| Citation: |
Muhammad Bilal, M. Shafiq, Iftikhar Ahmad, Imad Khan. First principle studies of structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of Zn-chalcogenides under pressure[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(7): 072001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/072001
M Bilal, M. Shafiq, I Ahmad, I Khan. First principle studies of structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of Zn-chalcogenides under pressure[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(7): 072001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/072001.
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
First principle studies of structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of Zn-chalcogenides under pressure
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/7/072001
More Information-
Abstract
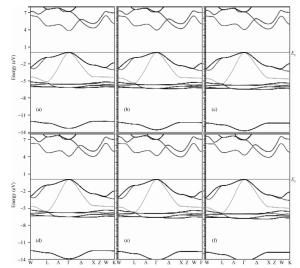
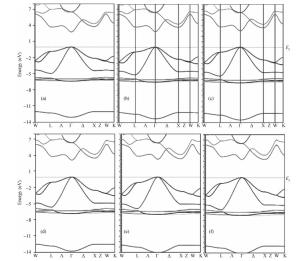
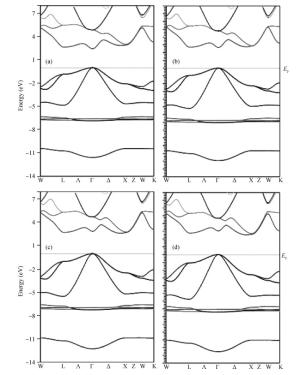
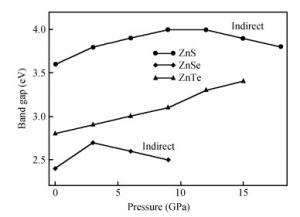
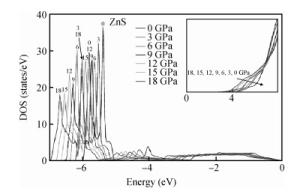
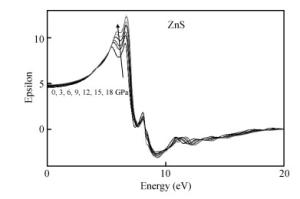
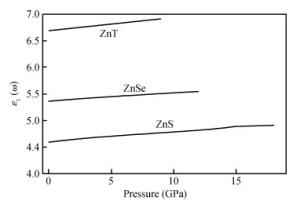
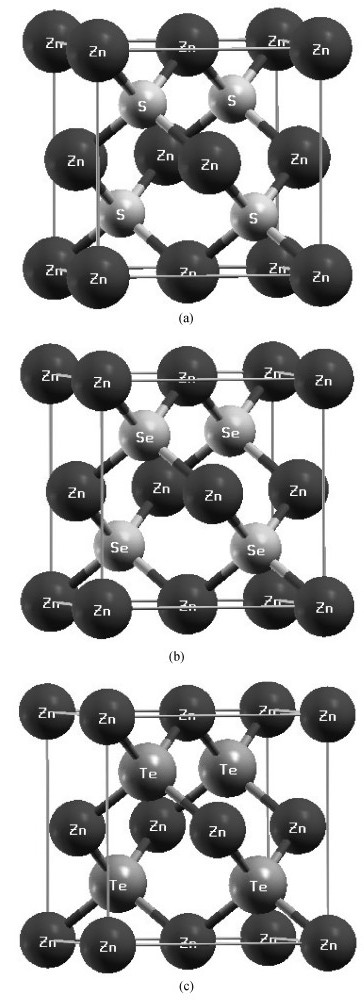
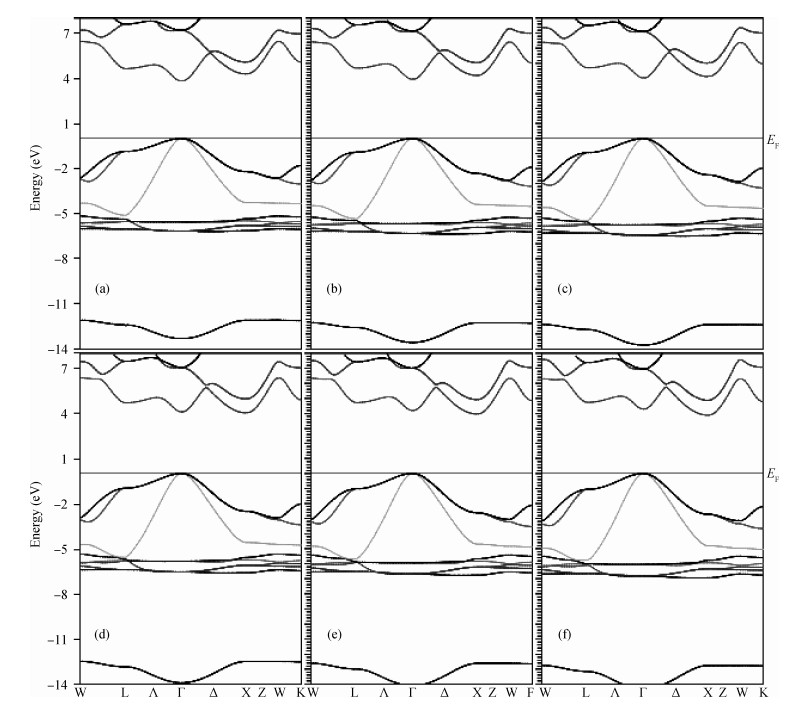
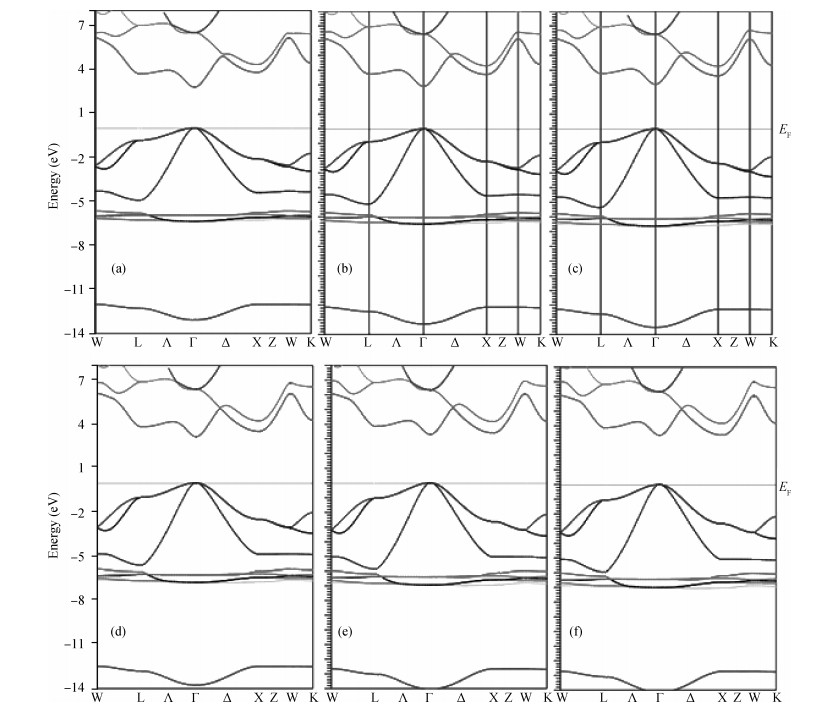
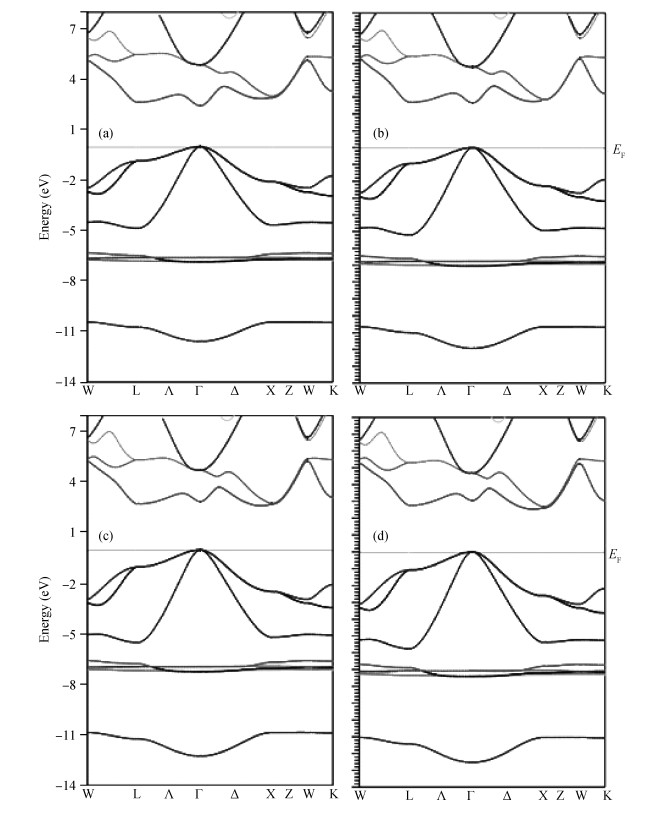
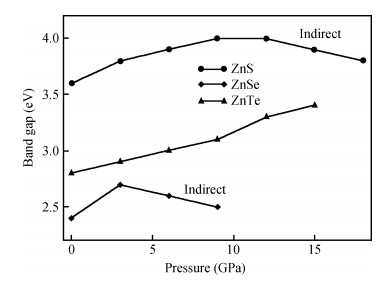
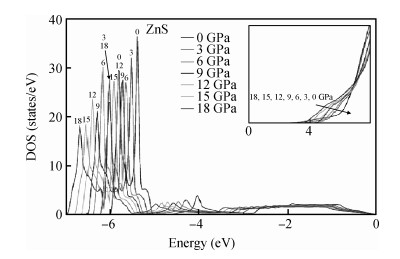
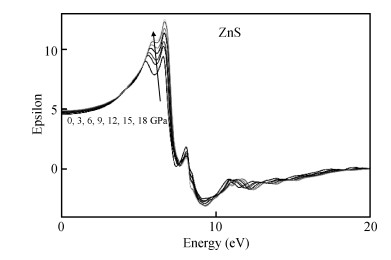
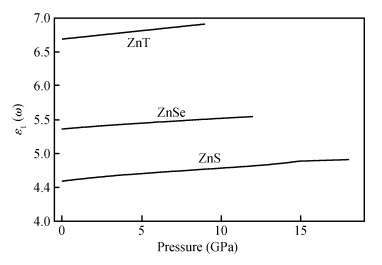
Structural, elastic, electronic and optical properties of zinc-chalcogenides (viz. ZnX, X=S, Se and Te) are studied in zinc-blende structure under hydrostatic pressure using the full-potential linearized augmented plane wave method. Generalized gradient approximation is used for exchange correlation potentials. Pressure-dependent lattice constants and bulk moduli are obtained using the optimization method. Young's modulus, Poisson's ratio, internal strain parameter and anisotropy are also calculated. The higher values of Young's modulus in comparison to the bulk modulus show that these materials are hard to break. Poisson's ratio is computed for the first time for these materials to the best of our knowledge and its values show higher ionic contribution in these materials. Modified Becke and Johnson (mBJ) method is used to study band gaps, density of states, dielectric function and refractive index. Electronic study shows direct band gaps convert to indirect band gaps with increasing pressure in the case of ZnS and ZnTe. We compared our results with other theoretical and experimental results. Our results are far better than other theoretical results because mBJ is the best technique to treat Ⅱ-Ⅵ semiconductors. -
References
[1] Fan H, Barnard A S, Zacharias M. ZnO nanowires and nanobelts: shape selection and thermodynamic modeling. Appl Phys Lett, 2007, 90(14): 143116 doi: 10.1063/1.2720715[2] Wei S H, Zhang S B. Structure stability and carrier localization in CdX (X = S, Se, Te) semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2000, 62(11): 6944 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.62.6944[3] Landolt-Bornstein: numerical data and functional relationships in science and technology. Madelung O, Schulz M, Weiss H, ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1982, 17b[4] Segura A, Sans J A, Manjon F J, et al. Optical properties and electronic structure of rock-salt ZnO under pressure. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83(2): 278 doi: 10.1063/1.1591995[5] Bilge M, Özdemir K S, Kart H H, et al. Mechanical and electronical properties of ZnS under pressure. J Achiev Mater Manufact Eng, 2008, 31(1): 29 https://www.mendeley.com/research-papers/mechanical-electronical-properties-zns-under-pressure/[6] Wang H Y, Cao J, Huang X Y, et al. Pressure dependence of elastic and dynamical properties of zinc-blende ZnS and ZnSe from first principle calculation. Condens Matter Phys, 2012, 15(1): 13705 doi: 10.5488/CMP.15.13705[7] Sorgel J, Scherz U. Ab initio calculation of elastic constants and electronic properties of ZnSe and ZnTe under uniaxial strain. Eur Phys J B, 1998, 5(1): 45 doi: 10.1007/s100510050417[8] Casali R A, Christensen N E. Elastic constants and deformation potentials of ZnS and ZnSe under pressure. Solid State Commun, 1998, 108(10): 793 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1098(98)00303-2[9] Soykan C, Ozdemir Kart S, Cagin T. Structural and mechanical properties of ZnTe in the zincblend phase. Arch Mater Sci Eng, 2010, 46(2): 115 http://www.oalib.com/paper/2660033[10] Khan I, Ahmad I. Theoretical studies of the band structure and optoelectronic properties of ZnOxS1-x. Int J Quantum Chem, 2013, 113(9): 1285 doi: 10.1002/qua.v113.9[11] Lee B H. Elastic constants of ZnTe and ZnSe between 77°-300°K. J Appl Phys, 1970, 41(7): 2984 doi: 10.1063/1.1659349[12] Hamdi I, Aouissi M, Qteish A, et al. Pressure dependence of vibrational, thermal, and elastic properties of ZnSe: an ab initio study. Phys Rev B, 2006, 73(17): 174114 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.73.174114[13] Khenata R, Bouhemadou A, Sahnoun M, et al. Elastic, electronic and optical properties of ZnS, ZnSe and ZnTe under pressure. Comput Mater Sci, 2006, 38(1): 29 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2006.01.013[14] Ghahramani E D, Moss D J, Sipe J E. Full-band-structure calculation of first-, second-, and third-harmonic optical response coefficients of ZnSe, ZnTe, and CdTe. Phys Rev B, 1991, 43(12): 9700 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.43.9700[15] Jaffe J E, Pandey R, Seel M J. Ab initio high-pressure structural and electronic properties of ZnS. Phys Rev B, 1993, 47(11): 6299 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.47.6299[16] Qteish A. Self-interaction-corrected local density approximation pseudopotential calculations of the structural phase transformations of ZnO and ZnS under high pressure. Condens Matter Phys, 2000, 12(26): 5639 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/12/26/311[17] Oshikiri M, Aryasetiawan F. Band gaps and quasiparticle energy calculations on ZnO, ZnS, and ZnSe in the zinc-blende structure by the GW approximation. Phys Rev B, 1999, 60(15): 10754 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.60.10754[18] Xie H Q, Zeng Y, Huang W Q. First principles study on electronic and optical properties of La-doped ZnS. Int J Phys Sci, 2010, 5(5): 2672 http://or.nsfc.gov.cn/handle/00001903-5/88649[19] Khan I, Ahmad I, Aliabad H A R, el al. Effect of phase transition on the optoelectronic properties of Zn1-xMgxS. J Appl Phys, 2012, 112(7): 073104 doi: 10.1063/1.4756040[20] Khan I, Ahmad I, Zhang D, et al. Electronic and optical properties of mixed Be-chalcogenides. Phys Chem Solids, 2013, 74(2): 181 doi: 10.1016/j.jpcs.2012.08.012[21] Khan I, Ahmad I, Aliabad H A R, et al. Conversion of optically isotropic to anisotropic CdSxSe1-x (0 < x < 1) alloy with S concentration. Compos Mater Sci, 2013, 77: 145 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.04.030[22] Khan I, Afaq A, Aliabad H A R, et al. Transition from optically inactive to active Mg-chalcogenides: a first principle study. Compos Mater Sci, 2012, 61: 278 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.04.036[23] Blaha P, Schwarz K, Madsen G K H, et al. WIEN2k: an augmented plane wave plus local orbitals program for calculating crystal properties. Vienna University of Technology, Vienna, Austria, 2001 http://www.mendeley.com/research/wien2k-augmented-planewave-local-orbitals-program-calculating-crystal-properties/[24] Mehl M J, Osburn J E, Papaconstantopoulos D A, et al. Structural properties of ordered high-melting-temperature intermetallic alloys from first-principles total-energy calculations. Phys Rev B, 1990, 41(15): 10311 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.41.10311[25] Wu J Z, Zhao E J, Xiang H P, et al. Crystal structures and elastic properties of superhard IrN2 and IrN3 from first principles. Phys Rev B, 2007, 76(5): 054115 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.76.054115[26] Varshney D, Shriya S, Khenata R. Structural phase transition and elastic properties of mercury chalcogenides. Mater Chem Phys, 2012, 135(2/3): 365 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0254058412004403[27] Chen K, Zhao L R, Tee J S. Ab initio study of elastic properties of Ir and Ir3X compounds. J Appl Phys, 2003, 93(5): 2414 doi: 10.1063/1.1540742[28] Shimizu H, Sasaki S. High-pressure brillouin studies and elastic properties of single-crystal H2S grown in a diamond cell. Science, 1992, 257(5069): 514 doi: 10.1126/science.257.5069.514[29] Kleinman L. Deformation potentials in silicon.Ⅰ. uniaxial strain. Phys Rev, 1962, 128(6): 2614 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.128.2614[30] Birch F. Finite elastic strain of cubic crystals. Phys Rev, 1947, 71(11): 809 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.71.809[31] Vagelatos N, Wehe D, King J S. Phonon dispersion and phonon densities of states for ZnS and ZnTe. J Chem Phys, 1974, 60(9): 3613 doi: 10.1063/1.1681581[32] Karze H, Potzel W, Kfferlein M, et al. Lattice dynamics and hyperfine interactions in ZnO and ZnSe at high external pressures. Phys Rev B, 1996, 53(17): 11425 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.53.11425[33] Madelung O, Weiss H, Schultz M. Landolt-Börnstein new series group Ⅲ: physics of Ⅱ-Ⅵ and Ⅰ-Ⅶ compounds, semimagnetic semiconductors. Berlin: Springer, 1982, 17b[34] Franco R, Sanchez P M, Recio J M. Theoretical compressibilities of high-pressure ZnTe polymorphs. Phys Rev B, 2003, 68(19): 195208 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.68.195208[35] Postnikov A V, Pagés O, Hugel J. Lattice dynamics of the mixed semiconductors (Be, Zn)Se from first-principles calculations. Phys Rev B, 2005, 71(11): 115206 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.71.115206[36] Wang S Q. A comparative first-principles study of ZnS and ZnO in zinc blende structure. J Cryst Growth, 2006, 287(1): 185 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.10.064[37] Merad A E, Kanoun M B, Merad G, et al. Full-potential investigation of the electronic and optical properties of stressed CdTe and ZnTe. Mat Chem Phys, 2005, 92(2/3): 333 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2004.10.031[38] Tiong S R, Hiramatsu M, Matsushima Y, et al. The phase transition pressures of zincsulfoselenide single crystals. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1989, 28(1): 291 http://iopscience.iop.org/1347-4065/28/2r/291[39] Yu S C, Spain I L, Skelton E F. High pressure phase transitions in tetrahedrally coordinated semiconducting compounds. Solid State Commun, 1978, 25(1): 49 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0038109878911687[40] Gangadharan R, Jayalakshmi V, Kalaiselvi J, et al. Electronic and structural properties of zinc chalcogenides ZnX (X = S, Se, Te). J Alloy Compd, 2003, 5(1/2): 22 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925838803001889[41] Qadri S B, Skelton E F, Dinsmore A D, et al. The effect of particle size on the structural transitions in zinc sulfide. Phys Rev B, 2001, 89: 115 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=5028164[42] Causa M, Dovesi R, Pisani C, et al. Electronic structure and stability of different crystal phases of magnesium oxide. Phys Rev B, 1986, 33(2): 1308 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.33.1308[43] Smelyansky V I, Tse J S. Theoretical study on the high-pressure phase transformation in ZnSe. Phys Rev B, 1995, 52(7): 4658 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.52.4658[44] Ves S, Strossner K, Christensen N E, et al. Pressure dependence of the lowest direct absorption edge of ZnSe. Solid State Commun, 1985, 56(6): 479 doi: 10.1016/0038-1098(85)90697-0[45] Ovsyannikov S V, Shchennikov V V. Phase transitions investigation in ZnTe by thermoelectric power measurements at high pressure. Solid State Commun, 2004, 132(5): 333 doi: 10.1016/j.ssc.2004.07.062[46] Sinko G V, Smirnow N A. Ab initio calculations of elastic constants and thermodynamic properties of bcc, fcc, and hcp Al crystals under pressure. Condens Matter Phys, 2002, 14(29): 6989 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/14/29/301[47] Berlincourt D, Jaffe H, Shiozawa L R. Electroelastic properties of the sulfides, selenides, and tellurides of zinc and cadmium. Phys Rev, 1963, 29(3): 1009 http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1963PhRv..129.1009B[48] Burenkov Y A, Davydov S Y, Nikanorov S P. Elastic properties of indium-arsenide. Soviet Physics Solid State, 1975, 17: 1446[49] Sahin O. Indentation load effect on Young's modulus and hardness of porous sialon ceramicby depth sensing indentation tests. Chin Phys Lett, 2007, 24: 3206 doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/24/11/051[50] Yuan P F, Ding Z J. Ab initio calculation of elastic properties of rock-salt and zinc-blend MgS under pressure. Physica B, 2008, 403(12): 1996 doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2007.11.004[51] Bouhemadou A, Khanate R, Kharoubi M. FP-APW+lo calculations of the elastic properties in zinc-blende Ⅲ-P compounds under pressure effects. Compute Mat Sci, 2009, 45(2): 474 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2008.11.013[52] Sverdlov V. Strain-induced effects in advanced MOSFETs. New York: Springer, 2011: 87 doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-0382-1[53] Rong C X, Cuie H, Yi Z Z, et al. First-principles calculations for elastic properties of ZnS under pressure. Chin Phys Lett, 2008, 25(3): 1064 doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/25/3/070[54] Monika G, Gupta B R K. Pressure induced phase transition in zinc sulfide (10 nm-ZnS) nano-crystal. Res J Recent Sci, 2012, 2: 21 http://www.isca.in/rjrs/archive/v2/iISC-2012/8.ISCA-ISC-2012-15PhyS-14.php[55] Yao L D, Wang F F, Shen X, et al. Structural stability and Raman scattering of ZnSe nanoribbons under high pressure. J Alloys Comp, 2009, 480(2): 798 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.02.105[56] Martin R. Elastic properties of ZnS structure semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 1970, 1(10): 4005 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.1.4005[57] Comphausen D L, Conel G A N, Paul W. Calculation of energy-band pressure coefficients from the dielectric theory of the chemical bond. Phys Rev Lett, 1971, 26(4): 184 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.26.184[58] Chang K J, Froyen S, Cohen M L. Pressure coefficients of band gaps in semiconductors. Solid State Commun, 1984, 50(2): 105 doi: 10.1016/0038-1098(84)90917-7[59] Khenata R, Baltache H, Sahnoun M, et al. Full potential linearized augmented plane wave calculations of structural and electronic properties of GeC, SnC and GeSn. Physica B, 2003, 336(2/3): 331 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921452603002989[60] Bagayoko D, Zhao G L, Franklin L, et al. Efficient band gap prediction for solids. Phys Rev Lett, 2010, 105(19): 196403 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.196403[61] Reiss P, Protiere M, Li L. Core/shell semiconductor nanocrystals. Small, 2009, 5(2): 154 doi: 10.1002/smll.200800841[62] Dou Y, Egdelly R G, Law D S L, et al. An experimental and theoretical investigation of the electronic structure of CdO. Condens Matter Phys, 1998, 10(38): 8447 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/10/38/006[63] Oshikiri M, Aryasetiawan F. Band gaps and quasiparticle energy calculations on ZnO, ZnS, and ZnSe in the zinc-blende structure by the GW approximation. Phys Rev B, 1999, 60(15): 10754 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.60.10754[64] Zakharov O, Rubio A, Blase X, et al. Quasiparticle band structures of six Ⅱ-Ⅵ compounds: ZnS, ZnSe, ZnTe, CdS, CdSe, and CdTe. Phys Rev B, 1994, 50(15): 10780 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.10780[65] Li J, Wang L. Band-structure-corrected local density approximation study of semiconductor quantum dots and wires. Phys Rev B, 2005, 72(12): 125325 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.72.125325[66] Kootstra F, de Boeij P L, Snijders J C. Application of time-dependent density-functional theory to the dielectric function of various nonmetallic crystals. Phys Rev B, 2000, 62(11): 7071 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.62.7071 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: