| Citation: |
Sheng Wang, Yun Kang, Xianli Li. Donor impurity-related optical absorption coefficients and refractive index changes in a rectangular GaAs quantum dot in the presence of electric field[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(11): 112001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/112001
****
S Wang, Y Kang, X L Li. Donor impurity-related optical absorption coefficients and refractive index changes in a rectangular GaAs quantum dot in the presence of electric field[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(11): 112001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/112001.
|
Donor impurity-related optical absorption coefficients and refractive index changes in a rectangular GaAs quantum dot in the presence of electric field
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/112001
More Information
-
Abstract
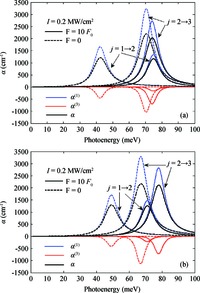
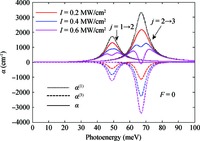
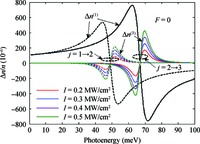
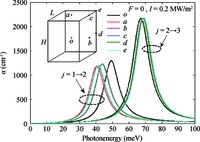
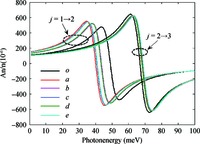
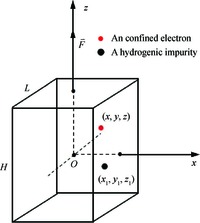
Within the quasi-one-dimensional effective potential model and effective mass approximation, we obtain the wavefunctions and energy eigenvalues of the ground (j=1) and first 2 excited states (j=2 and 3) of a donor impurity in a rectangular GaAs quantum dot in the presence of electric field. The donor impurity-related linear and nonlinear optical absorption as well as refractive index changes for the transitions j=1-2 and j=2-3 are investigated. The results show that the impurity position, incident optical intensity and electric field play important roles in the optical absorption coefficients and refractive index changes. We find that the impurity effect induces the blueshift for j=1-2 and redshift for j=3-2 in the absence of the electric field, but it leads to redshift for j=1-2 and blueshift for j=3-2 in the existence of the field. Also, the optical coefficient for the higher energy transitions j=2-3 is insensitive to variation of impurity positions, while that for the low energy transition j=1-2 depends significantly on the positions of impurity. In addition, the saturation and splitting phenomenon of the optical absorption are observed as the incident optical intensity increases. -
References
[1] Milanović V, Ikonić Z. Intraband absorption of infrared radiation in a semiconductor quantum dot. Phys Rev B, 1989, 39(11):7982 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.39.7982[2] Garduno-Nolasco E, Missous M, Donoval D, et al. Temperature dependence of InAs/GaAs quantum dots solar photovoltaic devices. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(5):054001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/054001[3] Peter A J. Hydrogenic impurities in cylindrical quantum wires in the presence of a magnetic field. Physica E, 2007, 39(1):115 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2007.01.008[4] Li S S, Xia J B. Electronic structure and binding energy of a hydrogenic impurity in a hierarchically self-assembled GaAs=AlxGa1-xAsGaAs=AlxGa1-xAs quantum dot. J Appl Phys, 2006, 100(8):083714 doi: 10.1063/1.2358406[5] Zounoubi A, Zorkani I, Messaoudi K E, et al. Magnetic field effect on the polarizability of shallow donor in cylindrical quantum dot. Phys Lett A, 2003, 312(3):220 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2033493780&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[6] Manaselyan A K, Kirakosyan A A. Effect of the dielectricconstant mismatch and magnetic field on the binding energy of hydrogenic impurities in a spherical quantum dot. Physica E, 2004, 22(4):825 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2003.09.045[7] Manaselyan A K, Kirakosyan A A. Barrier penetration in Kane type semiconductor nanostructures. Physica E, 2005, 28(4):452 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2026305909&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[8] Mazur Y I, Dorogan V G, Marega E, et al. Excited state coherent resonant electronic tunneling in quantum well-quantum dot hybrid structures. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98(8):083118 doi: 10.1063/1.3560063[9] Kang Yun, Wang Sheng, Li Xianli. Electron energy states in a two-dimensional GaAs quantum ring with hydrogenic donor impurity in the presence of magnetic field. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(3):032003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/3/032003[10] Kazarinov R F, Suris R A. Possibility of the amplification electromagnetic waves in a semiconductor with superlattice. Sov Phys Semicond, 1971, 5(3):707[11] Capasso F, Mohammed K, Cho A Y. Resonant tunneling through double barriers, perpendicular quantum transport phenomena in superlattices, and their device applications. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 1986, 22(9):1853 doi: 10.1109/JQE.1986.1073171[12] Miller A B. Quantum well optoelectronic switching devices. Int J High Speed Electron Syst, 1991, 1(1):19 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2064636165&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[13] Lee S W, Hirakava K, Shimada Y. Bound-to-continuum intersubband photoconductivity of self-assembled InAs quantum dots in modulation-doped heterostructures. Appl Phys Lett, 1999, 75(10):1428 doi: 10.1063/1.124715[14] Klimov V I, McBrauch D W, Leatherdale C A, et al. Electron and hole relaxation pathways in semiconductor quantum dots. Phys Rev B, 1999, 60(19):13740 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.60.13740[15] Mackowski S, Kyrychenko F, Karczewski G, et al. Thermal carrier escape and capture in CdTe quantum dots. Phys Status Solidi B, 2001, 224(2):465 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3951[16] Sauvage S, Boucaud P, Brunhes T, et al. Midinfrared absorption and photocurrent spectroscopy of InAs/GaAs self-assembled quantum dots. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78(16):2327 doi: 10.1063/1.1365411[17] Xie W. Absorption spectra of a donor impurity in a quantum ring. Physica Status Solidi B, 2009, 246(6):1313 doi: 10.1002/pssb.v246:6[18] Xie W. Nonlinear optical rectification of a hydrogenic impurity in a disc-like quantum dot. Physica B, 2009, 404(21):4142 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2009.07.177[19] Xie W. Impurity effects on optical property of a spherical quantum dot in the presence of an electric field. Physica B, 2010, 405(16):3436 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2010.05.019[20] Liang S, Xie W. Effects of the hydrostatic pressure and temperature on optical properties of a hydrogenic impurity in the discshaped quantum dot. Physica B, 2011, 406(11):2224 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2011.03.035[21] Chen T, Xie W, Liang S. The nonlinear optical rectification of an ellipsoidal quantum dot with impurity in the presence of an electric field. Physica E, 2012, 44(4):786 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2011.11.027[22] Özmen A, Yakar Y, Cakir B, et al. Computation of the oscillator strength and absorption coefficients for the intersubband transitions of the spherical quantum dot. Opt Commun, 2009, 282(19):3999 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2009.06.043[23] Yakar Y, Cakir B, Özmen A. Calculation of linear and nonlinear optical absorption coefficients of a spherical quantum dot with parabolic potential. Opt Commun, 2010, 283(9):1795 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2009.12.027[24] Cakir B, Yakar Y, Özmen A, et al. Linear and nonlinear optical absorption coefficients and binding energy of a spherical quantum dot. Superlattices Microstruct, 2010, 47(4):556 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2009.12.002[25] Yakar Y, Cakir B, Özmen A. Linear and nonlinear optical properties in spherical quantum dots. Commun Theory Phys, 2010, 53(6):1185 doi: 10.1088/0253-6102/53/6/39[26] Zhang L, Yu Z, Yao W, et al. Linear and nonlinear optical properties of strained GaN/AlN quantum dots:effects of impurities, radii of QDs, and the incident optical intensity. Superlattices Microstruct, 2010, 48(4):434 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2010.08.001[27] Chen B, Guo K X, Wang R Z, et al. Linear and nonlinear intersubband optical absorption in double triangular quantum wells. Solid State Commun, 2009, 149(7):310 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=2047467711&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn[28] Yuan J H, Huang J S, Yin M, et al. The correlation energies and nonlinear optical absorptions of an exciton in a disc-like quantum dot. Opt Commun, 2010, 283(18):3529 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2010.05.011[29] Sahin M. Third-order nonlinear optical properties of a one-and two-electron spherical quantum dot with and without a hydrogenic impurity. J Appl Phys, 2009, 106(6):063710 doi: 10.1063/1.3225100[30] Karimi M J, Rezaei G. Effects of external electric and magnetic fields on the linear and nonlinear intersubband optical properties of finite semi-parabolic quantum dots. Physica B, 2011, 406(23):4423 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2011.08.105[31] Zhang Z H, Guo K X, Chen B, et al. Theoretical studies on the optical absorption coefficients and refractive index changes in parabolic quantum dots in the presence of electric and magnetic fields. Superlattices Microstruct, 2010, 47(2):325 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2009.12.004[32] Niculescu E C. Dielectric mismatch effect on the photoionization cross section and intersublevel transitions in GaAs nanodots. Opt Commun, 2011, 284(13):3298 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2011.02.071[33] Burileanu L M, Radu A. THz laser field effect on the optical properties of cylindrical quantum well wires. Opt Commun, 2011, 284(7):2050 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2010.12.033[34] Tas H, Sahin M. The inter-sublevel optical properties of a spherical quantum dot-quantum well with and without a donor impurity. J Appl Phys, 2012, 112(5):053717 doi: 10.1063/1.4751483[35] Barseghyan M G, Restrepo R L, Mora-Ramos M E, et al. Donor impurity-related linear and nonlinear intraband optical absorption coefficients in quantum ring:effects of applied electric field and hydrostatic pressure. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2012, 7(1):538 doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-7-538[36] Cakir B, Yakar Y, Özmen A. Refractive index changes and absorption coefficients in a spherical quantum dot with parabolic potential. J Lumin, 2012, 132(10):2659 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2012.03.065[37] Duque C M, Mora-Ramos M E, Duque C A. On-center donor impurity-related nonlinear corrections to optical absorption and refractive index in a two-dimensional quantum ring. Opt Commun, 2012, 285(24):5456 doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2012.07.119[38] Yuan J, Xie W, He L. An off-center donor and nonlinear absorption spectra of spherical quantum dots. Physica E, 2009, 41(5):779 doi: 10.1016/j.physe.2008.12.012[39] Mora-Ramos M E, Duque C A, Kasapoglu E, et al. Linear and nonlinear optical properties in a semiconductor quantum well under intense laser radiation:effects of applied electromagnetic fields. J Lumin, 2012, 132(4):901 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2011.11.008[40] Kirak M, Yilmaz S, Sahin M, et al. The electric field effects on the binding energies and the nonlinear optical properties of a donor impurity in a spherical quantum dot. J Appl Phys, 2011, 109(9):094309 doi: 10.1063/1.3582137[41] Bednarek S, Szafran B, Chwiej T, et al. Effective interaction for charge carriers confined in quasi-one-dimensional nanostructures. Phys Rev B, 2003, 68(4):045328 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.68.045328[42] Wang S, Kang Y, Li X L. Binding energy of the ground and first few excited states of hydrogenic donor impurity in a rectangular GaAs quantum dot in the presence of electric field. Superlattices Microstruct, 2014, 76:221 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2014.10.010[43] Boyd W. Nonlinear optics. 2nd ed. New York:Academic Press, 2003 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: