| Citation: |
Beichen Zhang, Bingbing Yao, Liyuan Liu, Jian Liu, Nanjian Wu. High power-efficient asynchronous SAR ADC for IoT devices[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2017, 38(10): 105001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/10/105001
****
B C Zhang, B B Yao, L Y Liu, J Liu, N J Wu. High power-efficient asynchronous SAR ADC for IoT devices[J]. J. Semicond., 2017, 38(10): 105001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/10/105001.
|
High power-efficient asynchronous SAR ADC for IoT devices
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/38/10/105001
More Information
-
Abstract
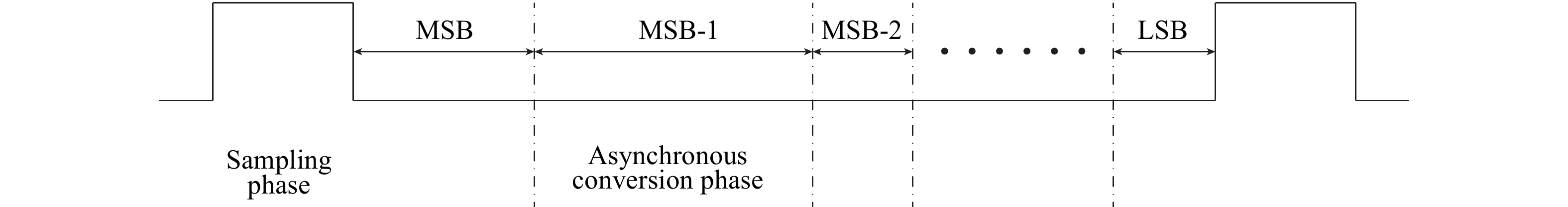
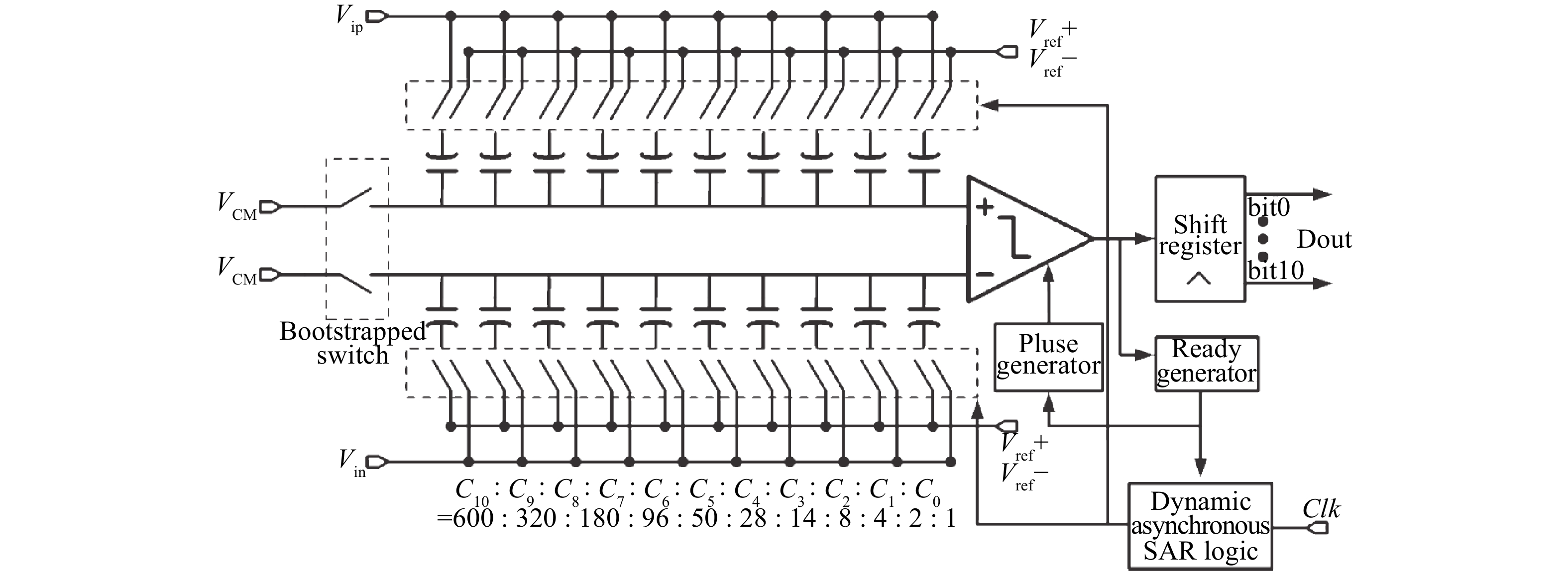
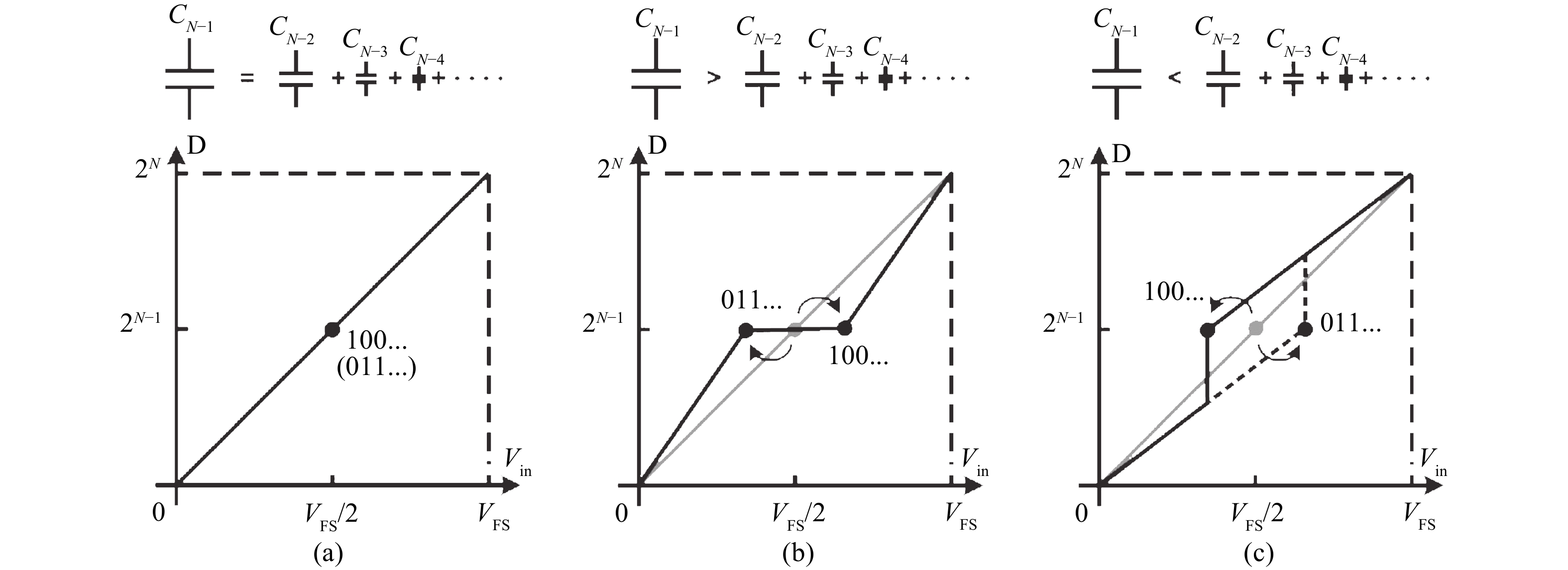
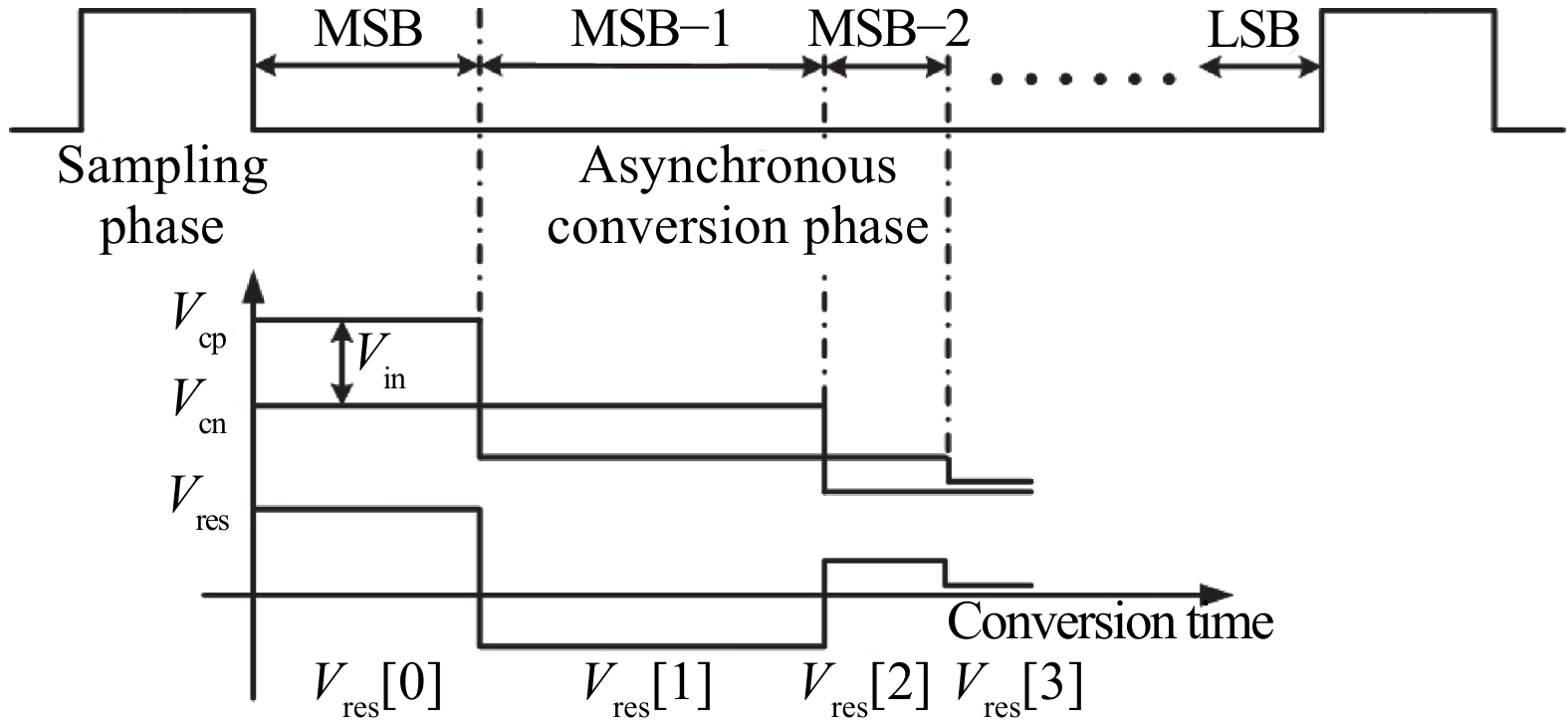
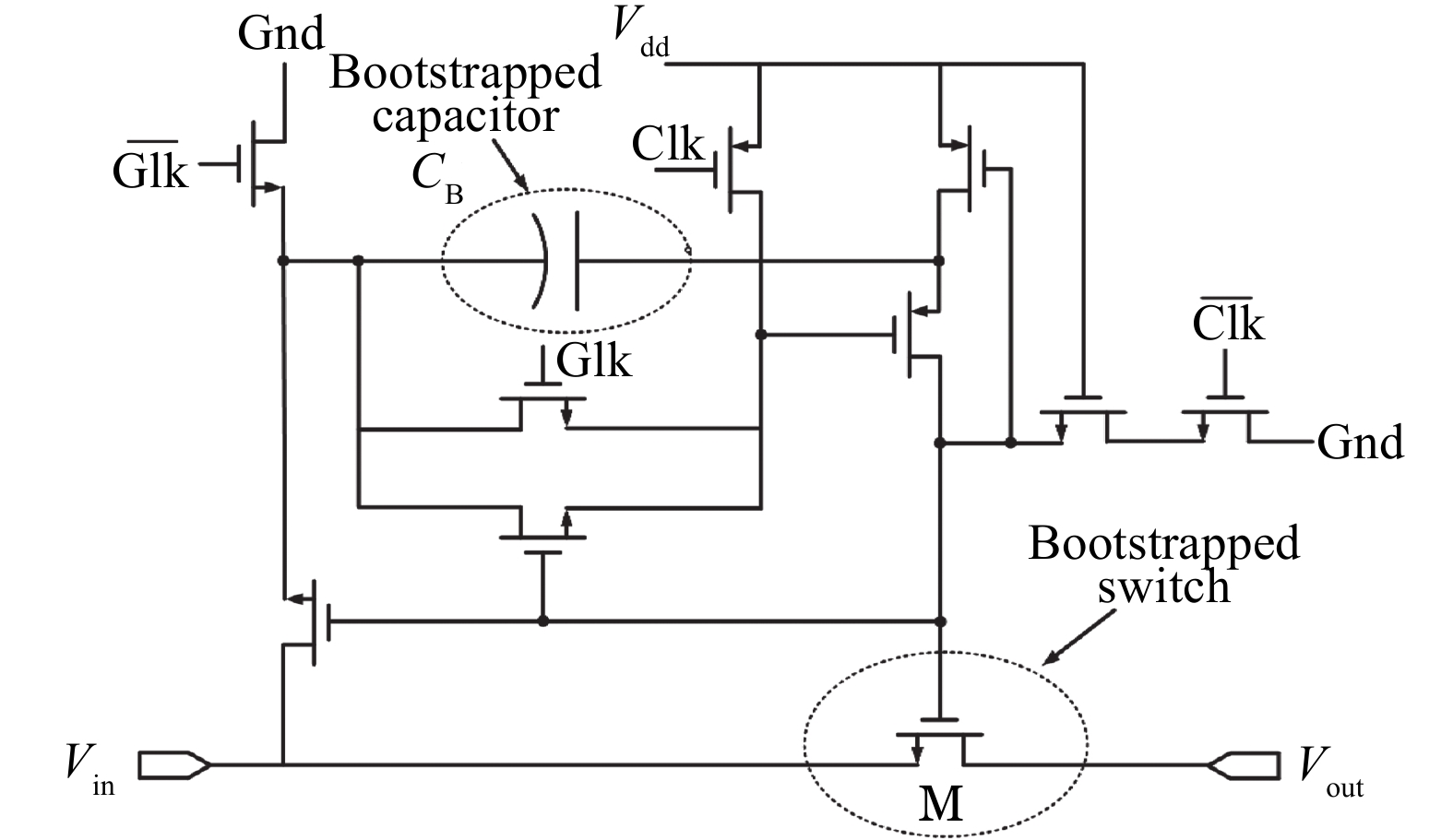
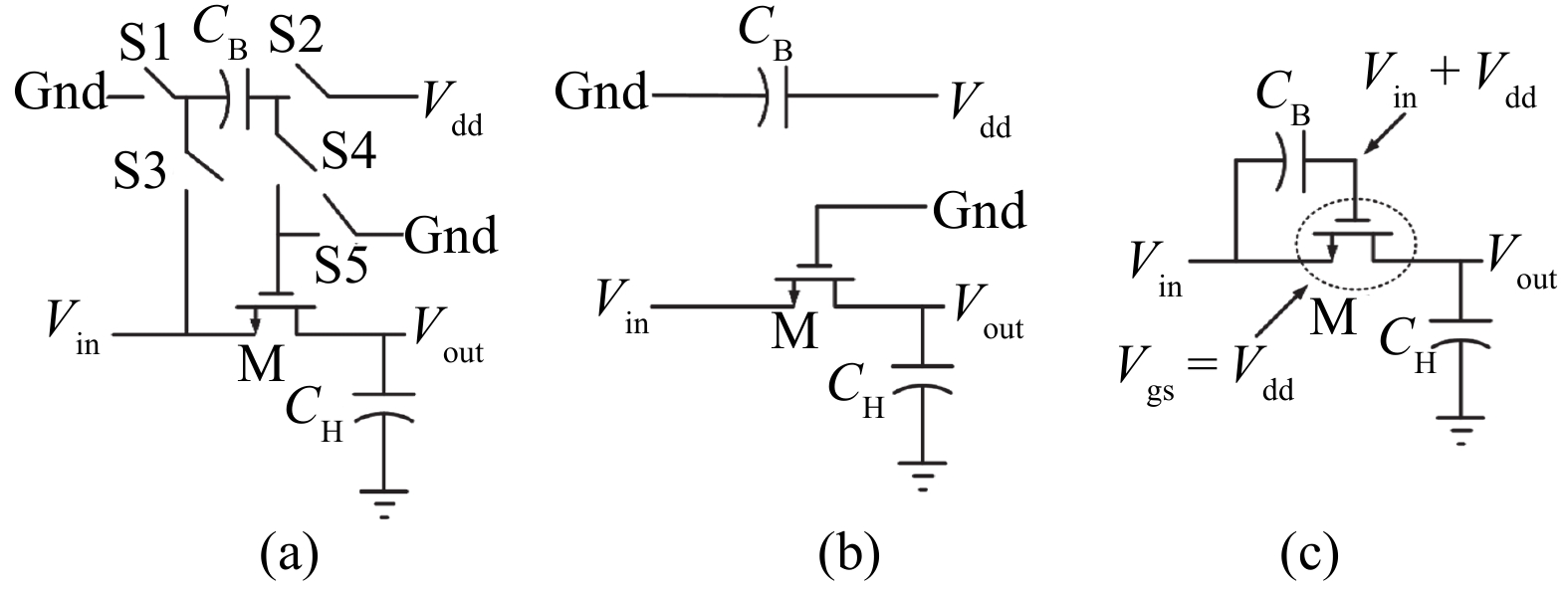
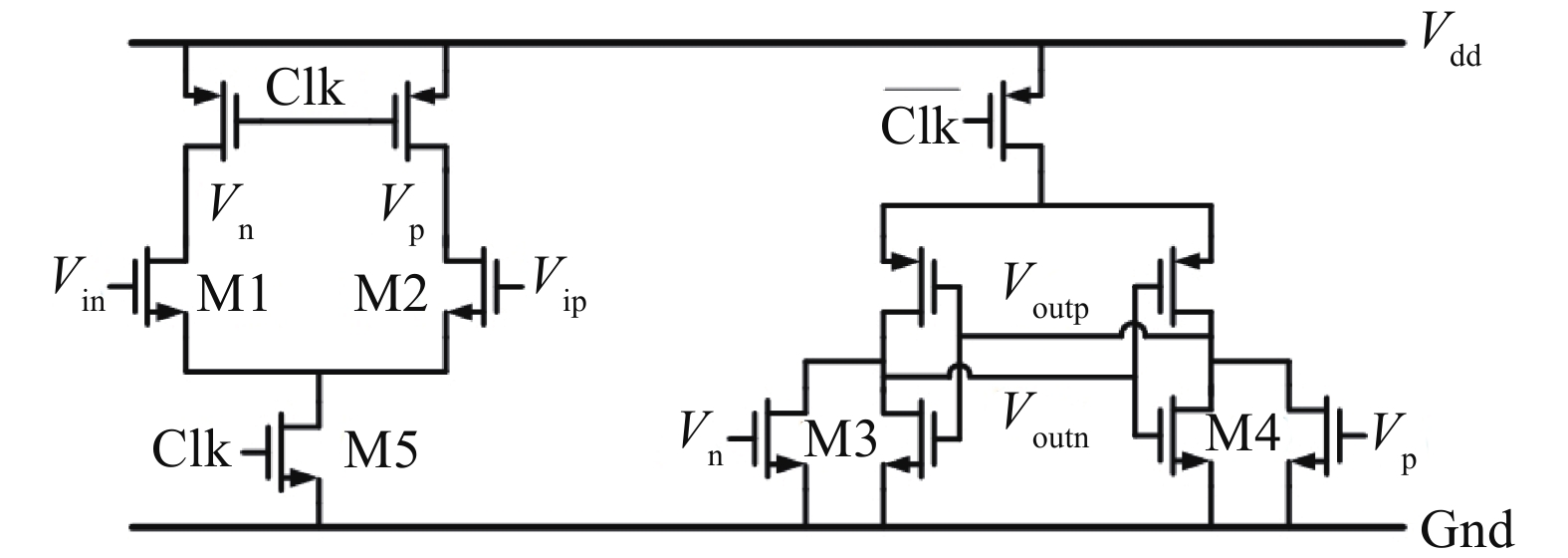
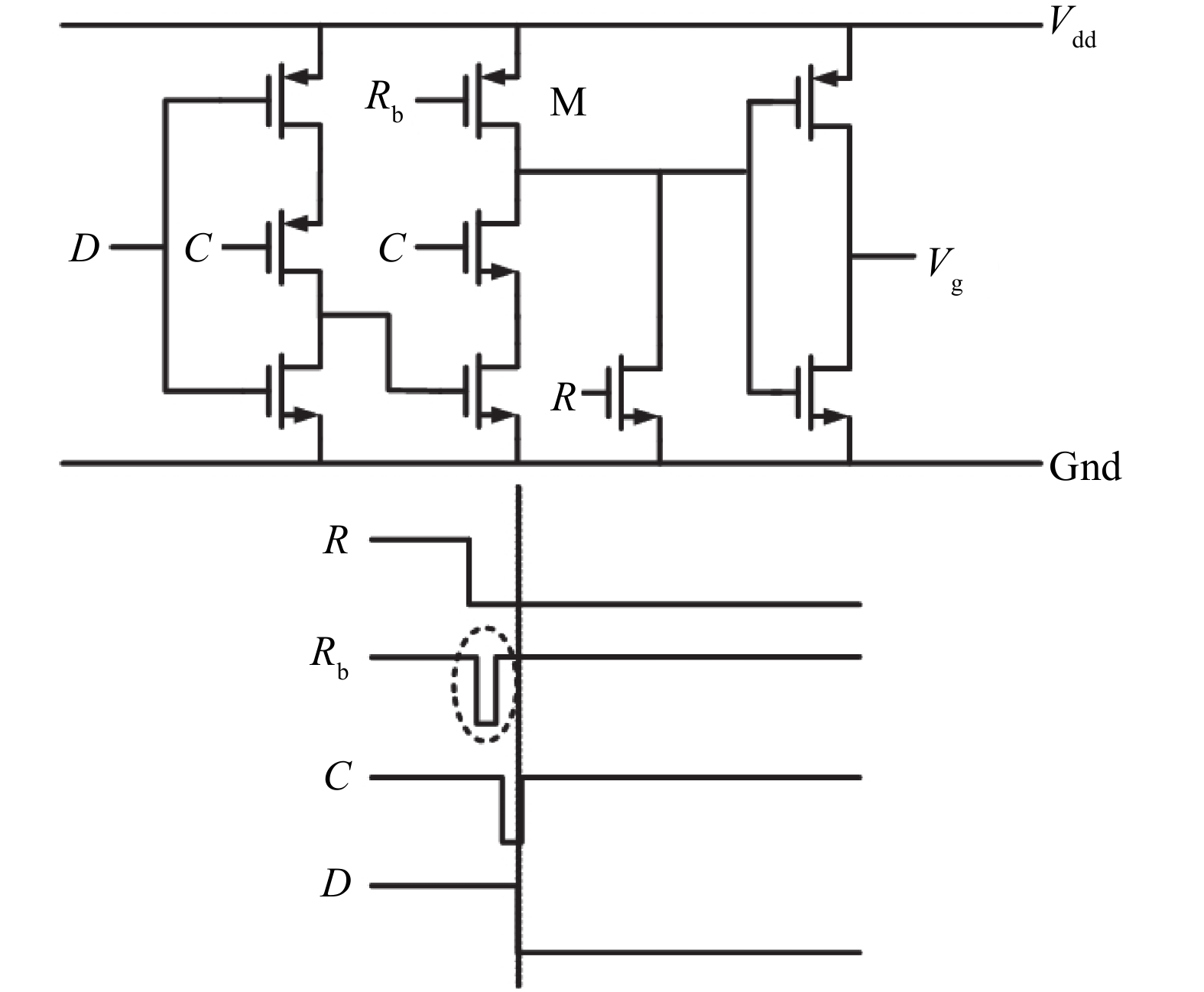
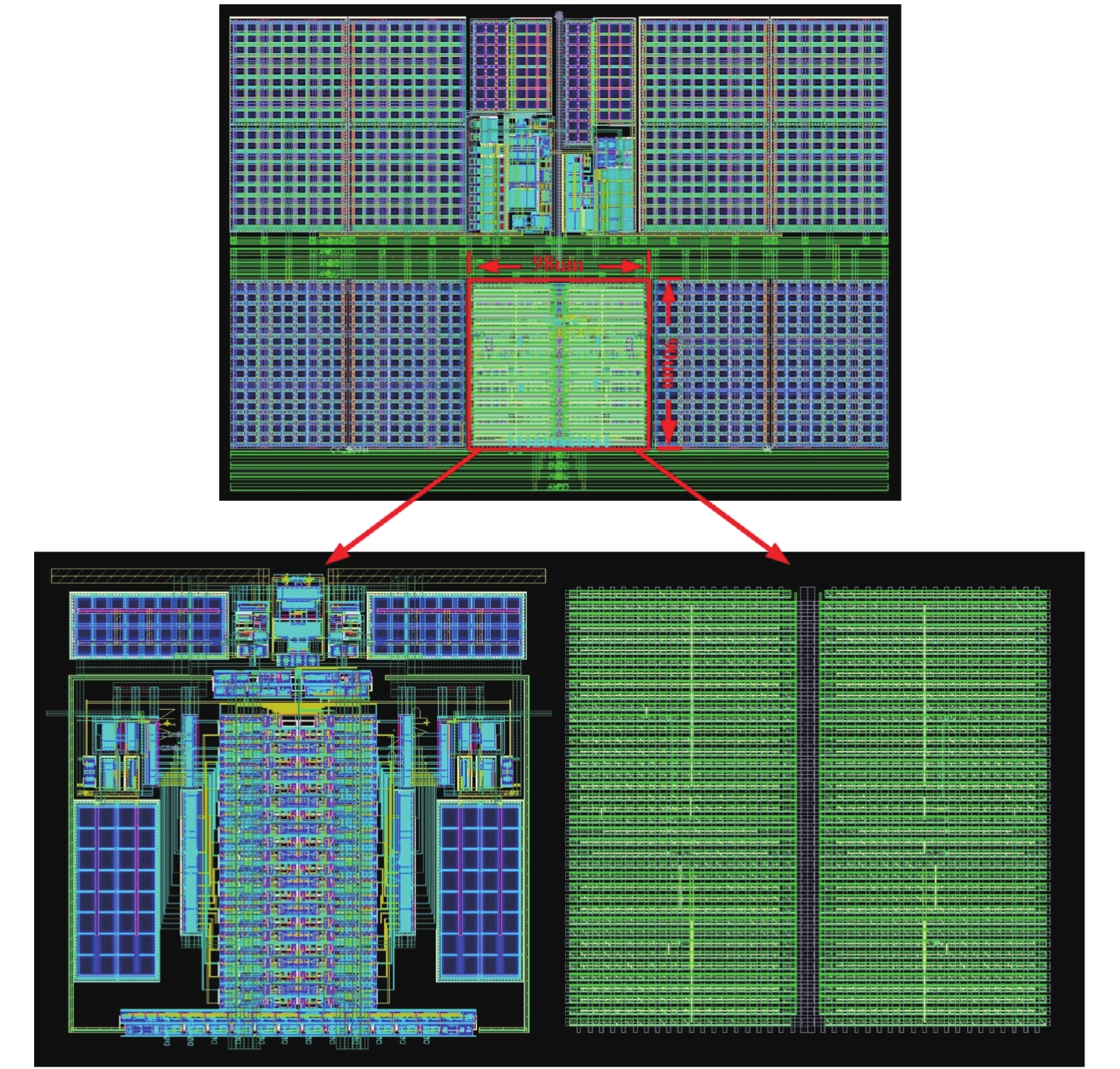
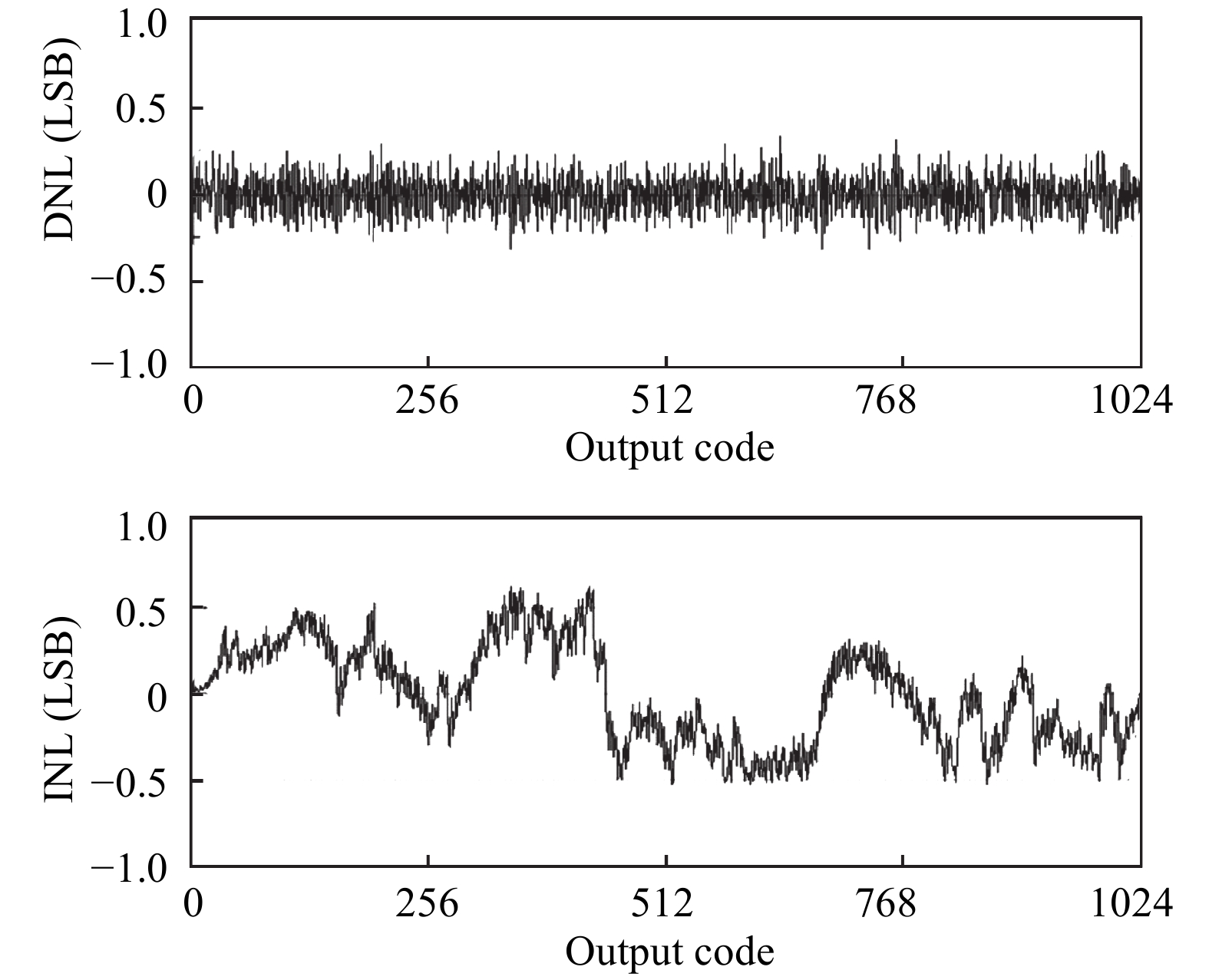
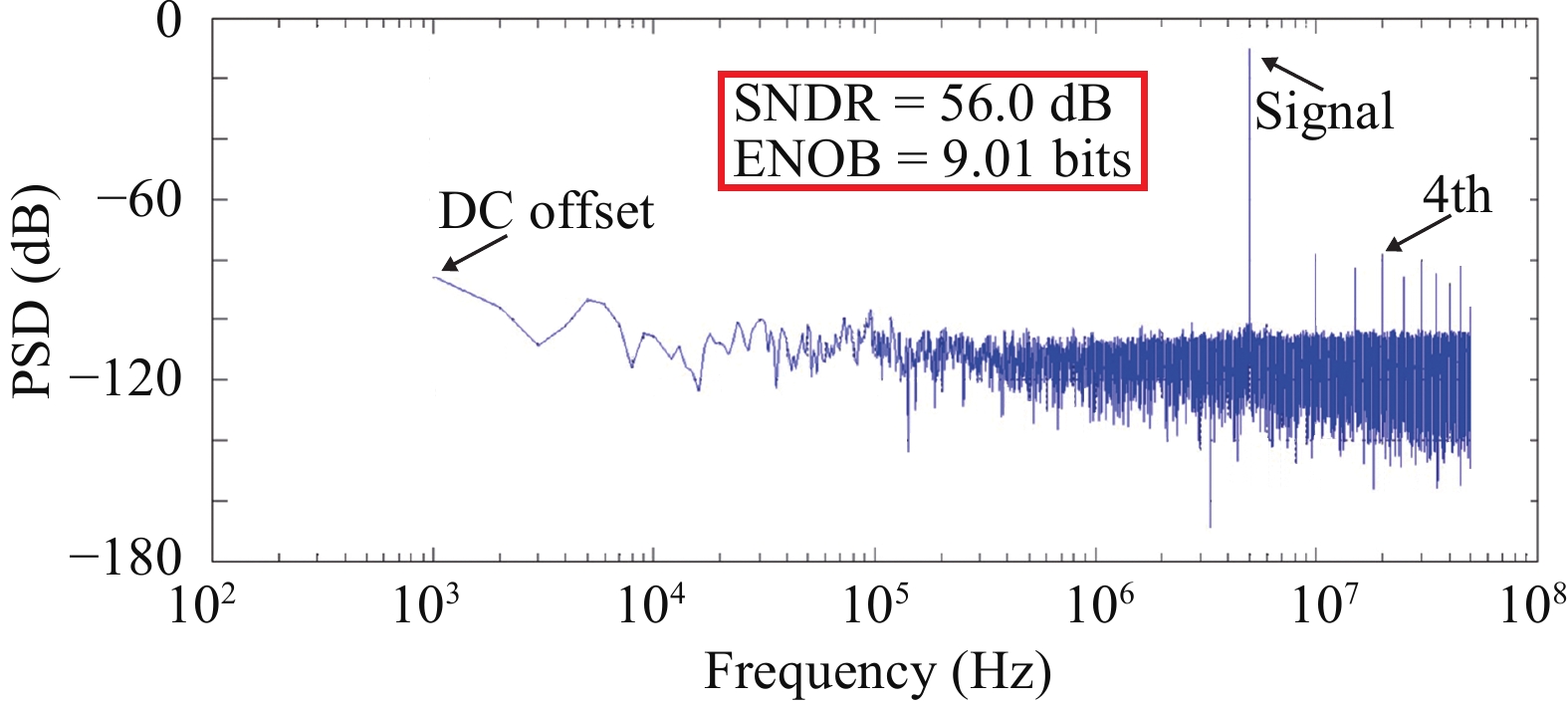
This paper presents a power-efficient 100-MS/s, 10-bit asynchronous successive approximation register (SAR) ADC. It includes an on-chip reference buffer and the total power dissipation is 6.8 mW. To achieve high performance with high power-efficiency in the proposed ADC, bootstrapped switch, redundancy, set-and-down switching approach, dynamic comparator and dynamic logic techniques are employed. The prototype was fabricated using 65 nm standard CMOS technology. At a 1.2-V supply and 100 MS/s, the ADC achieves an SNDR of 56.2 dB and a SFDR of 65.1 dB. The ADC core consumes only 3.1 mW, resulting in a figure of merit (FOM) of 30.27 fJ/conversionstep and occupies an active area of only 0.009 mm2.-
Keywords:
- SAR ADC,
- asynchronous,
- bootstrapped switch,
- dynamic logic,
- power efficiency
-
References
[1] Tsukamoto Y, Obata K, Matsukawa K, et al. High power efficient and scalable noise-shaping SAR ADC for IoT sensors. 2016 IEEE International Meeting for Future of Electron Devices, 2016: 1[2] Lu Y X, Sun L, Li Z, et al. A single-channel 10-bit 160 MS/s SAR ADC in 65 nm CMOS. J Semicond, 2014, 35(4): 045009 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/4/045009[3] Guo W J, Sun N. A 9.8 b-ENOB 5.5 fJ/step fully-passive compressive sensing SAR ADC for WSN applications. 42nd European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2016: 91[4] Li D, Meng Q, Li F. A 10 bit 50 MS/s SAR ADC with partial split capacitor switching scheme in 0.18 μm CMOS. J Semicond, 2016, 37(1): 015004 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/1/015004[5] Wang J J, Feng Z M, Xu R J, et al. A 100 MS/s 9 bit 0.43 mW SAR ADC with custom capacitor array. J Semicond, 2016, 37(5): 055003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/5/055003[6] Yu M Y, Li T, Yang J Q, et al. A 1 V 186-μW 50-MS/s 10-bit subrange SAR ADC in 130-nm CMOS process. J Semicond, 2016, 37(7): 075005 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/7/075005[7] Wulff C, Ytterdal T. A Compiled 9-bit 20-MS/s 3.5-fJ/conv. step SAR ADC in 28-nm FDSOI for bluetooth low energy receivers. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2017, PP(99): 1[8] Chen S W M, Brodersen R W. A 6-bit 600-MS/s 5.3-mW Asynchronous ADC in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2006, 41(12): 2669 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.884231[9] Boyacigiller Z, Weir B, Bradshaw P. An error-correcting 14b/20 μs CMOS A/D converter. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, 1981: 62[10] Liu W, Chang Y, Hsien S K, et al. A 600 MS/s 30 mW 0.13 μm CMOS ADC array achieving over 60 dB SFDR with adaptive digital equalization. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, 2009: 82[11] Lee H S, Hodges D. Self-calibration technique for A/D converters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 1983, 30(3): 188 doi: 10.1109/TCS.1983.1085339[12] Kobayashi T, Nogami K, Shirotori T, et al. A current-controlled latch sense amplifier and a static power-saving input buffer for low-power architecture. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1993, 28(4): 523 doi: 10.1109/4.210039[13] Abo A M, Gray P R. A 1.5-V, 10-bit, 14.3-MS/s CMOS pipeline analog-to-digital converter. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1999, 34(5): 599 doi: 10.1109/4.760369[14] Liu C C, Chang S J, Huang G Y, et al. A 10-bit 50-MS/s SAR ADC with a monotonic capacitor switching procedure. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(5): 731[15] Furuta M, Nozawa M, Itakura T. A 10-bit, 40-MS/s, 1.21 mW Pipelined SAR ADC using single-ended 1.5-bit/cycle conversion technique. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(6): 1360 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2126390[16] Zhou Y, Xu B W, Chiu Y. A 12 bit 160 MS/s two-step SAR ADC with background bit-weight calibration using a time-domain proximity detector. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50(4): 920 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2384025[17] Kull L, Toifl T, Schmatz M, et al. A 3.1 mW 8 b 1.2 GS/s single-channel asynchronous SAR ADC with alternate comparators for enhanced speed in 32 nm digital SOI CMOS. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, 2013: 468[18] Harpe P, Cantatore E, van Roermund A. An oversampled 12/14 b SAR ADC with noise reduction and linearity enhancements achieving up to 79.1 dB SNDR. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, 2014: 194[19] Fredenburg J A, Flynn M P. A 90-MS/s 11-MHz-Bandwidth 62-dB SNDR Noise-Shaping SAR ADC. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 47(12): 2898 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2217874[20] Chen Z J, Miyahara M, Matsuzawa A. A 2nd order fully-passive noise-shaping SAR ADC with embedded passive gain. IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2016: 309[21] Li P W, Chin M J, Gray P R, et al. A ratio-independent algorithmic analog-to-digital conversion technique. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1984, 19(6): 828 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.1984.1052233[22] Zhu Y, Chan C H, Sin S W, et al. A 34 fJ 10 b 500 MS/s partial-interleaving pipelined SAR ADC. Symposium on VLSI Circuits, 2012: 90[23] Wong S S, Chio U F, Zhu Y, et al. A 2.3 mW 10-bit 170 ms/s two-step binary-search assisted time-interleaved SAR ADC. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48(8): 1783 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2013.2258832[24] Jeon Y D, Cho Y K, Nam J W, et al. A 9.15 mW 0.22 mm2 10 b 204 MS/s pipelined SAR ADC in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, 2010: 1 -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: