| Citation: |
Xin Cong, Miaoling Lin, Ping-Heng Tan. Lattice vibration and Raman scattering of two-dimensional van der Waals heterostructure[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019, 40(9): 091001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/9/091001
****
X Cong, M L Lin, P H Tan, Lattice vibration and Raman scattering of two-dimensional van der Waals heterostructure[J]. J. Semicond., 2019, 40(9): 091001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/9/091001.
|
Lattice vibration and Raman scattering of two-dimensional van der Waals heterostructure
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/9/091001
More Information
-
Abstract
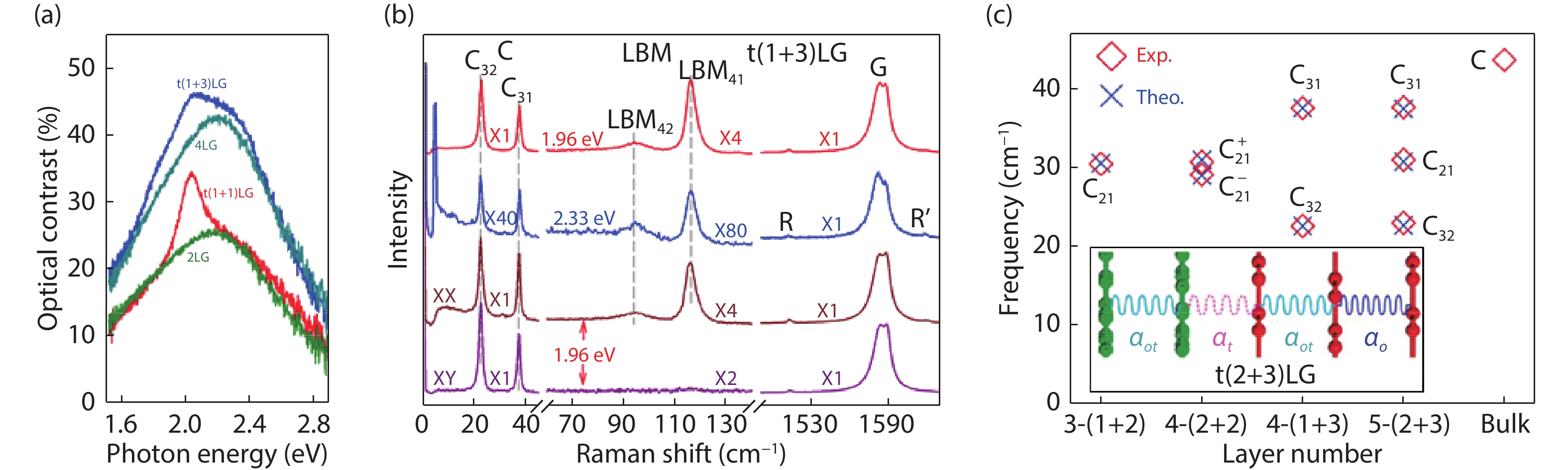
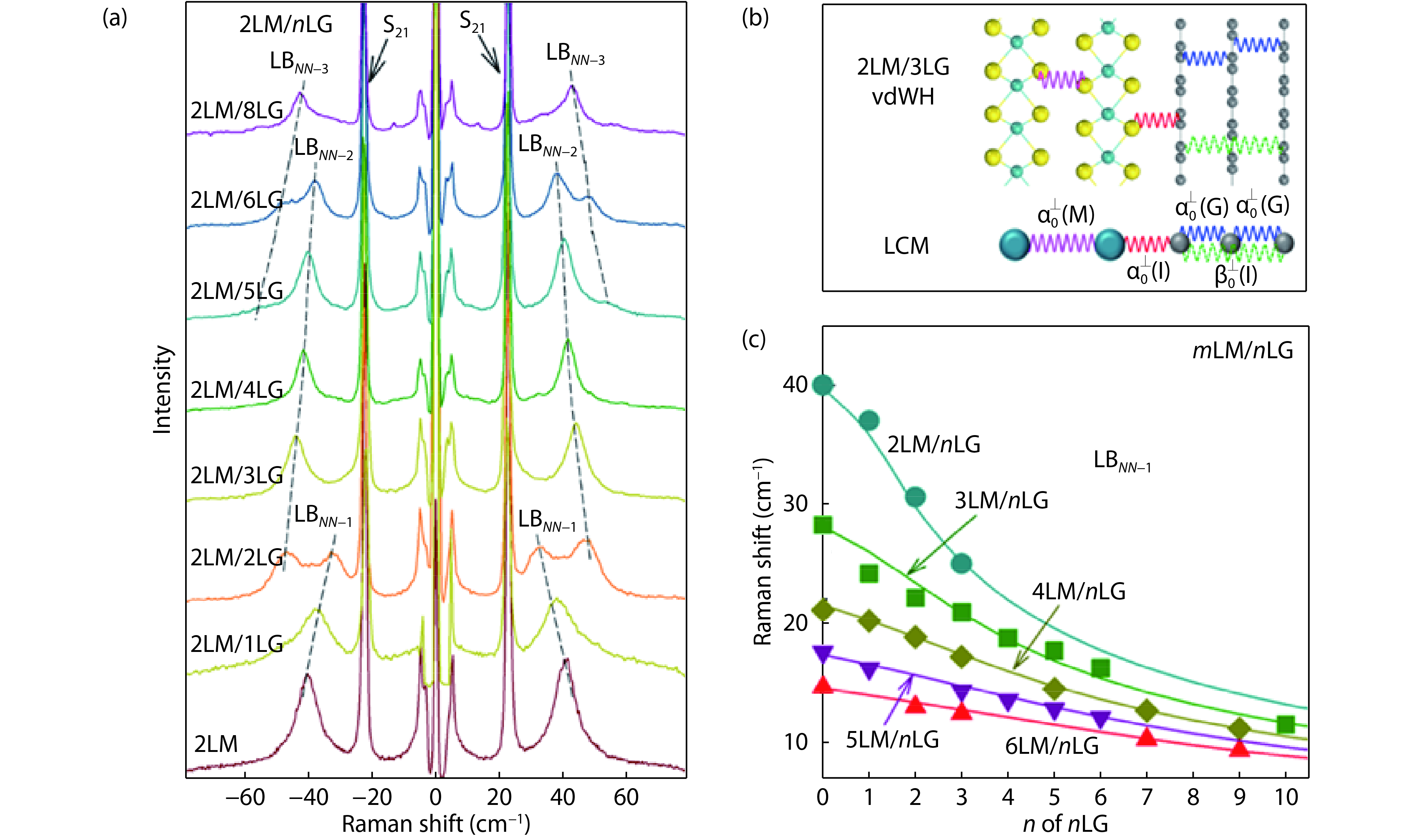
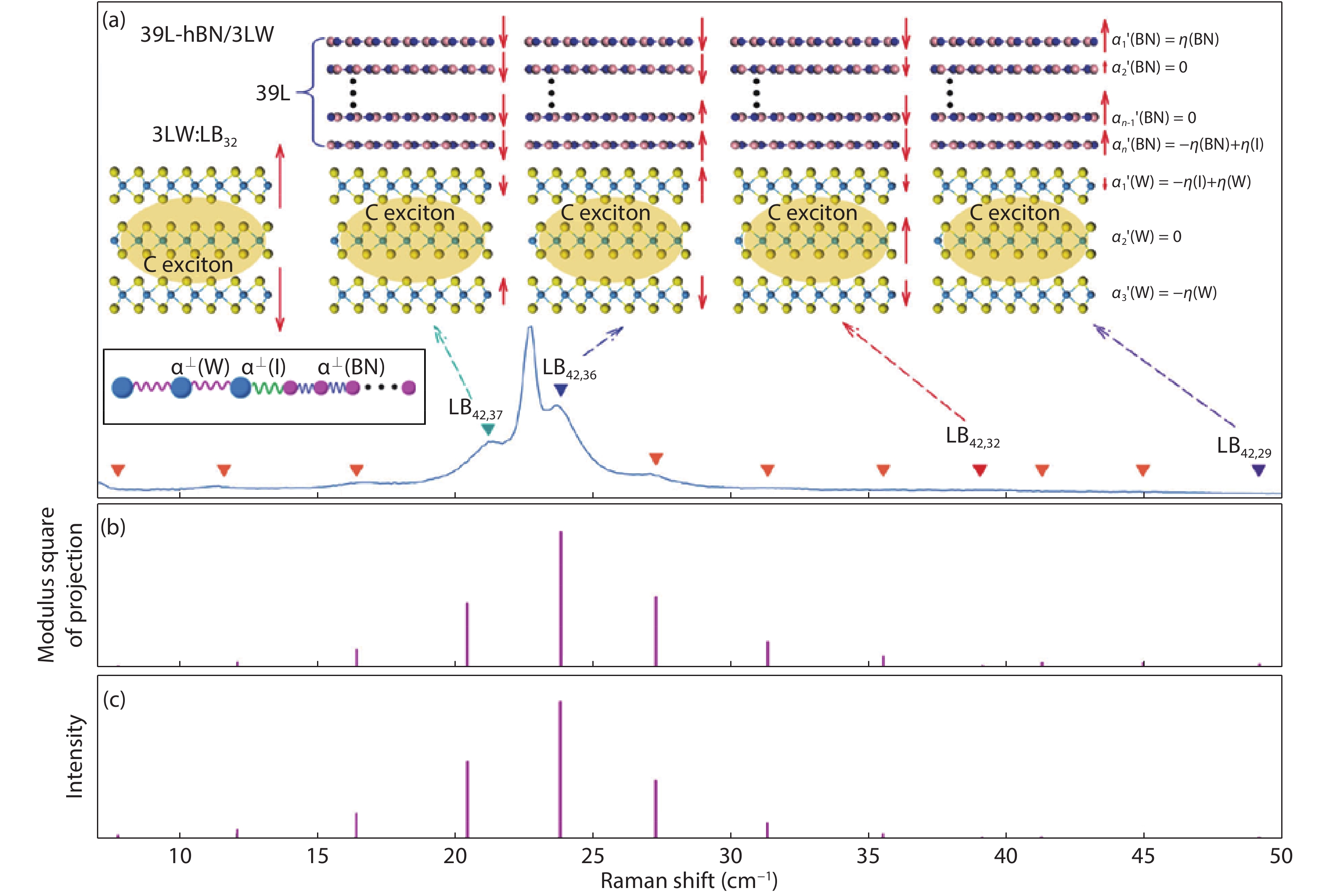
Research on two-dimensional (2D) materials and related van der Waals heterostructures (vdWHs) is intense and remains one of the leading topics in condensed matter physics. Lattice vibrations or phonons of a vdWH provide rich information, such as lattice structure, phonon dispersion, electronic band structure and electron–phonon coupling. Here, we provide a mini review on the lattice vibrations in vdWHs probed by Raman spectroscopy. First, we introduced different kinds of vdWHs, including their structures, properties and potential applications. Second, we discussed interlayer and intralayer phonon in twist multilayer graphene and MoS2. The frequencies of interlayer and intralayer modes can be reproduced by linear chain model (LCM) and phonon folding induced by periodical moiré potentials, respectively. Then, we extended LCM to vdWHs formed by distinct 2D materials, such as MoS2/graphene and hBN/WS2 heterostructures. We further demonstrated how to calculate Raman intensity of interlayer modes in vdWHs by interlayer polarizability model. -
References
[1] Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, et al. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science, 2004, 306(5696), 666 doi: 10.1126/science.1102896[2] Fiori G, Bonaccorso F, Iannaccone G, et al. Electronics based on two-dimensional materials. Nat Nanotechnol, 2014, 9(10), 768 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.207[3] Mounet N, Gibertini M, Schwaller P, et al. Two-dimensional materials from high-throughput computational exfoliation of experimentally known compounds. Nat Nanotechnol, 2018, 13(3), 246 doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0035-5[4] Novoselov K S, Geim A K, Morozov S V, et al. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature, 2005, 438(7065), 197 doi: 10.1038/nature04233[5] Mak K F, Lee C G, Hone J, et al. Atomically thin MoS2: A new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys Rev Lett, 2010, 105, 136805 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.136805[6] Li X L, Han W P, Wu J B, et al. Layer-number dependent optical properties of 2D materials and their application for thickness determination. Adv Funct Mater, 2017, 27(19), 1604468 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201604468[7] Wu J B, Zhang X Z, Ijäs M, et al. Resonant Raman spectroscopy of twisted multilayer graphene. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 5309 doi: 10.1038/ncomms6309[8] Wu J B, Hu Z X, Zhang X, et al. Interface coupling in twisted multilayer graphene by resonant Raman spectroscopy of layer breathing modes. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(7), 7440 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b02502[9] Wu J B, Lin M L, Cong X, et al. Raman spectroscopy of graphene-based materials and its applications in related devices. Chem Soc Rev, 2018, 47(5), 1822 doi: 10.1039/C6CS00915H[10] Liu Y, Huang Y, Duan X F. Van der Waals integration before and beyond twodimensional materials. Nature, 2019, 567(7748), 323 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1013-x[11] Novoselov K S, Mishchenko A, Carvalho A, et al. 2D materials and van der Waals heterostructures. Science, 2016, 353(6298), aac9439 doi: 10.1126/science.aac9439[12] Geim A K, Grigorieva I V. Van der Waals heterostructures. Nature, 2013, 499(7459), 419 doi: 10.1038/nature12385[13] Lin M L, Tan Q H, Wu J B, et al. Moiré phonons in twisted bilayer MoS2. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(8), 8770 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05006[14] Yu H Y, Liu G B, Tang J J. Moiré excitons: From programmable quantum emitter arrays to spin-orbit-coupled artificial lattices. Sci Adv, 2017, 3(11), e1701696 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701696[15] Seyler K L, Rivera P, Yu H Y, et al. Signatures of moiré-trapped valley excitons in MoSe2/WSe2 heterobilayers. Nature, 2019, 567(7746), 66 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0957-1[16] Tran K, Moody G, Wu F C, et al. Evidence for moiré excitons in van der Waals heterostructures. Nature, 2019, 567(7746), 71 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0975-z[17] Jin C H, Regan E C, Yan A M, et al. Observation of moiré excitons in WSe2/WS2 heterostructure superlattices. Nature, 2019, 567(7746), 76 doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0976-y[18] Zhou Z Q, Cui Y, Tan P H, et al. Optical and electrical properties of two-dimensional anisotropic materials. J Semicond, 2019, 40, 061001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/6/061001[19] Zhang X, Qiao X F, Shi W, et al. Phonon and Raman scattering of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides from monolayer, multilayer to bulk material. Chem Soc Rev, 2015, 44(9), 2757 doi: 10.1039/C4CS00282B[20] Tan P H. Raman Spectroscopy of two-dimensional materials. Singapore: Springer, 2019[21] Liang L B, Zhang J, Sumpter B G, et al. Low-frequency shear and layer-breathing modes in raman scattering of twodimensional materials. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(12), 11777 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b06551[22] Tan P H, Han W P, Zhao W J, et al. The shear mode of multilayer graphene. Nat Mater, 2012, 11(4), 294 doi: 10.1038/nmat3245[23] Zhang X, Han W P, Wu J B, et al. Raman spectroscopy of shear and layer breathing modes in multilayer MoS2. Phys Rev B, 2013, 87(11), 115413 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.87.115413[24] Lin M L, Zhou Y, Wu J B, et al. Cross-dimensional electron-phonon coupling in van der Waals heterostructures. Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1), 2419 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10400-z[25] Song Q J, Tan Q H, Zhang X, et al. Physical origin of davydov splitting and resonant Raman spectroscopy of davydov components in multilayer MoTe2. Phys Rev B, 2016, 93(11), 115409 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.115409[26] Tan Q H, Zhang X, Luo X D, et al. Layer-number dependent high-frequency vibration modes in few-layer transition metal dichalcogenides induced by interlayer couplings. J Semicond, 2017, 38(3), 031006 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/3/031006[27] Wu J B, Wang H, Li X L, et al. Raman spectroscopic characterization of stacking configuration and interlayer coupling of twisted multilayer graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition. Carbon, 2016, 110, 225 doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.09.006[28] Lin M L, Chen T, Lu W, et al. Identifying the stacking order of multilayer graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition via Raman spectroscopy. J Raman Spectrosc, 2018, 49(1), 46 doi: 10.1002/jrs.5219[29] Li H, Wu J B, Ran F R, et al. Interfacial interactions in van der Waals heterostructures of MoS2 and graphene. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(11), 11714 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07015[30] Yang J H, Lee J U, Cheong H. Excitation energy dependence of Raman spectra of few-layer WS2. FlatChem, 2017, 3, 64 doi: 10.1016/j.flatc.2017.06.001[31] Liang L B, Puretzky A A, Sumpter B G, et al. Interlayer bond polarizability model for stacking-dependent low-frequency Raman scattering in layered materials. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(40), 15340 doi: 10.1039/C7NR05839J -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: