| Citation: |
Chaohui Li, Jun Deng, Weiye Sun, Leilei He, Jianjun Li, Jun Han, Yanli Shi. Improvement of tunnel compensated quantum well infrared detector[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019, 40(12): 122902. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/12/122902
C H Li, J Deng, W Y Sun, L L He, J J Li, J Han, Y L Shi, Improvement of tunnel compensated quantum well infrared detector[J]. J. Semicond., 2019, 40(12): 122902. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/12/122902.
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
Improvement of tunnel compensated quantum well infrared detector
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/12/122902
More Information-
Abstract
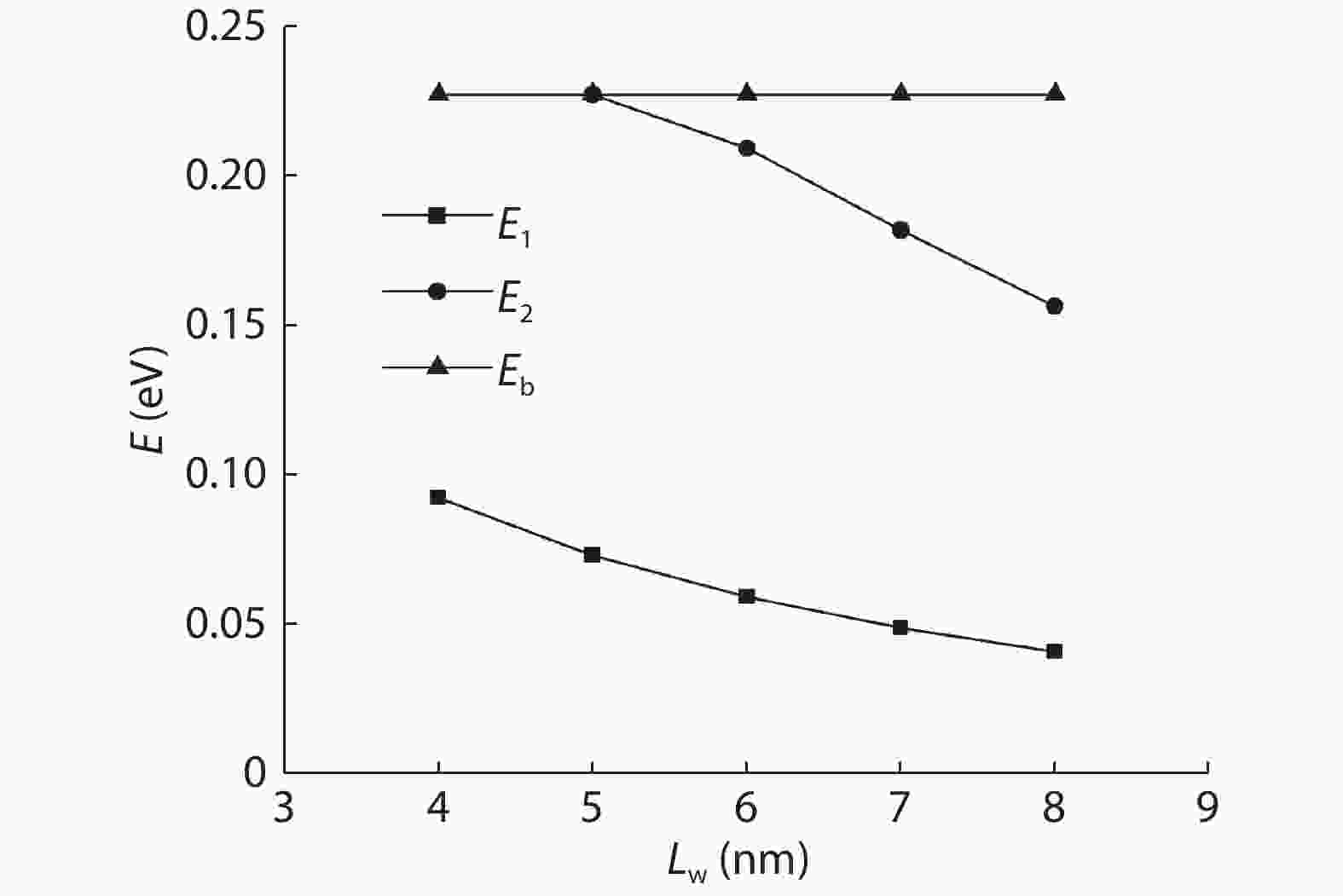
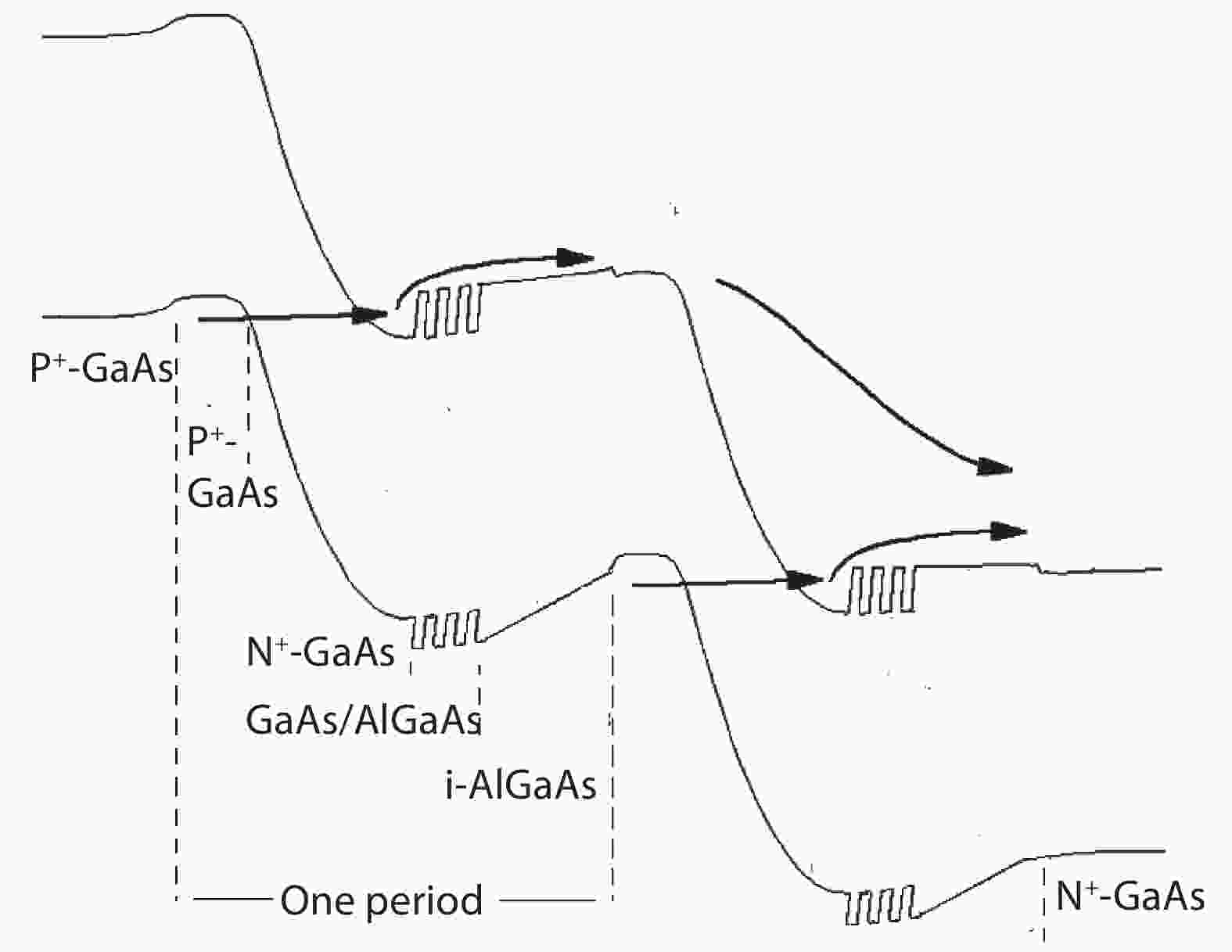
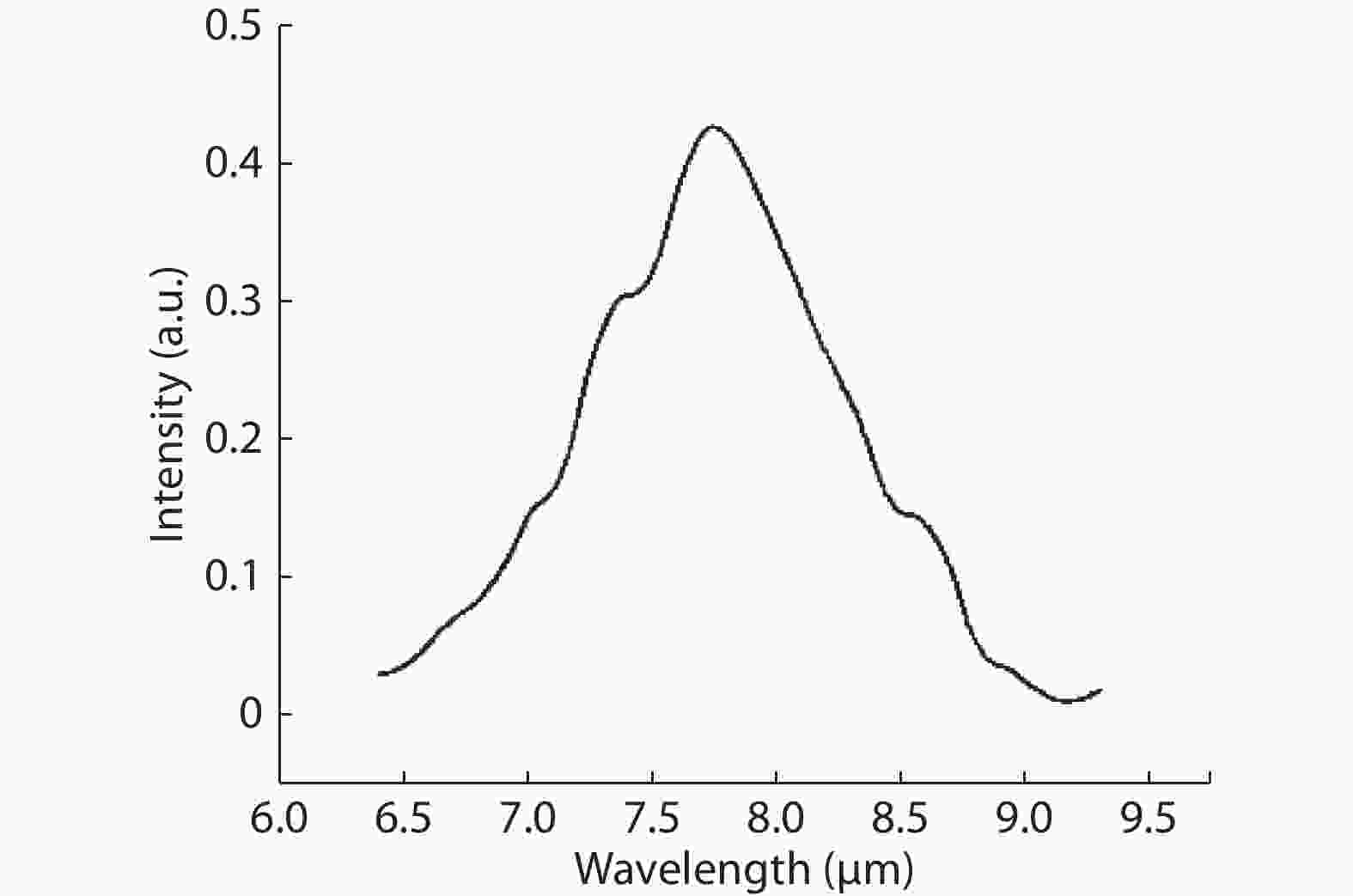
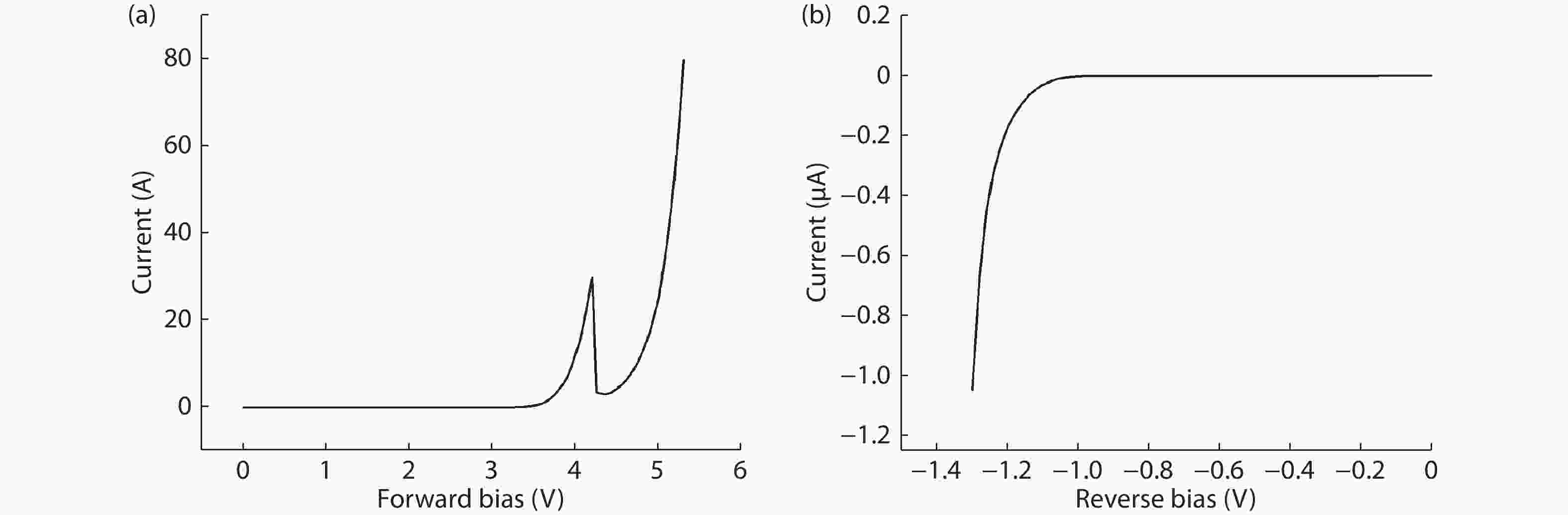
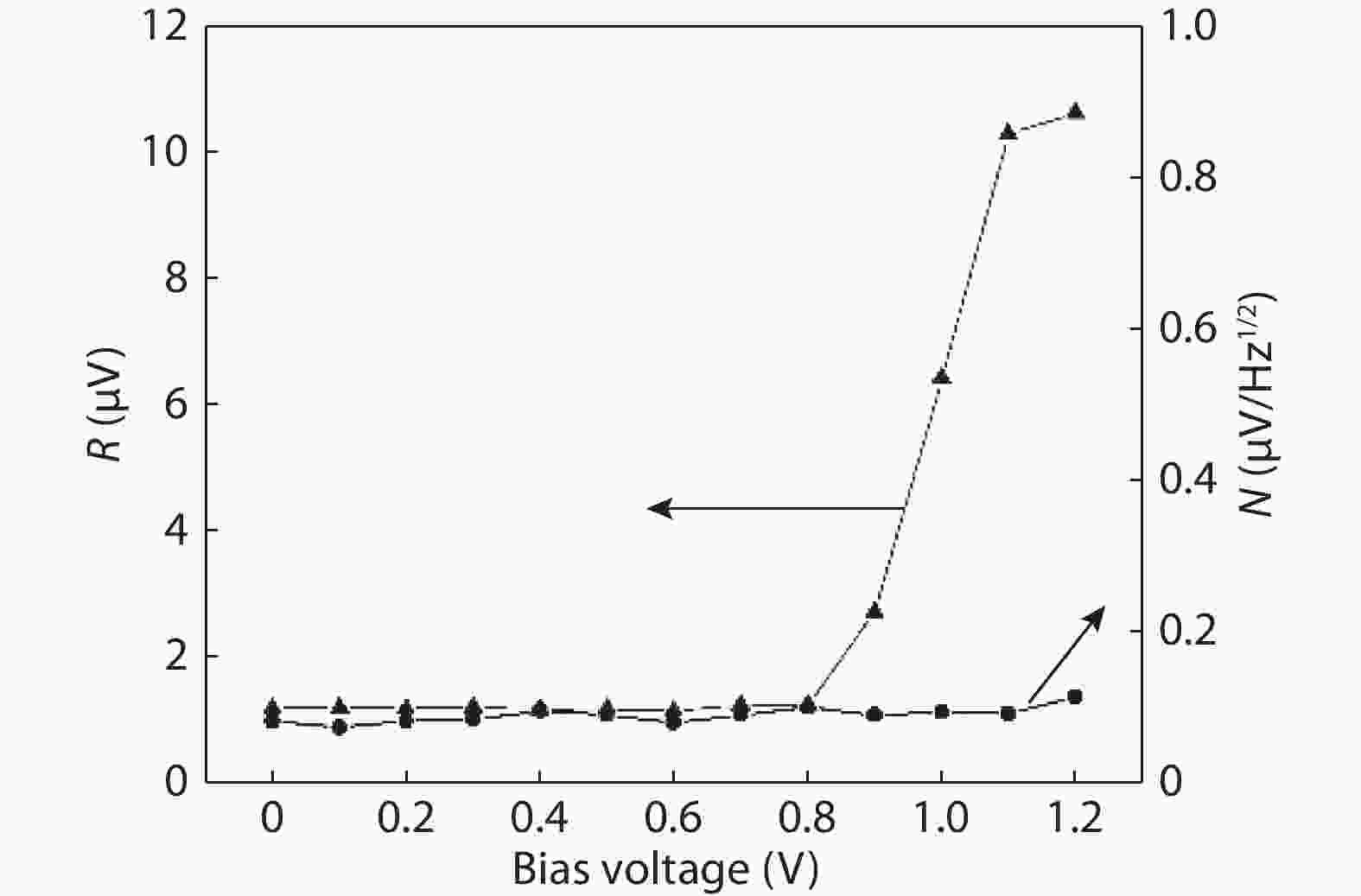
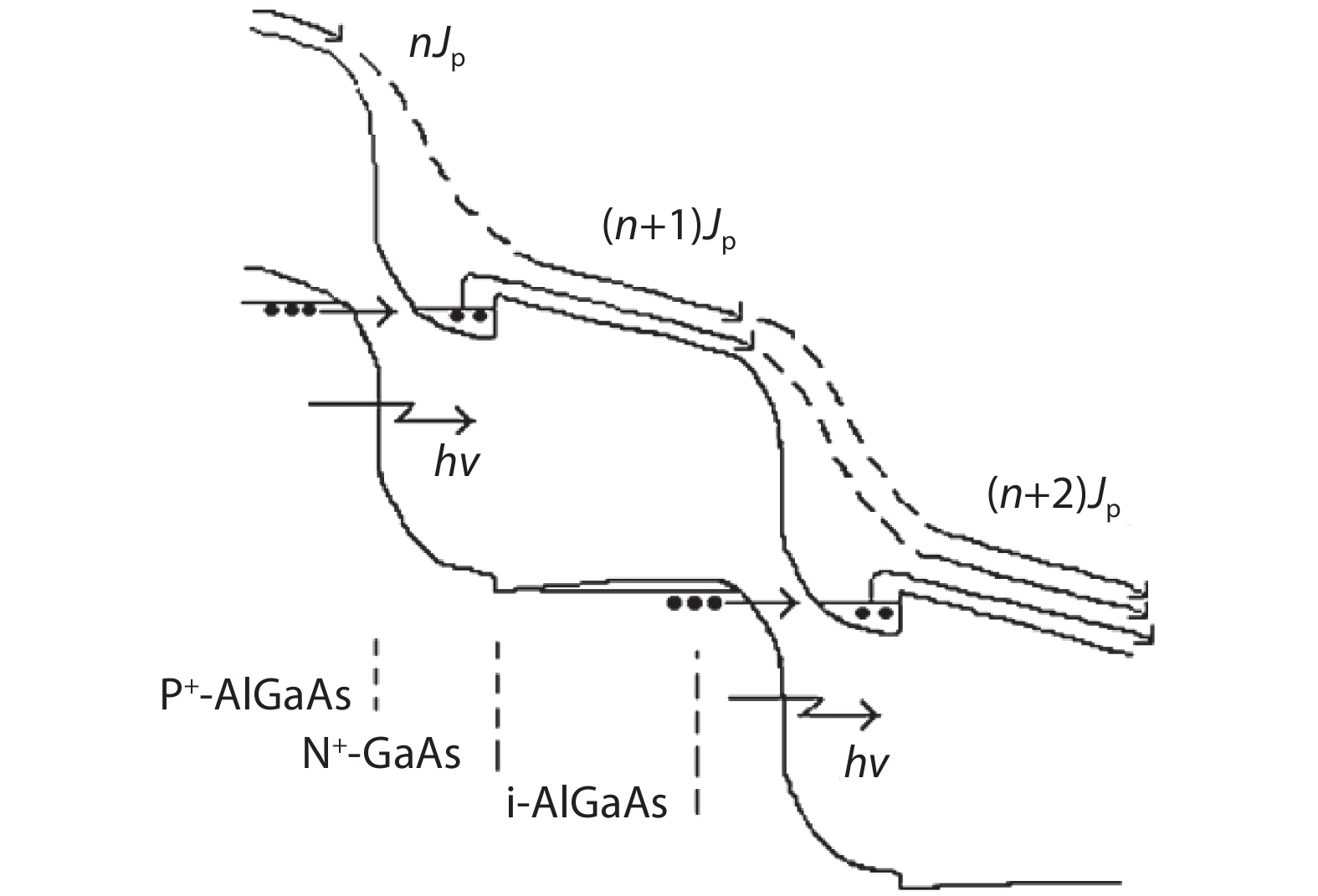
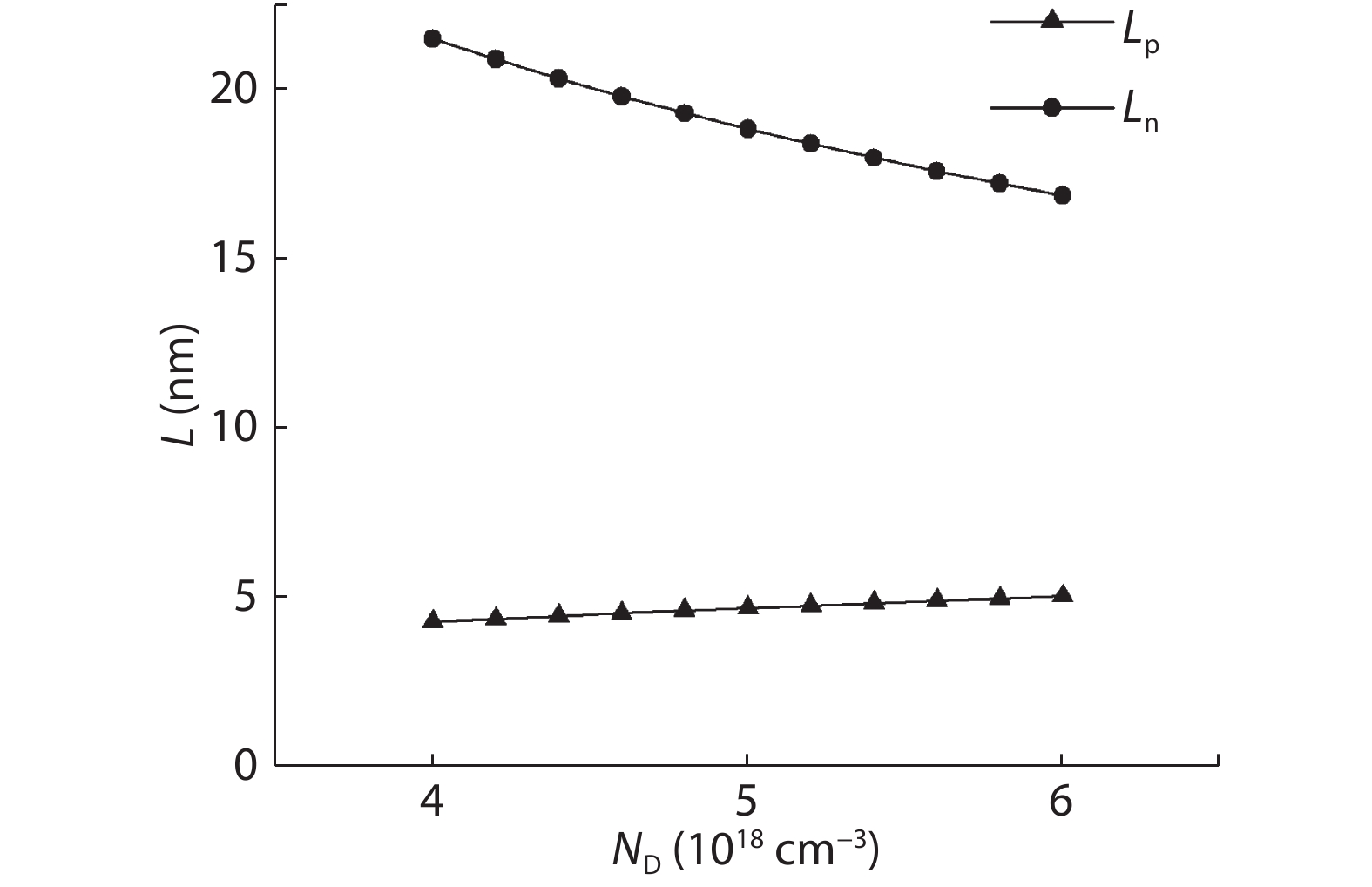
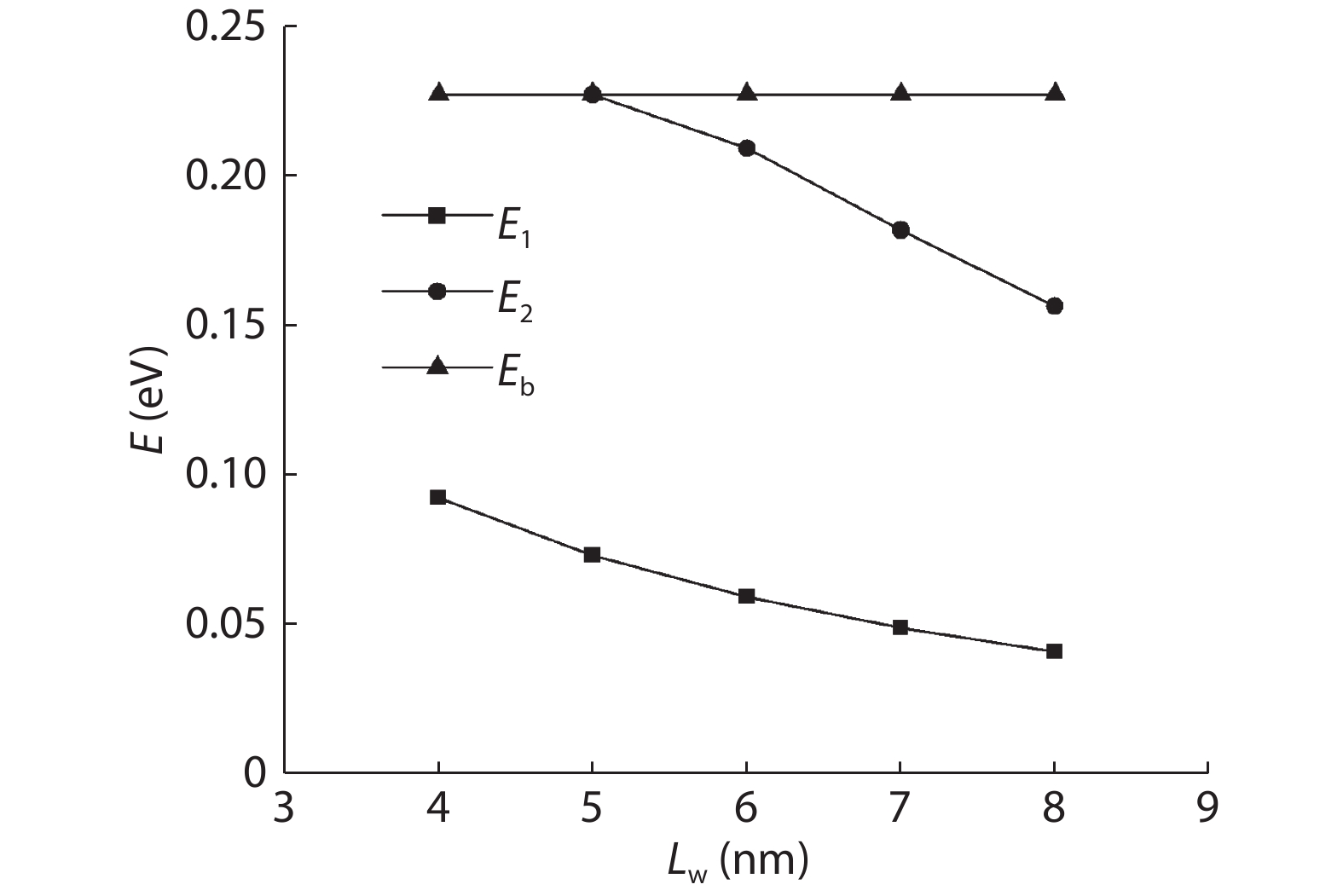
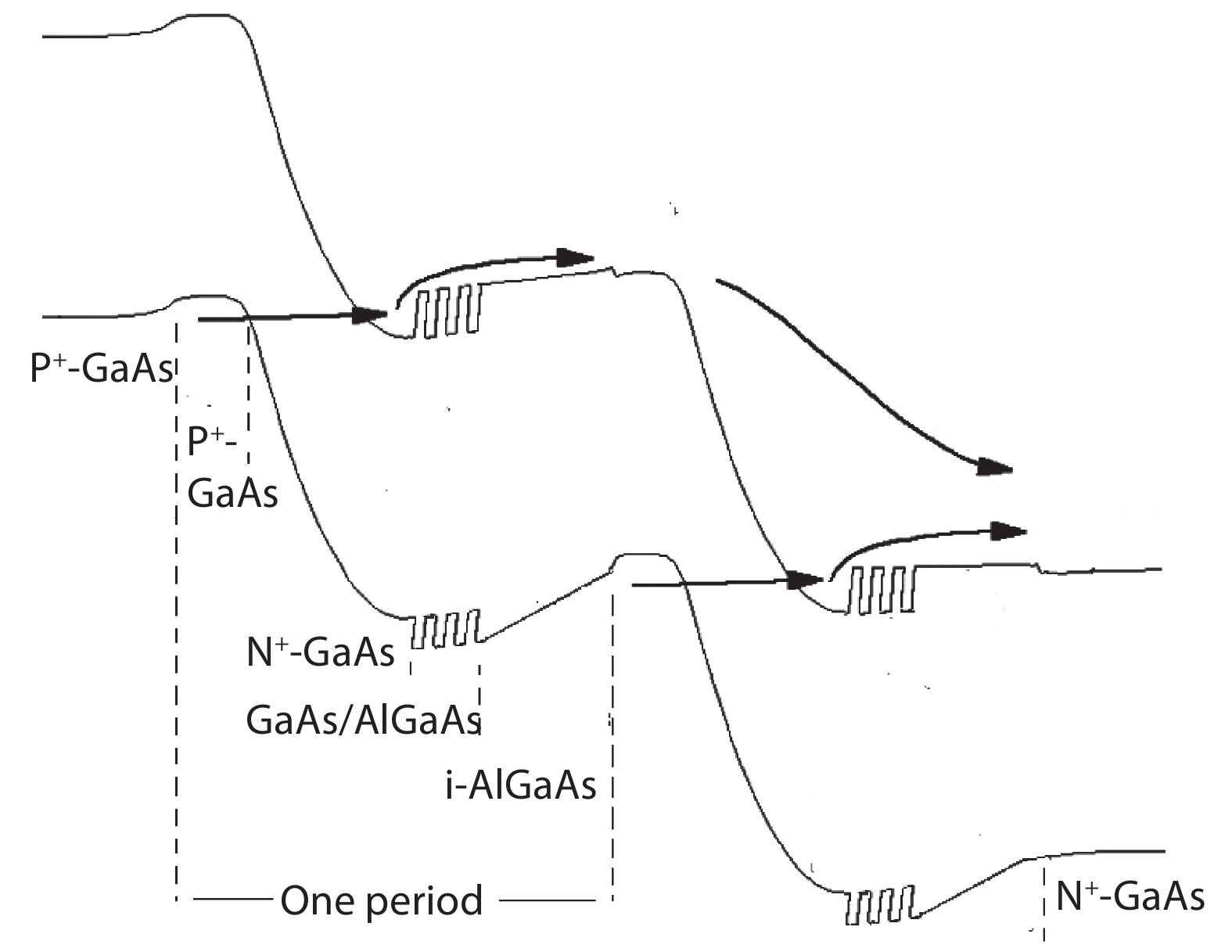
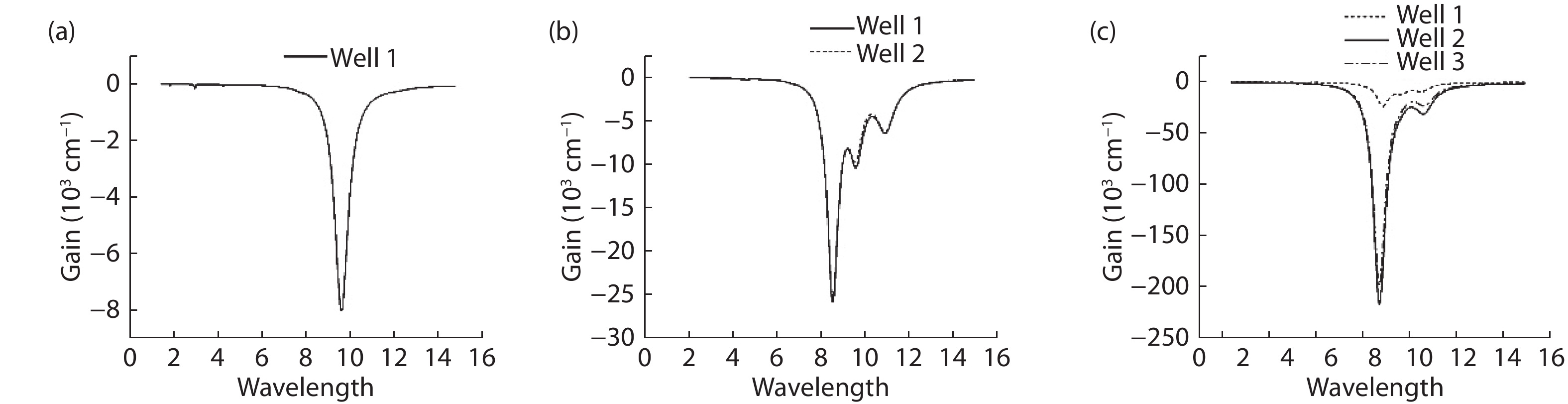
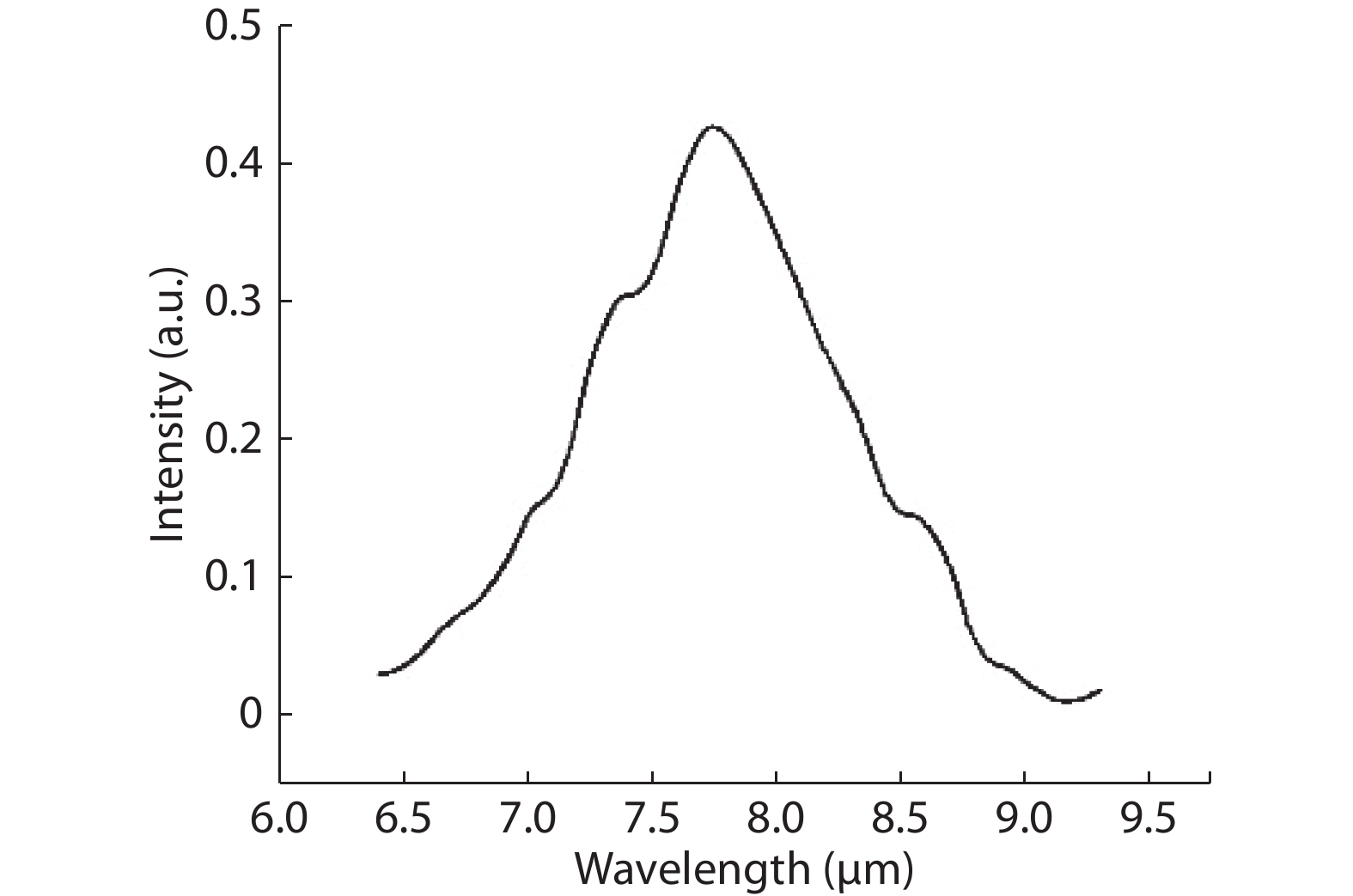
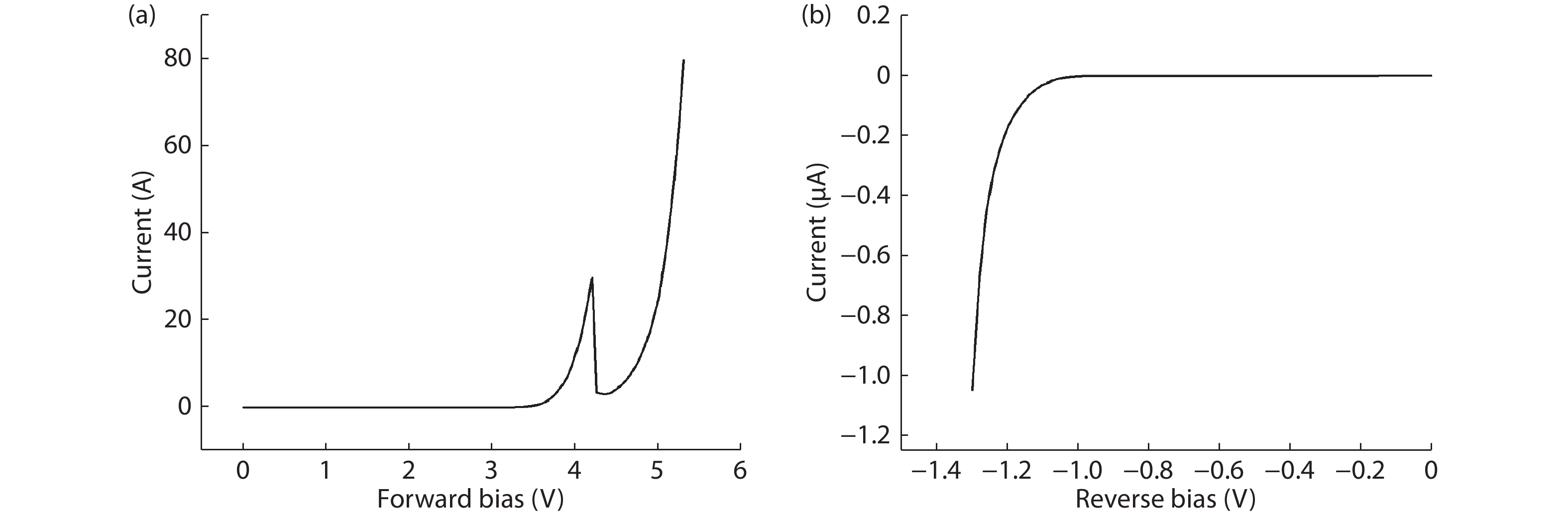
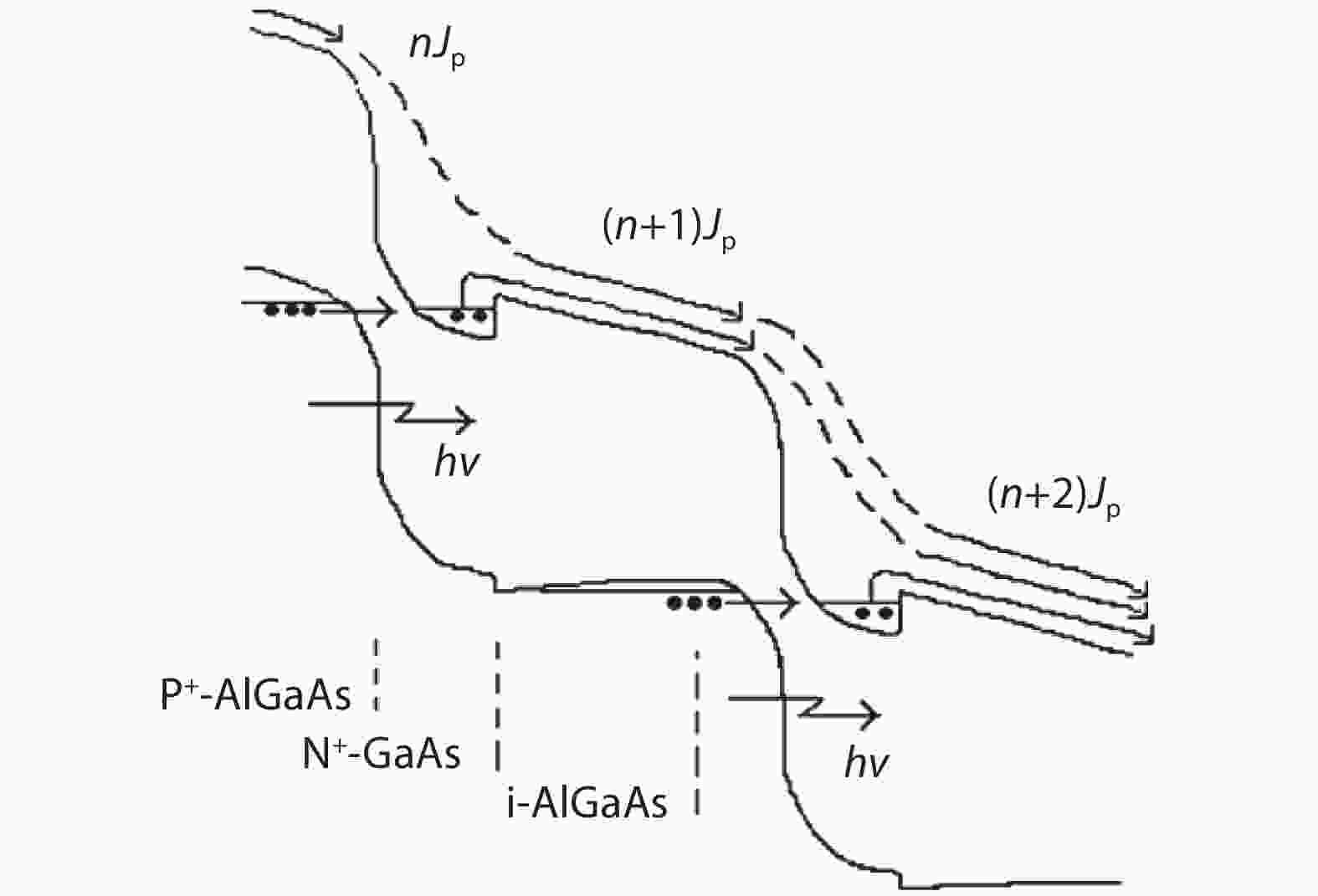
To reduce the difficulty of the epitaxy caused by multiple quantum well infrared photodetector (QWIP) with tunnel compensation structure, an improved structure is proposed. In the new structure, the superlattices are located between the tunnel junction and the barrier as the infrared absorption region, eliminating the effect of doping concentration on the well width in the original structure. Theoretical analysis and experimental verification of the new structure are carried out. The experimental sample is a two-cycle device, each cycle contains a tunnel junction, a superlattice infrared absorption region and a thick barrier. The photosurface of the detector is 200 × 200 μm2 and the light is optically coupled by 45° oblique incidence. The results show that the optimal operating voltage of the sample is –1.1 V, the dark current is 2.99 × 10–8 A, and the blackbody detectivity is 1.352 × 108 cm·Hz1/2·W–1 at 77 K. Our experiments show that the new structure can work normally.-
Keywords:
- infrared detector,
- tunnel compensation,
- superlattice
-
References
[1] Rogalski A. Recent progress in infrared detector technologies. Infrared Phys Technol, 2011, 54, 136 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2010.12.003[2] Kataria H, Asplund C, Lindberg A, et al. Novel high-resolution VGA QWIP detector. Proc SPIE, 2017, 10177[3] Roodenko K, Choi K K, Clark K P, et al. Control over the optical and electronic performance of GaAs/AlGaAs QWIPs grown by production MBE. Infrared Phys Technol, 2017, 84, 33 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2017.03.001[4] Jhabvala M, Choi K K, Monroy C, et al. Development of a 1 K × 1 K 8–12 μm QWIP array. Infrared Phys Technol, 2007, 50, 234 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2006.10.029[5] Kaya Y, Ravikumar A, Chen G P, et al. Two-band ZnCdSe/ZnCdMgSe quantum well infrared photodetector. AIP Adv, 2018, 8, 075105 doi: 10.1063/1.5013607[6] Li Z F, Jing Y L, Zhou Y W. Multi-band integrated quantum well infrared photodetectors. International Conference on Infrared Millimeter and Terahertz Waves, 2018[7] Wu Y, Liu H M, Li P Z. Dual-band quantum well infrared photodetector with metallic structure. Proc SPIE, 2018, 10697[8] Rogalski A. Infrared detectors: an overview. Infrared Phys Technol, 2002, 43, 187 doi: 10.1016/S1350-4495(02)00140-8[9] Haran T L, James J C, Lane S E, et al. Quantum efficiency and spatial noise tradeoffs for III–V focal plane arrays. Infrared Phys Technol, 2019, 97, 309 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2019.01.001[10] Eker S U, Hostut M, Ergun Y, et al. A new approach to quantum well infrared photodetectors: Staircase-like quantum well and barriers. Infrared Phys Technol, 2006, 48, 101 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2005.04.009[11] Choi K K, Allen S C, Sun J G, et al. Small pitch resonator-QWIP detectors and arrays. Infrared Phys Technol, 2018, 94, 118 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2018.09.006[12] DeCuir E A Jr, Choi K K, Sun J, et al. Progress in resonator quantum well infrared photodetector (R-QWIP) focal plane arrays. Infrared Phys Technol, 2015, 70, 138 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2014.09.018[13] Su G X, Liu L, Zang W B, et al. Highly efficient dielectric optical incoupler for quantum well infrared photodetectors. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2018, 30, 1167 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2018.2834927[14] Deng J, Shen G D, Lian P, et al. Optoelectronic transport mechanism from subband infrared absorption and tunneling regeneration. Curr Appl Phys, 2002, 2, 373 doi: 10.1016/S1567-1739(02)00142-6[15] Billaha A, Das M K . Influence of doping on the performance of GaAs/AlGaAs QWIP for long wavelength applications. Opto−Electron Rev, 2016, 24(1), 25 doi: 10.1515/oere-2016-0006[16] Deng J. Study on novel GaAs/AlGaAs multi-quantum wells infrared photodetecting mechanism and MOCVD epitaxy technology. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2005, 79 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: