| Citation: |
Qing Wang, Ning Chen, Shen Xu, Weifeng Sun, Longxing Shi. A novel trajectory prediction control for proximate time-optimal digital control DC-DC converters[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(9): 095010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/9/095010
Q Wang, N Chen, S Xu, W F Sun, L X Shi. A novel trajectory prediction control for proximate time-optimal digital control DC-DC converters[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(9): 095010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/9/095010.
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
A novel trajectory prediction control for proximate time-optimal digital control DC-DC converters
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/9/095010
More Information-
Abstract
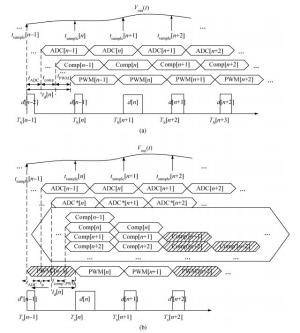
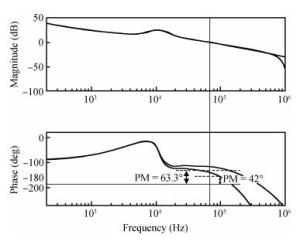
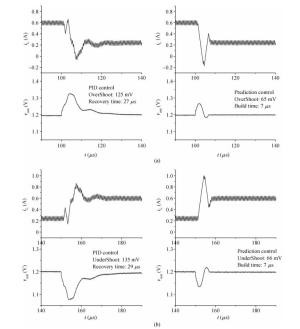
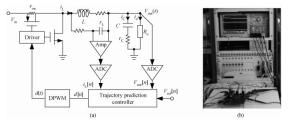
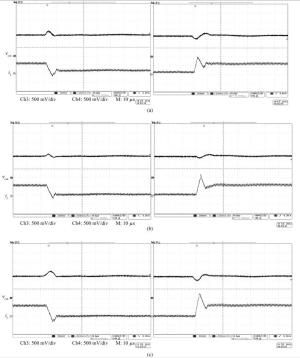
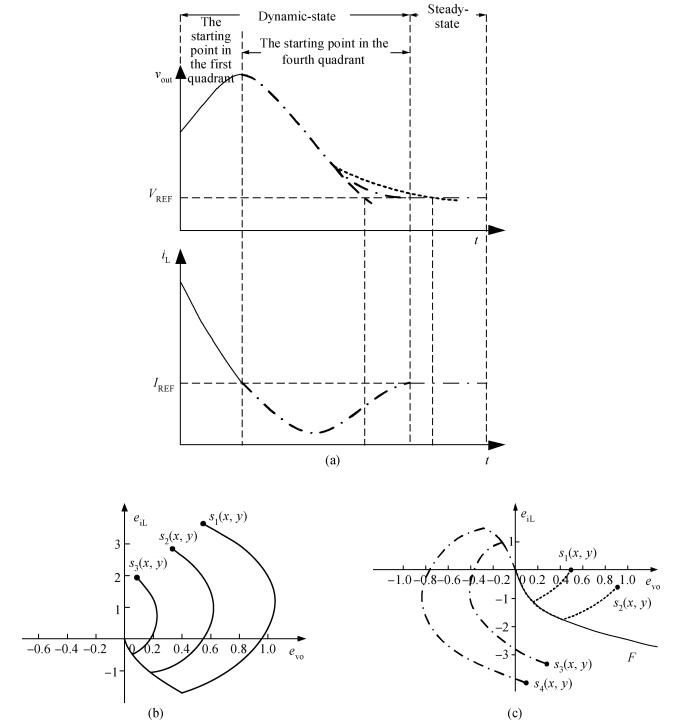
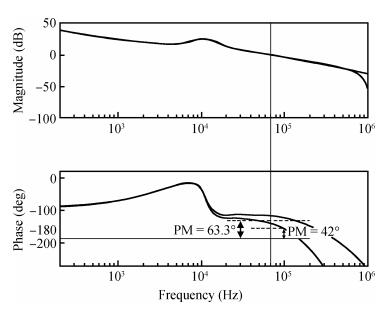
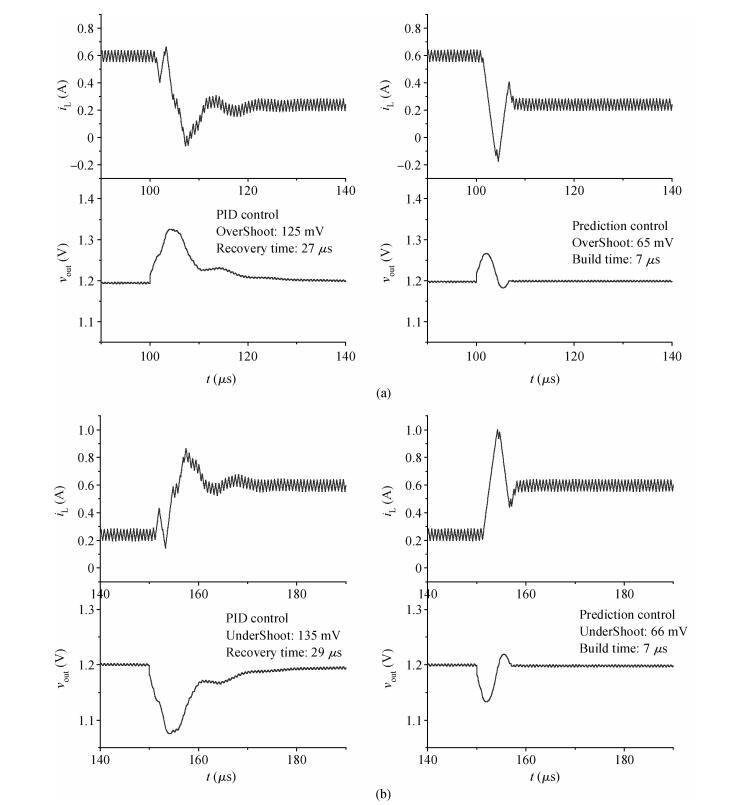
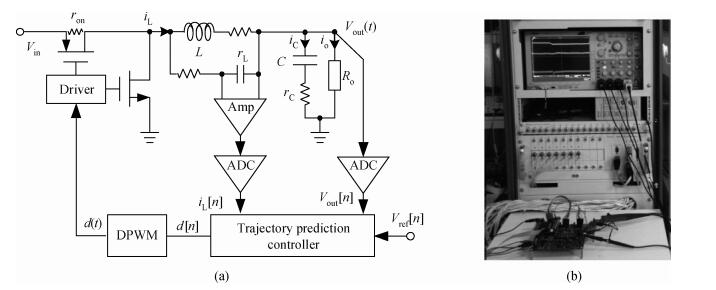
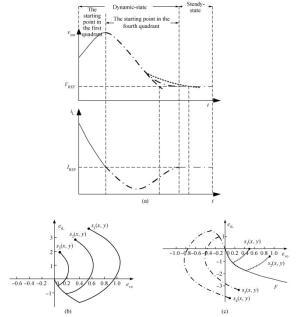
The purpose of this paper is to present a novel trajectory prediction method for proximate time-optimal digital control DC-DC converters. The control method provides pre-estimations of the duty ratio in the next several switching cycles, so as to compensate the computational time delay of the control loop and increase the control loop bandwidth, thereby improving the response speed. The experiment results show that the fastest transient response time of the digital DC-DC with the proposed prediction is about 8 μs when the load current changes from 0.6 to 0.1 A.-
Keywords:
- transient response,
- digital control,
- DC-DC converters,
- prediction,
- time delay
-
References
[1] Yan W, Li W H, Liu R. A noise-shaped buck DC-DC converter with improved light-load efficiency and fast transient response. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2011, 26(12):3908 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2011.2136361[2] Tsai J C, Chen C L, Lee Y H, et al. Modified hysteretic current control (MHCC) for improving transient response of boost converter. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Ⅰ:Regular Papers, 2011, 58(8):1967 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2011.2106231[3] Meyer E, Zhang Z L, Liu Y F. Controlled auxiliary circuit to improve the unloading transient response of buck converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2010, 25(4):806 doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2009.2032362[4] Smedley K M, Cuk S. One cycle control of switching converters. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 1995, 10(6):625 doi: 10.1109/63.471281[5] Bibian S, Jin H. Time delay compensation of digital control for DC switch mode power supplies using prediction techniques. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 2000, 15(5):835 doi: 10.1109/63.867672[6] Lee A T L, Chan P C H. Adaptive prediction in digitally controlled buck converter with fast load transient response. Proc 13th IEEE Control and Modeling for Power Electronics, Kyoto, Japan, 2012 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6251747/[7] Leung K K S, Chung H S H. State trajectory prediction control for boost converters. Proc 2004 Circuits and Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2004: V-556 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=1329720[8] Nasab T M M. Application of Smith prediction technique in designing of variable structure control systems for plants with time delay. Proc 1999 IEEE Industrial Electronics, Bled, Slovenia, 1999: 1111 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=796851[9] Kurokawa F, Maruta H, Sakemi J, et al. A new prediction based digital control DC-DC converter. Proc 2010 Ninth International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Washington, USA, 2010: 720 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/icp.jsp?arnumber=5708932[10] Kurokawa F, Ueno K, Maruta H, et al. A new digital control DC-DC converter with repetition neural network prediction. Proc 2011 IEEE Ninth International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, Singapore, 2011: 648 http://www.mendeley.com/research/new-digital-control-dcdc-converter-neural-network-predictor-1/ -
Proportional views
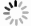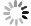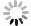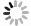




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: