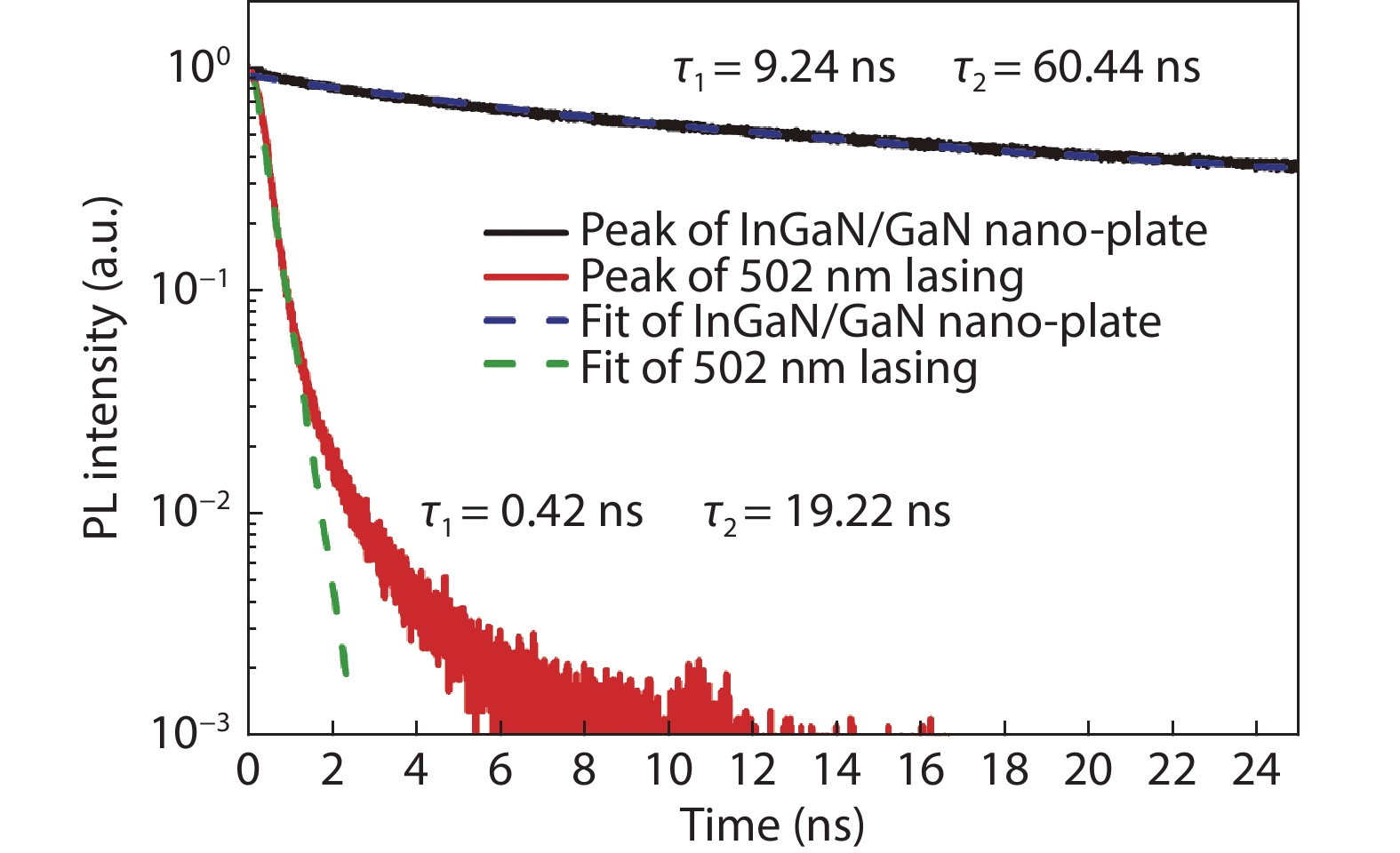
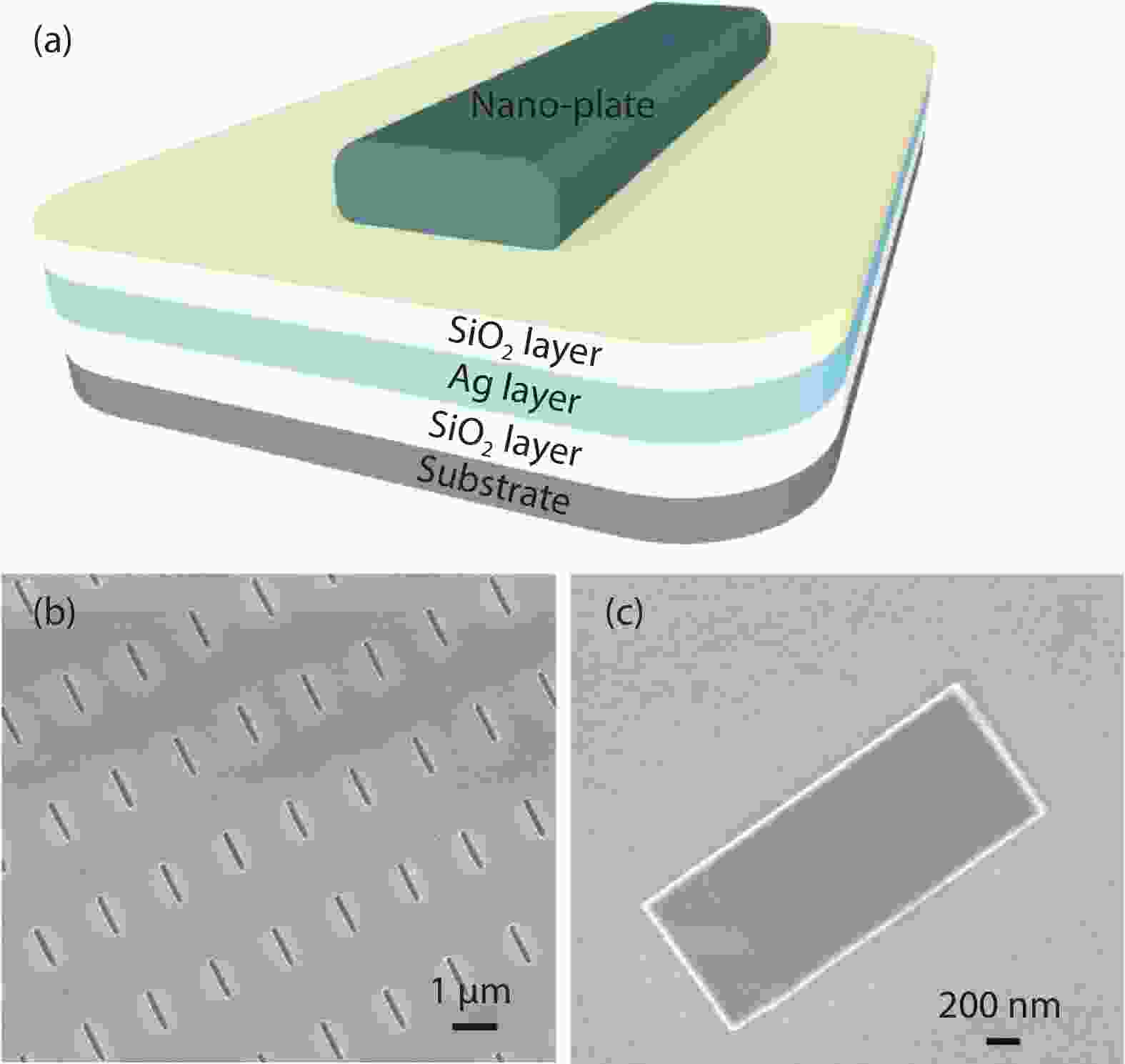
Plasmonic nanolaser as a new type of ultra-small laser, has gain wide interests due to its breaking diffraction limit of light and fast carrier dynamics characters. Normally, the main problem that need to be solved for plasmonic nanolaser is high loss induced by optical and ohmic losses, which leads to the low quality factor. In this work, InGaN/GaN nanoplate plasmonic nanolaser with large interface area were designed and fabricated, where the overlap between SPs and excitons can be enhanced. The lasing threshold is calculated to be ~6.36 kW/cm2, where the full width at half maximum (FWHM) drops from 27 to 4 nm. And the fast decay time at 502 nm (sharp peak of stimulated lasing) is estimated to be 0.42 ns. Enhanced lasing characters are mainly attributed to the strong confinement of electromagnetic wave in the low refractive index material, which improve the near field coupling between SPs and excitons. Such plasmonic laser should be useful in data storage applications, biological application, light communication, especially for optoelectronic devices integrated into a system on a chip.-
Keywords:
- surface plasmon,
- plasmonic laser,
- GaN
-
References
[1] Goh X M, Zheng Y H, Tan S J, et al. Three-dimensional plasmonic stereoscopic prints in full colour. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 1 doi: 10.1038/ncomms6361[2] Murphy E. Enabling optical communication. Nature Photon, 2010, 4, 287 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.107[3] Chen Y C, Chen Q S, Fan X D. Lasing in blood. Optica, 2016, 3, 809 doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.3.000809[4] Tchernycheva M, Messanvi A, de Luna Bugallo A, et al. Integrated photonic platform based on InGaN/GaN nanowire emitters and detectors. Nano Lett, 2014, 14, 3515 doi: 10.1021/nl501124s[5] Hill M T, Oei Y S, Smalbrugge B, et al. Lasing in metallic-coated nanocavities. Nat Photonics, 2007, 1, 589 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.171[6] Chang S W, Lin T R, Chuang S L. Theory of plasmonic fabry-perot nanolasers. Opt Express, 2010, 18, 15039 doi: 10.1364/OE.18.015039[7] McCall S L, Levi A F J, Slusher R E, et al. Whispering-gallery mode microdisk lasers. Appl Phys Lett, 1992, 60, 289 doi: 10.1063/1.106688[8] Ma R M, Wei X L, Dai L, et al. Light coupling and modulation in coupled nanowire ring-Fabry-Pérot cavity. Nano Lett, 2009, 9, 2697 doi: 10.1021/nl901190v[9] Bergman D J, Stockman M I. Surface plasmon amplification by stimulated emission of radiation: Quantum generation of coherent surface plasmons in nanosystems. Phys Rev Lett, 2003, 90, 027402 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.027402[10] Oulton R F, Sorger V J, Zentgraf T, et al. Plasmon lasers at deep subwavelength scale. Nature, 2009, 461, 629 doi: 10.1038/nature08364[11] Ma R M, Oulton R F, Sorger V J, et al. Room-temperature sub-diffraction-limited plasmon laser by total internal reflection. Nat Mater, 2011, 10, 110 doi: 10.1038/nmat2919[12] Lu Y J, Wang C Y, Kim J, et al. All-color plasmonic nanolasers with ultralow thresholds: Autotuning mechanism for single-mode lasing. Nano Lett, 2014, 14, 4381 doi: 10.1021/nl501273u[13] González-Tudela A, Huidobro P A, Martín-Moreno L, et al. Theory of strong coupling between quantum emitters and propagating surface plasmons. Phys Rev Lett, 2013, 110, 126801 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.126801[14] Eaton S W, Fu A, Wong A B, et al. Semiconductor nanowire lasers. Nat Rev Mater, 2016, 1, 1 doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.28[15] Liu S L, Sheng B W, Wang X Q, et al. Molecular beam epitaxy of single-crystalline aluminum film for low threshold ultraviolet plasmonic nanolasers. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112, 231904 doi: 10.1063/1.5033941[16] Ma Y G, Guo X, Wu X Q, et al. Semiconductor nanowire lasers. Adv Opt Photon, 2013, 5, 216 doi: 10.1364/AOP.5.000216[17] Zhang Q, Li G, Liu X, et al. A room temperature low-threshold ultraviolet plasmonic nanolaser. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 4953 doi: 10.1038/ncomms5953[18] Tian P F, McKendry J J D, Gu E D, et al. Fabrication, characterization and applications of flexible vertical InGaN micro-light emitting diode arrays. Opt Express, 2016, 24, 699 doi: 10.1364/OE.24.000699[19] Tao T, Zhi T, Liu B, et al. Manipulable and hybridized, ultralow-threshold lasing in a plasmonic laser using elliptical InGaN/GaN nanorods. Adv Funct Mater, 2017, 27, 1703198 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201703198[20] Tao T, Zhi T, Liu B, et al. Electron-beam-driven III-nitride plasmonic nanolasers in the deep-UV and visible region. Small, 2020, 16, 1906205 doi: 10.1002/smll.201906205[21] Liu B, Smith R, Athanasiou M, et al. Temporally and spatially resolved photoluminescence investigation of ($11\bar{2}2$ ) semi-polar InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells grown on nanorod templates. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 105, 261103 doi: 10.1063/1.4905191[22] Liu B, Zhang R, Xie Z L, et al. Nonpolar m-plane thin film GaN and InGaN/GaN light-emitting diodes on LiAlO2(100) substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 91, 253506 doi: 10.1063/1.2825419 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: