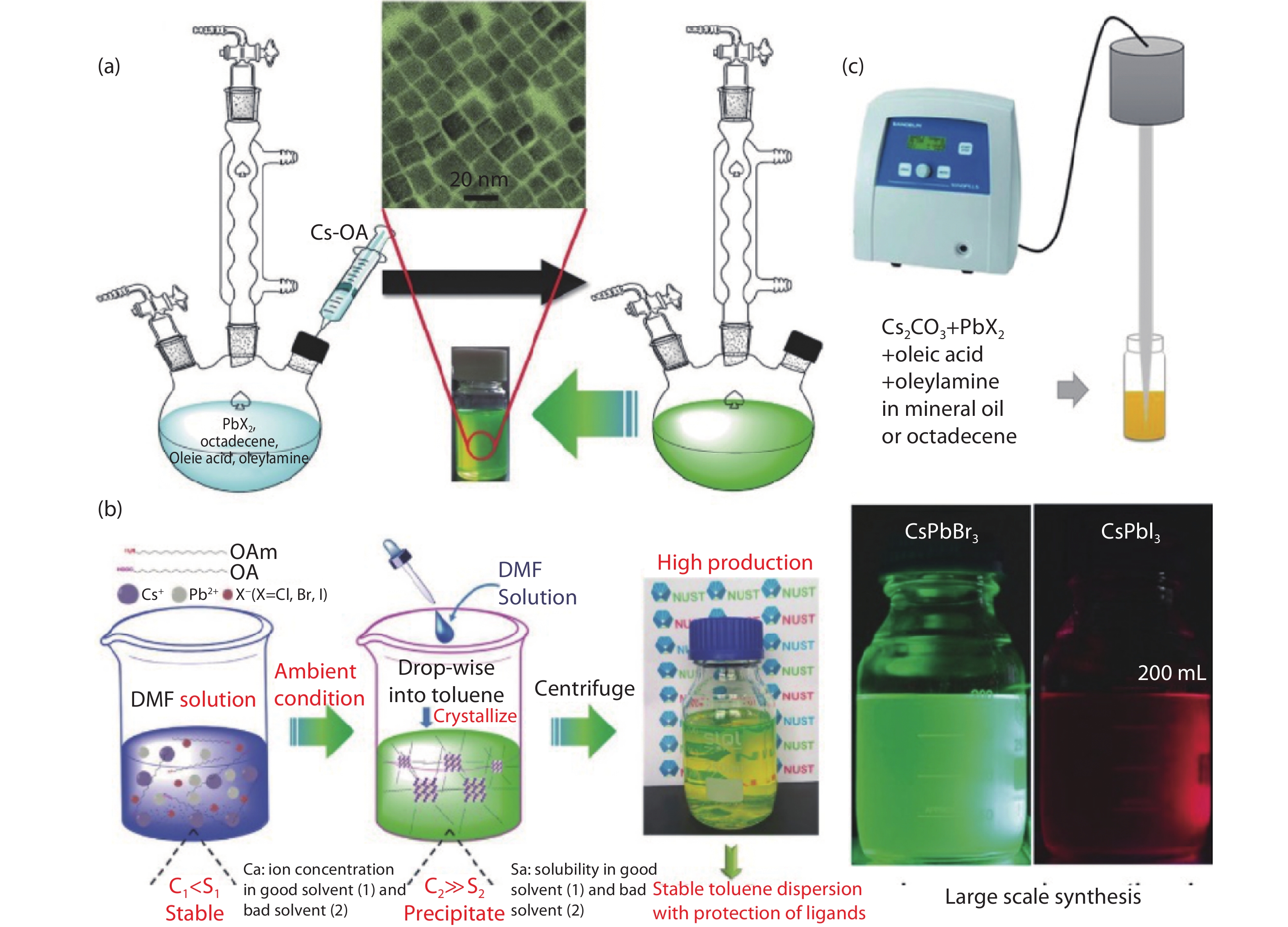
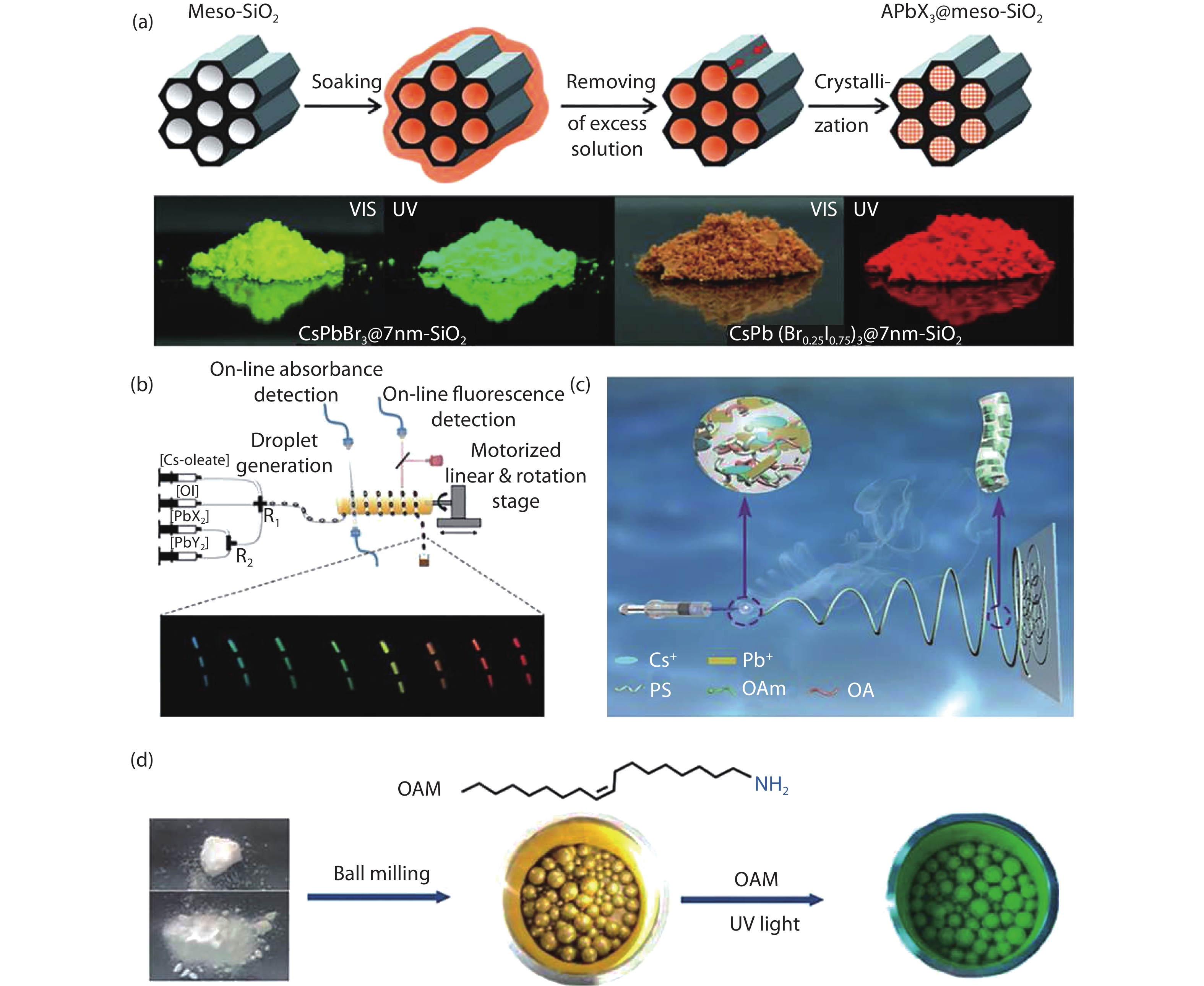
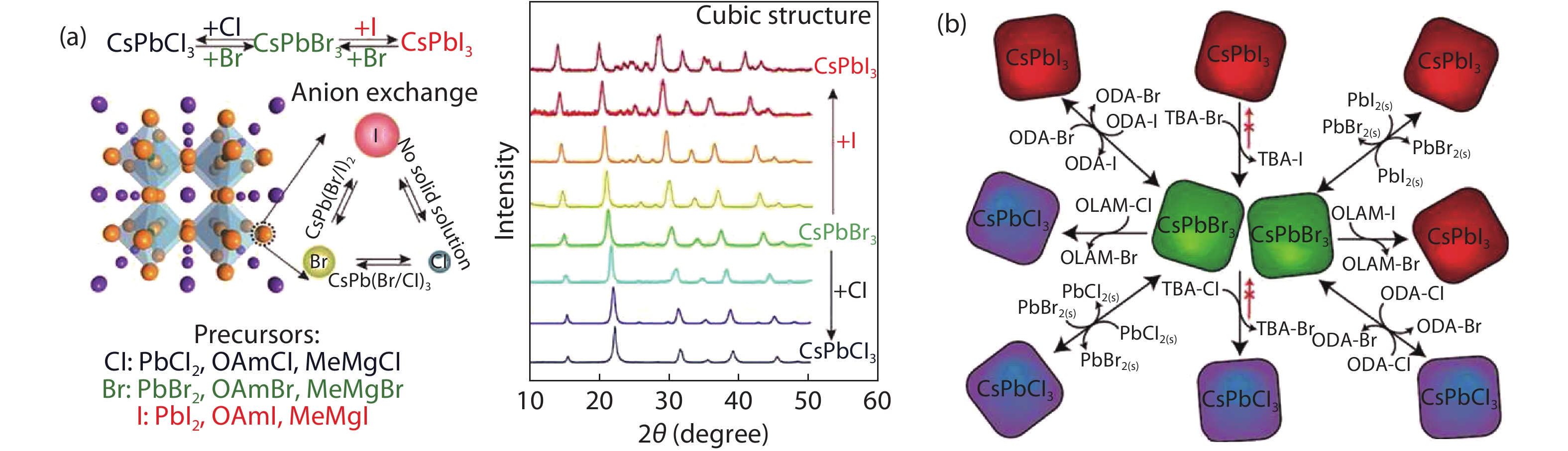
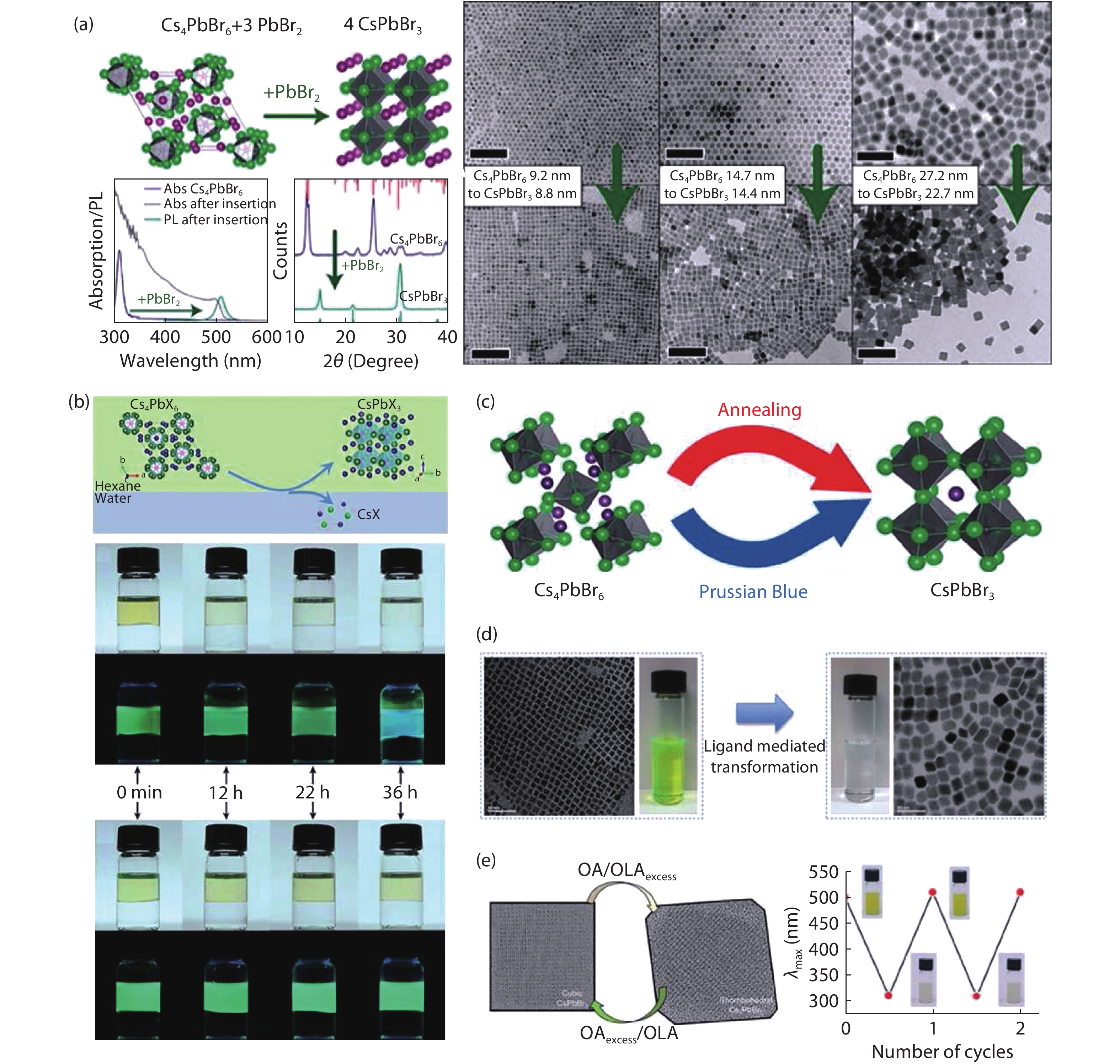
| Citation: |
Yi Yuan, Aiwei Tang. Progress on the controllable synthesis of all-inorganic halide perovskite nanocrystals and their optoelectronic applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2020, 41(1): 011201. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/1/011201
****
Y Yuan, A W Tang, Progress on the controllable synthesis of all-inorganic halide perovskite nanocrystals and their optoelectronic applications[J]. J. Semicond., 2020, 41(1): 011201. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/1/011201.
|
Progress on the controllable synthesis of all-inorganic halide perovskite nanocrystals and their optoelectronic applications
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/1/011201
More Information
-
Abstract
In the past five years, all-inorganic metal halide perovskite (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, I) nanocrystals have been intensely studied due to their outstanding optical properties and facile synthesis, which endow them with potential optoelectronic applications. In order to optimize their physical and chemical properties, different strategies have been developed to realize the controllable synthesis of CsPbX3 nanocrystals. In this short review, we firstly present a comprehensive and detailed summary of existed synthesis strategies of CsPbX3 nanocrystals and their analogues. Then, we introduce the regulations of several reaction parameters and their effects on the morphologies of CsPbX3 nanocrystals. At the same time, we provide stability improvement methods and representative applications. Finally, we propose the current challenges and future perspectives of the promising materials.-
Keywords:
- metal halide perovskite,
- nanocrystals,
- synthesis,
- optical properties
-
References
[1] Alivisatos A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science, 1996, 271, 933 doi: 10.1126/science.271.5251.933[2] El-Sayed M A. Small is different: shape-, size-, and composition-dependent properties of some colloidal semiconductor nanocrystals. Acc Chem Res, 2004, 37, 326 doi: 10.1021/ar020204f[3] Carey G H, Abdelhady A L, Ning Z, et al. Colloidal quantum dot solar cells. Chem Rev, 2015, 115, 12732 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00063[4] Li L, Hu J, Yang W, et al. Band gap variation of size- and shape-controlled colloidal CdSe quantum rods. Nano Lett, 2001, 1, 349 doi: 10.1021/nl015559r[5] Peng X, Manna L, Yang W, et al. Shape control of CdSe nanocrystals. Nature, 2000, 404, 59 doi: 10.1038/35003535[6] Kagan C R, Lifshitz E, Sargent E H, et al. Building devices from colloidal quantum dots. Science, 2016, 353, 5523 doi: 10.1126/science.aac5523[7] Caruge J M, Halpert J E, Wood V, et al. Colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes with metal-oxide charge transport layers. Nat Photon, 2008, 2, 247 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2008.34[8] Shirasaki Y, Supran G J, Bawendi M G, et al. Emergence of colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting technologies. Nat Photon, 2013, 7, 13 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2012.328[9] Kovalenko M V, Protesescu L, Bodnarchuk M I. Properties and potential optoelectronic applications of lead halide perovskite nanocrystals. Science, 2017, 358, 745 doi: 10.1126/science.aam7093[10] Amgar D, Aharon S, Etgar L. Inorganic and hybrid organo-metal perovskite nanostructures: synthesis, properties, and applications. Adv Funct Mater, 2016, 26, 8576 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201603752[11] Stoumpos C C, Kanatzidis M G. The renaissance of halide perovskites and their evolution as emerging semiconductors. Acc Chem Res, 2015, 48, 2791 doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.5b00229[12] Kojima A, Teshima K, Shirai Y, et al. Organometal halide perovskites as visible-light sensitizers for photovoltaic cells. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131, 6050 doi: 10.1021/ja809598r[13] Grätzel M. The light and shade of perovskite solar cells. Nat Mater, 2014, 13, 838 doi: 10.1038/nmat4065[14] Yang W S, Noh J H, Jeon N J, et al. High-performance photovoltaic perovskite layers fabricated through intramolecular exchange. Science, 2015, 348, 1234 doi: 10.1126/science.aaa9272[15] Green M A, Ho-Baillie A, Snaith H J. The emergence of perovskite solar cells. Nat Photon, 2014, 8, 506 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.134[16] Jiang Q, Zhao Y, Zhang X, et al. Surface passivation of perovskite film for efficient solar cells. Nat Photon, 2019, 13, 460 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0398-2[17] Xiao Z, Kerner R A, Zhao L, et al. Efficient perovskite light-emitting diodes featuring nanometre-sized crystallites. Nat Photon, 2017, 11, 108 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.269[18] Zhao Y, Zhu K. Organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskites for optoelectronic and electronic applications. Chem Soc Rev, 2016, 45, 655 doi: 10.1039/C4CS00458B[19] Jeon N J, Noh J H, Kim Y C, et al. Solvent engineering for high-performance inorganic-organic hybrid perovskite solar cells. Nat Mater, 2014, 13, 897 doi: 10.1038/nmat4014[20] Smith I C, Hoke E T, Solis-Ibarra D, et al. A layered hybrid perovskite solar-cell absorber with enhanced moisture stability. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2014, 53, 11232 doi: 10.1002/anie.201406466[21] Liang J, Wang C, Wang Y, et al. All-inorganic perovskite solar cells. J Am Chem Soc, 2016, 138, 15829 doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b10227[22] Shi Z, Li S, Li Y, et al. Strategy of solution-processed all-inorganic heterostructure for humidity/temperature-stable perovskite quantum dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 1462 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07856[23] Stoumpos C C, Malliakas C D, Peters J A, et al. Crystal growth of the perovskite semiconductor CsPbBr3: a new material for high-energy radiation detection. Cryst Growth Des, 2013, 13, 2722 doi: 10.1021/cg400645t[24] Li X, Cao F, Yu D, et al. All inorganic halide perovskites nanosystem: synthesis, structural features, optical properties and optoelectronic applications. Small, 2017, 13, 1603996 doi: 10.1002/smll.201603996[25] Ahmad W, Khan J, Niu G, et al. Inorganic CsPbI3 perovskite-based solar cells: A choice for a tandem device. Solar RRL, 2017, 1, 1700048 doi: 10.1002/solr.201700048[26] Protesescu L, Yakunin S, Bodnarchuk M I, et al. Nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, and I): novel optoelectronic materials showing bright emission with wide color gamut. Nano Lett, 2015, 15, 3692 doi: 10.1021/nl5048779[27] Yang D, Cao M, Zhong Q, et al. All-inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals: synthesis, surface engineering and applications. J Mater Chem C, 2019, 7, 757 doi: 10.1039/C8TC04381G[28] Huo C, Cai B, Yuan Z, et al. Two-dimensional metal halide perovskites: theory, synthesis, and optoelectronics. Small Methods, 2017, 1, 1600018 doi: 10.1002/smtd.201600018[29] Wang Y, Li X, Song J, et al. All-inorganic colloidal perovskite quantum dots: a new class of lasing materials with favorable characteristics. Adv Mater, 2015, 27, 7101 doi: 10.1002/adma.201503573[30] Veldhuis S A, Boix P P, Yantara N, et al. Perovskite materials for light-emitting diodes and lasers. Adv Mater, 2016, 28, 6804 doi: 10.1002/adma.201600669[31] Wells H L. Über die Cäsium-und Kalium-Bleihalogenide. Zeitschrift für anorganische Chemie, 1893, 3, 195 doi: 10.1002/zaac.18930030124[32] Møller C K. A phase transition in cæsium plumbochloride. Nature, 1957, 180, 981 doi: 10.1038/180981a0[33] Yarema M, Yarema O, Lin W M M, et al. Upscaling colloidal nanocrystal hot-injection syntheses via reactor underpressure. Chem Mater, 2017, 29, 796 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b04789[34] Chen X, Peng L, Huang K, et al. Non-injection gram-scale synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite quantum dots with controllable size and composition. Nano Res, 2016, 9, 1994 doi: 10.1007/s12274-016-1090-1[35] Zhang F, Zhong H, Chen C, et al. Brightly luminescent and color-tunable colloidal CH3NH3PbX3 (X = Br, I, Cl) quantum dots: potential alternatives for display technology. ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 4533 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b01154[36] Li X, Wu Y, Zhang S, et al. CsPbX3 quantum dots for lighting and displays: room-temperature synthesis, photoluminescence superiorities, underlying origins and white light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater, 2016, 26, 2435 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201600109[37] Tong Y, Bladt E, Aygüler M F, et al. Highly luminescent cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals with tunable composition and thickness by ultrasonication. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55, 13887 doi: 10.1002/anie.201605909[38] Li X, Liu Y, Song X, et al. Intercrossed carbon nanorings with pure surface states as low-cost and environment-friendly phosphors for white-light-emitting diodes. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2015, 54, 1759 doi: 10.1002/anie.201406836[39] Li J, Xu L, Wang T, et al. 50-fold EQE improvement up to 6.27% of solution-processed all-inorganic perovskite CsPbBr3 QLEDs via surface ligand density control. Adv Mater, 2017, 29, 1603885 doi: 10.1002/adma.201603885[40] Dirin D N, Protesescu L, Trummer D, et al. Harnessing defect-tolerance at the nanoscale: highly luminescent lead halide perovskite nanocrystals in mesoporous silica matrixes. Nano Lett, 2016, 16, 5866 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b02688[41] Pan Q, Hu H, Zou Y, et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of high-quality " all-inorganic” CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) perovskite nanocrystals and their application in light emitting diodes. J Mater Chem C, 2017, 5, 10947 doi: 10.1039/C7TC03774K[42] Niu G, Ruditskiy A, Vara M, et al. Toward continuous and scalable production of colloidal nanocrystals by switching from batch to droplet reactors. Chem Soc Rev, 2015, 44, 5806 doi: 10.1039/C5CS00049A[43] Lignos I, Stavrakis S, Nedelcu G, et al. Synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals in a droplet-based microfluidic platform: fast parametric space mapping. Nano Lett, 2016, 16, 1869 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04981[44] Liao H, Guo S, Cao S, et al. A general strategy for in situ growth of all-inorganic CsPbX3 (X = Br, I, and Cl) perovskite nanocrystals in polymer fibers toward significantly enhanced water/thermal stabilities. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6, 1800346 doi: 10.1002/adom.201800346[45] Zhu Z Y, Yang Q Q, Gao L F, et al. Solvent-free mechanosynthesis of composition-tunable cesium lead halide perovskite quantum dots. J Phys Chem Lett, 2017, 8, 1610 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b00431[46] De Roo J, Ibáñez M, Geiregat P, et al. Highly dynamic ligand binding and light absorption coefficient of cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 2071 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b06295[47] Friščić T, Halasz I, Beldon P J, et al. Real-time and in situ monitoring of mechanochemical milling reactions. Nat Chem, 2013, 5, 66 doi: 10.1038/nchem.1505[48] Chen J, Fu Y, Samad L, et al. Vapor-phase epitaxial growth of aligned nanowire networks of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, I). Nano Lett, 2016, 17, 460 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b04450[49] Nedelcu G, Protesescu L, Yakunin S, et al. Fast anion-exchange in highly luminescent nanocrystals of cesium lead halide perovskites (CsPbX3, X = Cl, Br, I). Nano Lett, 2015, 15, 5635 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b02404[50] Akkerman Q A, D’Innocenzo V, Accornero S, et al. Tuning the optical properties of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals by anion exchange reactions. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137, 10276 doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b05602[51] Dou L, Wong A B, Yu Y, et al. Atomically thin two-dimensional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites. Science, 2015, 349, 1518 doi: 10.1126/science.aac7660[52] D’Innocenzo V, Srimath Kandada A R, De Bastiani M, et al. Tuning the light emission properties by band gap engineering in hybrid lead halide perovskite. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136, 17730 doi: 10.1021/ja511198f[53] Yang H, Zhang Y, Pan J, et al. Room-temperature engineering of all-inorganic perovskite nanocrsytals with different dimensionalities . Chem Mater, 2017, 29, 8978 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04161[54] Wang K H, Wu L, Li L, et al. Large-scale synthesis of highly luminescent perovskite-related CsPb2Br5 nanoplatelets and their fast anion exchange. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55, 8328 doi: 10.1002/anie.201602787[55] Ruan L, Lin J, Shen W, et al. Ligand-mediated synthesis of compositionally related cesium lead halide CsPb2X5 nanowires with improved stability. Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 7658 doi: 10.1039/C8NR00883C[56] Zhang X, Xu B, Zhang J, et al. All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystals for high-efficiency light emitting diodes: dual-phase CsPbBr3-CsPb2Br5 composites. Adv Funct Mater, 2016, 26, 4595 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201600958[57] Tang X, Hu Z, Yuan W, et al. Perovskite CsPb2Br5 microplate laser with enhanced stability and tunable properties. Adv Opt Mater, 2017, 5, 1600788 doi: 10.1002/adom.201600788[58] Li J, Yu Q, He Y, et al. Cs2PbI2Cl2, all-inorganic two-dimensional Ruddlesden–Popper mixed halide perovskite with optoelectronic response. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140, 11085 doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b06046[59] Chen D, Wan Z, Chen X, et al. Large-scale room-temperature synthesis and optical properties of perovskite-related Cs4PbBr6 fluorophores. J Mater Chem C, 2016, 4, 10646 doi: 10.1039/C6TC04036E[60] Saidaminov M I, Almutlaq J, Sarmah S, et al. Pure Cs4PbBr6: highly luminescent zero-dimensional perovskite solids. ACS Energy Lett, 2016, 1, 840 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.6b00396[61] Wang Y, Yu D, Wang Z, et al. Solution-grown CsPbBr3/Cs4PbBr6 perovskite nanocomposites: toward temperature-insensitive optical gain. Small, 2017, 13, 1701587 doi: 10.1002/smll.201701587[62] Akkerman Q A, Park S, Radicchi E, et al. Nearly monodisperse insulator Cs4PbX6 (X = Cl, Br, I) nanocrystals, their mixed halide compositions, and their transformation into CsPbX3 nanocrystals. Nano Lett, 2017, 17, 1924 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b05262[63] Liu Z, Bekenstein Y, Ye X, et al. Ligand mediated transformation of cesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals to lead depleted Cs4PbBr6 nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139, 5309 doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01409[64] Li G, Wang H, Zhu Z, et al. Shape and phase evolution from CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocubes to tetragonal CsPb2Br5 nanosheets with an indirect bandgap. Chem Commun, 2016, 52, 11296 doi: 10.1039/C6CC05877A[65] Wu L, Hu H, Xu Y, et al. From nonluminescent Cs4PbX6 (X = Cl, Br, I) nanocrystals to highly luminescent CsPbX3 nanocrystals: water-triggered transformation through a CsX-stripping mechanism. Nano Lett, 2017, 17, 5799 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02896[66] Palazon F, Urso C, De Trizio L, et al. Postsynthesis transformation of insulating Cs4PbBr6 nanocrystals into bright perovskite CsPbBr3 through physical and chemical extraction of CsBr. ACS Energy Lett, 2017, 2, 2445 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b00842[67] Shen W, Ruan L, Shen Z, et al. Reversible light-mediated compositional and structural transitions between CsPbBr3 and CsPb2Br5 nanosheets. Chem Commun, 2018, 54, 2804 doi: 10.1039/C8CC00139A[68] Chung I, Song J H, Im J, et al. CsSnI3: semiconductor or metal? High electrical conductivity and strong near-infrared photoluminescence from a single material. High hole mobility and phase-transitions J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134, 8579 doi: 10.1021/ja301539s[69] Udayabhaskararao T, Houben L, Cohen H, et al. A mechanistic study of phase transformation in perovskite nanocrystals driven by ligand passivation. Chem Mater, 2017, 30, 84 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02425[70] Ruan L, Shen W, Wang A, et al. Alkyl-thiol ligand-induced shape-and crystalline phase-controlled synthesis of stable perovskite-related CsPb2Br5 nanocrystals at room temperature. J Phys Chem Lett, 2017, 8, 3853 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.7b01657[71] Huang L, Lambrecht W R L. Electronic band structure, phonons, and exciton binding energies of halide perovskites CsSnCl3, CsSnBr3, and CsSnI3. Phys Rev B, 2013, 88, 165203 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.88.165203[72] Yang B, Chen J, Hong F, et al. Lead-free, air-stable all-inorganic cesium bismuth halide perovskite nanocrystals. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2017, 56, 12471 doi: 10.1002/anie.201704739[73] Yang F, Hirotani D, Kapil G, et al. All-inorganic CsPb1– xGexI2Br perovskite with enhanced phase stability and photovoltaic performance. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2018, 57, 12745 doi: 10.1002/anie.201807270[74] Liang J, Liu Z, Qiu L, et al. Enhancing optical, electronic, crystalline, and morphological properties of cesium lead halide by Mn substitution for high-stability all-inorganic perovskite solar cells with carbon electrodes. Adv Energy Mater, 2018, 8, 1800504 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201800504[75] Xiao Z, Du K Z, Meng W, et al. Intrinsic instability of Cs2In(I)M(III)X6 (M = Bi, Sb; X = halogen) double perovskites: a combined density functional theory and experimental study. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139, 6054 doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b02227[76] Xiang S, Li W, Wei Y, et al. The synergistic effect of non-stoichiometry and Sb-doping on air-stable α-CsPbI3 for efficient carbon-based perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 9996 doi: 10.1039/C7NR09657G[77] Van der Stam W, Geuchies J J, Altantzis T, et al. Highly emissive divalent-ion-doped colloidal CsPb1– xMxBr3 perovskite nanocrystals through cation exchange. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139, 4087 doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b13079[78] Wang A, Yan X, Zhang M, et al. Controlled synthesis of lead-free and stable perovskite derivative Cs2SnI6 nanocrystals via a facile hot-injection process. Chem Mater, 2016, 28, 8132 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b01329[79] Xing G, Kumar M H, Chong W K, et al. Solution-processed tin-based perovskite for near-infrared lasing. Adv Mater, 2016, 28, 8191 doi: 10.1002/adma.201601418[80] Wang A, Guo Y, Muhammad F, et al. Controlled synthesis of lead-free cesium tin halide perovskite cubic nanocages with high stability. Chem Mater, 2017, 29, 6493 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02089[81] Wang Y, Tu J, Li T, et al. Convenient preparation of CsSnI3 quantum dots, excellent stability, and the highest performance of lead-free inorganic perovskite solar cells so far. J Mater Chem A, 2019, 7, 7683 doi: 10.1039/C8TA10901J[82] Pan A, He B, Fan X, et al. Insight into the ligand-mediated synthesis of colloidal CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals: the role of organic acid, base, and cesium precursors. ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 7943 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b03863[83] Sun S, Yuan D, Xu Y, et al. Ligand-mediated synthesis of shape-controlled cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals via reprecipitation process at room temperature. ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 3648 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b08193[84] Imran M, Di Stasio F, Dang Z, et al. Colloidal synthesis of strongly fluorescent CsPbBr3 nanowires with width tunable down to the quantum confinement regime. Chem Mater, 2016, 28, 6450 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b03081[85] Yuan Y, Liu Z, Liu Z, et al. Photoluminescence and self-assembly of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals: effects of chain length of organic amines and reaction temperature. Appl Surf Sci, 2017, 405, 280 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.024[86] Wang C, Zhang Y, Wang A, et al. Controlled synthesis of composition tunable formamidinium cesium double cation lead halide perovskite nanowires and nanosheets with improved stability. Chem Mater, 2017, 29, 2157 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b04848[87] Liang Z, Zhao S, Xu Z, et al. Shape-controlled synthesis of all-inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals with bright blue emission. ACS Appl Mater Inter, 2016, 8, 28824 doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b08528[88] Zhang D, Eaton S W, Yu Y, et al. Solution-phase synthesis of cesium lead halide perovskite nanowires. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137, 9230 doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b05404[89] Quan L N, Quintero-Bermudez R, Voznyy O, et al. Highly emissive green perovskite nanocrystals in a solid state crystalline matrix. Adv Mater, 2017, 29, 1605945 doi: 10.1002/adma.201605945[90] Bekenstein Y, Koscher B A, Eaton S W, et al. Highly luminescent colloidal nanoplates of perovskite cesium lead halide and their oriented assemblies. J Am Chem Soc, 2015, 137, 16008 doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b11199[91] Liu Y, Guo M, Dong S, et al. Room temperature colloidal synthesis of CsPbBr3 nanowires with tunable length, width and composition. J Mater Chem C, 2018, 6, 7797 doi: 10.1039/C8TC02636J[92] Amgar D, Stern A, Rotem D, et al. Tunable length and optical properties of CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) nanowires with a few unit cells. Nano Lett, 2017, 17, 1007 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b04381[93] Tang X, Zu Z, Shao H, et al. All-inorganic perovskite CsPb(Br/I)3 nanorods for optoelectronic application. Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 15158 doi: 10.1039/C6NR01828A[94] Yang D, Zou Y, Li P, et al. Large-scale synthesis of ultrathin cesium lead bromide perovskite nanoplates with precisely tunable dimensions and their application in blue light-emitting diodes. Nano Energy, 2018, 47, 235 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.03.019[95] Shamsi J, Dang Z, Bianchini P, et al. Colloidal synthesis of quantum confined single crystal CsPbBr3 nanosheets with lateral size control up to the micrometer range. J Am Chem Soc, 2016, 138, 7240 doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b03166[96] Seth S, Samanta A. A facile methodology for engineering the morphology of CsPbX3 perovskite nanocrystals under ambient condition. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 37693 doi: 10.1038/srep37693[97] Li G, Wang H, Zhang T, et al. Solvent-polarity-engineered controllable synthesis of highly fluorescent cesium lead halide perovskite quantum dots and their use in white light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater, 2016, 26, 8478 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201603734[98] Li Z J, Hofman E, Davis A H, et al. General strategy for the growth of CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, I) perovskite nanosheets from the assembly of nanorods. Chem Mater, 2018, 30, 3854 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b01283[99] Wang H, Sui N, Bai X, et al. Emission recovery and stability enhancement of inorganic perovskite quantum dots. J Phys Chem Lett, 2018, 9, 4166 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.8b01752[100] Wu L, Zhong Q, Yang D, et al. Improving the stability and size tunability of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals using trioctylphosphine oxide as the capping ligand. Langmuir, 2017, 33, 12689 doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b02963[101] Wang C, Chesman A S R, Jasieniak J J. Stabilizing the cubic perovskite phase of CsPbI3 nanocrystals by using an alkyl phosphinic acid. Chem Commun, 2017, 53, 232 doi: 10.1039/C6CC08282C[102] Pan J, Quan L N, Zhao Y, et al. Highly efficient perovskite-quantum-dot light-emitting diodes by surface engineering. Adv Mater, 2016, 28, 8718 doi: 10.1002/adma.201600784[103] Pan J, Sarmah S P, Murali B, et al. Air-stable surface-passivated perovskite quantum dots for ultra-robust, single-and two-photon-induced amplified spontaneous emission. J Phys Chem Lett, 2015, 6, 5027 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b02460[104] Palazon F, Akkerman Q A, Prato M, et al. X-ray lithography on perovskite nanocrystals films: from patterning with anion-exchange reactions to enhanced stability in air and water. ACS Nano, 2015, 10, 1224 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b06536[105] Wang Y, Zhi M, Chang Y Q, et al. Stable, ultralow threshold amplified spontaneous emission from CsPbBr3 nanoparticles exhibiting trion gain. Nano Lett, 2018, 18, 4976 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01817[106] Bohn B J, Tong Y, Gramlich M, et al. Boosting tunable blue luminescence of halide perovskite nanoplatelets through postsynthetic surface trap repair. Nano Lett, 2018, 18, 5231 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b02190[107] Woo J Y, Kim Y, Bae J, et al. Highly stable cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals through in situ lead halide inorganic passivation. Chem Mater, 2017, 29, 7088 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02669[108] Li F, Liu Y, Wang H, et al. Postsynthetic surface trap removal of CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, or I) quantum dots via a ZnX2/hexane solution toward an enhanced luminescence quantum yield. Chem Mater, 2018, 30, 8546 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b03442[109] Wu Y, Wei C, Li X, et al. In situ passivation of PbBr64– octahedra toward blue luminescent CsPbBr3 nanoplatelets with near 100% absolute quantum yield. ACS Energy Lett, 2018, 3, 2030 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b01025[110] Huang S, Wang B, Zhang Q, et al. Postsynthesis potassium-modification method to improve atability of CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6, 1701106 doi: 10.1002/adom.201701106[111] Lu M, Zhang X, Bai X, et al. Spontaneous silver doping and surface passivation of CsPbI3 perovskite active layer enable light-emitting devices with an external quantum efficiency of 11.2%. ACS Energy Lett, 2018, 3, 1571 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.8b00835[112] Wang H C, Lin S Y, Tang A C, et al. Mesoporous silica particles integrated with all-inorganic CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum-dot nanocomposites (MP-PQDs) with high stability and wide color gamut used for backlight display. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55, 7924 doi: 10.1002/anie.201603698[113] Sun C, Shen X, Zhang Y, et al. Highly luminescent, stable, transparent and flexible perovskite quantum dot gels towards light-emitting diodes. Nanotechnology, 2017, 28, 365601 doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa7c86[114] Luo B, Pu Y C, Lindley S A, et al. Organolead halide perovskite nanocrystals: branched capping ligands control crystal size and stability. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55, 8864 doi: 10.1002/anie.201602236[115] Loiudice A, Saris S, Oveisi E, et al. CsPbBr3 QD/AlOx inorganic nanocomposites with exceptional stability in water, light, and heat. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2017, 56, 10696 doi: 10.1002/anie.201703703[116] Zhou L, Yu K, Yang F, et al. All-inorganic perovskite quantum dot/mesoporous TiO2 composite-based photodetectors with enhanced performance. Dalton Trans, 2017, 46, 1766 doi: 10.1039/C6DT04758K[117] Wu H, Kang Z, Zhang Z, et al. Interfacial charge behavior modulation in perovskite quantum dot-monolayer MoS2 0D-2D mixed-dimensional van der Waals heterostructures. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 28, 1802015 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201802015[118] Chen W, Hao J, Hu W, et al. Enhanced stability and tunable photoluminescence in perovskite CsPbX3/ZnS quantum dot heterostructure. Small, 2017, 13, 1604085 doi: 10.1002/smll.201604085[119] Xu Y F, Yang M Z, Chen B X, et al. A CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dot/graphene oxide composite for photocatalytic CO2 reduction. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139, 5660 doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b00489[120] Li X, Yu D, Chen J, et al. Constructing fast carrier tracks into flexible perovskite photodetectors to greatly improve responsivity. ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 2015 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b08194[121] Wei Y, Deng X, Xie Z, et al. Enhancing the stability of perovskite quantum dots by encapsulation in crosslinked polystyrene beads via a swelling-shrinking strategy toward superior water resistance. Adv Funct Mater, 2017, 27, 1703535 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201703535[122] Wang Y, Zhu Y, Huang J, et al. CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots-based monolithic electrospun fiber membrane as an ultrastable and ultrasensitive fluorescent sensor in aqueous medium. J Phys Chem Lett, 2016, 7, 4253 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b02045[123] Zhang M, Wang M, Yang Z, et al. Preparation of all-inorganic perovskite quantum dots-polymer composite for white LEDs application. J Alloy Compd, 2018, 748, 537 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.179[124] Hai J, Li H, Zhao Y, et al. Designing of blue, green, and red CsPbX3 perovskite-codoped flexible films with water resistant property and elimination of anion-exchange for tunable white light emission. Chem Commun, 2017, 53, 5400 doi: 10.1039/C7CC01152K[125] Meyns M, Perálvarez M, Heuer-Jungemann A, et al. Polymer-enhanced stability of inorganic perovskite nanocrystals and their application in color conversion LEDs. ACS Appl Mater Inter, 2016, 8, 19579 doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b02529[126] Hou S, Guo Y, Tang Y, et al. Synthesis and stabilization of colloidal perovskite nanocrystals by multidentate polymer micelles. ACS Appl Mater Inter, 2017, 9, 18417 doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b03445[127] Guo Y, Wang Q, Saidi W A. Structural stabilities and electronic properties of high-angle grain boundaries in perovskite cesium lead halides. J Phys Chem C, 2017, 121, 1715 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b11434[128] Koscher B A, Swabeck J K, Bronstein N D, et al. Essentially trap-free CsPbBr3 colloidal nanocrystals by postsynthetic thiocyanate surface treatment. J Am Chem Soc, 2017, 139, 6566 doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b02817[129] Swarnkar A, Chulliyil R, Ravi V K, et al. Colloidal CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals: luminescence beyond traditional quantum dots. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2015, 54, 15424 doi: 10.1002/anie.201508276[130] Kulbak M, Cahen D, Hodes G. How important is the organic part of lead halide perovskite photovoltaic cells? Efficient CsPbBr3 cells. J Phys Chem Lett, 2015, 6, 2452 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00968[131] Wang P, Zhang X, Zhou Y, et al. Solvent-controlled growth of inorganic perovskite films in dry environment for efficient and stable solar cells. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 2225 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04636-4[132] Sanehira E M, Marshall A R, Christians J A, et al. Enhanced mobility CsPbI3 quantum dot arrays for record-efficiency, high-voltage photovoltaic cells. Sci Adv, 2017, 3, eaao4204 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aao4204[133] Choi H, Jeong J, Kim H B, et al. Cesium-doped methylammonium lead iodide perovskite light absorber for hybrid solar cells. Nano Energy, 2014, 7, 80 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.04.017[134] Eperon G E, Paterno G M, Sutton R J, et al. Inorganic caesium lead iodide perovskite solar cells. J Mater Chem A, 2015, 3, 19688 doi: 10.1039/C5TA06398A[135] Yao J S, Ge J, Han B N, et al. Ce3+-doping to modulate photoluminescence kinetics for efficient CsPbBr3 nanocrystals based light-emitting diodes. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140, 3626 doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b11955[136] Veldhuis S A, Ng Y F, Ahmad R, et al. Crown ethers enable room-temperature synthesis of CsPbBr3 quantum dots for light-emitting diodes. ACS Energy Lett, 2018, 3, 526 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.7b01257[137] Li Y, Lv Y, Guo Z, et al. One-step preparation of long-term stable and flexible CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dots/ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer composite films for white light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl Mater Inter, 2018, 10, 15888 doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b02857[138] Song X, Liu X, Yu D, et al. Boosting two-dimensional MoS2/CsPbBr3 photodetectors via enhanced light absorbance and interfacial carrier separation. ACS Appl Mater Inter, 2018, 10, 2801 doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b14745[139] Ramasamy P, Lim D H, Kim B, et al. All-inorganic cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals for photodetector applications. Chem Commun, 2016, 52, 2067 doi: 10.1039/C5CC08643D[140] Bao C, Yang J, Bai S, et al. High performance and stable all-inorganic metal halide perovskite-based photodetectors for optical communication applications. Adv Mater, 2018, 30, 1803422 doi: 10.1002/adma.201803422[141] Chen Q, Wu J, Ou X, et al. All-inorganic perovskite nanocrystal scintillators. Nature, 2018, 561, 88 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0451-1[142] Yakunin S, Protesescu L, Krieg F, et al. Low-threshold amplified spontaneous emission and lasing from colloidal nanocrystals of caesium lead halide perovskites. Nat Commun, 2015, 6, 8056 doi: 10.1038/ncomms9056[143] Liu Z, Yang J, Du J, et al. Robust subwavelength single-mode perovskite nanocuboid laser. ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 5923 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b02143[144] Zhang Q, Su R, Liu X, et al. High-quality whispering-gallery-mode lasing from cesium lead halide perovskite nanoplatelets. Adv Funct Mater, 2016, 26, 6238 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201601690[145] Hou J, Cao S, Wu Y, et al. Inorganic colloidal perovskite quantum dots for robust solar CO2 reduction. Chem-Eur J, 2017, 23, 9481 doi: 10.1002/chem.201702237[146] Zhou L, Xu Y F, Chen B X, et al. Synthesis and photocatalytic application of stable lead-free Cs2AgBiBr6 perovskite nanocrystals. Small, 2018, 14, 1703762 doi: 10.1002/smll.201703762[147] Song J, Fang T, Li J, et al. Organic-inorganic hybrid passivation enables perovskite QLEDs with an EQE of 16.48%. Adv Mater, 2018, 30, 1805409 doi: 10.1002/adma.201805409[148] Lin K, Xing J, Quan L N, et al. Perovskite light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 20 percent. Nature, 2018, 562, 245 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0575-3[149] Song J, Xu L, Li J, et al. Monolayer and few-layer all-inorganic perovskites as a new family of two-dimensional semiconductors for printable optoelectronic devices. Adv Mater, 2016, 28, 4861 doi: 10.1002/adma.201600225[150] Christians J A, Schulz P, Tinkham J S, et al. Tailored interfaces of unencapsulated perovskite solar cells for > 1000 hour operational stability. Nat Energy, 2018, 3, 68 doi: 10.1038/s41560-017-0067-y[151] Sutton R J, Eperon G E, Miranda L, et al. Bandgap-tunable cesium lead halide perovskites with high thermal stability for efficient solar cells. Adv Energy Mater, 2016, 6, 1502458 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201502458[152] Swarnkar A, Marshall A R, Sanehira E M, et al. Quantum dot-induced phase stabilization of α-CsPbI3 perovskite for high-efficiency photovoltaics. Science, 2016, 354, 92 doi: 10.1126/science.aag2700[153] Yang S, Chen S, Mosconi E, et al. Stabilizing halide perovskite surfaces for solar cell operation with wide-bandgap lead oxysalts. Science, 2019, 365, 473 doi: 10.1126/science.aax3294[154] Bian H, Bai D, Jin Z, et al. Graded bandgap CsPbI2+ xBr1- x perovskite solar cells with a stabilized efficiency of 14.4%. Joule, 2018, 2, 1500 doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2018.04.012[155] Wang Y, Dar M I, Ono L K, et al. Thermodynamically stabilized β-CsPbI3-based perovskite solar cells with efficiencies > 18%. Science, 2019, 365, 591 doi: 10.1126/science.aav8680[156] Zhang X, Lin H, Huang H, et al. Enhancing the brightness of cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystal based green light-emitting devices through the interface engineering with perfluorinated ionomer. Nano Lett, 2016, 16, 1415 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b04959[157] Song J, Li J, Li X, et al. Quantum dot light-emitting diodes based on inorganic perovskite cesium lead halides (CsPbX3). Adv Mater, 2015, 27, 7162 doi: 10.1002/adma.201502567[158] Yettapu G R, Talukdar D, Sarkar S, et al. Terahertz conductivity within colloidal CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals: remarkably high carrier mobilities and large diffusion lengths. Nano Lett, 2016, 16, 4838 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b01168[159] Li F, Ma C, Wang H, et al. Ambipolar solution-processed hybrid perovskite phototransistors. Nat Commun, 2015, 6, 8238 doi: 10.1038/ncomms9238[160] Huo C, Liu X, Wang Z, et al. High-performance low-voltage-driven phototransistors through CsPbBr3-2D crystal van der Waals heterojunctions. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6, 1800152 doi: 10.1002/adom.201800152[161] Senanayak S P, Yang B, Thomas T H, et al. Understanding charge transport in lead iodide perovskite thin-film field-effect transistors. Sci Adv, 2017, 3, e1601935 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1601935[162] Liu X, Yu D, Song X, et al. Metal halide perovskites: synthesis, ion migration, and application in field-effect transistors. Small, 2018, 14, 1801460 doi: 10.1002/smll.201801460[163] Jellicoe T C, Richter J M, Glass H F J, et al. Synthesis and optical properties of lead-free cesium tin halide perovskite nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc, 2016, 138, 2941 doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b13470[164] Leng M, Chen Z, Yang Y, et al. Lead-free, blue emitting bismuth halide perovskite quantum dots. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2016, 55, 15012 doi: 10.1002/anie.201608160[165] Reiss P, Protiere M, Li L. Core/shell semiconductor nanocrystals. Small, 2009, 5, 154 doi: 10.1002/smll.200800841 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: