| Citation: |
Mengjia Li, Zuolin Zhang, Jie Sun, Fan Liu, Jiangzhao Chen, Liming Ding, Cong Chen. Perovskite solar cells with NiOx hole-transport layer[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(10): 100201. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/10/100201
****
M J Li, Z L Zhang, J Sun, F Liu, J Z Chen, L M Ding, C Chen. Perovskite solar cells with NiOx hole-transport layer[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(10): 100201. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/10/100201
|
Perovskite solar cells with NiOx hole-transport layer
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/10/100201
More Information
-
References
[1] Li Z, Li B, Wu X, et al. Organometallic-functionalized interfaces for highly efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Science, 2022, 376, 416 doi: 10.1126/science.abm8566[2] Luo M, Zong X, Zhao M, et al. Synergistic effect of amide and fluorine of polymers assist stable inverted perovskite solar cells with fill factor > 83%. Chem Eng J, 2022, 442, 136136 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136136[3] Li M J, Li H Y, Zhuang Q X, et al. Stabilizing perovskite precursor by synergy of functional groups for NiO x-based inverted solar cells with 23.5 % efficiency. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2022, 61, e202206914 doi: 10.1002/anie.202206914[4] Jiang F, Choy W C H, Li X C, et al. Post-treatment-free solution-processed non-stoichiometric NiO(x) nanoparticles for efficient hole-transport layers of organic optoelectronic devices. Adv Mater, 2015, 27, 2930 doi: 10.1002/adma.201405391[5] Zhang H, Cheng J Q, Lin F, et al. Pinhole-free and surface-nanostructured NiOx film by room-temperature solution process for high-performance flexible perovskite solar cells with good stability and reproducibility. ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 1503 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b07043[6] Lee J H, Noh Y W, Jin I S, et al. A solution-processed cobalt-doped nickel oxide for high efficiency inverted type perovskite solar cells. J Power Sources, 2019, 412, 425 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.11.081[7] Jung J W, Chueh C C, Jen A K Y. A low-temperature, solution-processable, Cu-doped nickel oxide hole-transporting layer via the combustion method for high-performance thin-film perovskite solar cells. Adv Mater, 2015, 27, 7874 doi: 10.1002/adma.201503298[8] Zhang H, Zhao C X, Yao J X, et al. Dopant-free NiO x nanocrystals: A low-cost and stable hole transport material for commercializing perovskite optoelectronics. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2023, 62, e202219307 doi: 10.1002/anie.202219307[9] Zhang S H, Wang H Y, Duan X, et al. Printable and homogeneous NiO x hole transport layers prepared by a polymer-network gel method for large-area and flexible perovskite solar cells. Adv Funct Materials, 2021, 31, 2106495 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202106495[10] Wu T H, Ono L K, Yoshioka R, et al. Elimination of light-induced degradation at the nickel oxide-perovskite heterojunction by aprotic sulfonium layers towards long-term operationally stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ Sci, 2022, 15, 4612 doi: 10.1039/D2EE01801B[11] Chen W, Wu Y Z, Yue Y F, et al. Efficient and stable large-area perovskite solar cells with inorganic charge extraction layers. Science, 2015, 350, 944 doi: 10.1126/science.aad1015[12] Chen W, Liu F Z, Feng X Y, et al. Cesium doped NiO x as an efficient hole extraction layer for inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Adv Energy Mater, 2017, 7, 1700722 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201700722[13] Wei Y, Yao K, Wang X F, et al. Improving the efficiency and environmental stability of inverted planar perovskite solar cells via silver-doped nickel oxide hole-transporting layer. Appl Surf Sci, 2018, 427, 782 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.184[14] Chen W, Wu Y H, Fan J, et al. Understanding the doping effect on NiO: Toward high-performance inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv Energy Mater, 2018, 8, 1703519 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201703519[15] Zhang J K, Mao W J, Hou X, et al. Solution-processed Sr-doped NiOx as hole transport layer for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells. Sol Energy, 2018, 174, 1133 doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2018.10.004[16] Wan X X, Jiang Y N, Qiu Z W, et al. Zinc as a new dopant for NiO x-based planar perovskite solar cells with stable efficiency near 20%. ACS Appl Energy Mater, 2018, 1, 3947 doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b00671[17] Chen X F, Xu L, Chen C, et al. Rare earth ions doped NiO x hole transport layer for efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. J Power Sources, 2019, 444, 227267 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227267[18] Hou D G, Zhang J, Gan X L, et al. Pb and Li co-doped NiOx for efficient inverted planar perovskite solar cells. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2020, 559, 29 doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.09.087[19] Di Girolamo D, Di Giacomo F, Matteocci F, et al. Progress, highlights and perspectives on NiO in perovskite photovoltaics. Chem Sci, 2020, 11, 7746 doi: 10.1039/D0SC02859B[20] Dong X T, Wu G C, Cui G L, et al. Boosting efficiency and stability with KBr interface modification for NiOx-based inverted perovskite solar cells. Mater Sci Semicond Process, 2023, 160, 107454 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2023.107454[21] Chen W, Zhou Y C, Chen G C, et al. Alkali chlorides for the suppression of the interfacial recombination in inverted planar perovskite solar cells. Adv Energy Mater, 2019, 9, 1803872 doi: 10.1002/aenm.201803872[22] Wang S J, Li Y K, Yang J B, et al. Critical role of removing impurities in nickel oxide on high-efficiency and long-term stability of inverted perovskite solar cells. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2022, 61, e202116534 doi: 10.1002/anie.202116534[23] Li C Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X J, et al. Efficient inverted perovskite solar cells with a fill factor over 86% via surface modification of the nickel oxide hole contact. Adv Funct Mater, 2023, 33, 2214774 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202214774[24] Yin X, Zhai J F, Ingabire P B, et al. Design of NiO x/carbon heterostructure interlayer to improve hole extraction efficiency of inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv Materials Inter, 2021, 8, 2100862 doi: 10.1002/admi.202100862[25] Lin Y B, Zhang Y D, Zhang J X, et al. 18.9% efficient organic solar cells based on n-doped bulk-heterojunction and halogen-substituted self-assembled monolayers as hole extracting interlayers. Adv Energy Mater, 2022, 12, 2202503 doi: 10.1002/aenm.202202503[26] Li Z N, Tan Q, Chen G C, et al. Simple and robust phenoxazine phosphonic acid molecules as self-assembled hole selective contacts for high-performance inverted perovskite solar cells. Nanoscale, 2023, 15, 1676 doi: 10.1039/D2NR05677A[27] Sun J J, Shou C H, Sun J S, et al. NiO x-seeded self-assembled monolayers as highly hole-selective passivating contacts for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. Sol RRL, 2021, 5, 2100663 doi: 10.1002/solr.202100663[28] Li L D, Wang Y R, Wang X Y, et al. Flexible all-perovskite tandem solar cells approaching 25% efficiency with molecule-bridged hole-selective contact. Nat Energy, 2022, 7, 708 doi: 10.1038/s41560-022-01045-2[29] Zhang J Q, Yang J, Dai R Y, et al. Elimination of interfacial lattice mismatch and detrimental reaction by self-assembled layer dual-passivation for efficient and stable inverted perovskite solar cells. Adv Energy Mater, 2022, 12, 2103674 doi: 10.1002/aenm.202103674[30] Wang Y S, Ju H, Mahmoudi T, et al. Cation-size mismatch and interface stabilization for efficient NiO x-based inverted perovskite solar cells with 21.9% efficiency. Nano Energy, 2021, 88, 106285 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106285[31] Li H Y, Zhang C, Gong C, et al. 2D/3D heterojunction engineering at the buried interface towards high-performance inverted methylammonium-free perovskite solar cells. Nat Energy, 2023, 8, 946 doi: 10.1038/s41560-023-01295-8 -
Proportional views





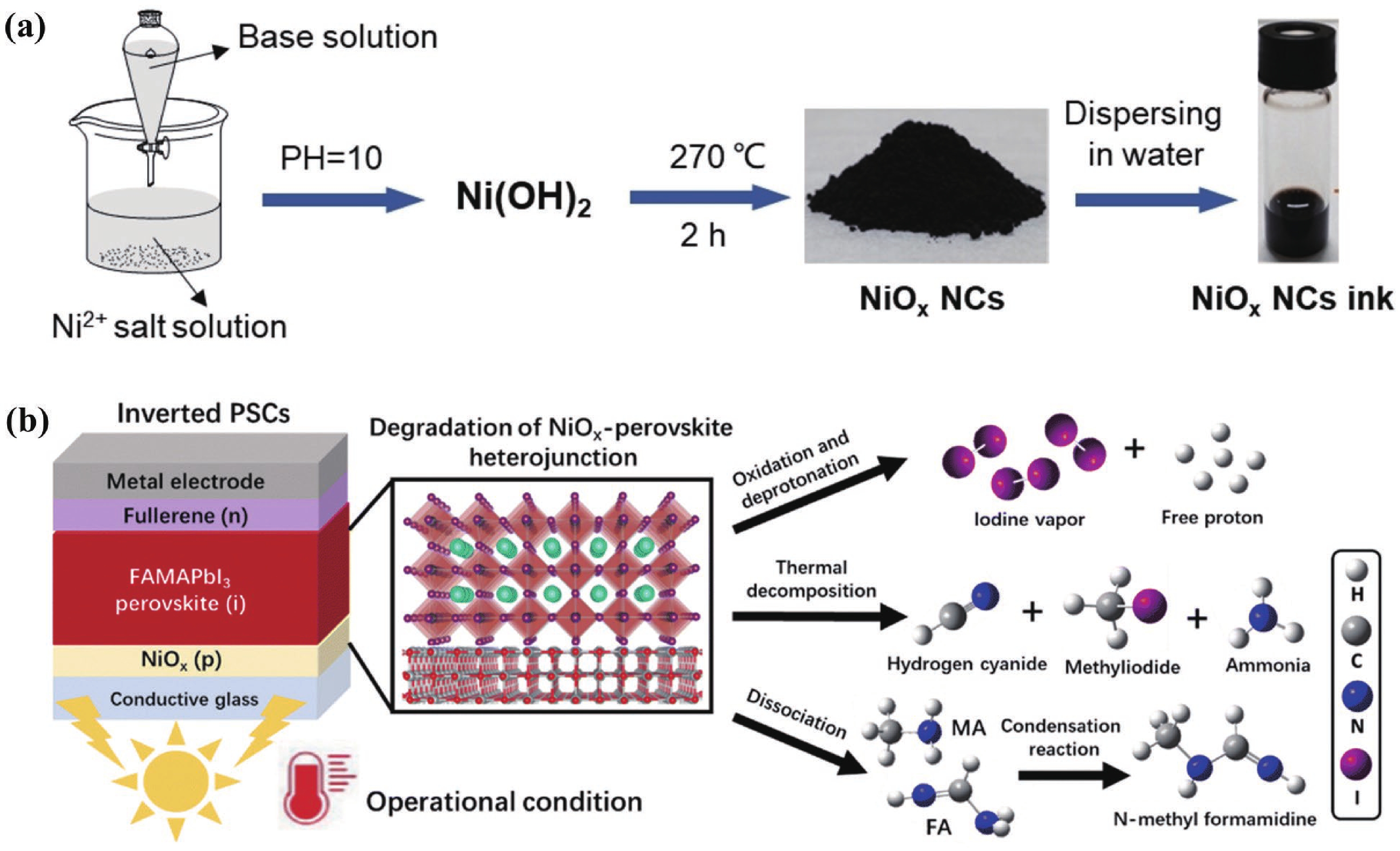
 DownLoad:
DownLoad:











 Mengjia Li:received her BE from Hebei University of Technology in June 2020. Currently, she is a PhD student in School of Materials Science and Engineering under the supervision of Prof. Cong Chen at Hebei University of Technology. Her research focuses on perovskite solar cells
Mengjia Li:received her BE from Hebei University of Technology in June 2020. Currently, she is a PhD student in School of Materials Science and Engineering under the supervision of Prof. Cong Chen at Hebei University of Technology. Her research focuses on perovskite solar cells Zuolin Zhang:received his BE from Hebei University of Technology in June 2021. Currently, he is a Master Student in School of Materials Science and Engineering under the supervision of Prof. Cong Chen at Hebei University of Technology. His research focuses on perovskite solar cells
Zuolin Zhang:received his BE from Hebei University of Technology in June 2021. Currently, he is a Master Student in School of Materials Science and Engineering under the supervision of Prof. Cong Chen at Hebei University of Technology. His research focuses on perovskite solar cells Jie Sun:got her BS from Minzu University of China in 2021. Now she is a PhD student at University of Chinese Academy of Sciences under the supervision of Prof. Liming Ding. Her research focuses on perovskite devices
Jie Sun:got her BS from Minzu University of China in 2021. Now she is a PhD student at University of Chinese Academy of Sciences under the supervision of Prof. Liming Ding. Her research focuses on perovskite devices Fan Liu:received his BS in Materials Science from Liaoning Shihua University. Now he is a PhD student under the supervision of Prof. Chuancheng Duan at the Department of Chemical Engineering, Kansas State University. His research focuses on protonic ceramic electrochemical cells
Fan Liu:received his BS in Materials Science from Liaoning Shihua University. Now he is a PhD student under the supervision of Prof. Chuancheng Duan at the Department of Chemical Engineering, Kansas State University. His research focuses on protonic ceramic electrochemical cells Jiangzhao Chen:is a professor at College of Optoelectronic Engineering in Chongqing University. He received PhD from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and then worked as a postdoc at Sungkyunkwan University and at the University of Hong Kong, respectively. His work focuses on perovskite solar cells
Jiangzhao Chen:is a professor at College of Optoelectronic Engineering in Chongqing University. He received PhD from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, and then worked as a postdoc at Sungkyunkwan University and at the University of Hong Kong, respectively. His work focuses on perovskite solar cells Liming Ding:got his PhD from University of Science and Technology of China (was a joint student at Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, CAS). He started his research on OSCs and PLEDs in Olle Ingans Lab in 1998. Later on, he worked at National Center for Polymer Research, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and Argonne National Lab (USA). He joined Konarka as a Senior Scientist in 2008. In 2010, he joined National Center for Nanoscience and Technology as a full professor. His research focuses on innovative materials and devices. He is RSC Fellow, and the Associate Editor for Journal of Semiconductors
Liming Ding:got his PhD from University of Science and Technology of China (was a joint student at Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, CAS). He started his research on OSCs and PLEDs in Olle Ingans Lab in 1998. Later on, he worked at National Center for Polymer Research, Wright-Patterson Air Force Base and Argonne National Lab (USA). He joined Konarka as a Senior Scientist in 2008. In 2010, he joined National Center for Nanoscience and Technology as a full professor. His research focuses on innovative materials and devices. He is RSC Fellow, and the Associate Editor for Journal of Semiconductors Cong Chen:is currently an associate professor at Hebei University of Technology. He received his PhD from Jilin University in June 2019. His research focuses on solar cells and NIR photodetectors
Cong Chen:is currently an associate professor at Hebei University of Technology. He received his PhD from Jilin University in June 2019. His research focuses on solar cells and NIR photodetectors



