| Citation: |
Yitian Bao, Xiaorui Wang, Shijie Xu. Sub-bandgap refractive indexes and optical properties of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 semiconductor thin films[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2022, 43(6): 062802. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/6/062802
Y T Bao, X R Wang, S J Xu. Sub-bandgap refractive indexes and optical properties of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 semiconductor thin films[J]. J. Semicond, 2022, 43(6): 062802. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/6/062802
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
Sub-bandgap refractive indexes and optical properties of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 semiconductor thin films
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/6/062802
More Information-
Abstract
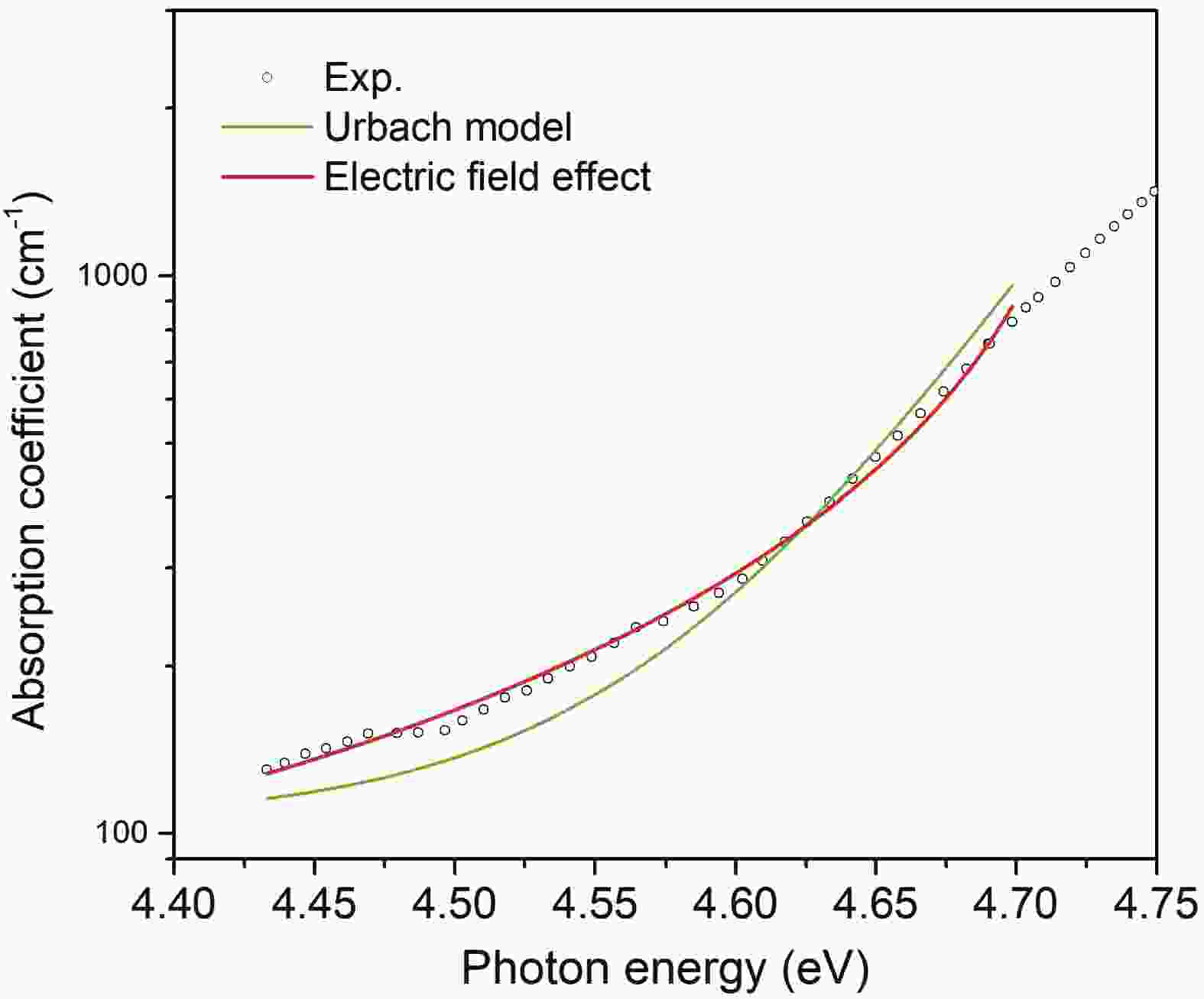
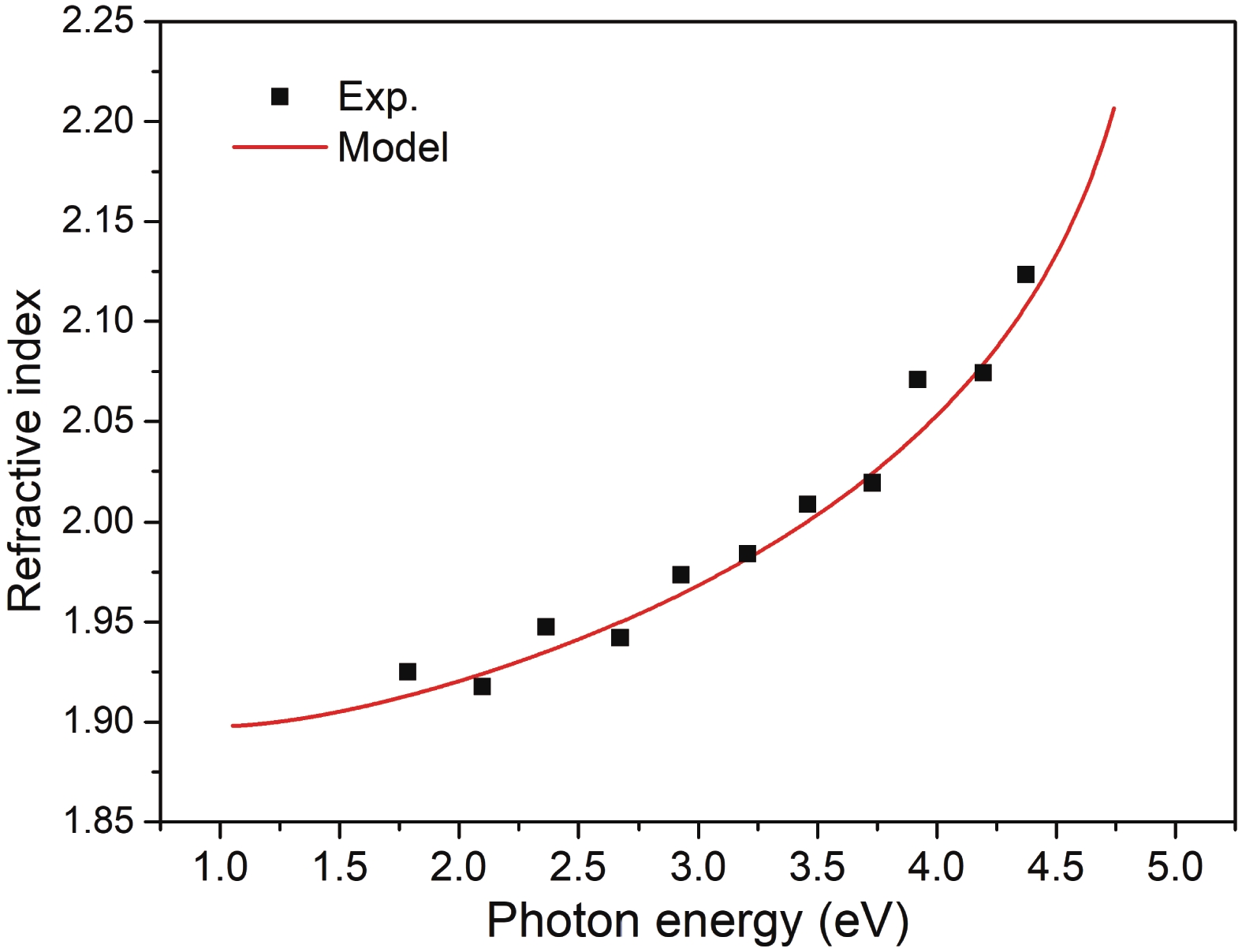
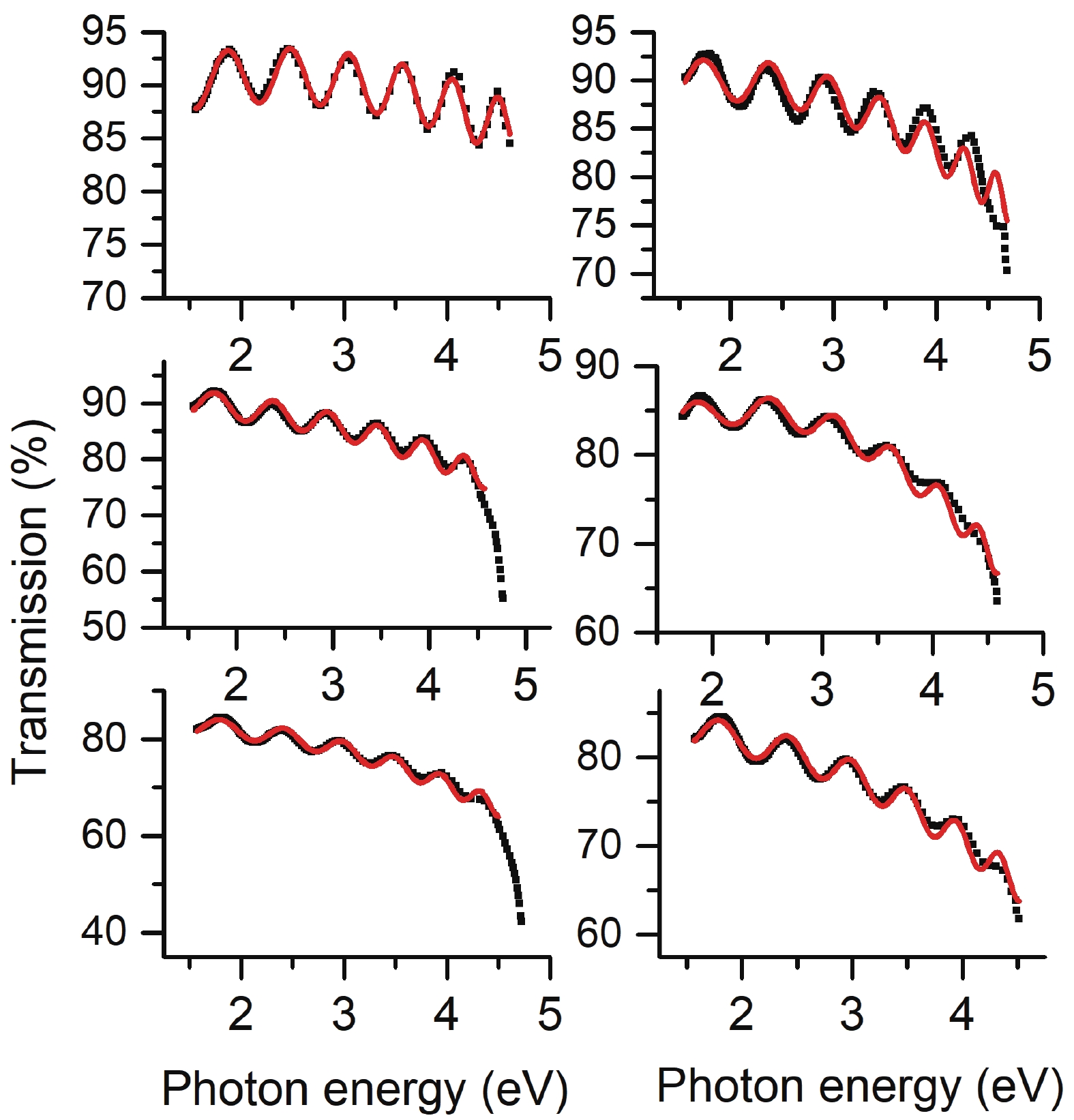
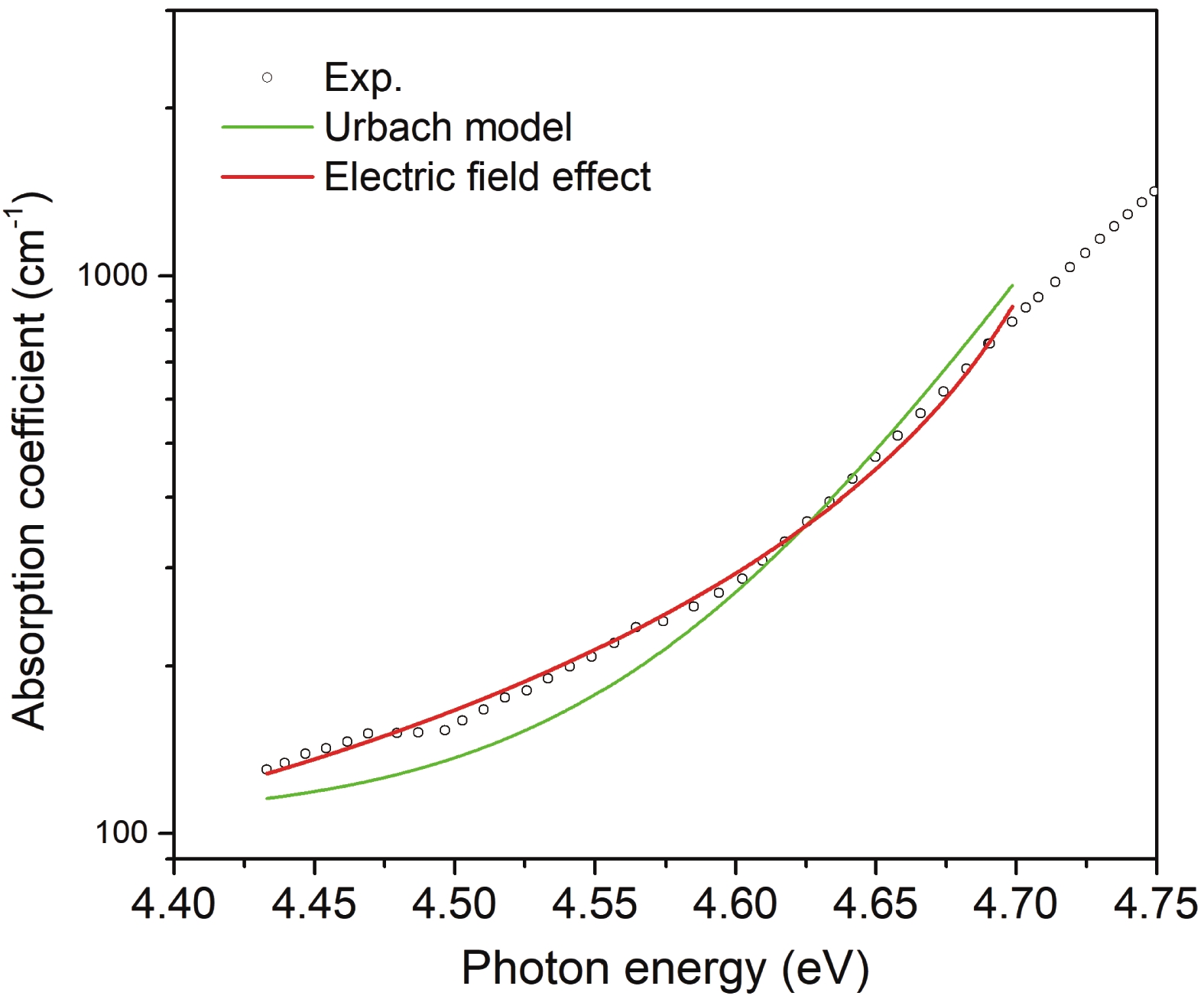
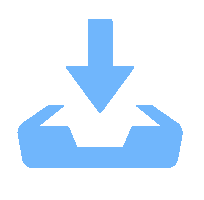
In this article, we present a theoretical study on the sub-bandgap refractive indexes and optical properties of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 thin films based on newly developed models. The measured sub-bandgap refractive indexes of β-Ga2O3 thin film are explained well with the new model, leading to the determination of an explicit analytical dispersion of refractive indexes for photon energy below an effective optical bandgap energy of 4.952 eV for the β-Ga2O3 thin film. Then, the oscillatory structures in long wavelength regions in experimental transmission spectra of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 thin films with different Si doping concentrations are quantitively interpreted utilizing the determined sub-bandgap refractive index dispersion. Meanwhile, effective optical bandgap values of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 thin films are further determined and are found to decrease with increasing the Si doping concentration as expectedly. In addition, the sub-bandgap absorption coefficients of Si-doped β-Ga2O3 thin film are calculated under the frame of the Franz–Keldysh mechanism due to the electric field effect of ionized Si impurities. The theoretical absorption coefficients agree with the available experimental data. These key parameters obtained in the present study may enrich the present understanding of the sub-bandgap refractive indexes and optical properties of impurity-doped β-Ga2O3 thin films. -
References
[1] Pearton S J, Yang J, Cary IV P H, et al. A review of Ga2O3 materials, processing, and device. Appl Phys Rev, 2018, 5, 011301 doi: 10.1063/1.5006941[2] Mohamed H F, Xia C, Sai Q, et al. Growth and fundamentals of bulk β-Ga2O3 single crystals. J Semicond, 2019, 40, 011801 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/1/011801[3] Zhang F, Arita M, Wang X, et al. Toward controlling the carrier density of Si doped Ga2O3 films by pulsed laser deposition. Appl Phys Lett, 2016, 109, 102105 doi: 10.1063/1.4962463[4] Hu D, Wang Y, Zhuang S, et al. Surface morphology evolution and optoelectronic properties of heteroepitaxial Si-doped β-Ga2O3 thin films grown by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition. Ceram Internation, 2018, 44, 3122 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.079[5] Pearton S J, Ren F, Tadjer M, et al. Perspective: Ga2O3 for ultra-high power rectifiers and MOSFETS. J Appl Phys, 2018, 124, 220901 doi: 10.1063/1.5062841[6] Yang J, Ahn S, Ren F, et al. High breakdown voltage (−201) β-Ga2O3 Schottky rectifiers. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2017, 38, 906 doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2703609[7] Wang B, Xiao M, Yan X, et al. High-voltage vertical Ga2O3 power rectifiers operational at high temperatures up to 600 K. Appl Phys Lett, 2019, 115, 263503 doi: 10.1063/1.5132818[8] Chabak K D, McCandless J P, Moser N A, et al. Recessed-gate enhancement-mode β-Ga2O3 MOSFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2018, 39, 67 doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2779867[9] Green A J, Chabak K D, Baldini M, et al. β-Ga2O3 MOSFETs for radio frequency operation. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2017, 38, 790 doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2694805[10] Moser N, McCandless J, Crespo A, et al. Ge-doped β-Ga2O3 MOSFETs. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2017, 38, 775 doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2697359[11] Oh S, Kim C K, Kim J. High responsivity β-Ga2O3 metal–semiconductor–metal solar-blind photodetectors with ultraviolet transparent graphene electrodes. ACS Photon, 2018, 5, 1123 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01486[12] Chen Y C, Lu Y J, Liu Q, et al. Ga2O3 photodetector arrays for solar-blind imaging. J Mater Chem C, 2019, 7, 2557 doi: 10.1039/C8TC05251D[13] Xu J, Zheng W, Huang F. Gallium oxide solar-blind ultraviolet photodetectors: a review. J Mater Chem C, 2019, 7, 8753 doi: 10.1039/C9TC02055A[14] Liu Z, Wang X, Liu Y, et al. A high-performance ultraviolet solar-blind photodetector based on a β-Ga2O3 Schottky photodiode. J Mater Chem C, 2019, 7, 13920 doi: 10.1039/C9TC04912F[15] Zhang L, Xiu X, Li Y, et al. Solar-blind ultraviolet photodetector based on vertically aligned single-crystalline β-Ga2O3 nanowire arrays. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9, 0295 doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0336[16] Xie C, Lu X, Liang Y, et al. Patterned growth of β-Ga2O3 thin films for solar-blind deep-ultraviolet photodetectors array and optical imaging application. J Mater Sci Technol, 2021, 72, 189 doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.09.015[17] Rebien M, Henrion W, Hong M, et al. Optical properties of gallium oxide thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81, 250 doi: 10.1063/1.1491613[18] Bao Y, Xu S. Variable-period oscillations in optical spectra in sub-bandgap long wavelength region: Signatures of new dispersion of refractive index. J Phys D, 2021, 54, 155102 doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/abd6d4[19] Bhaumik I, Bhatt R, Ganesamoorthy S, et al. Temperature-dependent index of refraction of monoclinic Ga2O3 single crystal. Appl Opt, 2011, 50, 6006 doi: 10.1364/AO.50.006006[20] Ueda N, Hosono H, Waseda R, et al. Anisotropy of electrical and optical properties in β-Ga2O3 single crystals. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 71, 933 doi: 10.1063/1.119693[21] Hilfiker M, Kilic U, Mock A, et al. Dielectric function tensor (1.5 eV to 9.0 eV), anisotropy, and band to band transitions of monoclinic β-(Al xGa1– x)2O3 (x ≤ 0.21) films. Appl Phys Lett, 2019, 114, 231901 doi: 10.1063/1.5097780[22] Furthmüller J, Bechstedt F. Quasiparticle bands and spectra of Ga2O3 polymorphs. Phys Rev B, 2016, 93, 115204 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.115204[23] Yan J, Qu C. Electronic structure and optical properties of F-doped-Ga2O3 from first principles calculations. J Semicond, 2016, 37, 042002 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/4/042002[24] Mock A, Korlacki R, Briley C, et al. Band-to-band transitions, selection rules, effective mass, and excitonic contributions in monoclinic β-Ga2O3. Phys Rev B, 2017, 96, 245205 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.96.245205[25] Galazka Z. β-Ga2O3 for wide-bandgap electronics and optoelectronics. Semicond Sci Technol, 2018, 33, 113001 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aadf78[26] Redfield D. Effect of defect fields on the optical absorption edge. Phys Rev, 1963, 130, 916 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.130.916[27] Tharmalingam K. Optical absorption in the presence of a uniform field. Phys Rev, 1963, 130, 2204 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.130.2204[28] Bao Y, Xu S. Dopant-induced electric fields and their influence on the band-edge absorption of GaN. ACS Omega, 2019, 4, 15401 doi: 10.1021/acsomega.9b01394[29] Rafique S, Han L, Mou S, et al. Temperature and doping concentration dependence of the energy band gap in β-Ga2O3 thin films grown on sapphire. Opt Mater Express, 2017, 7, 3561 doi: 10.1364/OME.7.003561[30] Subrina R, Han L, Zhao H. Synthesis of wide bandgap Ga2O3 (Eg ~ 4.6–4.7 eV) thin films on sapphire by low pressure chemical vapor deposition. Phys Status Solidi A, 2016, 213, 1002 doi: 10.1002/pssa.201532711[31] Zhang J, Shi J, Qi D C, et al. Recent progress on the electronic structure, defect, and doping properties of Ga2O3. APL Mater, 2020, 8, 020906 doi: 10.1063/1.5142999[32] Peelaers H, Van de Walle C G. Sub-band-gap absorption in Ga2O3. Appl Phys Lett, 2017, 111, 182104 doi: 10.1063/1.5001323[33] Bechstedt F, Furthmüller J. Influence of screening dynamics on excitons in Ga2O3 polymorphs. Appl Phys Lett, 2019, 114, 122101 doi: 10.1063/1.5084324[34] Guo R, Su J, Yuan H, et al. Surface functionalization modulates the structural and optoelectronic properties of two-dimensional Ga2O3. Mater Today Phys, 2020, 12, 100192 doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2020.100192[35] Shi S L, Xu S J. Determination of effective mass of heavy hole from phonon-assisted excitonic luminescence spectra in ZnO. J Appl Phys, 2011, 109, 053510 doi: 10.1063/1.3549724[36] Wang X, Yu D, Xu S. Determination of absorption coefficients and Urbach tail depth of ZnO below the bandgap with two-photon photoluminescence. Opt Express, 2020, 28, 13817 doi: 10.1364/OE.391534[37] Ye H G, Su Z C, Tang F, et al. Role of free electrons in phosphorescence in n-type wide bandgap semiconductors. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2017, 19, 30332 doi: 10.1039/C7CP05796B[38] Ye H, Su Z, Tang F, et al. Probing defects in ZnO by persistent phosphorescence. Opto-Electron Adv, 2018, 1, 180011 doi: 10.29026/oea.2018.180011 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: