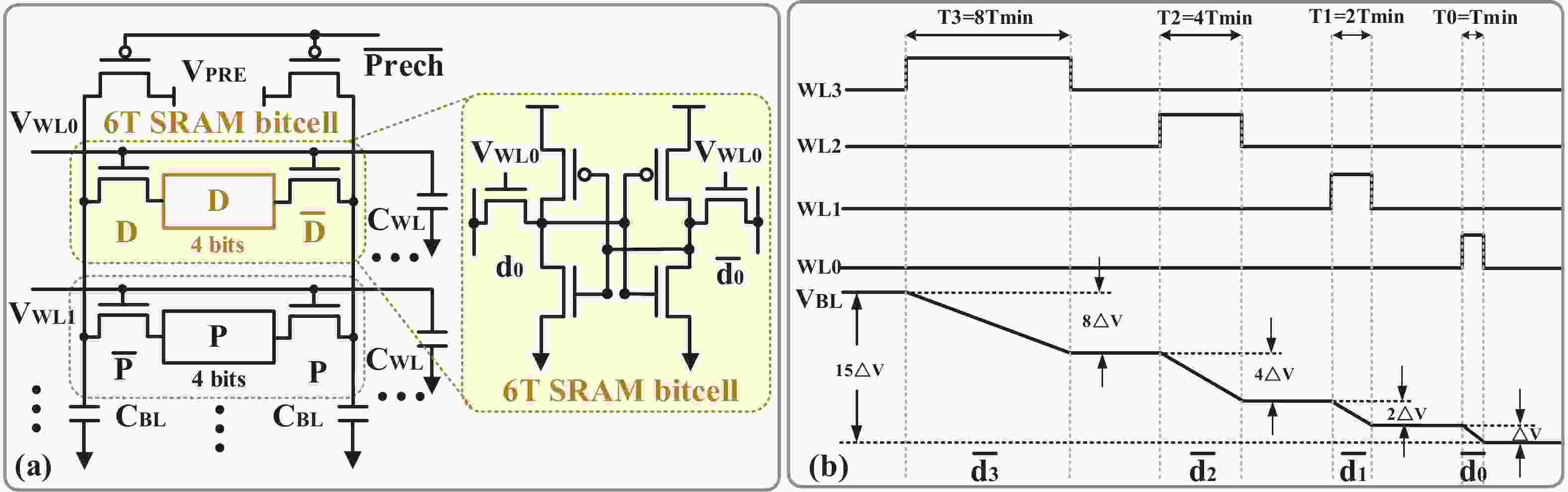
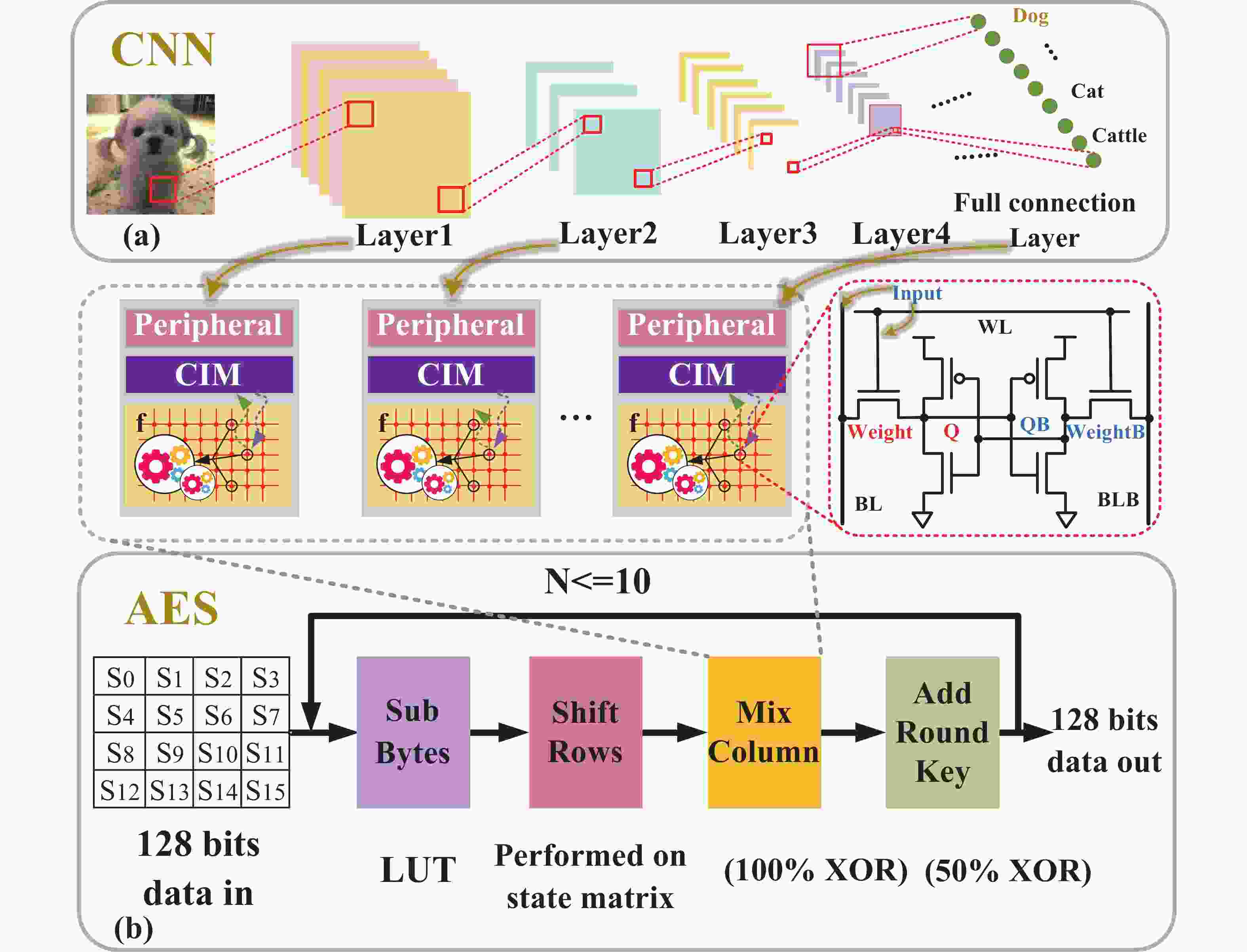
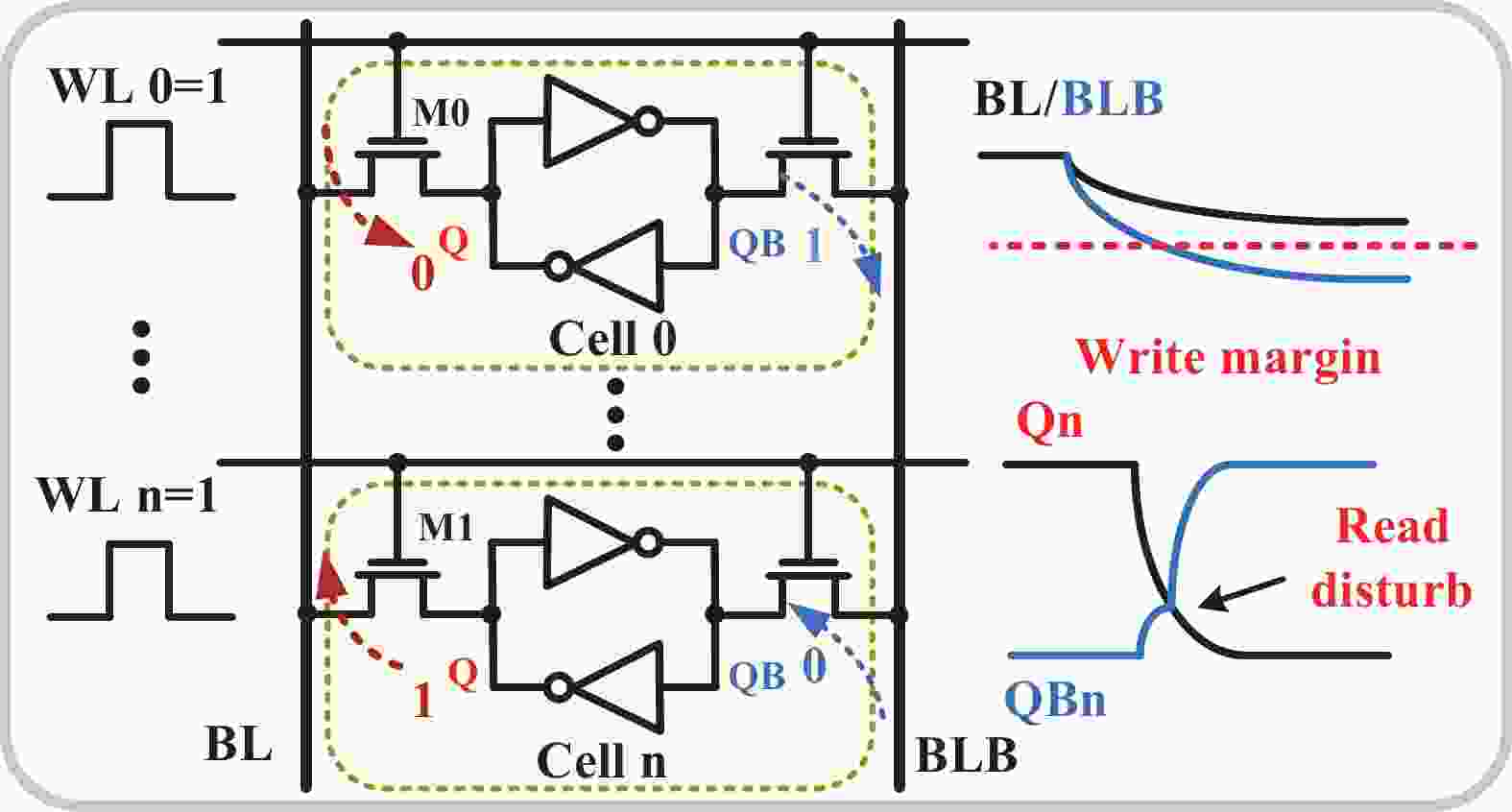
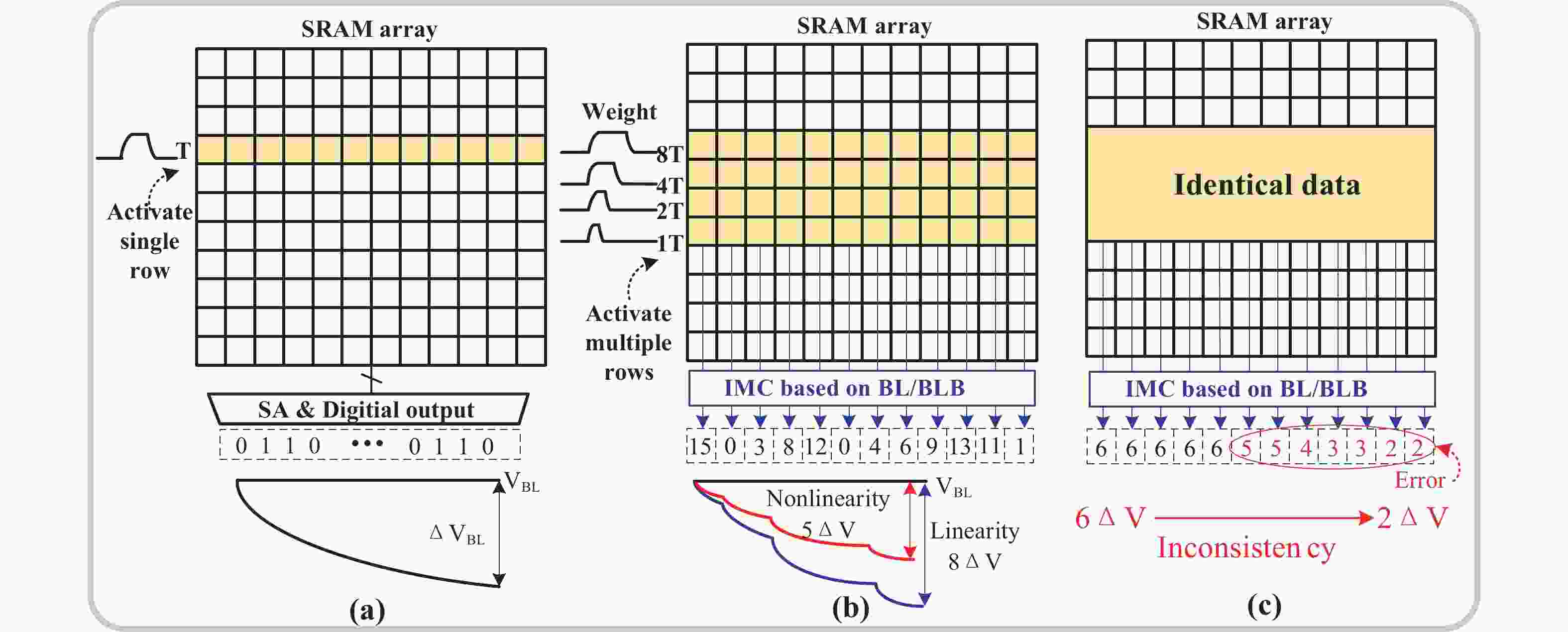
| Citation: |
Zhiting Lin, Zhongzhen Tong, Jin Zhang, Fangming Wang, Tian Xu, Yue Zhao, Xiulong Wu, Chunyu Peng, Wenjuan Lu, Qiang Zhao, Junning Chen. A review on SRAM-based computing in-memory: Circuits, functions, and applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(3): 031401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/3/031401
Z T Lin, Z Z Tong, J Zhang, F M Wang, T Xu, Y Zhao, X L Wu, C Y Peng, W J Lu, Q Zhao, J N Chen, A review on SRAM-based computing in-memory: Circuits, functions, and applications[J]. J. Semicond., 2022, 43(3): 031401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/3/031401.
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
A review on SRAM-based computing in-memory: Circuits, functions, and applications
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/3/031401
More Information-
Abstract
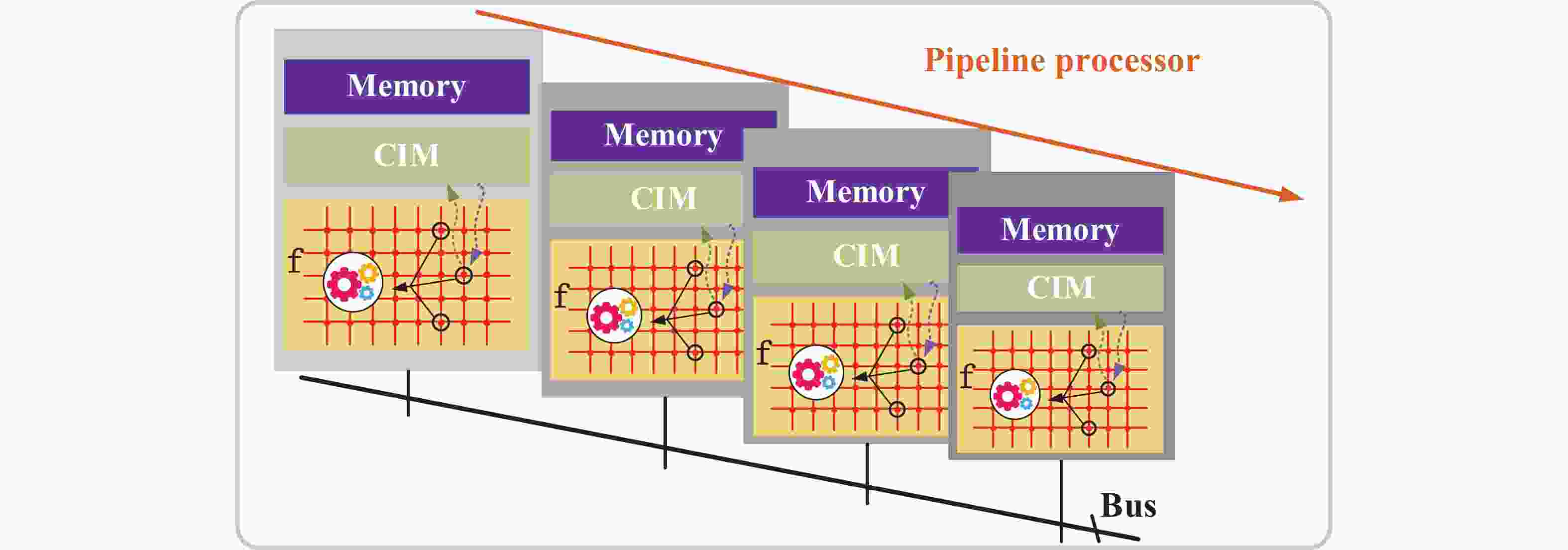
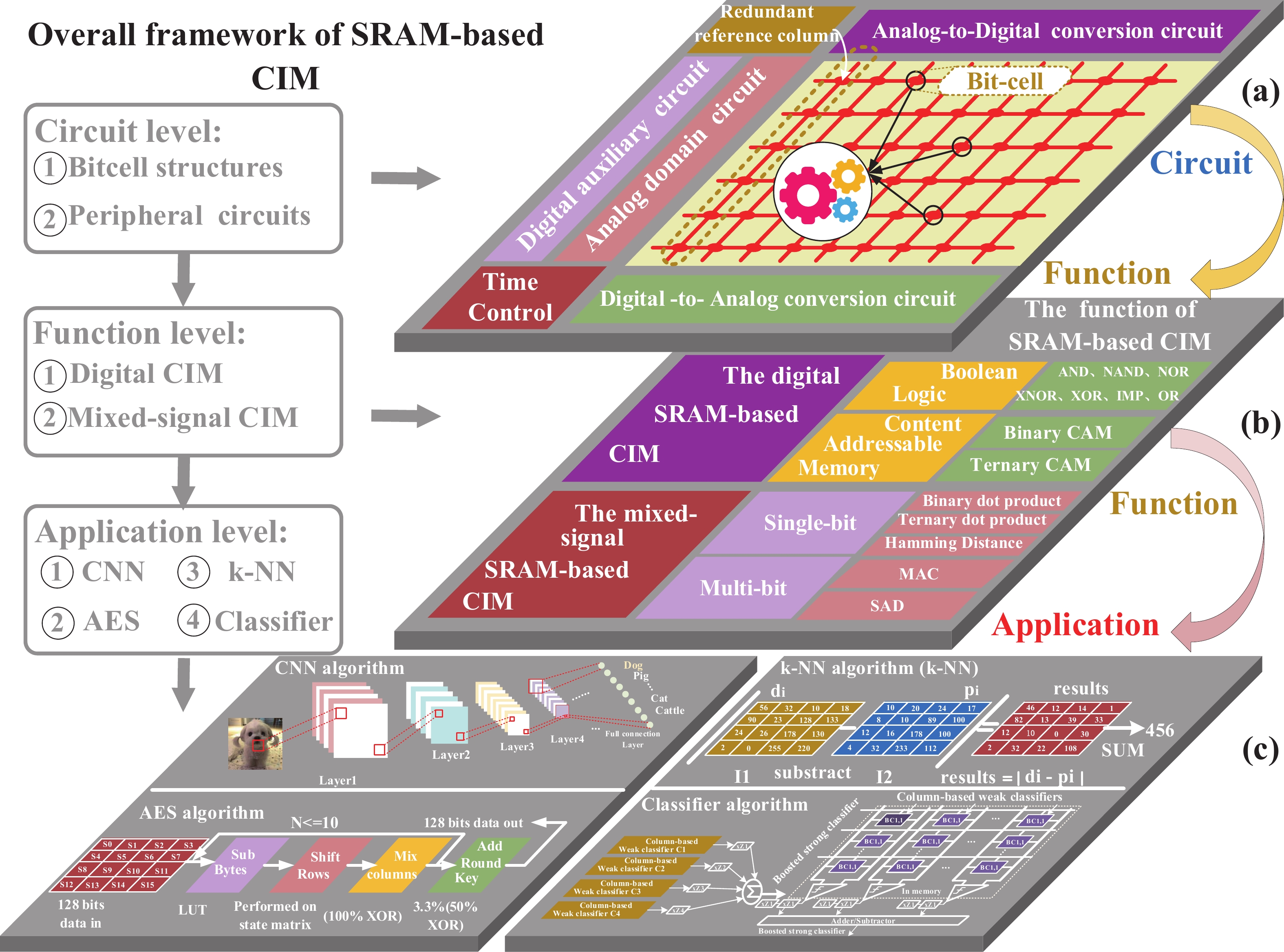
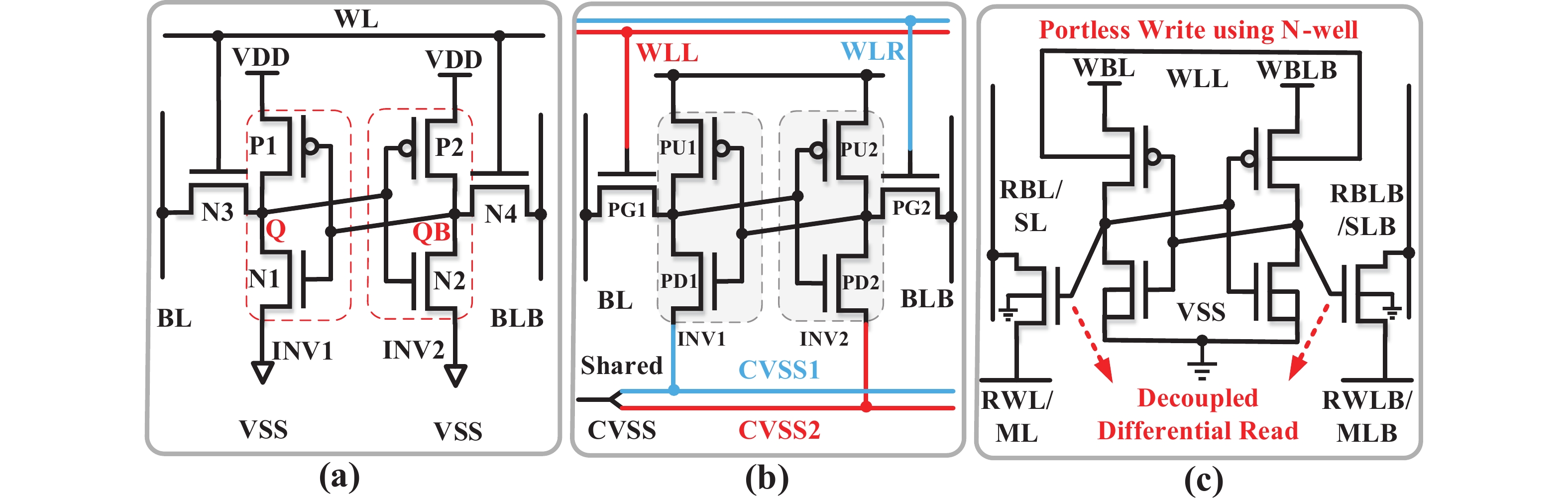
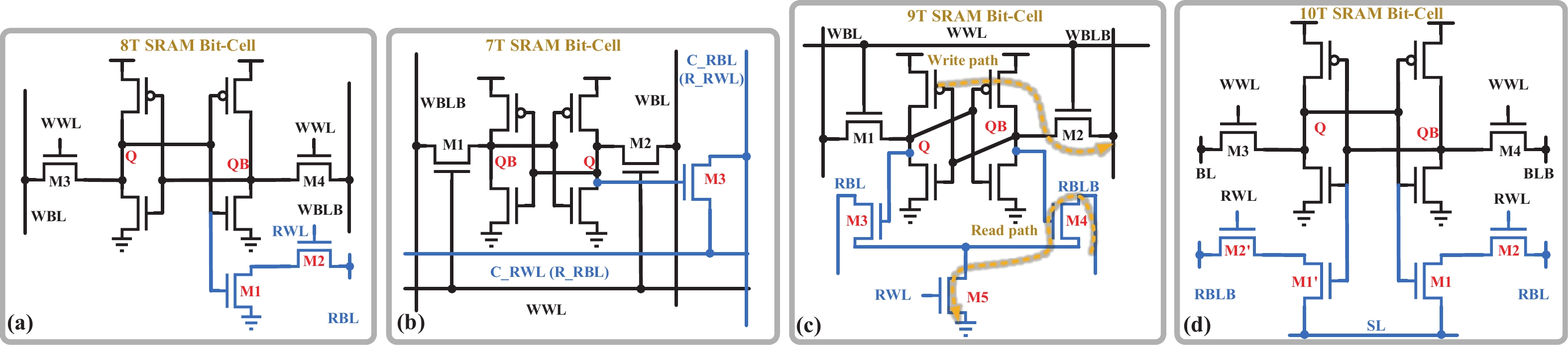
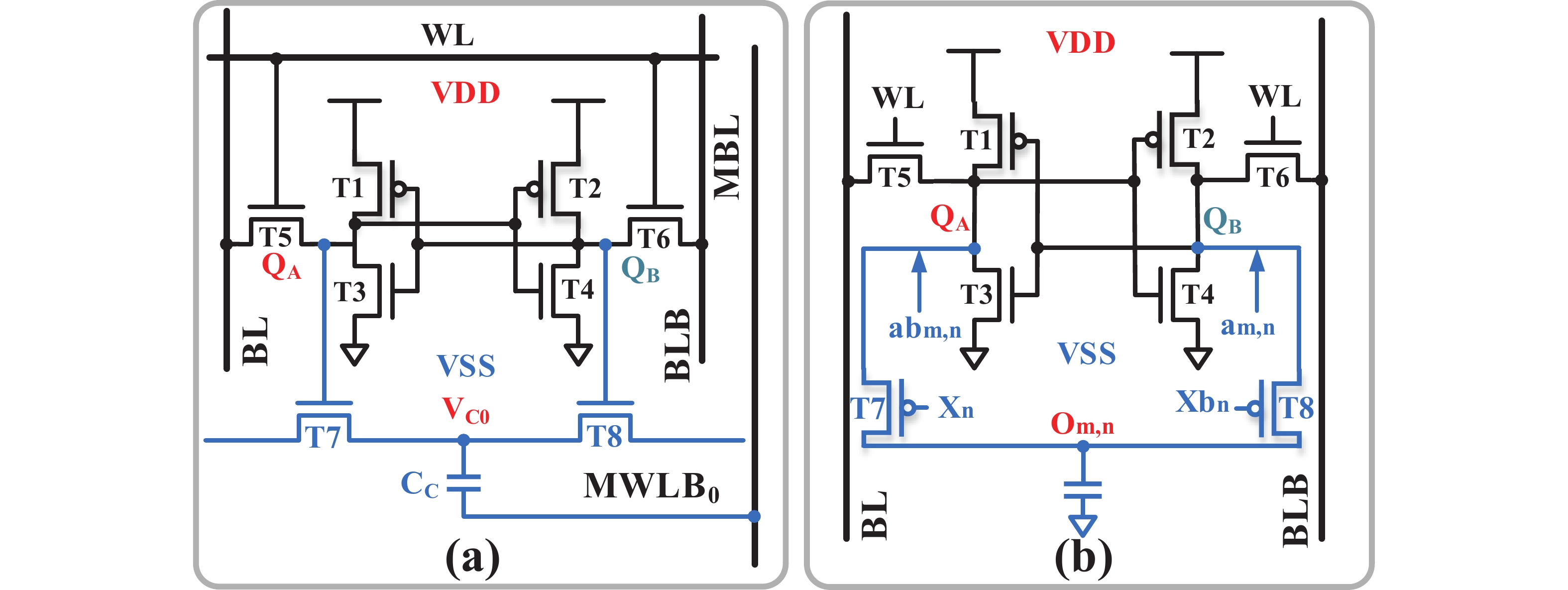
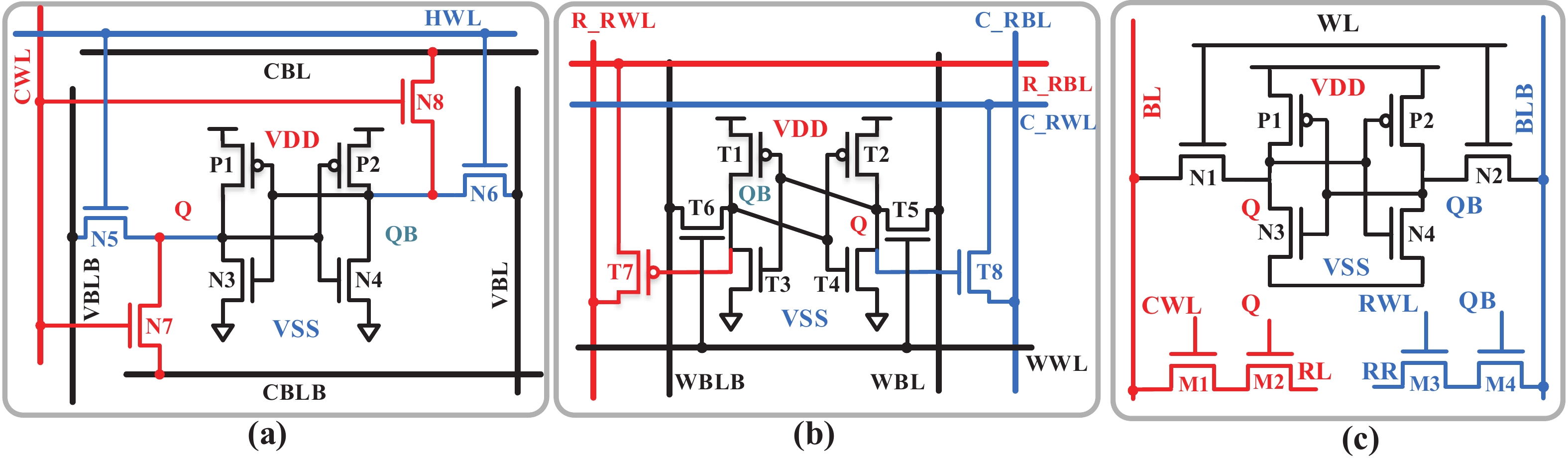
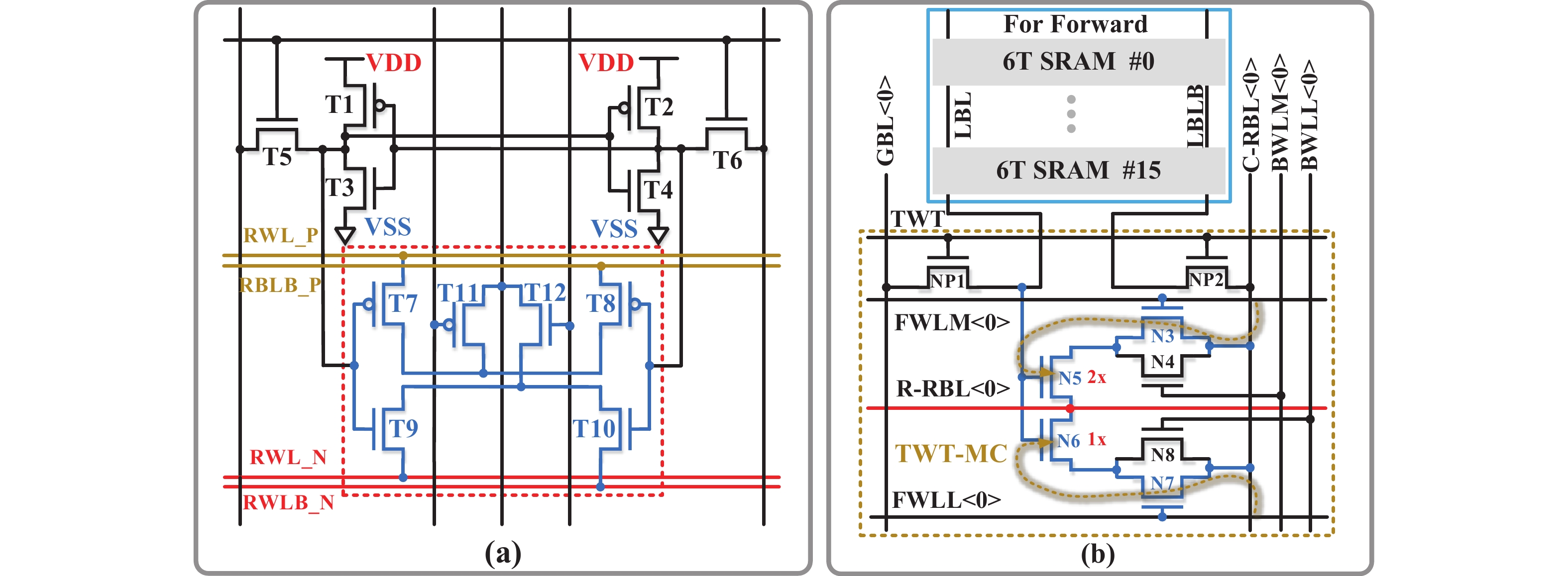
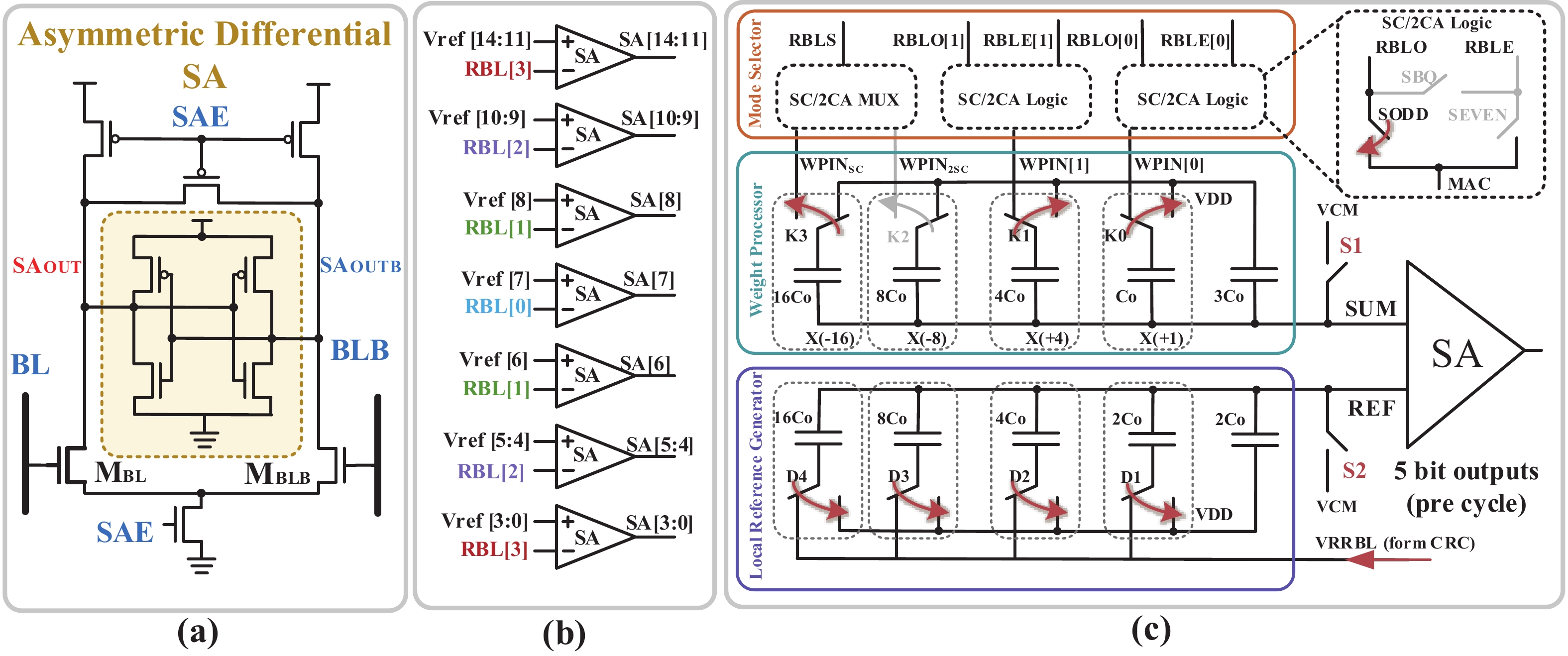
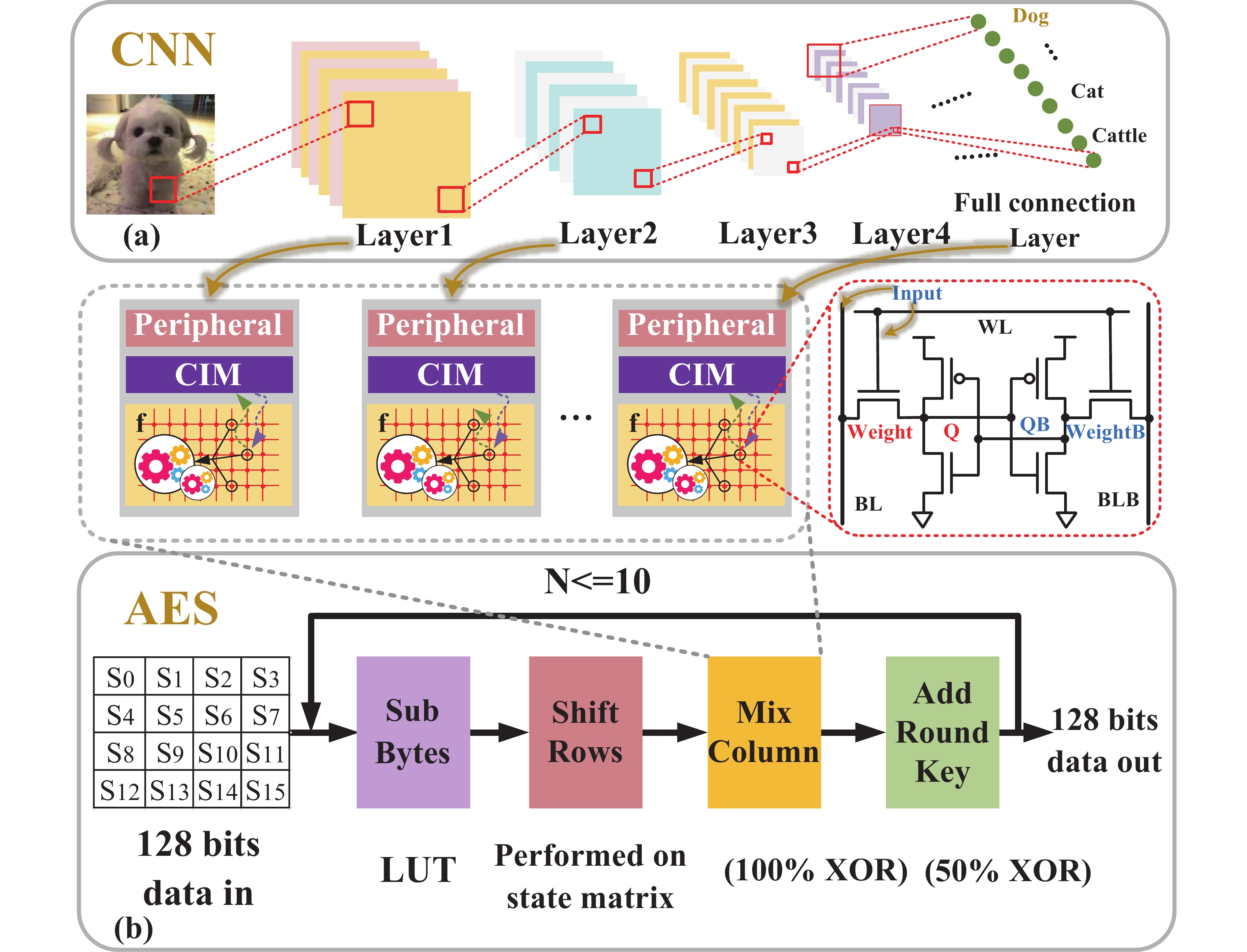
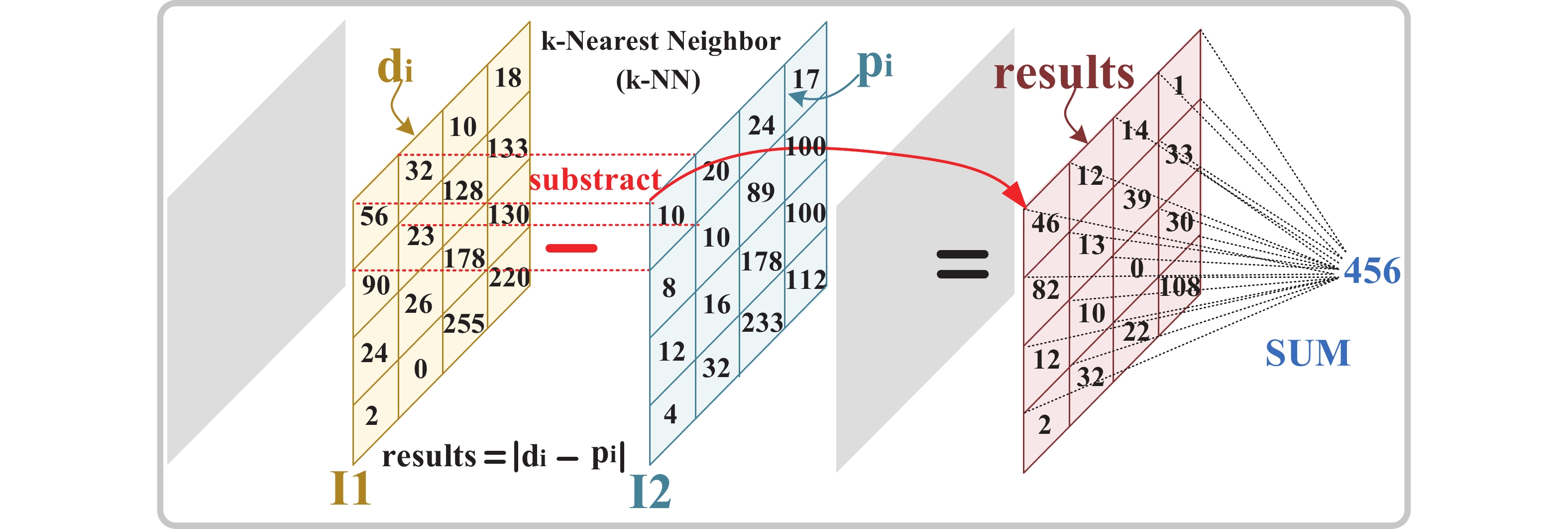
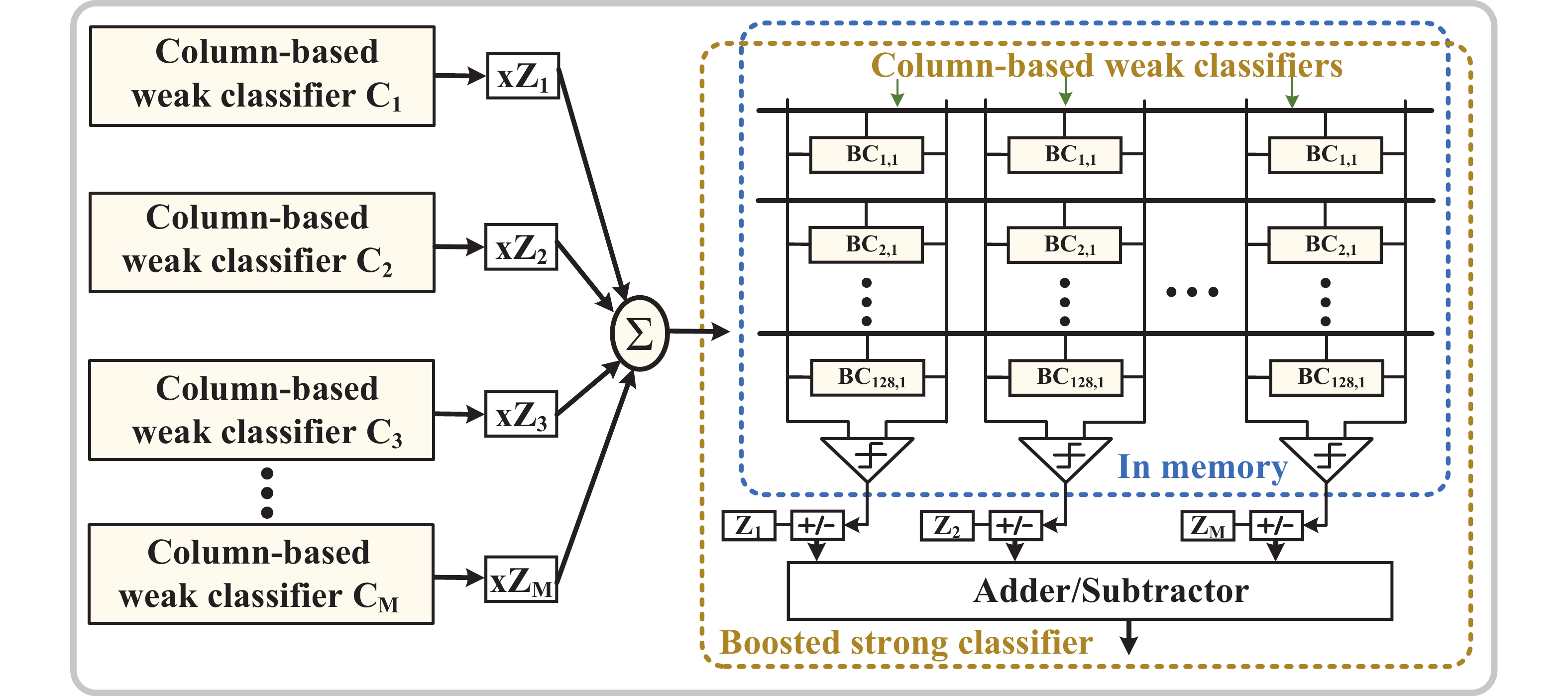
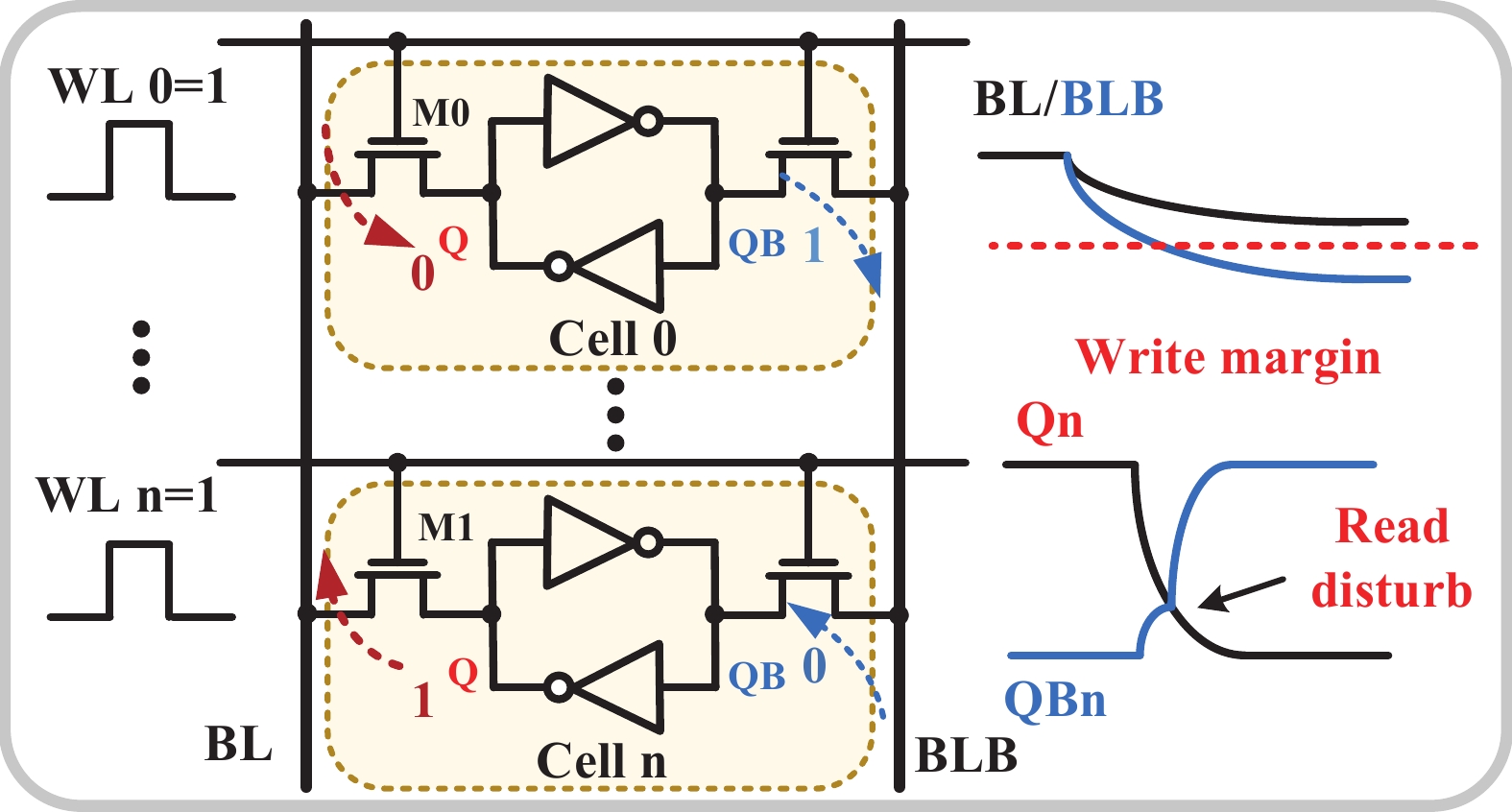
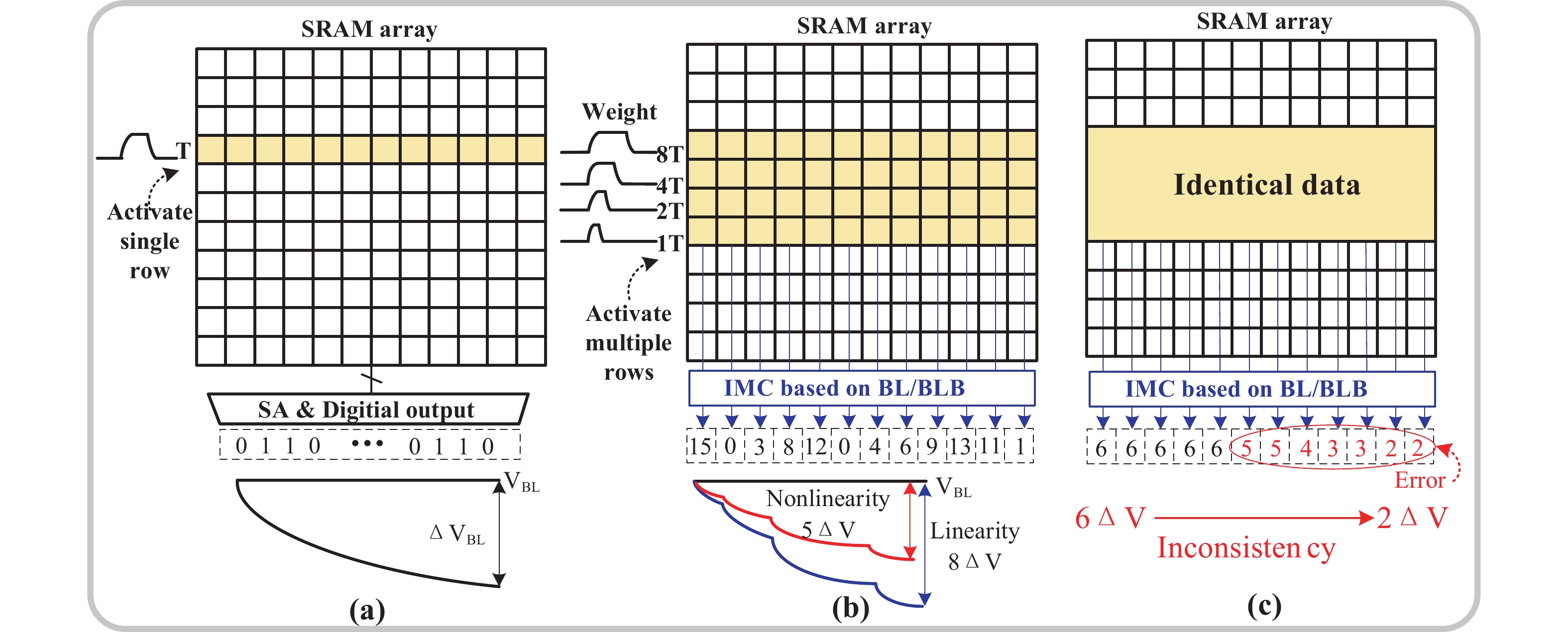
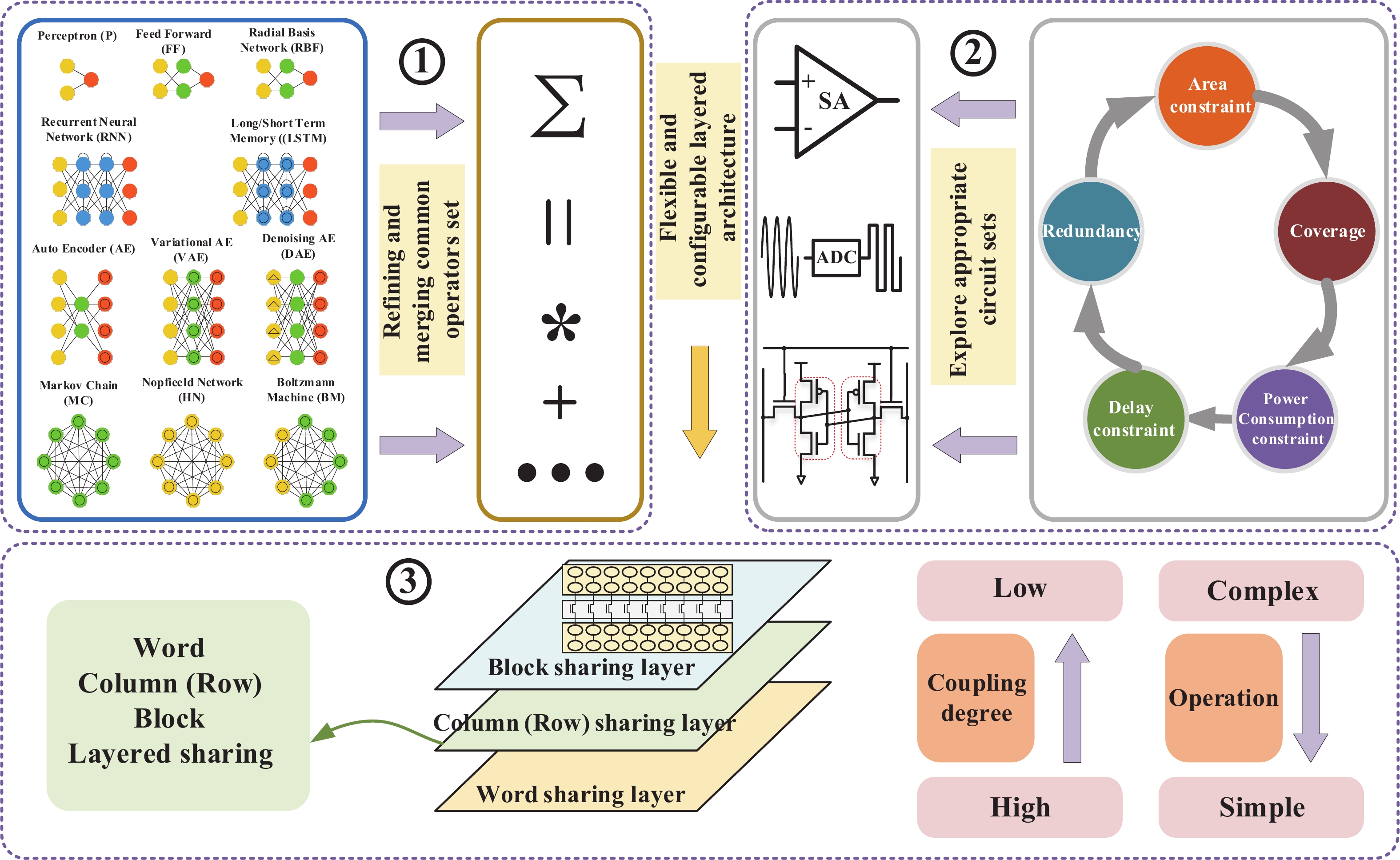
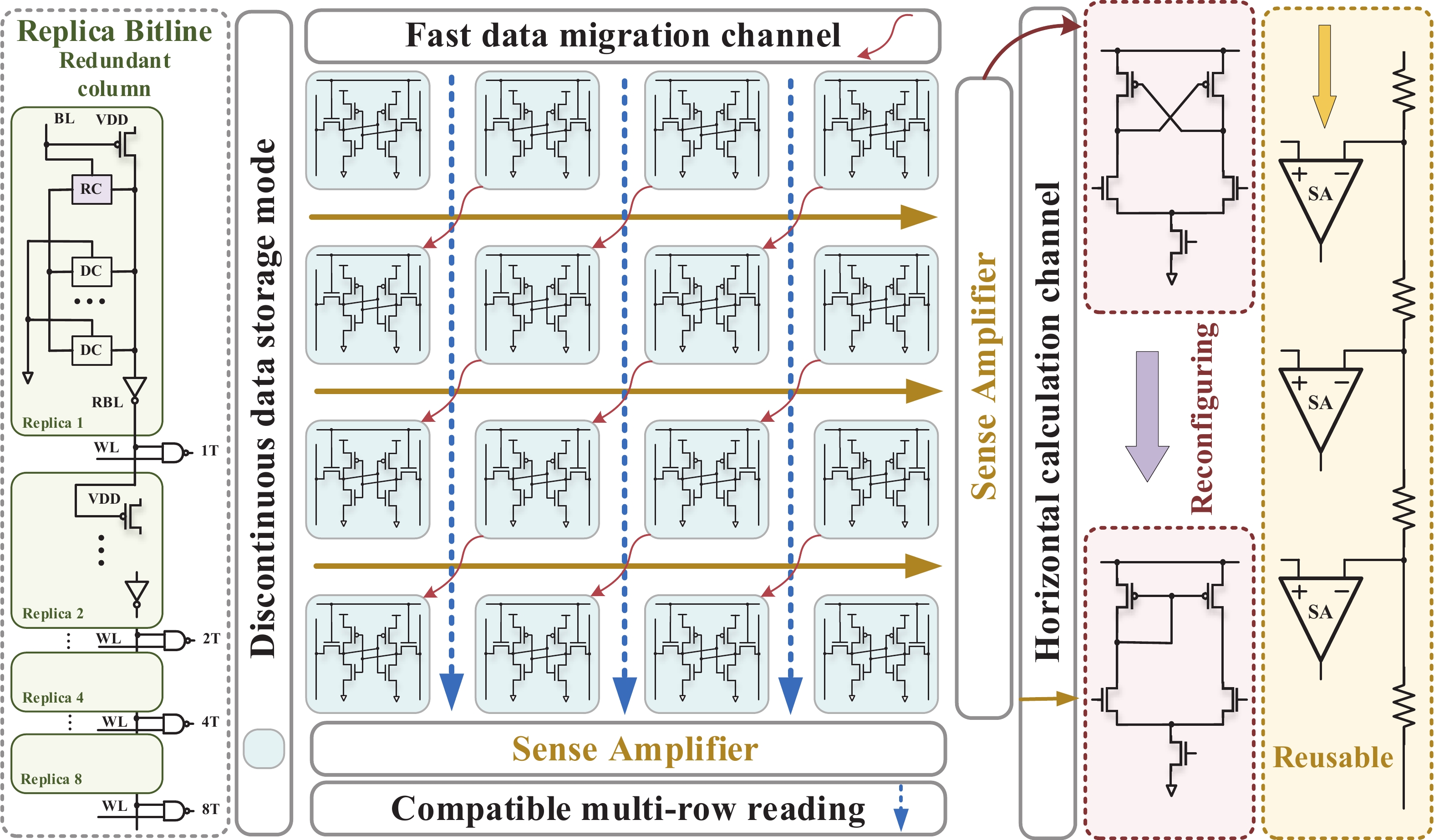
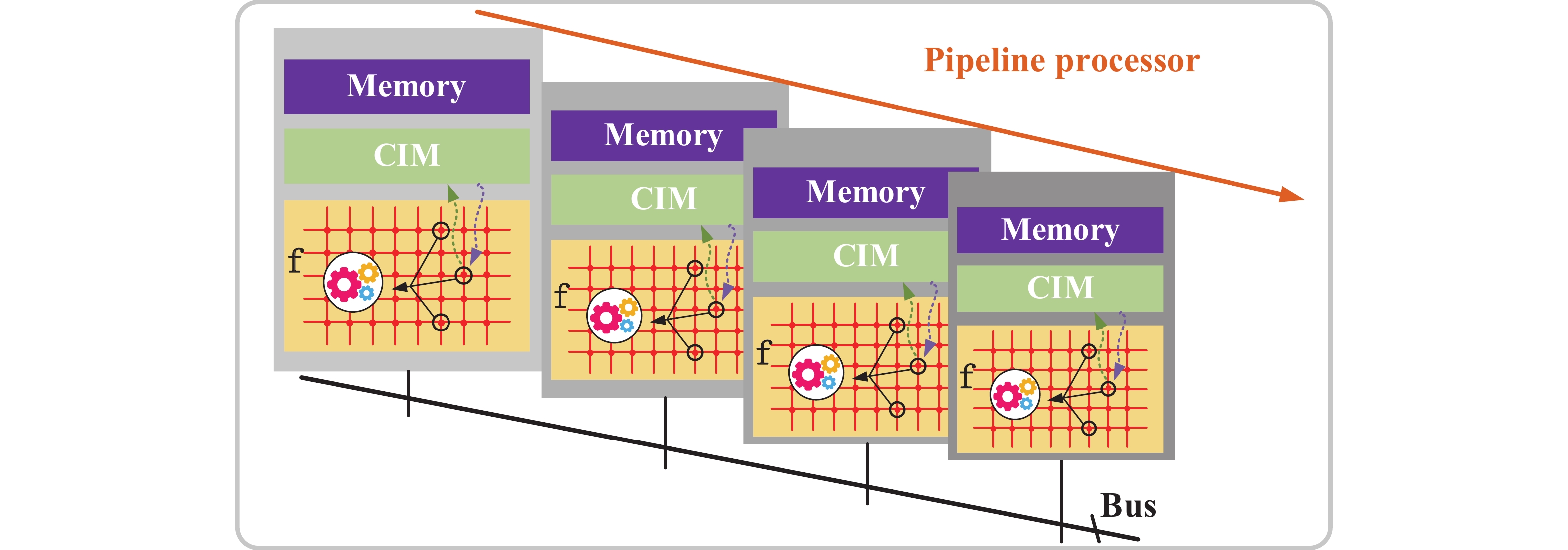
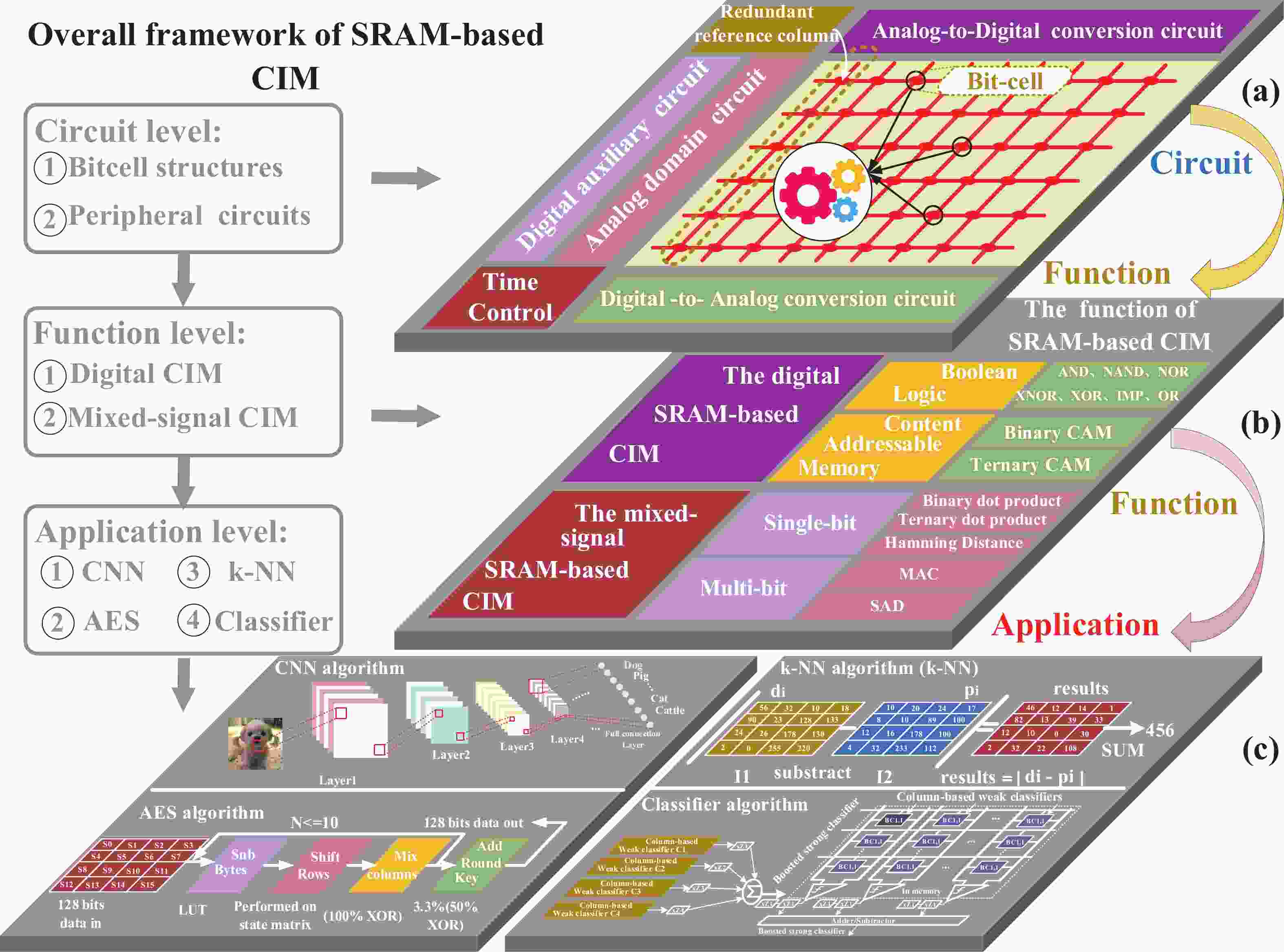
Artificial intelligence (AI) processes data-centric applications with minimal effort. However, it poses new challenges to system design in terms of computational speed and energy efficiency. The traditional von Neumann architecture cannot meet the requirements of heavily data-centric applications due to the separation of computation and storage. The emergence of computing in-memory (CIM) is significant in circumventing the von Neumann bottleneck. A commercialized memory architecture, static random-access memory (SRAM), is fast and robust, consumes less power, and is compatible with state-of-the-art technology. This study investigates the research progress of SRAM-based CIM technology in three levels: circuit, function, and application. It also outlines the problems, challenges, and prospects of SRAM-based CIM macros. -
References
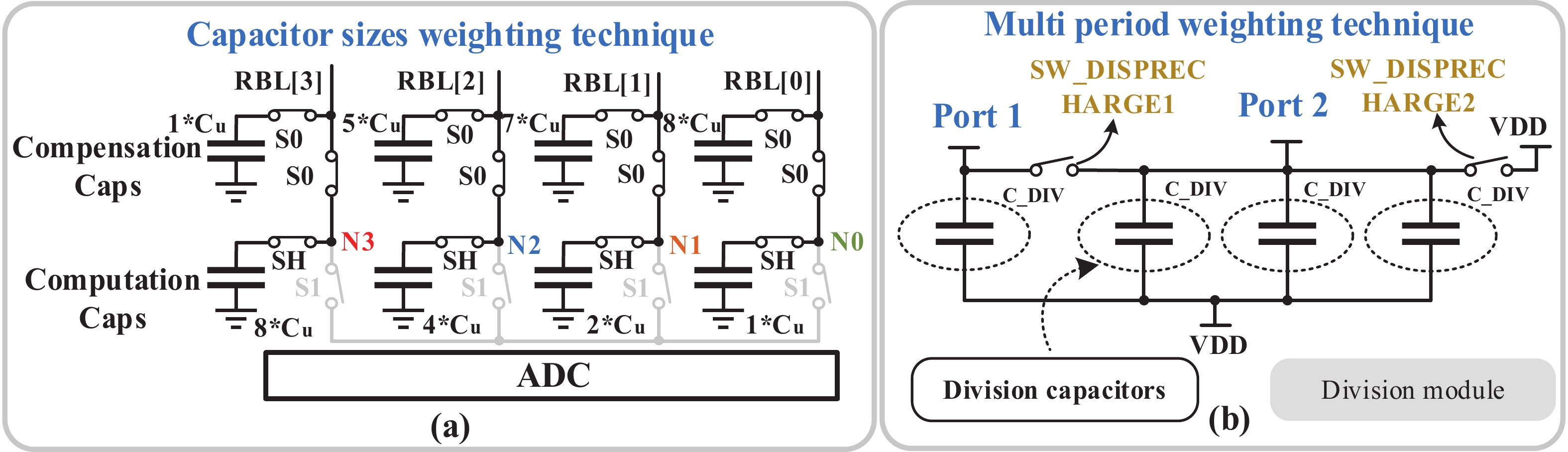
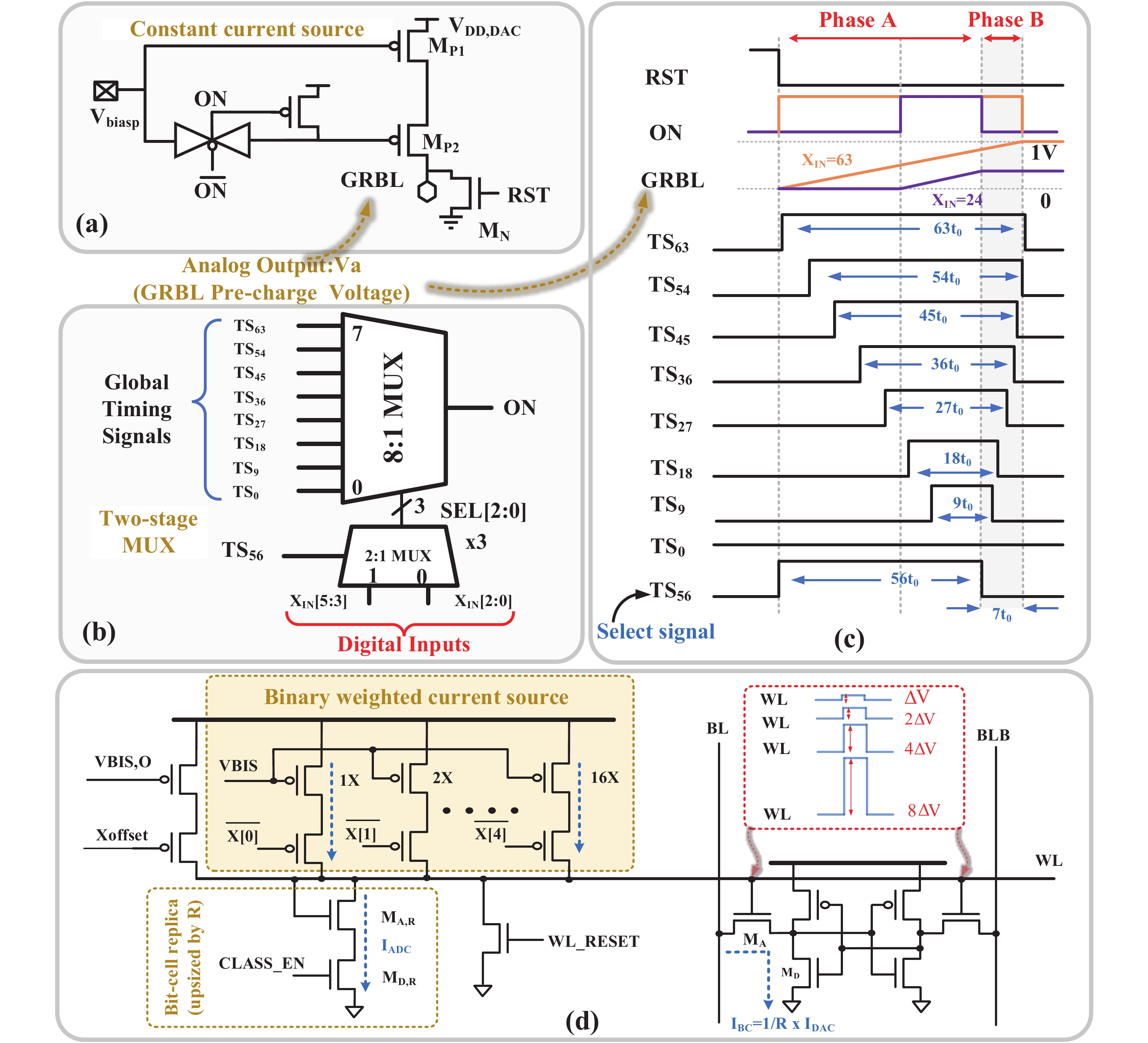
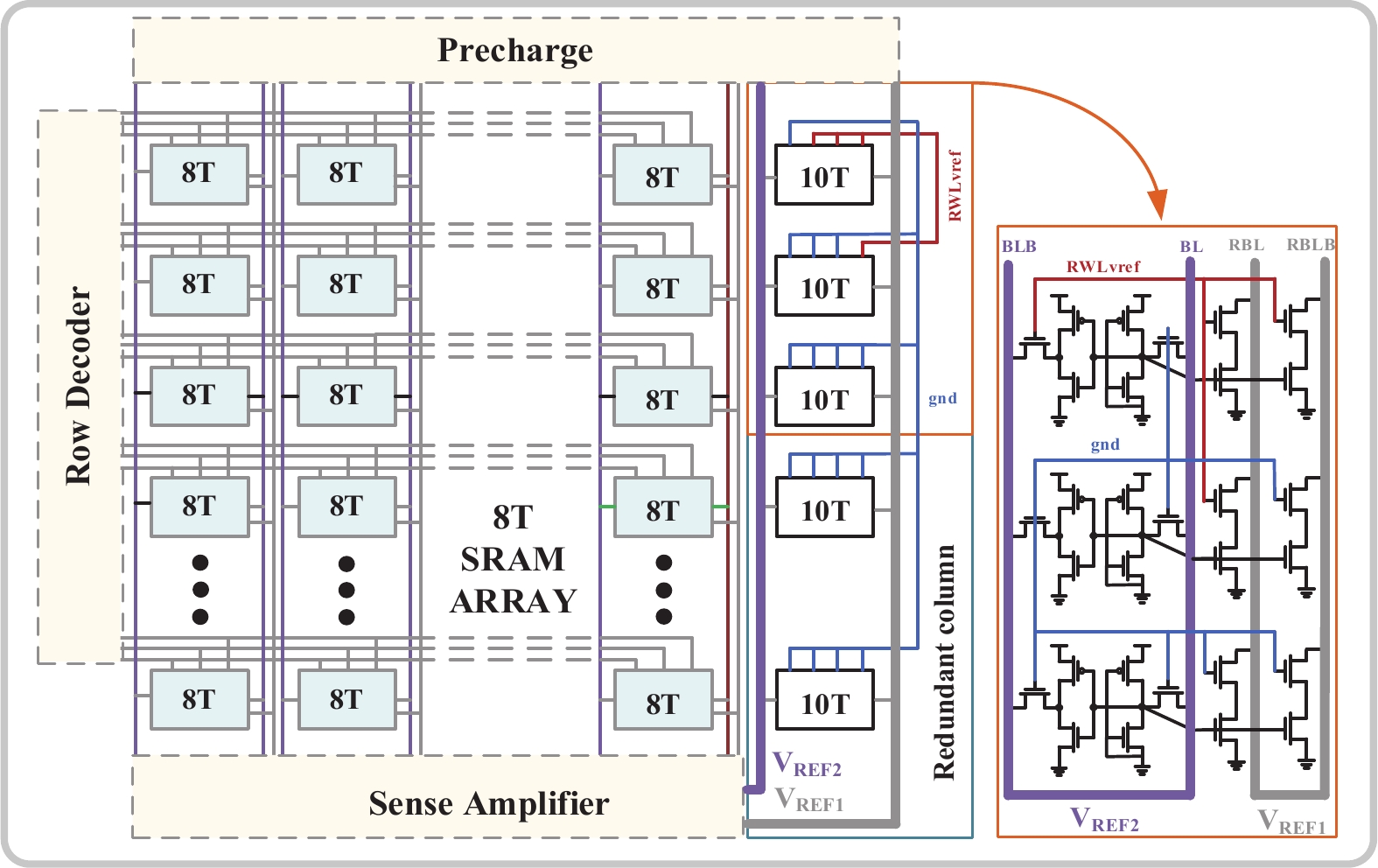
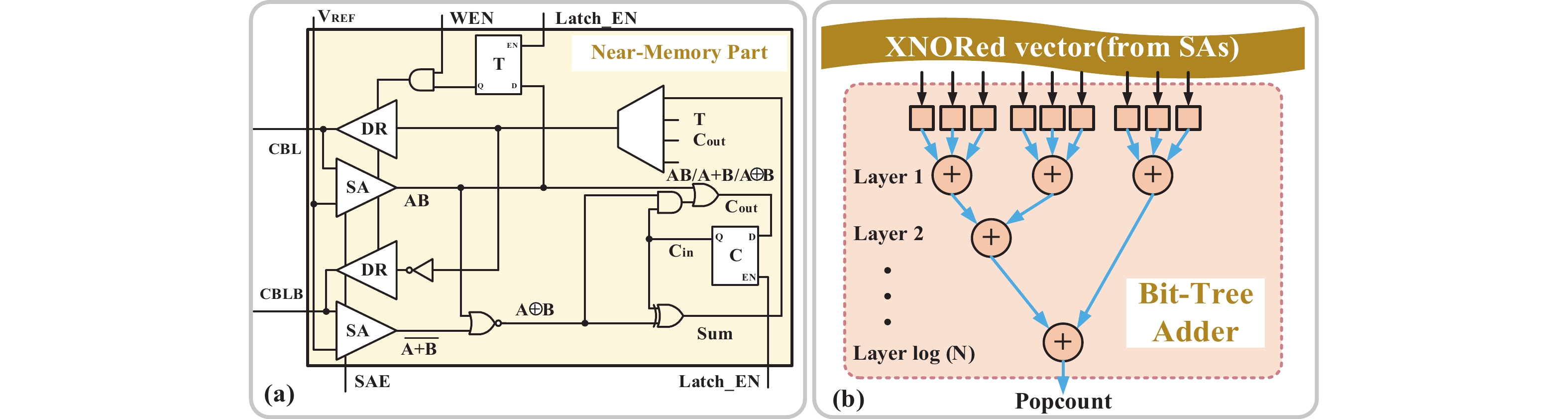
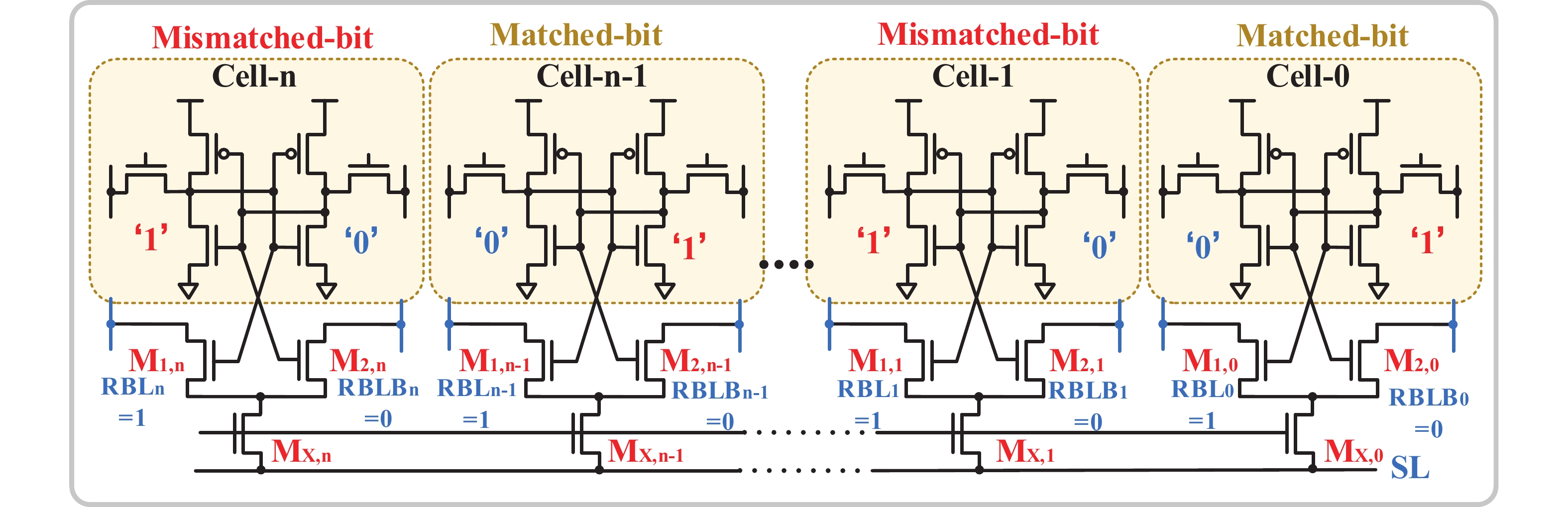
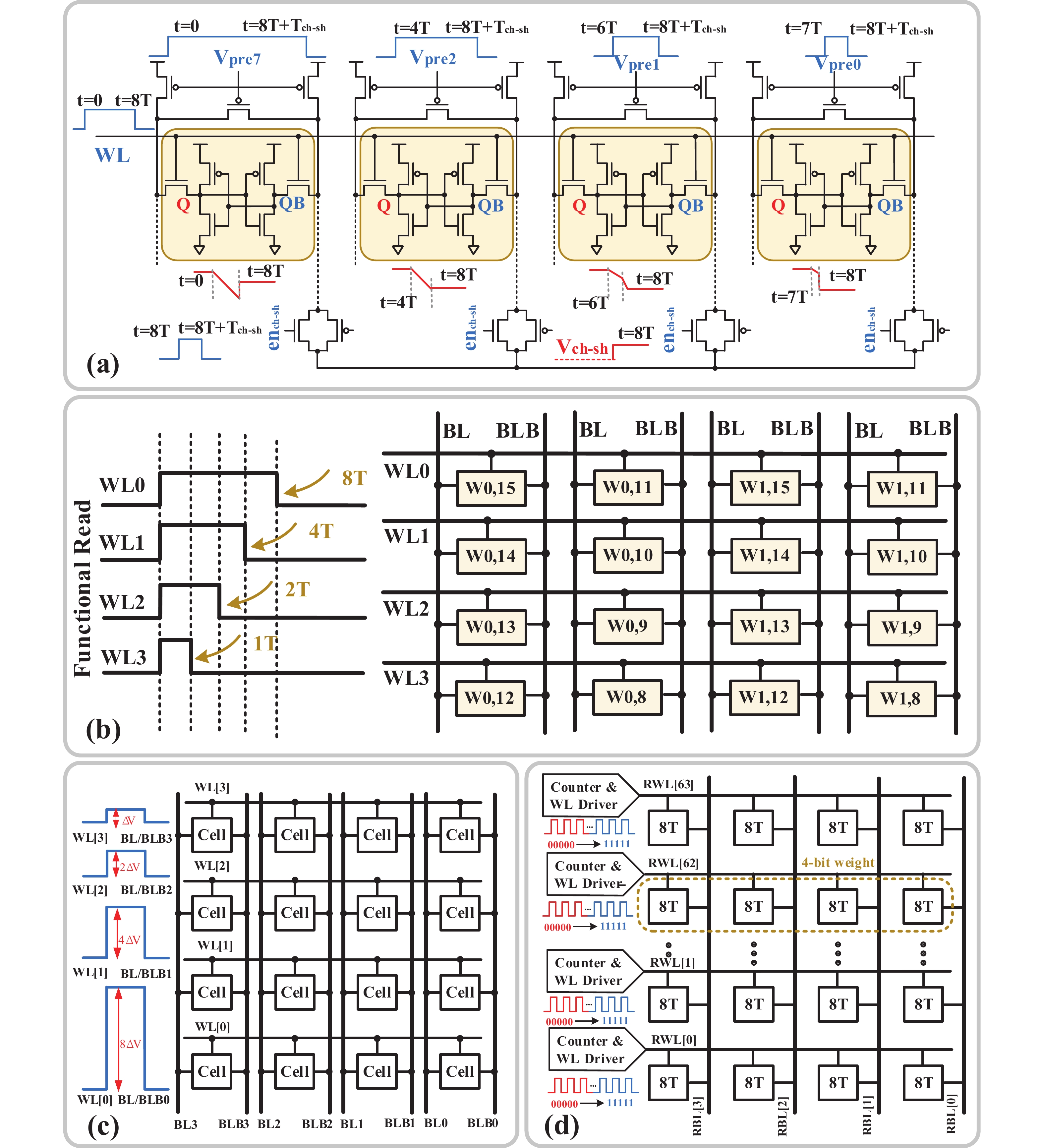
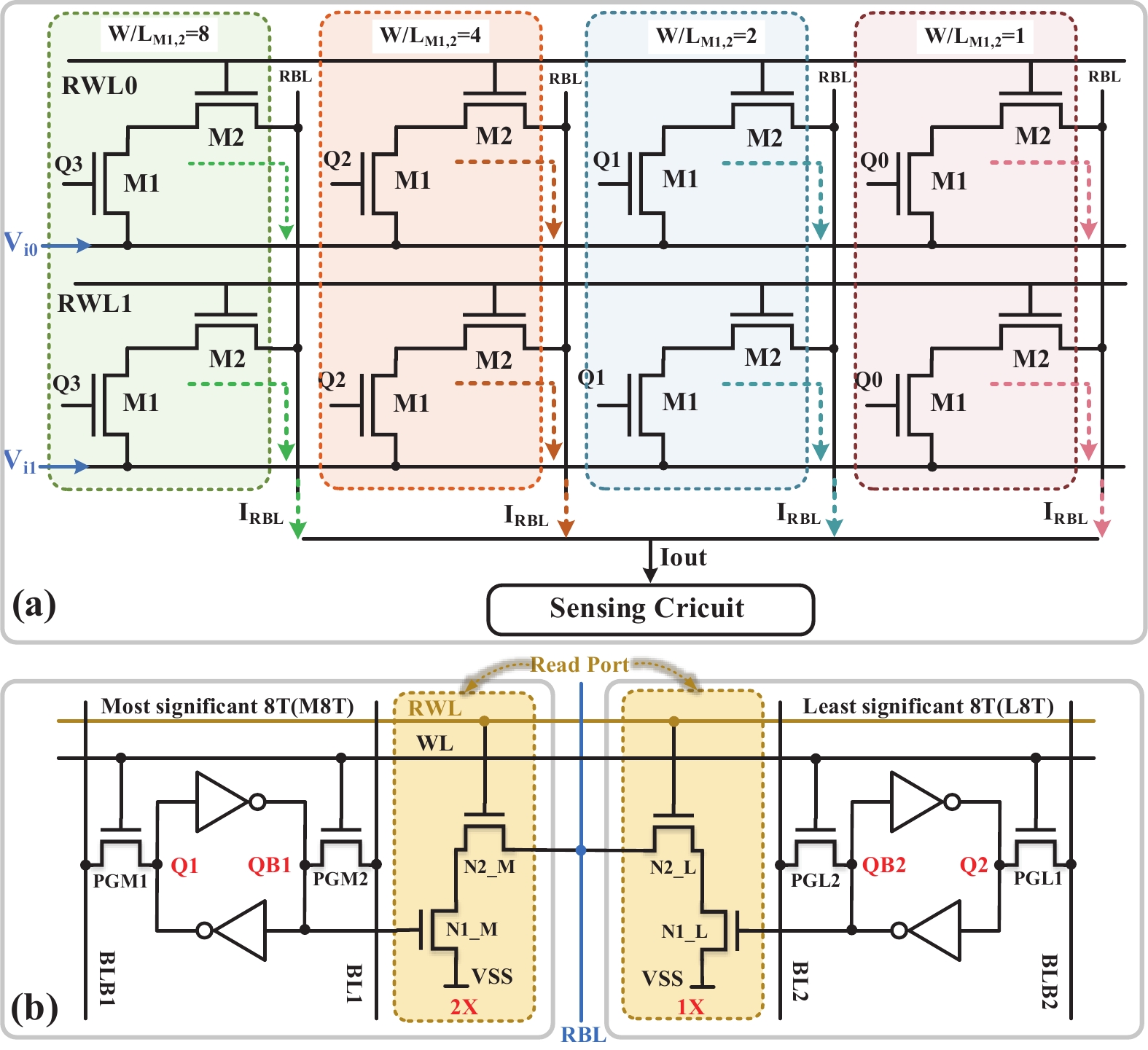
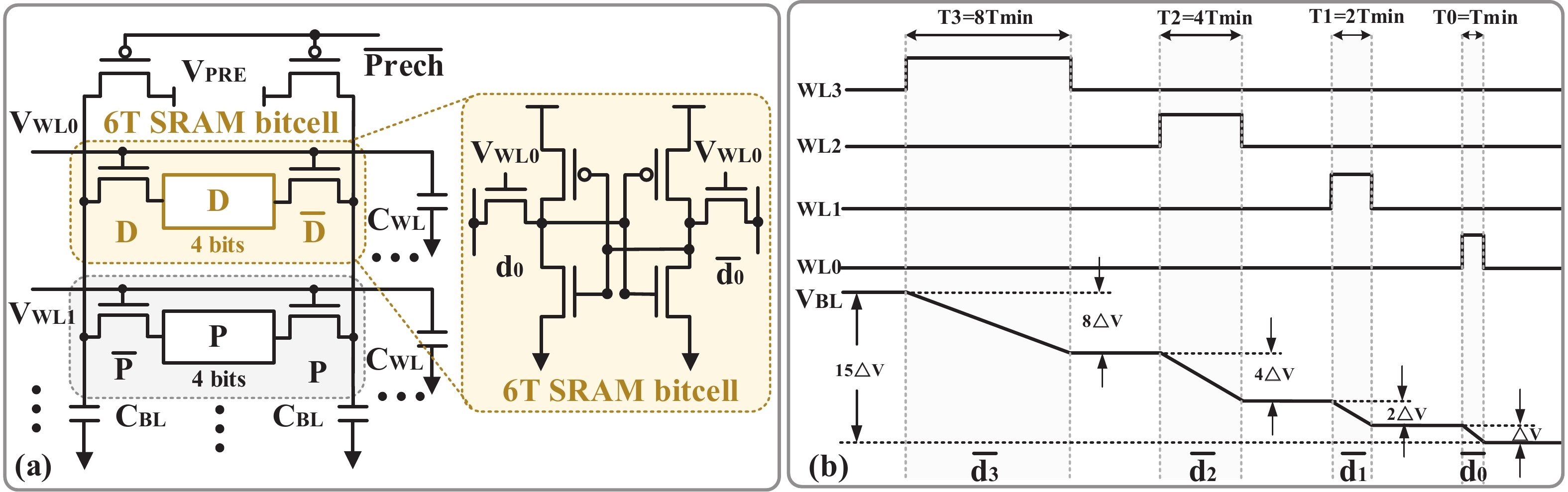
[1] Si X, Khwa W S, Chen J J, et al. A dual-split 6T SRAM-based computing-in-memory unit-macro with fully parallel product-sum operation for binarized DNN edge processors. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2019, 66, 4172 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2928043[2] Khwa W S, Chen J J, Li J F, et al. A 65nm 4Kb algorithm-dependent computing-in-memory SRAM unit-macro with 2.3ns and 55.8TOPS/W fully parallel product-sum operation for binary DNN edge processors. 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2018, 496[3] Jaiswal A, Chakraborty I, Agrawal A, et al. 8T SRAM cell as a multibit dot-product engine for beyond von Neumann computing. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2019, 27, 2556 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2929245[4] Lu L, Yoo T, Le V L, et al. A 0.506-pJ 16-kb 8T SRAM with vertical read wordlines and selective dual split power lines. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2020, 28, 1345 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2956232[5] Lin Z T, Zhan H L, Li X, et al. In-memory computing with double word lines and three read Ports for four operands. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2020, 28, 1316 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.2976099[6] Srinivasa S, Chen W H, Tu Y N, et al. Monolithic-3D integration augmented design techniques for computing in SRAMs. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2019, 1[7] Zeng J M, Zhang Z, Chen R H, et al. DM-IMCA: A dual-mode in-memory computing architecture for general purpose processing. IEICE Electron Express, 2020, 17, 20200005 doi: 10.1587/elex.17.20200005[8] Ali M, Agrawal A, Roy K. RAMANN: in-SRAM differentiable memory computations for memory-augmented neural networks. Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, 2020, 61[9] Agrawal A, Jaiswal A, Roy D, et al. Xcel-RAM: Accelerating binary neural networks in high-throughput SRAM compute arrays. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2019, 66, 3064 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2019.2907488[10] Biswas A, Chandrakasan A P. CONV-SRAM: An energy-efficient SRAM with in-memory dot-product computation for low-power convolutional neural networks. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2019, 54, 217 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2880918[11] Lin Z T, Zhu Z Y, Zhan H L, et al. Two-direction in-memory computing based on 10T SRAM with horizontal and vertical decoupled read Ports. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2021, 56, 2832 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3061260[12] Wang J C, Wang X W, Eckert C, et al. A 28-nm compute SRAM with bit-serial logic/arithmetic operations for programmable in-memory vector computing. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2020, 55, 76 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2939682[13] Wang J C, Wang X W, Eckert C, et al. A compute SRAM with bit-serial integer/floating-point operations for programmable in-memory vector acceleration. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2019, 224[14] Jiang H W, Peng X C, Huang S S, et al. CIMAT: a transpose SRAM-based compute-in-memory architecture for deep neural network on-chip training. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Memory Systems, 2019, 490[15] Zhang J T, Wang Z, Verma N. In-memory computation of a machine-learning classifier in a standard 6T SRAM array. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2017, 52, 915 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2642198[16] Zhang J T, Wang Z, Verma N. A machine-learning classifier implemented in a standard 6T SRAM array. 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits, 2016, 1[17] Jiang Z W, Yin S H, Seok M, et al. XNOR-SRAM: In-memory computing SRAM macro for binary/ternary deep neural networks. 2018 IEEE Symp VLSI Technol, 2018, 173[18] Agrawal A, Jaiswal A, Lee C, et al. X-SRAM: Enabling in-memory Boolean computations in CMOS static random access memories. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2018, 65, 4219 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2848999[19] Jeloka S, Akesh N B, Sylvester D, et al. A 28 nm configurable memory (TCAM/BCAM/SRAM) using push-rule 6T bit cell enabling logic-in-memory. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2016, 51, 1009 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2016.2515510[20] Dong Q, Jeloka S, Saligane M, et al. A 4 2T SRAM for searching and in-memory computing with 0.3-V VDDmin. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2018, 53, 1006 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2776309[21] Rajput A K, Pattanaik M. Implementation of Boolean and arithmetic functions with 8T SRAM cell for in-memory computation. 2020 International Conference for Emerging Technology, 2020, 1[22] Jaiswal A, Agrawal A, Ali M F, et al. I-SRAM: Interleaved wordlines for vector Boolean operations using SRAMs. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2020, 67, 4651 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.3005783[23] Surana N, Lavania M, Barma A, et al. Robust and high-performance 12-T interlocked SRAM for in-memory computing. 2020 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, 2020, 1323[24] Simon W A, Qureshi Y M, Rios M, et al. BLADE: an in-cache computing architecture for edge devices. IEEE Trans Comput, 2020, 69, 1349 doi: 10.1109/TC.2020.2972528[25] Chen J, Zhao W F, Ha Y J. Area-efficient distributed arithmetic optimization via heuristic decomposition and in-memroy computing. 2019 IEEE 13th International Conference on ASIC, 2019, 1[26] Lee K, Jeong J, Cheon S, et al. Bit parallel 6T SRAM in-memory computing with reconfigurable bit-precision. 2020 57th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, 2020, 1[27] Simon W, Galicia J, Levisse A, et al. A fast, reliable and wide-voltage-range in-memory computing architecture. Proceedings of the 56th Annual Design Automation Conference, 2019, 1[28] Chen H C, Li J F, Hsu C L, et al. Configurable 8T SRAM for enbling in-memory computing. 2019 2nd International Conference on Communication Engineering and Technology, 2019, 139[29] Gupta N, Makosiej A, Vladimirescu A, et al. 1.56GHz/0.9V energy-efficient reconfigurable CAM/SRAM using 6T-CMOS bitcell. ESSCIRC 2017 - 43rd IEEE European Solid State Circuits Conference, 2017, 316[30] Sun X Y, Liu R, Peng X C, et al. Computing-in-memory with SRAM and RRAM for binary neural networks. 2018 14th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology, 2018, 1[31] Jiang Z W, Yin S H, Seo J S, et al. C3SRAM: in-memory-computing SRAM macro based on capacitive-coupling computing. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett, 2019, 2, 131 doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2019.2934831[32] Si X, Chen J J, Tu Y N, et al. A twin-8T SRAM computation-in-memory unit-macro for multibit CNN-based AI edge processors. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2020, 55, 189 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2952773[33] Chiu Y C, Zhang Z X, Chen J J, et al. A 4-kb 1-to-8-bit configurable 6T SRAM-based computation-in-memory unit-macro for CNN-based AI edge processors. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2020, 55, 2790 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3005754[34] Chen Z Y, Yu Z H, Jin Q, et al. CAP-RAM: A charge-domain in-memory computing 6T-SRAM for accurate and precision-programmable CNN inference. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2021, 56, 1924 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3056447[35] Kang M G, Gonugondla S K, Patil A, et al. A multi-functional in-memory inference processor using a standard 6T SRAM array. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2018, 53, 642 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2782087[36] Kang M, Gonugondla S K, Keel M, et al. An energy-efficient memory-based high-throughput VLSI architecture for convolutional networks. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2015, 1037[37] Dong Q, Sinangil M E, Erbagci B, et al. A 351TOPS/W and 372.4GOPS compute-in-memory SRAM macro in 7nm FinFET CMOS for machine-learning applications. 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2020, 242[38] Sinangil M E, Erbagci B, Naous R, et al. A 7-nm compute-in-memory SRAM macro supporting multi-bit input, weight and output and achieving 351 TOPS/W and 372.4 GOPS. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2021, 56, 188 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.3031290[39] Kang M G, Gonugondla S, Patil A, et al. A 481pJ/decision 3.4M decision/s multifunctional deep In-memory inference processor using standard 6T sram array. arXiv: 1610.07501, 2016[40] Kang M G, Gonugondla S K, Shanbhag N R. A 19.4 nJ/decision 364K decisions/s in-memory random forest classifier in 6T SRAM array. ESSCIRC 2017 - 43rd IEEE European Solid State Circuits Conference, 2017, 263[41] Chang J, Chen Y H, Chan G, et al. A 5nm 135Mb SRAM in EUV and high-mobility-channel FinFET technology with metal coupling and charge-sharing write-assist circuitry schemes for high-density and low-VMIN applications. 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2020, 238[42] Si X, Tu Y N, Huang W H, et al. A 28nm 64Kb 6T SRAM computing-in-memory macro with 8b MAC operation for AI edge chips. 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2020, 246[43] Su J W, Si X, Chou Y C, et al. A 28nm 64Kb inference-training two-way transpose multibit 6T SRAM compute-in-memory macro for AI edge chips. 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2020, 240[44] Ali M, Jaiswal A, Kodge S, et al. IMAC: in-memory multi-bit multiplication and ACcumulation in 6T SRAM array. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2020, 67, 2521 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2020.2981901[45] Gonugondla S K, Kang M G, Shanbhag N. A 42pJ/decision 3.12TOPS/W robust in-memory machine learning classifier with on-chip training. 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2018, 490[46] Huang S S, Jiang H W, Peng X C, et al. XOR-CIM: compute-in-memory SRAM architecture with embedded XOR encryption. Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, 2020, 1[47] Kim H, Chen Q, Kim B. A 16K SRAM-based mixed-signal in-memory computing macro featuring voltage-mode accumulator and row-by-row ADC. 2019 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2019, 35[48] Jain S, Lin L Y, Alioto M. Broad-purpose in-memory computing for signal monitoring and machine learning workloads. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett, 2020, 3, 394 doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2020.3024838[49] Bose S K, Mohan V, Basu A. A 75kb SRAM in 65nm CMOS for in-memory computing based neuromorphic image denoising. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2020, 1[50] Kang M G, Keel M S, Shanbhag N R, et al. An energy-efficient VLSI architecture for pattern recognition via deep embedding of computation in SRAM. 2014 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2014, 8326[51] Gong M X, Cao N Y, Chang M Y, et al. A 65nm thermometer-encoded time/charge-based compute-in-memory neural network accelerator at 0.735pJ/MAC and 0.41pJ/update. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II, 2021, 68, 1408 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.3027801[52] Lee E, Han T, Seo D, et al. A charge-domain scalable-weight in-memory computing macro with dual-SRAM architecture for precision-scalable DNN accelerators. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2021, 68, 3305 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2021.3080042[53] Kim J, Koo J, Kim T, et al. Area-efficient and variation-tolerant in-memory BNN computing using 6T SRAM array. 2019 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, 2019, C118[54] Noel J P, Pezzin M, Gauchi R, et al. A 35.6 TOPS/W/mm2 3-stage pipelined computational SRAM with adjustable form factor for highly data-centric applications. IEEE Solid State Circuits Lett, 2020, 3, 286 doi: 10.1109/LSSC.2020.3010377[55] Jiang H W, Peng X C, Huang S S, et al. CIMAT: A compute-in-memory architecture for on-chip training based on transpose SRAM arrays. IEEE Trans Comput, 2020, 69, 944[56] Biswas A, Chandrakasan A P. Conv-RAM: An energy-efficient SRAM with embedded convolution computation for low-power CNN-based machine learning applications. 2018 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2018, 488[57] Nguyen V T, Kim J S, Lee J W. 10T SRAM computing-in-memory macros for binary and multibit MAC operation of DNN edge processors. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 71262 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3079425[58] Jiang Z W, Yin S H, Seo J S, et al. C3SRAM: an in-memory-computing SRAM macro based on robust capacitive coupling computing mechanism. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2020, 55, 1888 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.2992886[59] Jia H Y, Ozatay M, Tang Y Q, et al. A programmable neural-network inference accelerator based on scalable in-memory computing. 2021 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2021, 236[60] Jia H Y, Valavi H, Tang Y Q, et al. A programmable heterogeneous microprocessor based on bit-scalable in-memory computing. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2020, 55, 2609 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2020.2987714[61] Valavi H, Ramadge P J, Nestler E, et al. A mixed-signal binarized convolutional-neural-network accelerator integrating dense weight storage and multiplication for reduced data movement. 2018 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits, 2018, 141[62] Su J W, Chou Y C, Liu R H, et al. A 28nm 384kb 6T-SRAM computation-in-memory macro with 8b precision for AI edge chips. 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, 2021, 250[63] Khaddam-Aljameh R, Francese P A, Benini L, et al. An SRAM-based multibit in-memory matrix-vector multiplier with a precision that scales linearly in area, time, and power. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integr VLSI Syst, 2020, 29, 372 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2020.3037871[64] Zhang J, Lin Z T, Wu X L, et al. An 8T SRAM array with configurable word lines for in-memory computing operation. Electronics, 2021, 10, 300 doi: 10.3390/electronics10030300[65] Nasrin S, Ramakrishna S, Tulabandhula T, et al. Supported-BinaryNet: Bitcell array-based weight supports for dynamic accuracy-energy trade-offs in SRAM-based binarized neural network. 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2020, 1[66] Gonugondla S K, Kang M G, Shanbhag N R. A variation-tolerant in-memory machine learning classifier via on-chip training. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2018, 53, 3163 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2018.2867275[67] Wang B, Nguyen T Q, Do A T, et al. Design of an ultra-low voltage 9T SRAM with equalized bitline leakage and CAM-assisted energy efficiency improvement. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2015, 62, 441 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2014.2360760[68] Xue C X, Zhao W C, Yang T H, et al. A 28-nm 320-kb TCAM macro using split-controlled single-load 14T cell and triple-margin voltage sense amplifier. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2019, 54, 2743 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2915577[69] Jiang H W, Liu R, Yu S M. 8T XNOR-SRAM based parallel compute-in-memory for deep neural network accelerator. 2020 IEEE 63rd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2020, 257[70] Kang M G, Shanbhag N R. In-memory computing architectures for sparse distributed memory. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2016, 10, 855 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2016.2545402[71] Jain S, Lin L Y, Alioto M. ±CIM SRAM for signed in-memory broad-purpose computing from DSP to neural processing. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2021, 56, 2981 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3092759[72] Yue J S, Feng X Y, He Y F, et al. A 2.75-to-75.9TOPS/W computing-in-memory NN processor supporting set-associate block-wise zero skipping and Ping-pong CIM with simultaneous computation and weight updating. 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference, 2021, 238[73] Yang X X, Zhu K R, Tang X Y, et al. An in-memory-computing charge-domain ternary CNN classifier. 2021 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2021, 1[74] LeCun Y. Deep learning hardware: Past, present, and future. 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2019, 12[75] Chih Y D, Lee P H, Fujiwara H, et al. 16.4 an 89TOPS/W and 16.3TOPS/mm2 all-digital SRAM-based full-precision compute-in memory macro in 22nm for machine-learning edge applications. 2021 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2021, 252[76] Sie S H, Lee J L, Chen Y R, et al. MARS: multi-macro architecture SRAM CIM-based accelerator with co-designed compressed neural networks. IEEE Trans Comput Aided Des Integr Circuits Syst, 2021, in press doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2021.3082107[77] Agrawal A, Kosta A, Kodge S, et al. CASH-RAM: Enabling in-memory computations for edge inference using charge accumulation and sharing in standard 8T-SRAM arrays. IEEE J Emerg Sel Top Circuits Syst, 2020, 10, 295 doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2020.3014250[78] Yue J S, Yuan Z, Feng X Y, et al. A 65nm computing-in-memory-based CNN processor with 2.9-to-35.8TOPS/W system energy efficiency using dynamic-sparsity performance-scaling architecture and energy-efficient inter/intra-macro data reuse. 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2020, 234[79] Lin Z T, Zhan H L, Chen Z W, et al. Cascade current mirror to improve linearity and consistency in SRAM in-memory computing. IEEE J Solid State Circuits, 2021, 56, 2550 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2021.3063719[80] Lin Z T, Fang Y Q, Peng C Y, et al. Current mirror-based compensation circuit for multi-row read in-memory computing. Electron Lett, 2019, 55, 1176 doi: 10.1049/el.2019.2415[81] Kim Y, Kim H, Park J, et al. Mapping binary resnets on computing-in-memory hardware with low-bit ADCs. 2021 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, 2021, 856 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: