| Citation: |
Hang Zhou, Jingrong Yan, Jialin Li, Huan Ge, Tao Zhu, Bingke Zhang, Shucheng Chang, Junmin Sun, Xue Bai, Xiaoguang Wei, Fei Yang. A review of the etched terminal structure of a 4H-SiC PiN diode[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(11): 113101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/11/113101
H Zhou, J R Yan, J L Li, H Ge, T Zhu, B K Zhang, S C Chang, J M Sun, X Bai, X G Wei, F Yang. A review of the etched terminal structure of a 4H-SiC PiN diode[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(11): 113101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/11/113101
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
A review of the etched terminal structure of a 4H-SiC PiN diode
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/11/113101
More Information-
Abstract
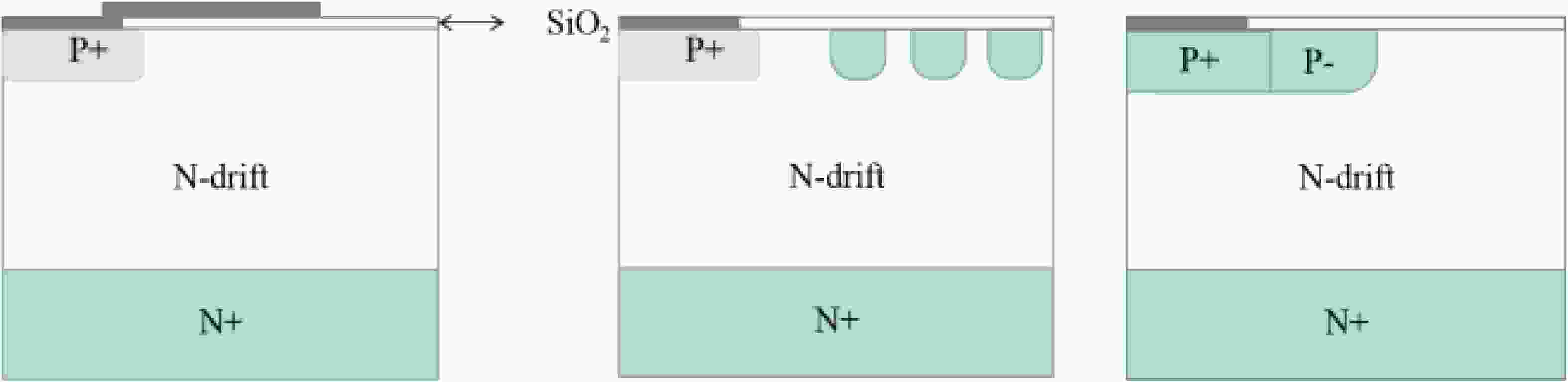
The comparison of domestic and foreign studies has been utilized to extensively employ junction termination extension (JTE) structures for power devices. However, achieving a gradual doping concentration change in the lateral direction is difficult for SiC devices since the diffusion constants of the implanted aluminum ions in SiC are much less than silicon. Many previously reported studies adopted many new structures to solve this problem. Additionally, the JTE structure is strongly sensitive to the ion implantation dose. Thus, GA-JTE, double-zone etched JTE structures, and SM-JTE with modulation spacing were reported to overcome the above shortcomings of the JTE structure and effectively increase the breakdown voltage. They provided a theoretical basis for fabricating terminal structures of 4H-SiC PiN diodes. This paper summarized the effects of different terminal structures on the electrical properties of SiC devices at home and abroad. Presently, the continuous development and breakthrough of terminal technology have significantly improved the breakdown voltage and terminal efficiency of 4H-SiC PiN power diodes. -
References
[1] Baliga B J. Analysis of a high-voltage merged p-i-n/Schottky (MPS) rectifier. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 1987, 8, 407 doi: 10.1109/EDL.1987.26676[2] Li X, Tone K, Fursin L, et al. Multistep junction termination extension for SiC power devices. Electron Lett, 2001, 37, 392 doi: 10.1049/el:20010258[3] Fedison J B, Ramungul N, Chow T P, et al. Electrical characteristics of 4.5 kV implanted anode 4H-SiC p-i-n junction rectifiers. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2001, 22, 130 doi: 10.1109/55.910619[4] Singh R, Cooper J A, Melloch M R, et al. SiC power Schottky and PiN diodes. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2002, 49, 665 doi: 10.1109/16.992877[5] Funaki T, Kimoto T, Hikihara T. Evaluation of high frequency switching capability of SiC Schottky barrier diode, based on junction capacitance model. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2008, 23, 2602 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2008.2002096[6] Wolborski M, Bakowski M, Schöner A. Analysis of bulk and surface components of leakage current in 4H-SiC PiN MESA diodes. Microelectron Eng, 2006, 83, 75 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2005.10.029[7] Niwa H, Feng G, Suda J, et al. Breakdown characteristics of 20 kV-class 4H-SiC PIN diodes with improved junction termination structures. 24th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs (ISPSD), 2012, 381 doi: 10.1109/ISPSD.2012.6229101[8] Zhou C N, Wang Y, Yue R F, et al. Step JTE, an edge termination for UHV SiC power devices with increased tolerances to JTE dose and surface charges. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2017, 64, 1193 doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2648886[9] Temple V A K, Tantraporn W. Junction termination extension for near-ideal breakdown voltage in p-n junctions. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1986, 33, 1601 doi: 10.1109/T-ED.1986.22713[10] Baliga B J. Power semiconductor devices. Boston: PWS, Publishing Co., 1995[11] Sheridan D C, Niu G F, Cressler J D. Design of single and multiple zone junction termination extension structures for SiC power devices. Solid State Electron, 2001, 45, 1659 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1101(01)00052-1[12] Kimoto T, Danno K, Jun S D. Lifetime-killing defects in 4H-SiC epilayers and lifetime control by low-energy electron irradiation. Phys Stat Sol (b), 2008, 245, 1327 doi: 10.1002/pssb.200844076[13] Klein P B, Shanabrook B V, Huh S W, et al. Lifetime-limiting defects in n-4H-SiC epilayers. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 88, 052110 doi: 10.1063/1.2170144[14] Hull B A, Das M K, Richmond J T, et al. A 180 amp/4.5 kV 4H-SiC PiN diode for high current power modules. 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and IC's, 2006, 1 doi: 10.1109/ISPSD.2006.1666125[15] Nakayama K, Tanaka A, Nishimura M, et al. Characteristics of a 4H-SiC pin diode with carbon implantation/thermal oxidation. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2012, 59, 895 doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2181516[16] Okamoto D, Tanaka Y, Mizushima T, et al. 13-kV, 20-a 4H-SiC PiN diodes for power system applications. Mater Sci Forum, 2014, 778−780, 855 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.778-780.855[17] Sugawara Y, Takayama D, Asano K, et al. 12-19 kV 4H-SiC pin diodes with low power loss. Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices & ICs. IPSD '01 (IEEE Cat. No. 01CH37216), 2002, 27 doi: 10.1109/ISPSD.2001.934552[18] Perez R, Tournier D, Perez-Tomas A, et al. Planar edge termination design and technology considerations for 1.7-kV 4H-SiC PiN diodes. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52, 2309 doi: 10.1109/TED.2005.856805[19] Das M K, Hull B A, Richmond J T, et al. Ultra high power 10 kV, 50 A SiC PiN diodes. Proceedings of ISPSD '05. The 17th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs, 2005, 299 doi: 10.1109/ISPSD.2005.1488010[20] Hiyoshi T, Hori T, Jun S D, et al. Simulation and experimental study on the junction termination structure for high-voltage 4H-SiC PiN diodes. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2008, 55, 1841 doi: 10.1109/TED.2008.926643[21] Ghandi R, Buono B, Domeij M, et al. High-voltage 4H-SiC PiN diodes with etched junction termination extension. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2009, 30, 1170 doi: 10.1109/LED.2009.2030374[22] Ghandi R, Lee H S, Domeij M, et al. Fabrication of 2700-V 12 mΩ·cm2 non ion-implanted 4H-SiCBJTs with common-emitter current gain of 50. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2008, 29, 1135 doi: 10.1109/LED.2008.2004419[23] Konstantinov A O, Wahab Q, Nordell N, et al. Ionization rates and critical fields in 4H silicon carbide. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 71, 90 doi: 10.1063/1.119478[24] Niwa H, Gan F, Jun S D, et al. Breakdown characteristics of 15-kV-class 4H-SiC PiN diodes with various junction termination structures. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2012, 59, 2748 doi: 10.1109/TED.2012.2210044[25] Kawahara K, Jun S D, Kimoto T. Analytical model for reduction of deep levels in SiC by thermal oxidation. J Appl Phys, 2012, 111, 053710 doi: 10.1063/1.3692766[26] Luts J, Schlangenotto H, Scheuermann U, et al. Semiconductor power devices. Springer-Verlag, 2011[27] Noborio M, Jun S D, Kimoto T. P-channel MOSFETs on 4H-SiC {0001} and nonbasal faces fabricated by oxide deposition and N2O annealing. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2009, 56, 1953 doi: 10.1109/TED.2009.2025909[28] Ghandi R, Buono B, Domeij M, et al. Surface-passivation effects on the performance of 4H-SiC BJTs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2011, 58, 259 doi: 10.1109/TED.2010.2082712[29] Kimoto T, Kanzaki Y, Noborio M, et al. Interface properties of metal–oxide–semiconductor structures on 4H-SiC {0001} and (1120) formed by N2O oxidation. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2005, 44, 1213 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.44.1213[30] Kaji N, Niwa H, Jun S D, et al. Ultrahigh-voltage SiC p-i-n diodes with improved forward characteristics. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2015, 62, 374 doi: 10.1109/TED.2014.2352279[31] Hino S, Hatta H, Sadamatsu K, et al. Demonstration of SiC-MOSFET embedding Schottky barrier diode for inactivation of parasitic body diode. Mater Sci Forum, 2017, 897, 477 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.897.477[32] Zhang F S. Simulation and fabrication of high-voltage 4H-SiC PiN diode with JTE. Chinese Journal of Coputational Physics, 2011, 28, 306[33] Yuan L, Zhang Y M, Zhang Y M, et al. Design of an effective junction termination structure for 4H-SiC BJTs (in Chinese). 2013 National Doctoral Academic Forum-Electronic Thin Film and Integrated Device, 2013, 71[34] Okuto Y, Crowell C R. Threshold energy effect on avalanche breakdown voltage in semiconductor junctions. Solid State Electron, 1975, 18, 161 doi: 10.1016/0038-1101(75)90099-4[35] McKay K G. Avalanche breakdown in silicon. Phys Rev, 1954, 94, 877 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.94.877[36] Li J T, Xiao C Q, Xu X L, et al. High-voltage 4H-SiC PiN diodes with the etched implant junction termination extension. J Semicond, 2017, 38, 024003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/2/024003[37] Wu J, Wang G Y, Yang C, et al. Development of high quality factor SiC PiN diode. High Power Converter Technology, 2016, 1096[38] Zou X, Yue R F, Wang Y. Etched junction termination extension with floating guard rings and middle rings for ultrahigh-voltage 4H-SiC PiN diodes. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC), 2016, 418 doi: 10.1109/EDSSC.2016.7785297[39] Zou X, Yue R F, Wang Y. Development of 3.6 kV 4H-SiC PiN power diodes. 2017 International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits (EDSSC), 2017, 1 doi: 10.1109/EDSSC.2017.8126407[40] Tao M L, Deng X C, Hu R, et al. Design, fabrication and characterization of 6.5kV/100A 4H-SiC PiN power rectifier. 2021 IEEE Workshop on Wide Bandgap Power Devices and Applications in Asia (WiPDA Asia), 2022, 228 doi: 10.1109/WiPDAAsia51810.2021.9656038[41] Deng X C, Li L J, Wu J, et al. A multiple-ring-modulated JTE technique for 4H-SiC power device with improved JTE-dose window. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2017, 64, 5042 doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2761995[42] Hu R, Deng X C, Xu X J, et al. An improved composite JTE termination technique for ultrahigh voltage 4H-SiC power devices. 2019 16th China International Forum on Solid State Lighting & 2019 International Forum on Wide Bandgap Semiconductors China (SSLChina: IFWS), 2020, 18 doi: 10.1109/SSLChinaIFWS49075.2019.9019794[43] Tao M L, Deng X C, Wu H, et al. Design, fabrication and characterization of 10kV/100A 4H-SiC PiN power rectifier. Mater Sci Forum, 2020, 1014, 115 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.1014.115[44] Saitoh Y, Masuda T, Michikoshi H, et al. V-groove trench gate SiC MOSFET with a double reduced surface field junction termination extensions structure. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2019, 58, SBBD11 doi: 10.7567/1347-4065/aaffba[45] Hirao T, Onose H, Kan Y S, et al. Edge termination with enhanced field-limiting rings insensitive to surface charge for high-voltage SiC power devices. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2020, 67, 2850 doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.2992577 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
























































