| Citation: |
Qirui Ren, Xiaofan Sun, Xiangqu Fu, Shuaidi Zhang, Yiyang Yuan, Hao Wu, Xiaoran Li, Xinghua Wang, Feng Zhang. A review of automatic detection of epilepsy based on EEG signals[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(12): 121401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/12/121401
Q R Ren, X F Sun, X Q Fu, S D Zhang, Y Y Yuan, H Wu, X R Li, X H Wang, F Zhang. A review of automatic detection of epilepsy based on EEG signals[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(12): 121401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/12/121401
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
A review of automatic detection of epilepsy based on EEG signals
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/12/121401
More Information-
Abstract
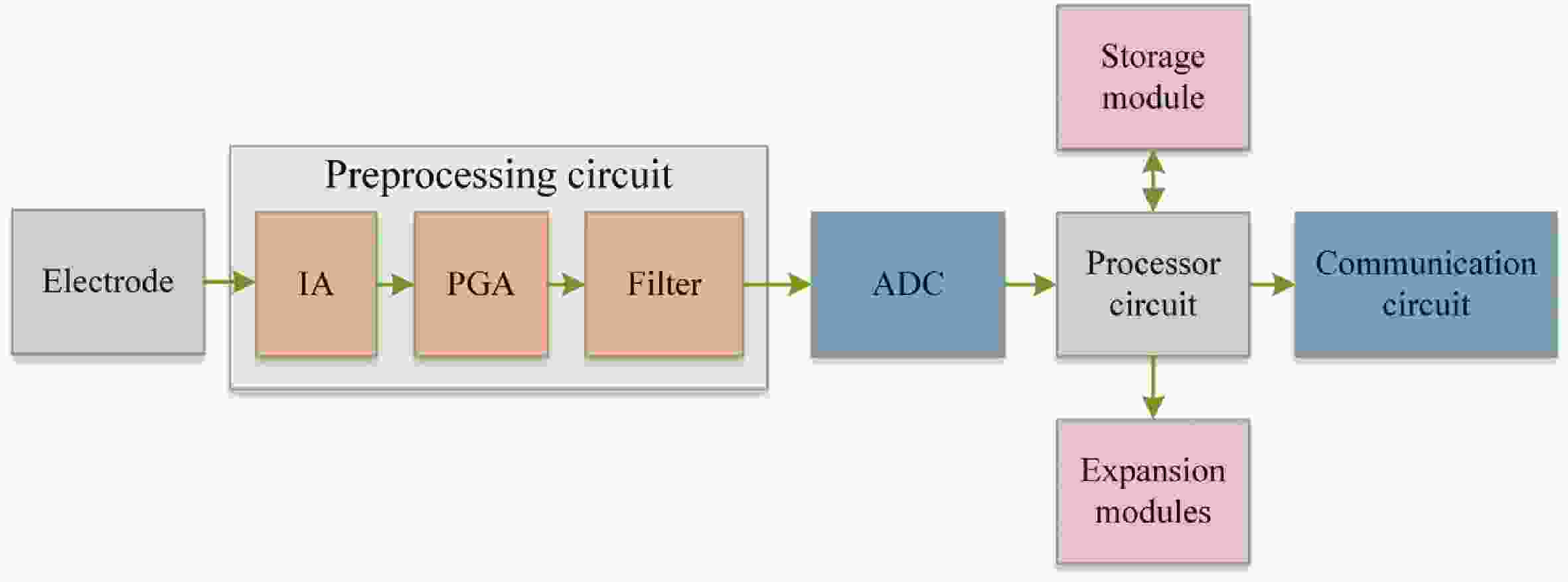
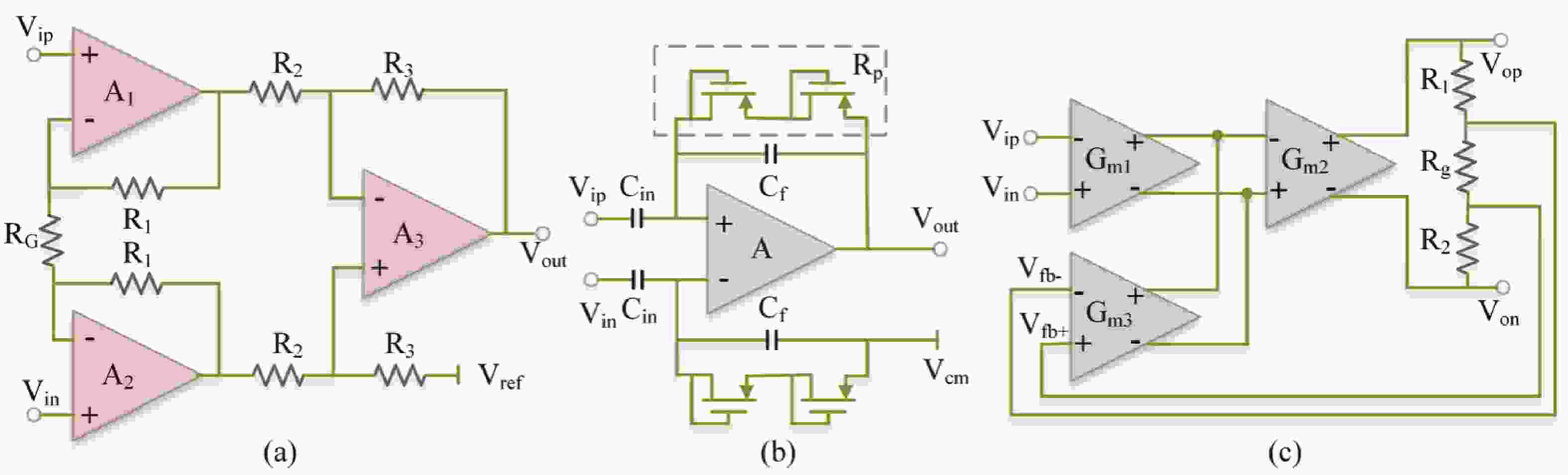
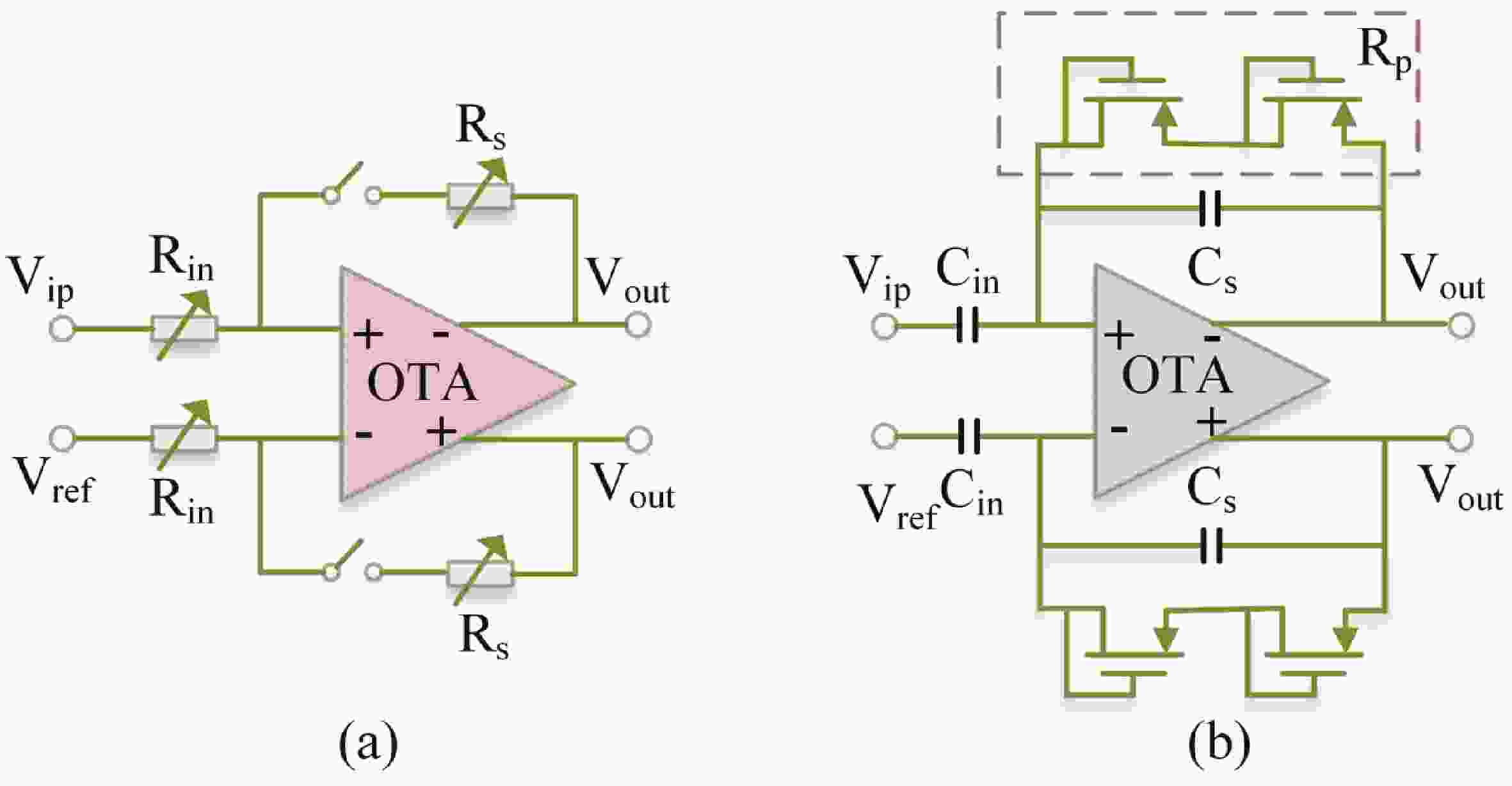
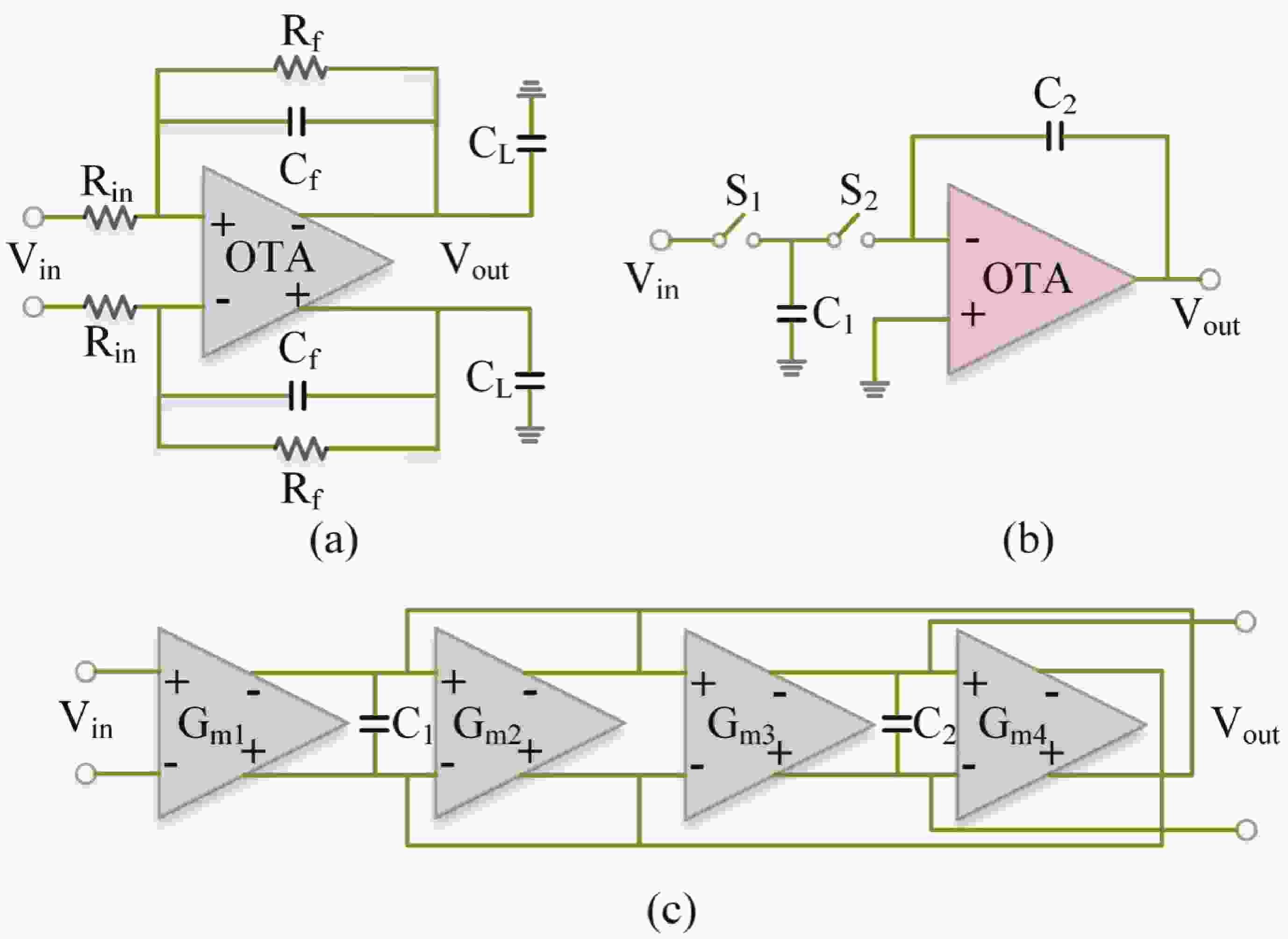
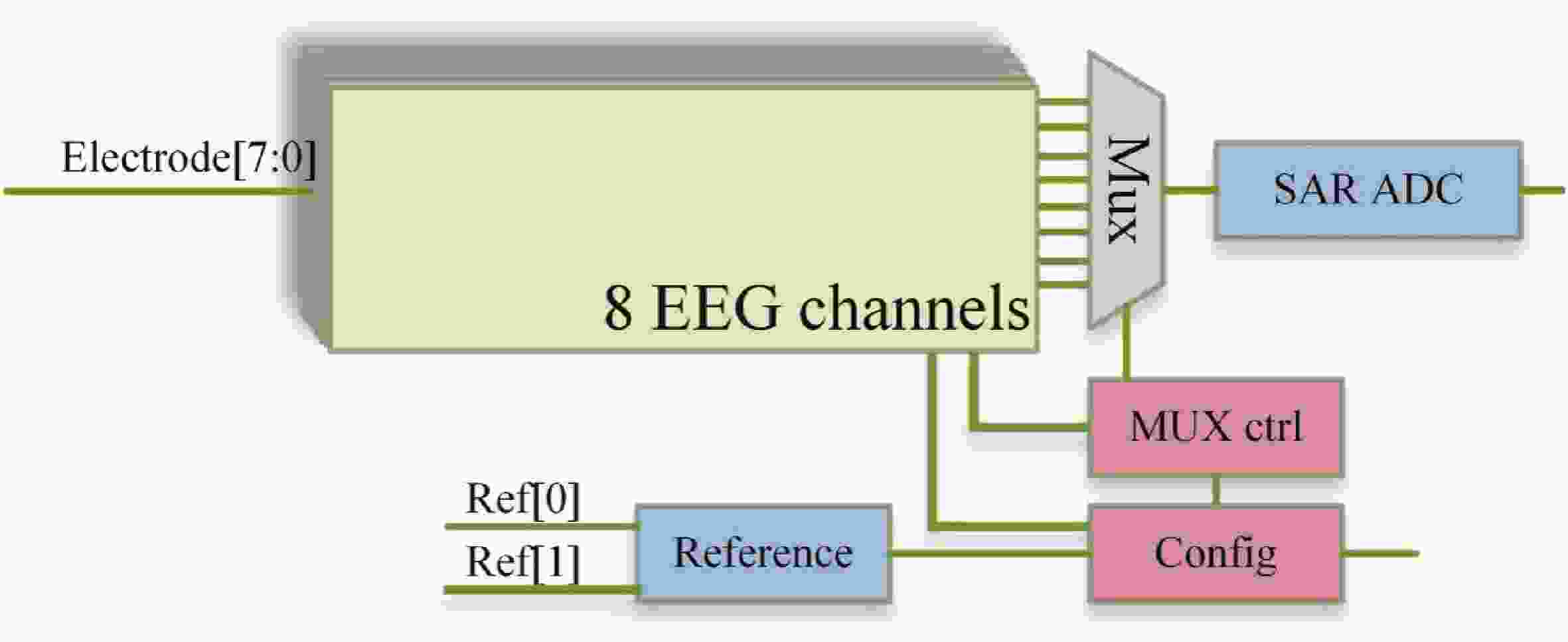
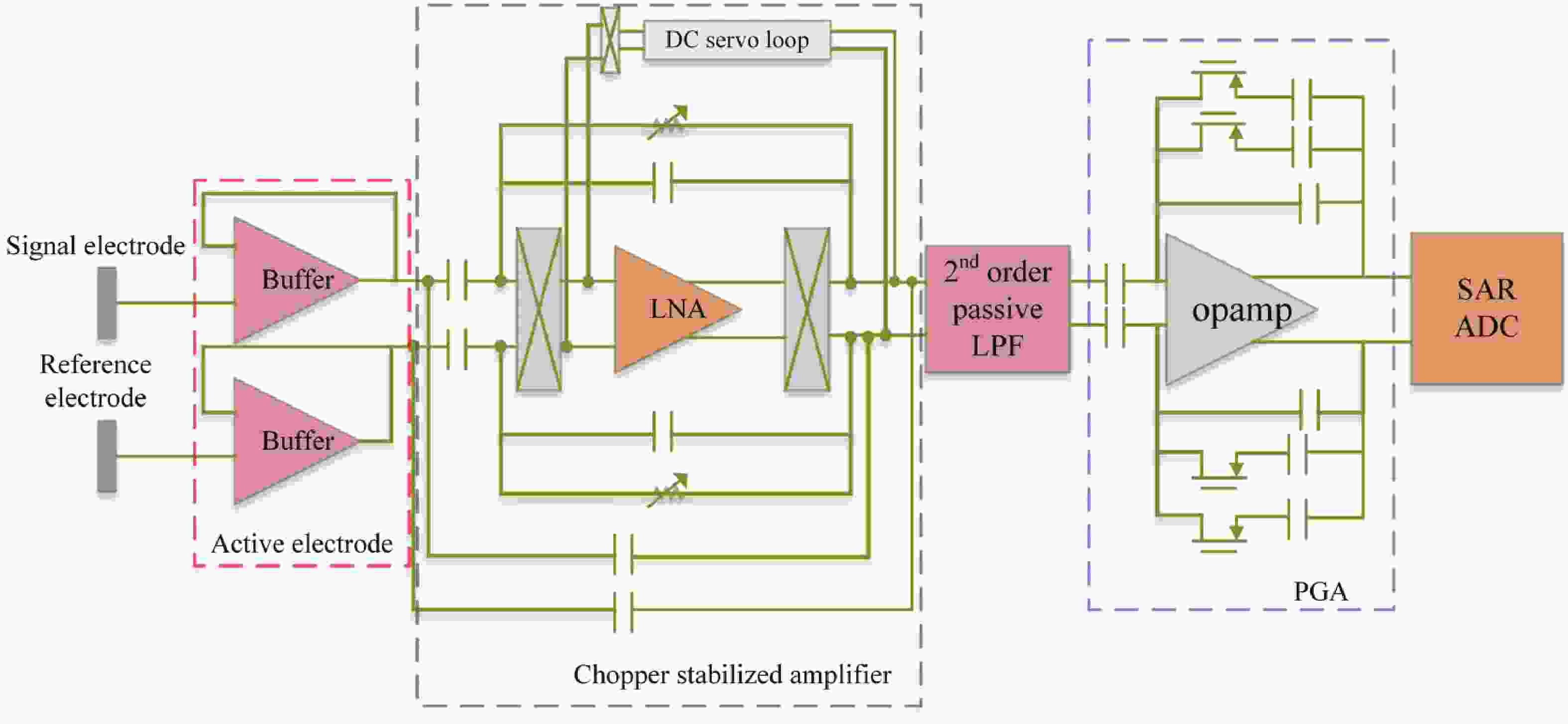
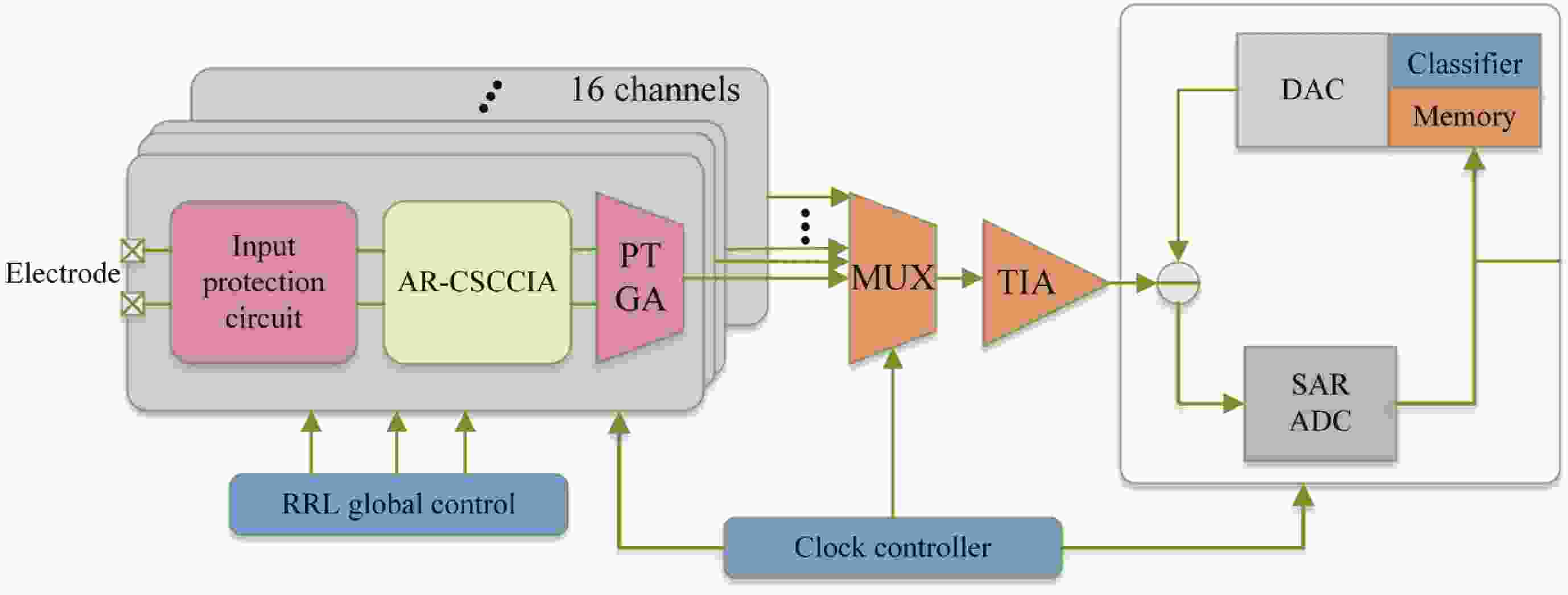
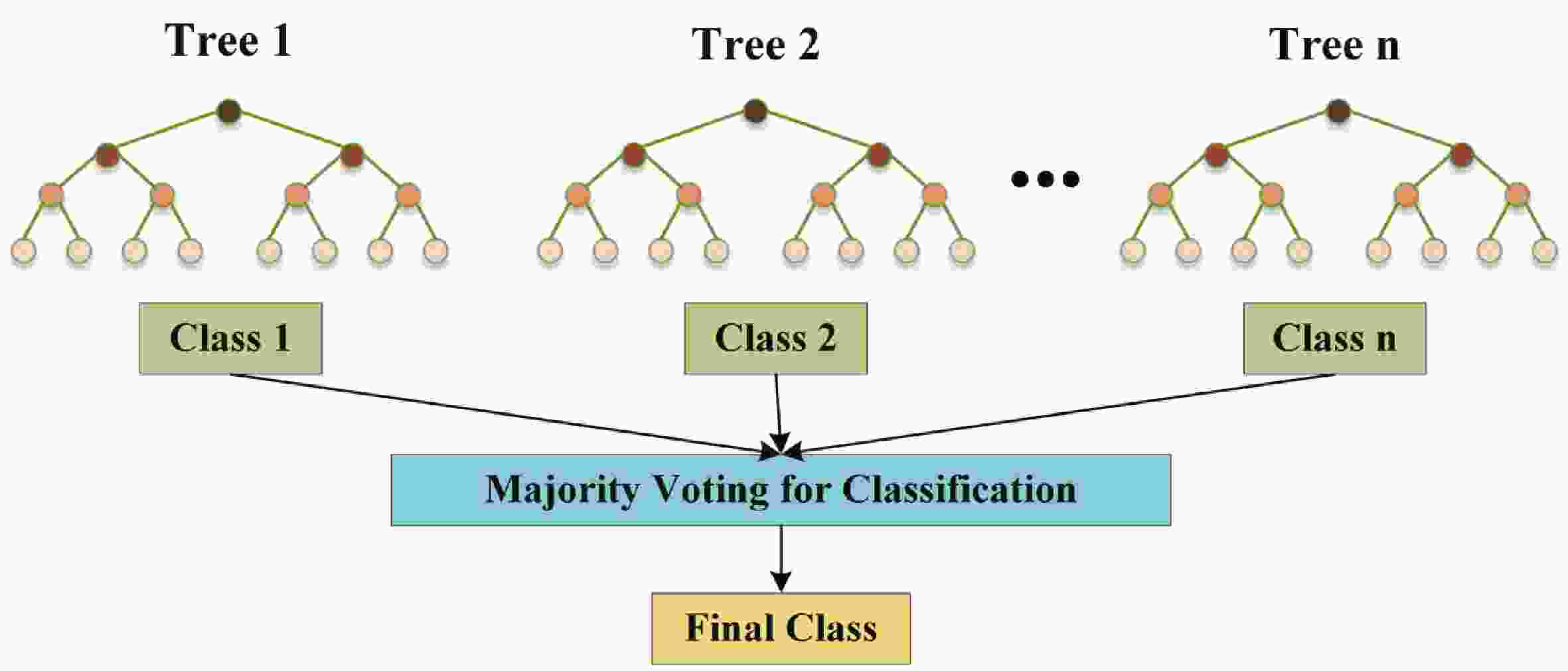
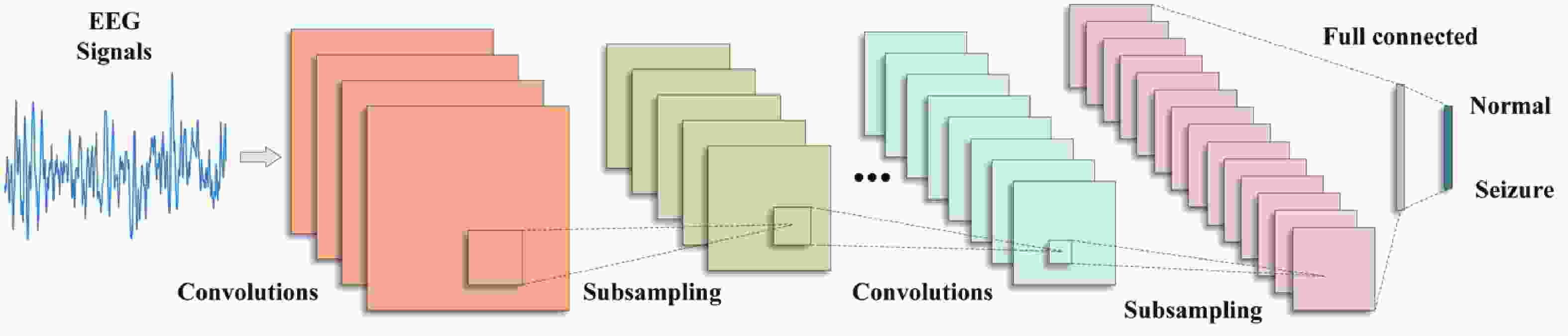
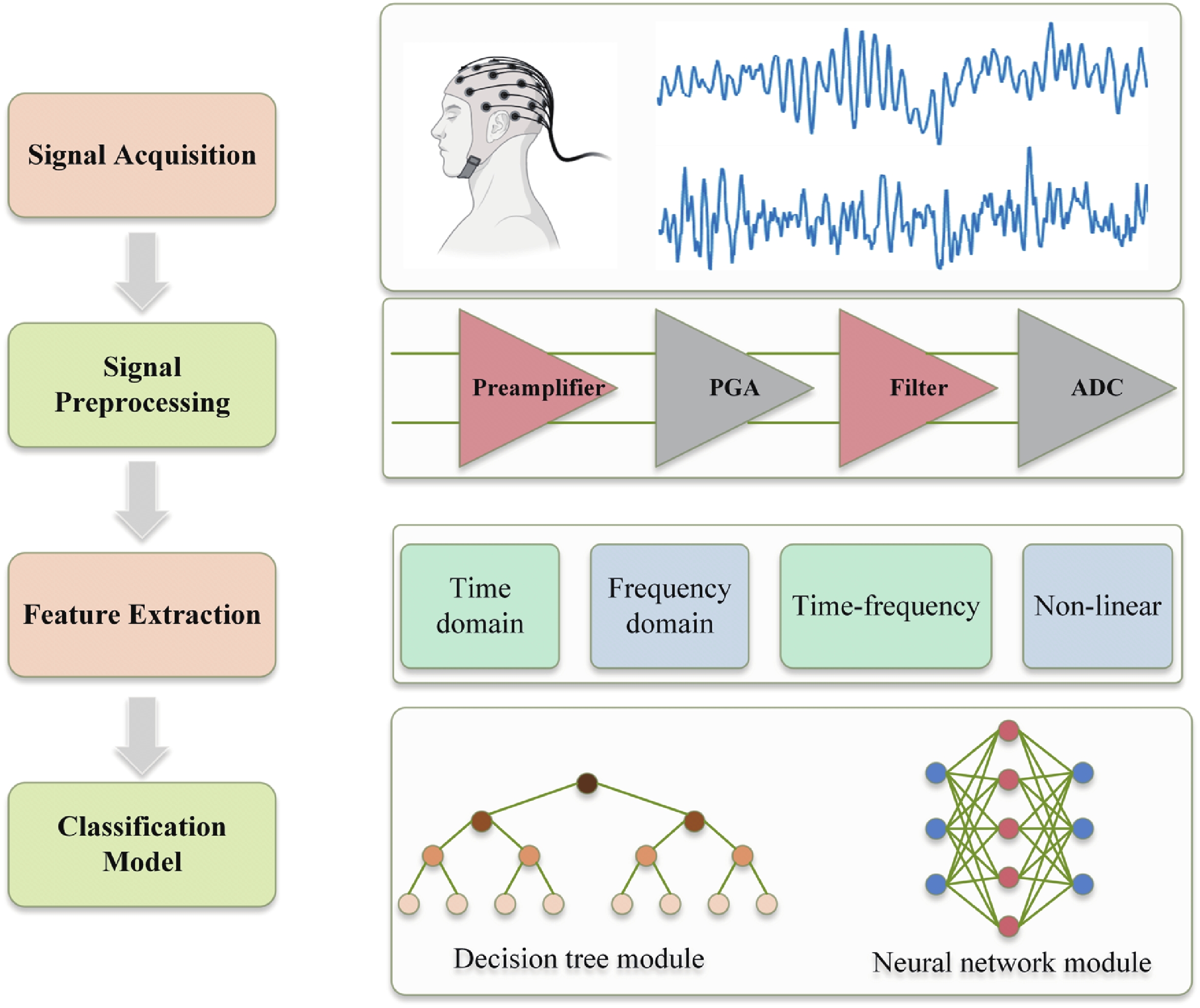
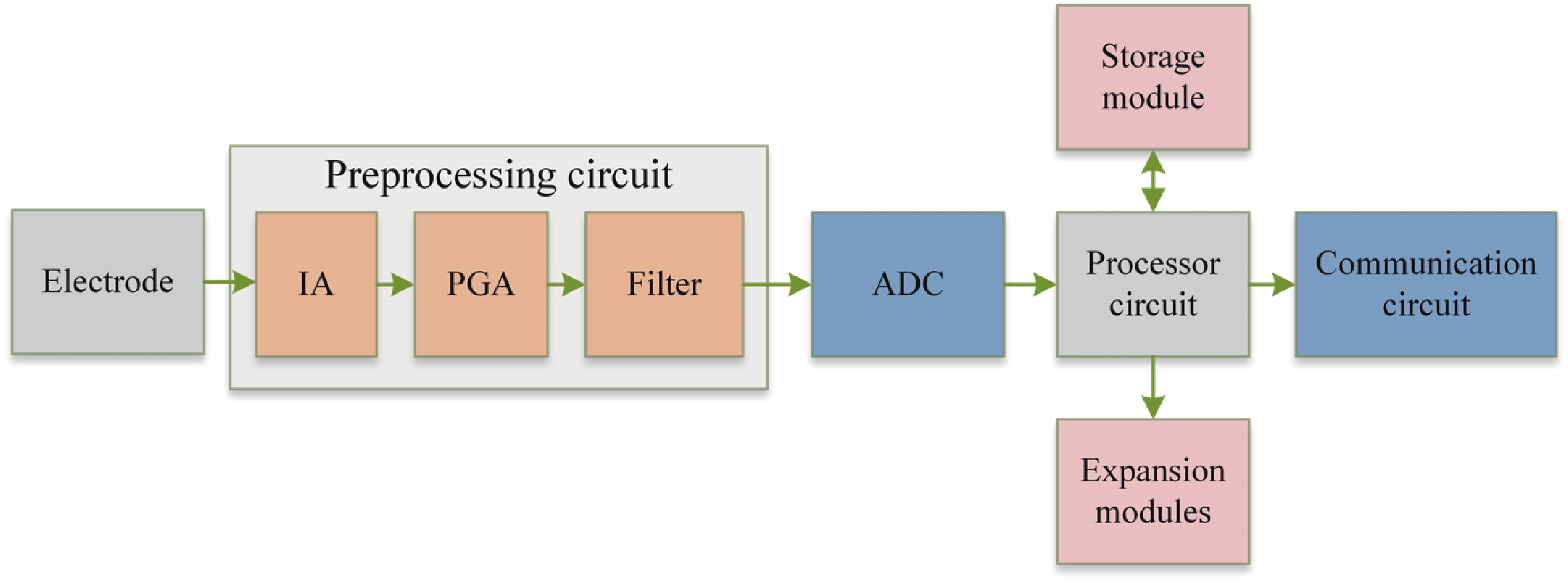
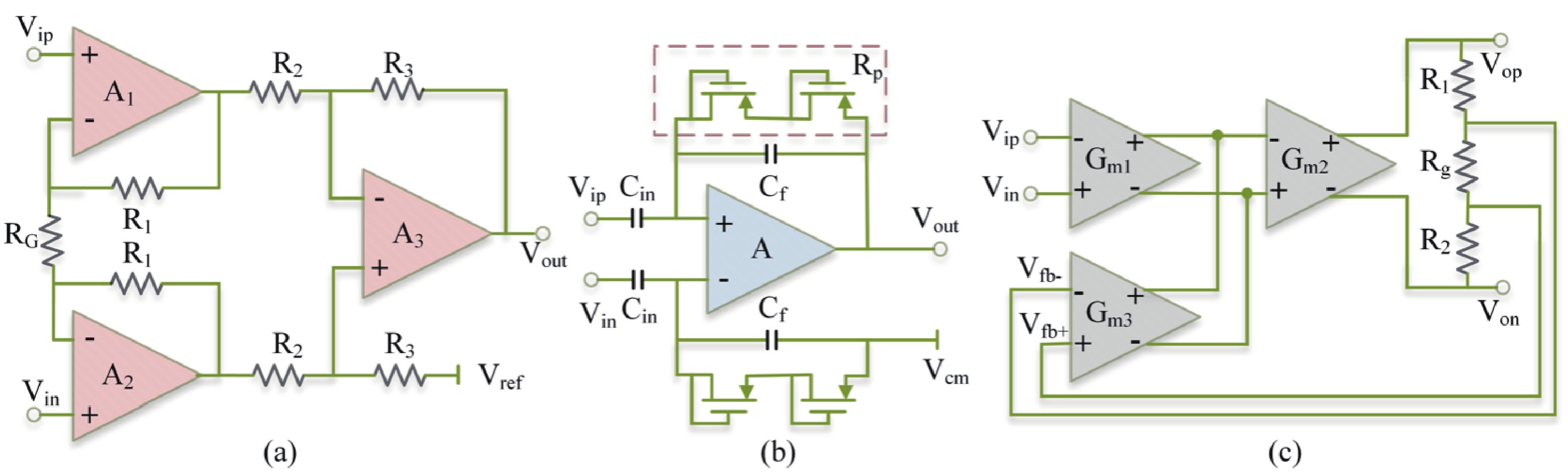
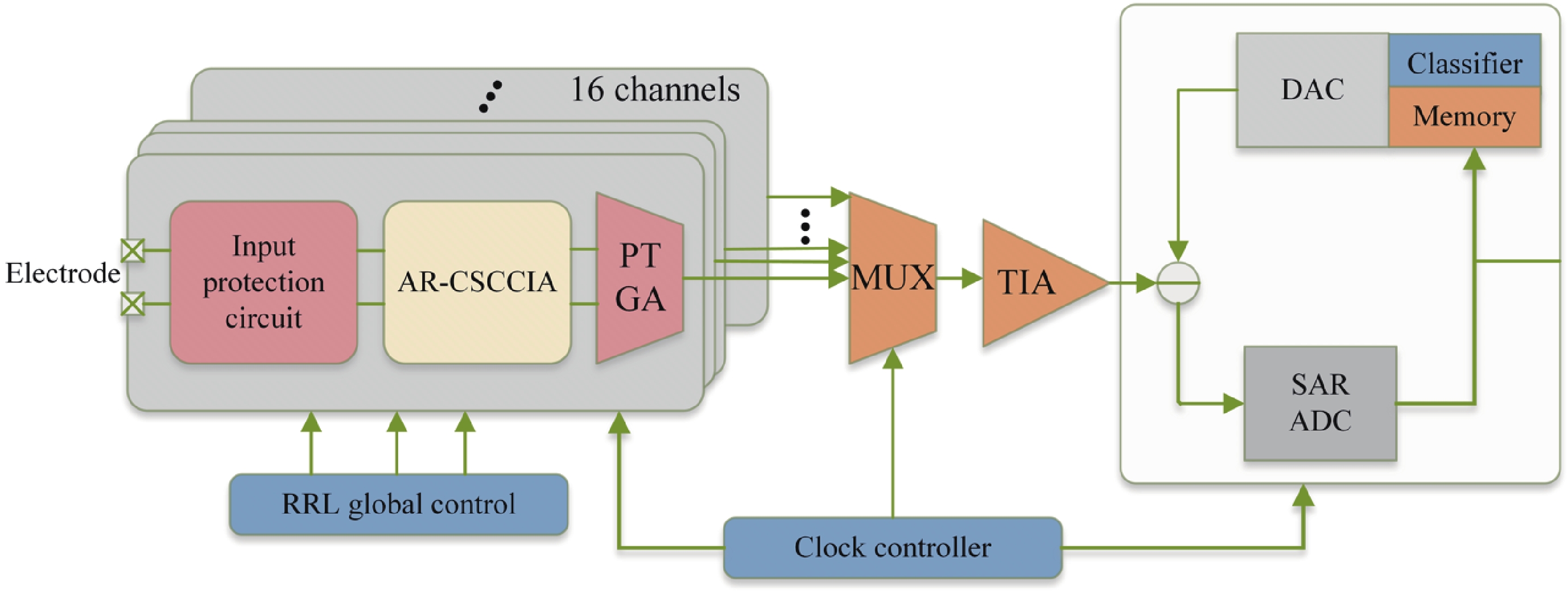
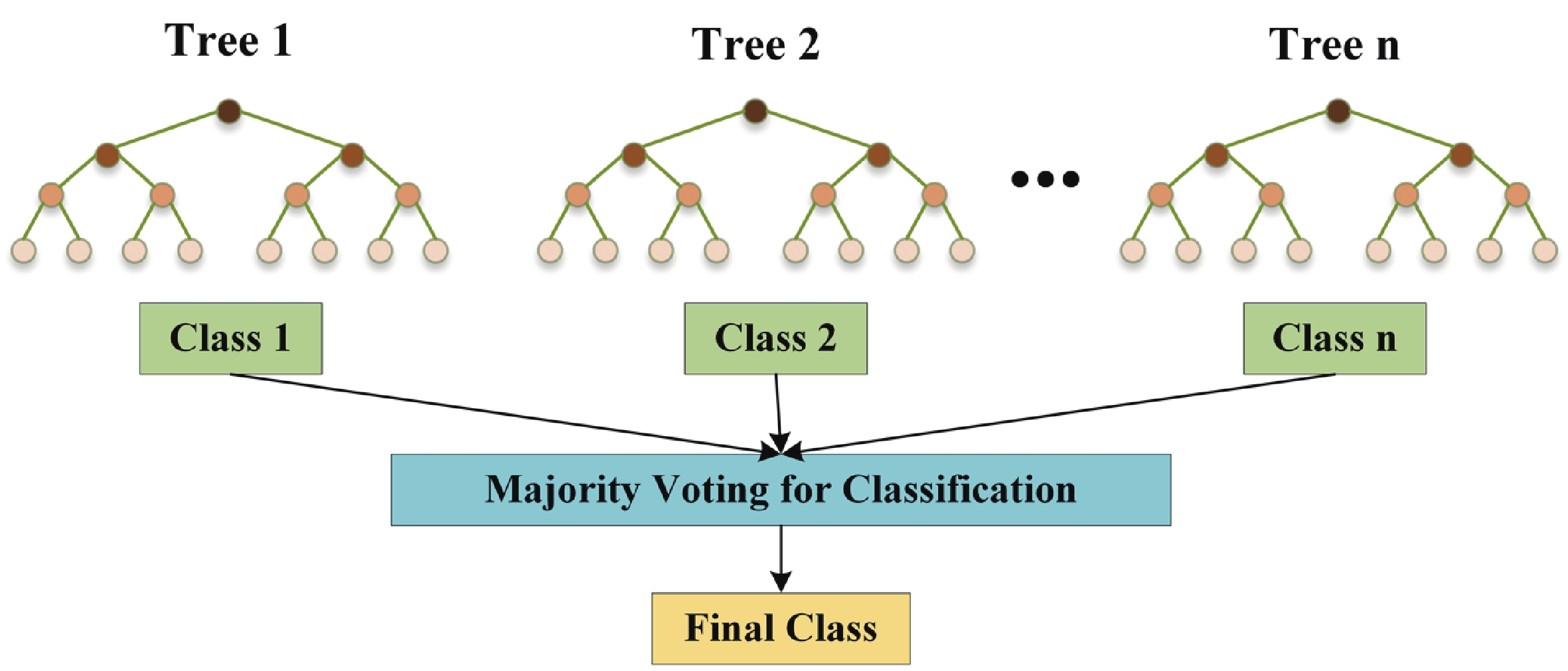
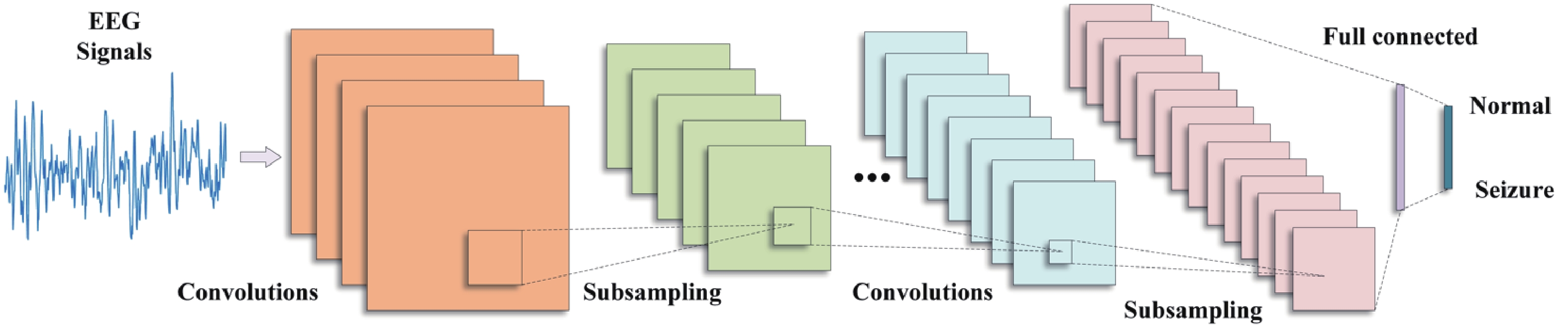
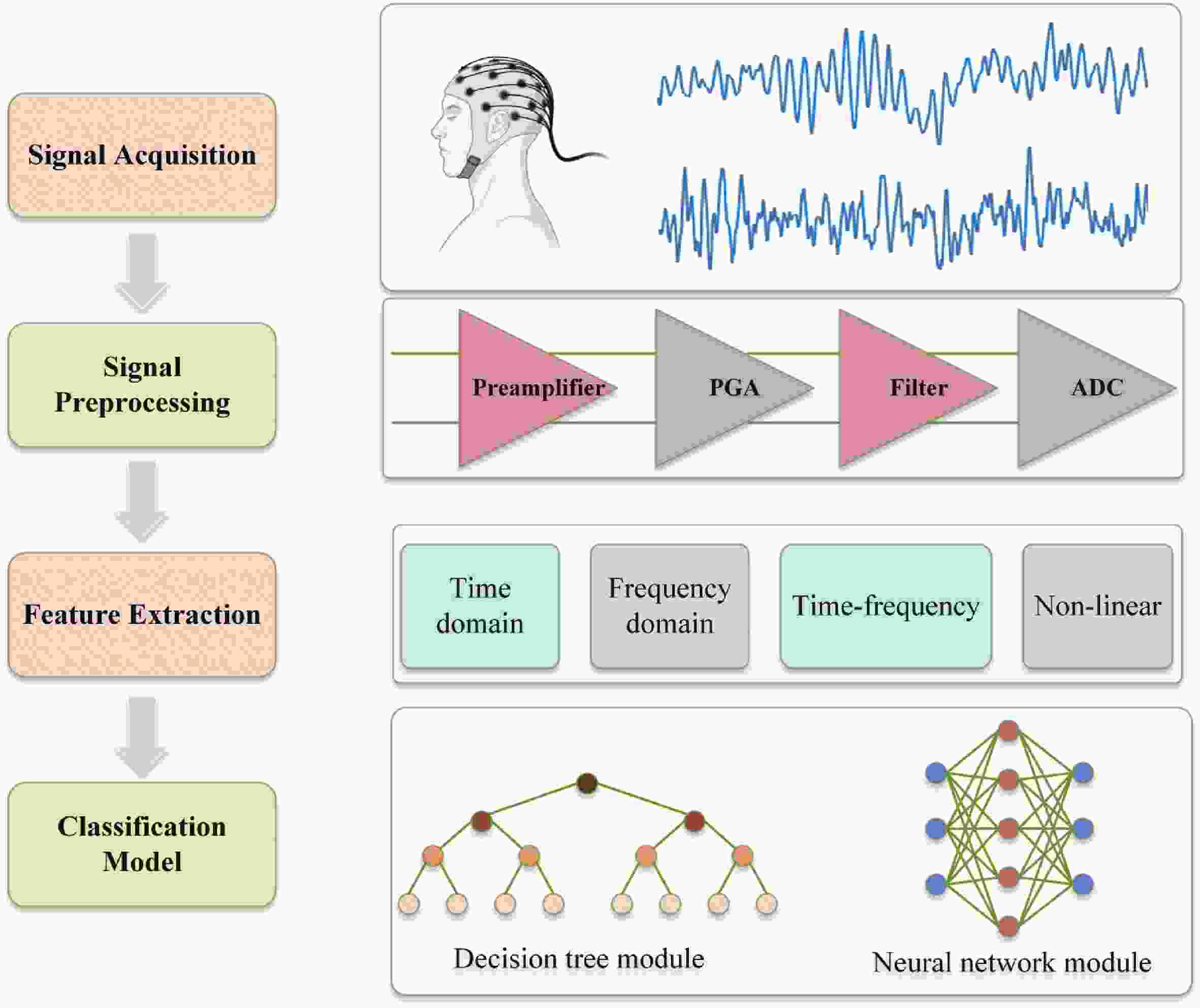
Epilepsy is a common neurological disorder that occurs at all ages. Epilepsy not only brings physical pain to patients, but also brings a huge burden to the lives of patients and their families. At present, epilepsy detection is still achieved through the observation of electroencephalography (EEG) by medical staff. However, this process takes a long time and consumes energy, which will create a huge workload to medical staff. Therefore, it is particularly important to realize the automatic detection of epilepsy. This paper introduces, in detail, the overall framework of EEG-based automatic epilepsy identification and the typical methods involved in each step. Aiming at the core modules, that is, signal acquisition analog front end (AFE), feature extraction and classifier selection, method summary and theoretical explanation are carried out. Finally, the future research directions in the field of automatic detection of epilepsy are prospected. -
References
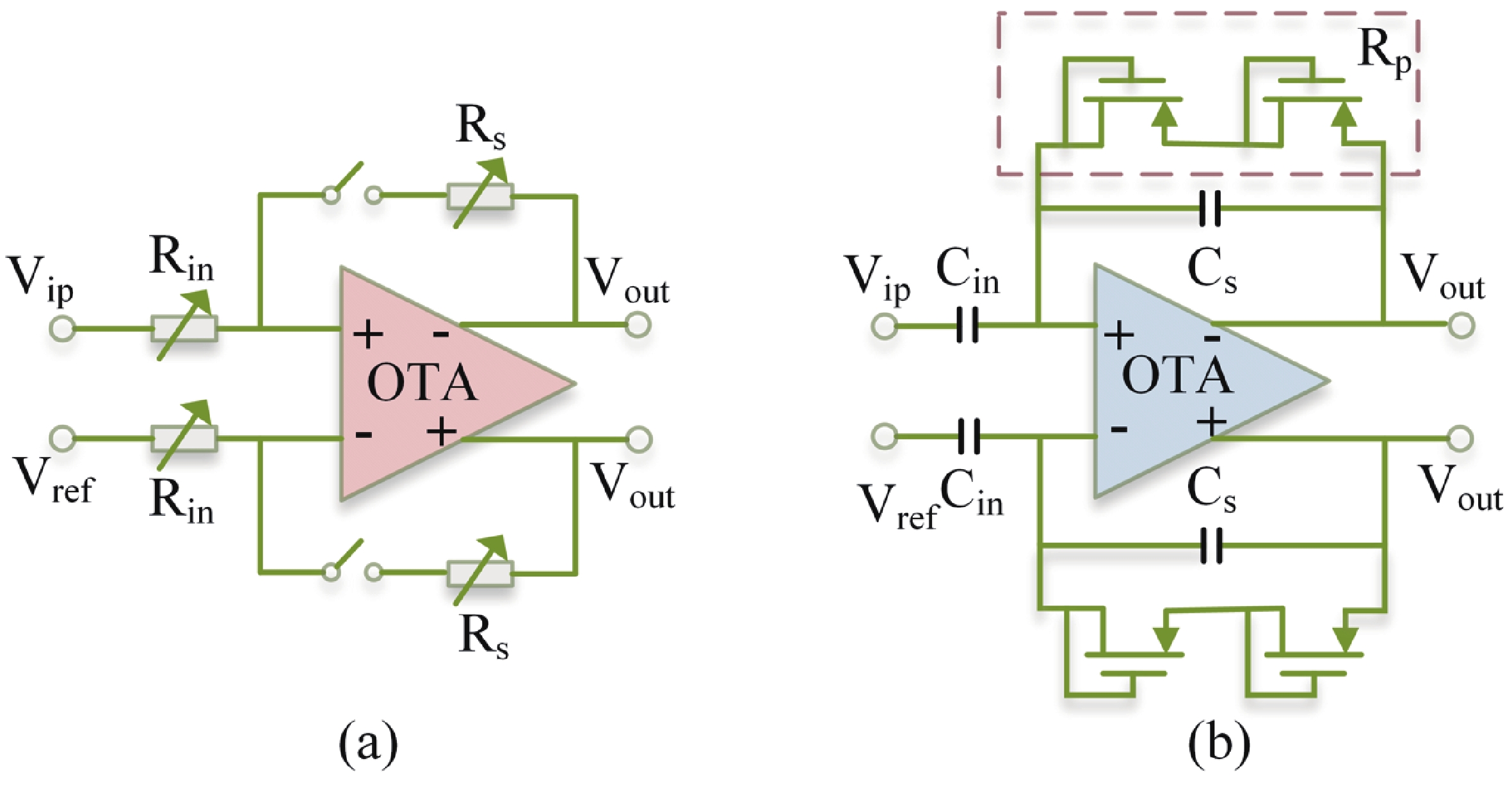
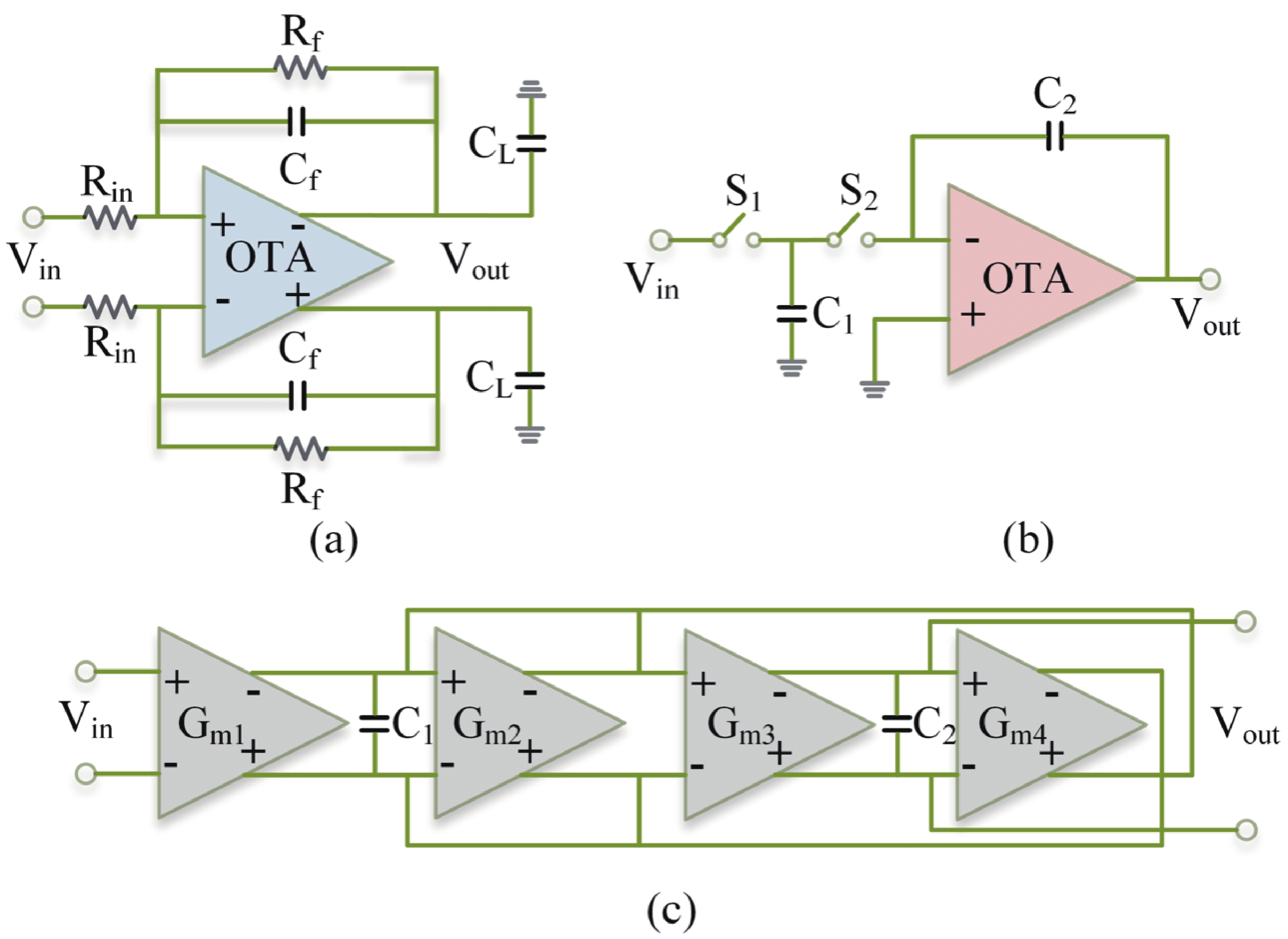
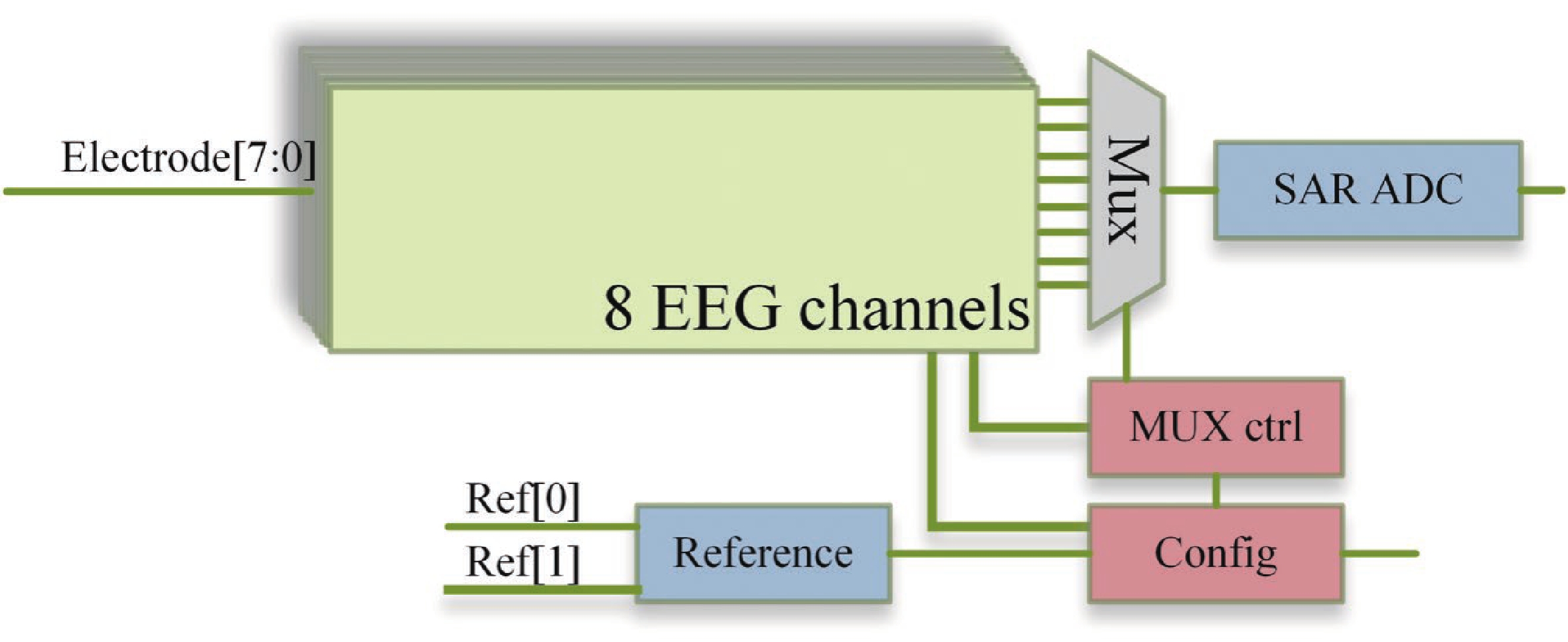
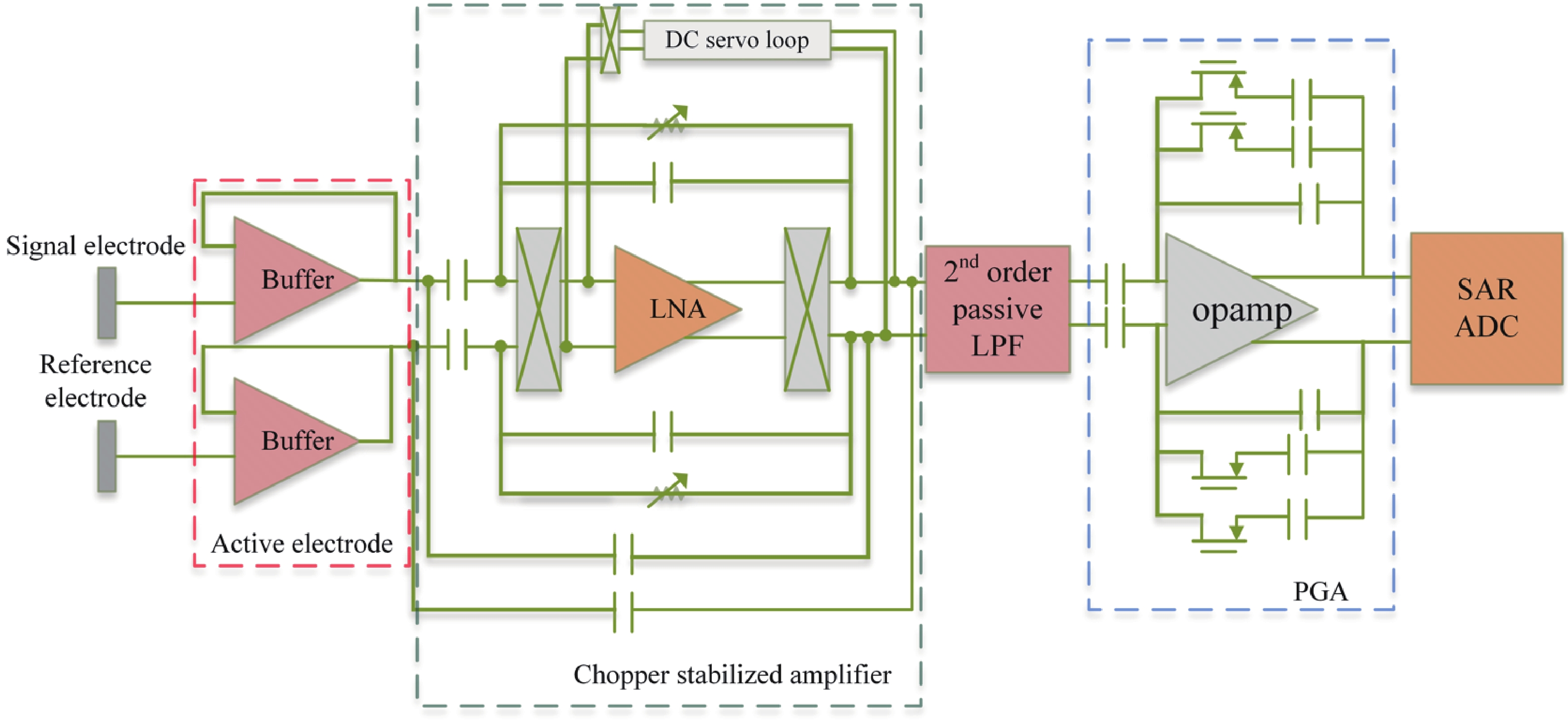
[1] Casson A J, Yates D C, Smith S J M, et al. Wearable electroencephalography. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag, 2010, 29, 44 doi: 10.1109/MEMB.2010.936545[2] Stevens J R. Seizure occurrence and interspike interval. Arch Neurol, 1972, 26, 409 doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490110043004[3] Noachtar S, Rémi J. The role of EEG in epilepsy: A critical review. Epilepsy Behav, 2009, 15, 22 doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2009.02.035[4] Piccolino M, Bresadola M. Drawing a spark from darkness: John Walsh and electric fish. Trends Neurosci, 2002, 25, 51 doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(00)02003-8[5] Ilyas M Z, Saad P, Ahmad M I. A survey of analysis and classification of EEG signals for brain-computer interfaces. 2015 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering (ICoBE), 2015, 1 doi: 10.1109/ICoBE.2015.7235129[6] Dunseath W J R, Kelly E F. Multichannel PC-based data-acquisition system for high-resolution EEG. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 1995, 42, 1212 doi: 10.1109/10.476129[7] Pribyl W, Hadl H. 32+32+8 channel data acquisition system for bio-signals in routine and research applications. 1992 14th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 1992, 2685 doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.1992.5761510[8] Ratti E, Waninger S, Berka C, et al. Comparison of medical and consumer wireless EEG systems for use in clinical trials. Front Hum Neurosci, 2017, 11, 398 doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00398[9] Xu J W, Mitra S, Matsumoto A, et al. A wearable 8-channel active-electrode EEG/ETI acquisition system for body area networks. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49, 2005 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2325557[10] Xu J W, Büsze B, Van Hoof C, et al. A 15-channel digital active electrode system for multi-parameter biopotential measurement. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50, 2090 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2422798[11] Ng K A, Xu Y P. A low-power, high CMRR neural amplifier system employing CMOS inverter-based OTAs with CMFB through supply rails. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2016, 51, 724 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2512935[12] Park S Y, Cho J, Na K, et al. Modular 128-channel Δ-Δσ analog front-end architecture using spectrum equalization scheme for 1024-channel 3-D neural recording microsystems. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2018, 53, 501 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2017.2764053[13] Karimi-Bidhendi A, Malekzadeh-Arasteh O, Lee M C, et al. CMOS ultralow power brain signal acquisition front-ends: Design and human testing. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2017, 11, 1111 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2017.2723607[14] Wang H, Mercier P P. A current-mode capacitively-coupled chopper instrumentation amplifier for biopotential recording with resistive or capacitive electrodes. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs, 2018, 65, 699 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2017.2780171[15] Wu C Y, Cheng C H, Chen Z X. A 16-channel CMOS chopper-stabilized analog front-end ECoG acquisition circuit for a closed-loop epileptic seizure control system. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2018, 12, 543 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2018.2808415[16] Tohidi M, Madsen J K, Heck M J R, et al. A low-power analog front-end neural acquisition design for seizure detection. 2016 IFIP/IEEE International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI-SoC), 2016, 1 doi: 10.1109/VLSI-SoC.2016.7753541[17] Zheng J W, Ki W H, Hu L Y, et al. Chopper capacitively coupled instrumentation amplifier capable of handling large electrode offset for biopotential recordings. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Express Briefs, 2017, 64, 1392 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2017.2741348[18] Zheng J W, Ki W H, Tsui C Y. A fully integrated analog front end for biopotential signal sensing. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap, 2018, 65, 3800 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2018.2854741[19] Tallgren P, Vanhatalo S, Kaila K, et al. Evaluation of commercially available electrodes and gels for recording of slow EEG potentials. Clin Neurophysiol, 2005, 116, 799 doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2004.10.001[20] Griss P, Enoksson P, Tolvanen-Laakso H K, et al. Micromachined electrodes for biopotential measurements. J Microelectromechanical Syst, 2001, 10, 10 doi: 10.1109/84.911086[21] Huang Y J, Wu C Y, Wong A M K, et al. Novel active comb-shaped dry electrode for EEG measurement in hairy site. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2015, 62, 256 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2014.2347318[22] Liao L D, Wang I J, Chen S F, et al. Design, fabrication and experimental validation of a novel dry-contact sensor for measuring electroencephalography signals without skin preparation. Sensors, 2011, 11, 5819 doi: 10.3390/s110605819[23] Harland C J, Clark T D, Prance R J. Remote detection of human electroencephalograms using ultrahigh input impedance electric potential sensors. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81, 3284 doi: 10.1063/1.1516861[24] Sullivan T J, Deiss S R, Cauwenberghs G. A low-noise, non-contact EEG/ECG sensor. 2007 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, 2008, 154 doi: 10.1109/BIOCAS.2007.4463332[25] Renshaw B, Forbes A, Morison B R. Activity of isocortex and hippocampus: Electrical studies with micro-electrodes. J Neurophysiol, 1940, 3, 74 doi: 10.1152/jn.1940.3.1.74[26] McNaughton B L, O'Keefe J, Barnes C A. The stereotrode: A new technique for simultaneous isolation of several single units in the central nervous system from multiple unit records. J Neurosci Methods, 1983, 8, 391 doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(83)90097-3[27] Moxon K A, Leiser S C, Gerhardt G A, et al. Ceramic-based multisite electrode arrays for chronic single-neuron recording. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2004, 51, 647 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2003.821037[28] Adrega T, Lacour S P. Stretchable gold conductors embedded in PDMS and patterned by photolithography: Fabrication and electromechanical characterization. J Micromech Microeng, 2010, 20, 055025 doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/20/5/055025[29] Webster J G, Clark J W. Medical instrumentation: application and design. John Wiley & Sons, 2010[30] Huhta J C, Webster J G. 60-HZ interference in electrocardiography. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 1973, 20, 91[31] Winokur E S, Delano M K, Sodini C G. A wearable cardiac monitor for long-term data acquisition and analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2013, 60, 189 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2217958[32] Spinelli E M, Mayosky M A. Two-electrode biopotential measurements: Power line interference analysis. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2005, 52, 1436 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2005.851488[33] Serrano R E, Gasulla M, Casas O, et al. Power line interference in ambulatory biopotential measurements. Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37439), Cancun, 2003, 3024 doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2003.1280777[34] Higashi Y, Yokota Y, Naruse Y. Signal correlation between wet and original dry electrodes in electroencephalogram according to the contact impedance of dry electrodes. 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2017, 1062 doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2017.8037010[35] Guermandi M, Scarselli E F, Guerrieri R. A driving right leg circuit (DgRL) for improved common mode rejection in bio-potential acquisition systems. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2016, 10, 507 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2015.2446753[36] Costa J A, Pimenta T C. CMOS analog front-end IC for EEG applications with high powerline interference rejection. 2018 IEEE 9th Latin American Symposium on Circuits & Systems (LASCAS), 2018, 1 doi: 10.1109/LASCAS.2018.8399946[37] Kaur R, Malhotra R, Deb S. MAC based FIR filter: A novel approach for low-power real-time de-noising of ECG signals. 2015 19th International Symposium on VLSI Design and Test, 2015, 1 doi: 10.1109/ISVDAT.2015.7208065[38] Liu Y, An F L, Lang X, et al. Remove motion artifacts from scalp single channel EEG based on noise assisted least square multivariate empirical mode decomposition. 2020 13th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), 2020, 568 doi: 10.1109/CISP-BMEI51763.2020.9263581[39] Bakker A, Huijsing J. High-accuracy CMOS smart temperature sensors. Springer, 2000[40] Jain A, Kandpal K. Design of a high gain, temperature compensated biomedical instrumentation amplifier for EEG applications. 2017 11th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Control (ISCO), Coimbatore, India, 2017, 292 doi: 10.1109/ISCO.2017.7856001[41] Huang G C, Yin T, Wu Q S, et al. A 1.3 μW 0.7 μRMS chopper current-reuse instrumentation amplifier for EEG applications. 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2015, 2624 doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2015.7169224[42] Dong Y T, Tang L H, Yang X L, et al. A 1.8 μW 32 nV/√Hz current-reuse capacitively-coupled instrumentation amplifier for EEG detection. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2017, 1 doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2017.8050494[43] Lee C J, Song J I. A chopper stabilized current-feedback instrumentation amplifier for EEG acquisition applications. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 11565 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2892502[44] Hoseini Z, Nazari M, Lee K S, et al. Current feedback instrumentation amplifier with built-In differential electrode offset cancellation loop for ECG/EEG sensing frontend. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2021, 70, 1 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3031205[45] Zhou Y Z, Zhao M L, Dong Y T, et al. A low-power low-noise biomedical instrumentation amplifier using novel ripple-reduction technique. 2018 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), 2018, 1 doi: 10.1109/BIOCAS.2018.8584744[46] Chebli R, Sawan M. Chopped logarithmic programmable gain amplifier intended to EEG acquisition interface. 2013 25th International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), 2014, 1 doi: 10.1109/ICM.2013.6734989[47] Babušiak B, Borik Š. Bio-Amplifier with programmable gain and adjustable leads. 2013 36th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), 2013, 616 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.6614009[48] AbuShawish I Y, Mahmoud S A. Digitally programmable gain and tunable band-width DPOTA based bio-medical amplifier. 2021 18th International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), 2021, 147 doi: 10.1109/ISOCC53507.2021.9613859[49] Marchon N, Naik G. A novel linear phase FIR high pass filter for biomedical signals. 2018 IEEE Distributed Computing, VLSI, Electrical Circuits and Robotics (DISCOVER), 2019, 147 doi: 10.1109/DISCOVER.2018.8674120[50] Winkler I, Debener S, Müller K R, et al. On the influence of high-pass filtering on ICA-based artifact reduction in EEG-ERP. 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2015, 4101 doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2015.7319296[51] Abdallah A, Diab M, Mahmoud S. A micropower EEG detection system applicable for paralyzed hand artifical control. 2017 40th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), 2017, 411 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.8076017[52] Wang K N, Chang C H, Onabajo M. A fully-differential CMOS low-pass Notch filter for biosignal measurement devices with high interference rejection. 2014 IEEE 57th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), 2014, 1041 doi: 10.1109/MWSCAS.2014.6908596[53] Kumar Sahu A, Kumar Sahu A. A review on different filter design techniques and topologies for bio-potential signal acquisition systems. 2018 3rd International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), 2019, 934 doi: 10.1109/CESYS.2018.8723912[54] Soni G K, Singh H, Arora H, et al. Ultra low power CMOS low pass filter for biomedical ECG/EEG application. 2020 Fourth International Conference on Inventive Systems and Control (ICISC), 2020, 558 doi: 10.1109/ICISC47916.2020.9171138[55] Yang X L, Zhou Y, Zhao M L, et al. A 12b 238kS/s SAR ADC with novel built-in digital calibration method for EEG acquisition applications. 2015 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), 2015, 1 doi: 10.1109/BioCAS.2015.7348308[56] Yang X L, Zhao M L, Dong Y T, et al. A 14.9μW analog front-end with capacitively-coupled instrumentation amplifier and 14-bit SAR ADC for epilepsy diagnosis system. 2016 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), 2017, 268 doi: 10.1109/BioCAS.2016.7833783[57] França H, Ataei M, Boegli A, et al. A 100nW 10-bit 400S/s SAR ADC for ultra low-power bio-sensing applications. 2017 6th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision & 2017 7th International Symposium in Computational Medical and Health Technology (ICIEV-ISCMHT), Himeji, Japan, 2017, 1 doi: 10.1109/ICIEV.2017.8338602[58] Lai W C. SAR ADC with optical frontend for biosensor applications. 2020 IEEE Electrical Design of Advanced Packaging and Systems (EDAPS), 2021, 1 doi: 10.1109/EDAPS50281.2020.9312885[59] Arif R, Wijaya S K, Prawito, et al. Design of EEG data acquisition system based on Raspberry Pi 3 for acute ischemic stroke identification. 2018 International Conference on Signals and Systems (ICSigSys), 2018, 271 doi: 10.1109/ICSIGSYS.2018.8372771[60] Martins R, Selberherr S, Vaz FA. A CMOS IC for portable EEG acquisition systems. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 1998, 47, 1191 doi: 10.1109/19.746581[61] Qian C L, Parramon J, Sanchez-Sinencio E. A micropower low-noise neural recording front-end circuit for epileptic seizure detection. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46, 1392 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2126370[62] Robinet S, Audebert P, Regis G, et al. A low-power 0.7 μVrms 32-channel mixed-signal circuit for ECoG recordings. IEEE J Emerg Sel Topics Circuits Syst, 2011, 1, 451 doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2011.2180835[63] Zhou H Y, Voelker M, Hauer J. A mixed-signal front-end ASIC for EEG acquisition system. 2012 19th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits, and Systems (ICECS 2012), 2013, 649 doi: 10.1109/ICECS.2012.6463642[64] Yoo J, Yan L, El-Damak D, et al. An 8-channel scalable EEG acquisition SoC with patient-specific seizure classification and recording processor. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2013, 48, 214 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2221220[65] Muller R, Le H P, Li W, et al. A minimally invasive 64-channel wireless μECoG implant. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50, 344 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2364824[66] Smith W A, Mogen B J, Fetz E E, et al. Exploiting electrocorticographic spectral characteristics for optimized signal chain design: A 1.08 W analog front end with reduced ADC resolution requirements. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2016, 10, 1171 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2016.2518923[67] Tohidi M, Kargaard Madsen J, Moradi F. Low-power high-input-impedance EEG signal acquisition SoC with fully integrated IA and signal-specific ADC for wearable applications. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2019, 13, 1437 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2019.2936534[68] Tang T, Goh W L, Yao L, et al. A TDM-based 16-channel AFE ASIC with enhanced system-level CMRR for wearable EEG recording with dry electrodes. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2020, 14, 516 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2020.2979931[69] Gao D, Liu L X. A two-stage time-division multiplexing AFE with input impedance boosting DDA for EEG signal acquisition. 2021 IEEE 14th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), 2021, 1 doi: 10.1109/ASICON52560.2021.9620328[70] Huang C W, Wang J J, Hung C C, et al. Design of CMOS analog front-end electroencephalography (EEG) amplifier with ±1-V common-mode and ±10-mV differential-mode artifact removal. 2022 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), 2022, 714 doi: 10.1109/BioCAS54905.2022.9948692[71] Goldberger A L, Amaral L A N, Glass L, et al. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet. Circulation, 2000, 101, e215 doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215[72] Burrello A, Cavigelli L, Schindler K, et al. Laelaps: an energy-efficient seizure detection algorithm from long-term human iEEG recordings without false alarms. 2019 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), 2019, 752 doi: 10.23919/DATE.2019.8715186[73] Andrzejak R G, Schindler K, Rummel C. Nonrandomness, nonlinear dependence, and nonstationarity of electroencephalographic recordings from epilepsy patients. Phys Rev E, 2012, 86, 046206 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.86.046206[74] San-Segundo R, Gil-Martín M, D'Haro-Enríquez L F, et al. Classification of epileptic EEG recordings using signal transforms and convolutional neural networks. Comput Biol Med, 2019, 109, 148 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.04.031[75] Freiburg seizure prediction project. Freiburg, Germany. http://epilepsy.uni-freiburg.de/freiburg-seizure-prediction-project/eeg-database (2003).[76] Jaiswal A K, Banka H. Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signal with GModPCA and support vectormachine. Bio Med Mater Eng, 2017, 28, 141 doi: 10.3233/BME-171663[77] Jaiswal A K, Banka H. Epileptic seizure detection in EEG signal using machine learning techniques. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med, 2018, 41, 81 doi: 10.1007/s13246-017-0610-y[78] Acharya U, Oh S L, Hagiwara Y, et al. Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput Biol Med, 2018, 100, 270 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.09.017[79] Sharmila A, Geethanjali P. Effect of filtering with time domain features for the detection of epileptic seizure from EEG signals. J Med Eng Technol, 2018, 42, 217 doi: 10.1080/03091902.2018.1464075[80] Saini J, Dutta M. Epilepsy classification using optimized artificial neural network. Neurol Res, 2018, 40, 982 doi: 10.1080/01616412.2018.1508544[81] Al-Hadeethi H, Abdulla S, Diykh M, et al. Adaptive boost LS-SVM classification approach for time-series signal classification in epileptic seizure diagnosis applications. Expert Syst Appl, 2020, 161, 113676 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113676[82] Eltrass A, Tayel M, EL-qady A F. Automatic epileptic seizure detection approach based on multi-stage Quantized Kernel Least Mean Square filters. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2021, 70, 103031 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103031[83] Zeng M, Zhang X N, Zhao C Y, et al. GRP-DNet: A gray recurrence plot-based densely connected convolutional network for classification of epileptiform EEG. J Neurosci Methods, 2021, 347, 108953 doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108953[84] Hu X M, Yuan S S, Xu F Z, et al. Scalp EEG classification using deep Bi-LSTM network for seizure detection. Comput Biol Med, 2020, 124, 103919 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103919[85] Quintero-Rincón A, D'Giano C, Batatia H. A quadratic linear-parabolic model-based EEG classification to detect epileptic seizures. J Biomed Res, 2020, 34, 205 doi: 10.7555/JBR.33.20190012[86] Gao Z, Lu G L, Yan P, et al. Automatic change detection for real-time monitoring of EEG signals. Front Physiol, 2018, 9, 325 doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00325[87] Li Y, Wang X D, Luo M L, et al. Epileptic seizure classification of EEGs using time–frequency analysis based multiscale radial basis functions. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2018, 22, 386 doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2017.2654479[88] Choubey H, Pandey A. A new feature extraction and classification mechanisms For EEG signal processing. Multidimens Syst Signal Process, 2019, 30, 1793 doi: 10.1007/s11045-018-0628-7[89] Gupta V, Pachori R B. Epileptic seizure identification using entropy of FBSE based EEG rhythms. Biomed Signal Proces, 2019, 53, 101569. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101569[90] de la O Serna J A, Paternina M R A, Zamora-Méndez A, et al. EEG-rhythm specific Taylor–Fourier filter bank implemented with O-splines for the detection of epilepsy using EEG signals. IEEE Sens J, 2020, 20, 6542 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2976519[91] Mathur P, Chakka V K, Shah S B. Ramanujan periodic subspace based epileptic EEG signals classification. IEEE Sens Lett, 2021, 5(7), 1 doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2021.3086755[92] Na J Y, Wang Z P, Lv S Q, et al. An extended K nearest neighbors-based classifier for epilepsy diagnosis. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 73910 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3081767[93] Pal H, Kumar A. Stability analysis of multiscale bubble entropy and power metric based seizure detection technique with MLA. IETE J Res, 2023, 69, 3455 doi: 10.1080/03772063.2021.1912650[94] Wang Z P, Na J Y, Zheng B Y. An improved kNN classifier for epilepsy diagnosis. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 100022 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2996946[95] Mansouri A, Singh S P, Sayood K. Online EEG seizure detection and localization. Algorithms, 2019, 12, 176 doi: 10.3390/a12090176[96] Birjandtalab J, Baran Pouyan M, Cogan D, et al. Automated seizure detection using limited-channel EEG and non-linear dimension reduction. Comput Biol Med, 2017, 82, 49 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.01.011[97] Zhang J, Wei Z C, Zou J Z, et al. Automatic epileptic EEG classification based on differential entropy and attention model. Eng Appl Artif Intell, 2020, 96, 103975 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103975[98] Iešmantas T, Alzbutas R. Convolutional neural network for detection and classification of seizures in clinical data. Med Biol Eng Comput, 2020, 58, 1919 doi: 10.1007/s11517-020-02208-7[99] Sharmila A, Mahalakshmi P. Wavelet-based feature extraction for classification of epileptic seizure EEG signal. J Med Eng Technol, 2017, 41, 670 doi: 10.1080/03091902.2017.1394388[100] Liu Q, Zhao X G, Hou Z G, et al. Epileptic seizure detection based on the kernel extreme learning machine. Technol Health Care, 2017, 25, 399 doi: 10.3233/THC-171343[101] Sharma R R, Varshney P, Pachori R B, et al. Automated system for epileptic EEG detection using iterative filtering. IEEE Sens Lett, 2018, 2(4), 1 doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2018.2882622[102] Tsipouras M G. Spectral information of EEG signals with respect to epilepsy classification. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process, 2019, 2019, 1 doi: 10.1186/s13634-018-0596-y[103] Mahjoub C, Le Bouquin Jeannès R, Lajnef T, et al. Epileptic seizure detection on EEG signals using machine learning techniques and advanced preprocessing methods. Biomedical Engineering / Biomedizinische Technik, 2019, 65, 1[104] Chiang H S, Chen M Y, Huang Y J. Wavelet-based EEG processing for epilepsy detection using fuzzy entropy and associative petri net. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 103255 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2929266[105] Chen S N, Zhang X, Chen L L, et al. Automatic diagnosis of epileptic seizure in electroencephalography signals using nonlinear dynamics features. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 61046 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2915610[106] Aliyu I, Lim C G. Selection of optimal wavelet features for epileptic EEG signal classification with LSTM. Neural Comput & Applic, 2023, 35, 1077 doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05666-0[107] Anuragi A, Singh Sisodia D, Pachori R B. Epileptic-seizure classification using phase-space representation of FBSE-EWT based EEG sub-band signals and ensemble learners. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2022, 71, 103138 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103138[108] Ashokkumar S R, Anupallavi S, Premkumar M, et al. Implementation of deep neural networks for classifying electroencephalogram signal using fractional S-transform for epileptic seizure detection. Int J Imaging Syst Tech, 2021, 31, 895 doi: 10.1002/ima.22565[109] Ashokkumar S R, MohanBabu G, Anupallavi S. A novel two-band equilateral wavelet filter bank method for an automated detection of seizure from EEG signals. Int J Imaging Syst Tech, 2020, 30, 978 doi: 10.1002/ima.22441[110] Nasiri S, Clifford G D. Generalizable seizure detection model using generating transferable adversarial features. IEEE Signal Process Lett, 2021, 28, 568 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3060967[111] Zeng K, Ouyang G X, Chen H, et al. Characterizing dynamics of absence seizure EEG with spatial-temporal permutation entropy. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275, 577 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.09.007[112] Zhan Q Y, Hu W. An epilepsy detection method using multiview clustering algorithm and deep features. Comput Math Methods Med, 2020, 2020, 1 doi: 10.1155/2020/5128729[113] Mu J W, Dai L Y, Liu J X, et al. Automatic detection for epileptic seizure using graph-regularized nonnegative matrix factorization and Bayesian linear discriminate analysis. Biocybern Biomed Eng, 2021, 41, 1258 doi: 10.1016/j.bbe.2021.08.009[114] Mohammadpoory Z, Nasrolahzadeh M, Haddadnia J. Epileptic seizure detection in EEGs signals based on the weighted visibility graph entropy. Seizure, 2017, 50, 202 doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2017.07.001[115] Li P, Karmakar C, Yearwood J, et al. Detection of epileptic seizure based on entropy analysis of short-term EEG. PLoS One, 2018, 13, e0193691 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193691[116] Lahmiri S, Shmuel A. Accurate classification of seizure and seizure-free intervals of intracranial EEG signals from epileptic patients. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas, 2019, 68, 791 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2855518[117] Attia A, Moussaoui A, Chahir Y. Epileptic seizures identification with autoregressive model and firefly optimization based classification. Evol Syst, 2021, 12, 827 doi: 10.1007/s12530-019-09319-z[118] Brari Z, Belghith S. A novel machine learning model for the detection of epilepsy and epileptic seizures using electroencephalographic signals based on chaos and fractal theories. Math Probl Eng, 2021, 2021, 1 doi: 10.1155/2021/2107113[119] Gao X Z, Yan X Y, Gao P, et al. Automatic detection of epileptic seizure based on approximate entropy, recurrence quantification analysis and convolutional neural networks. Artificial intelligence in medicine, 2019, 102, 101711 doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2019.101711[120] Goshvarpour A, Goshvarpour A. Diagnosis of epileptic EEG using a lagged Poincare plot in combination with the autocorrelation. Signal Image and Video Processing, 2020, 14, 1309 doi: 10.1007/s11760-020-01672-w[121] Priyasad D, Fernando T, Denman S, et al. Interpretable seizure classification using unprocessed EEG with multi-channel attentive feature fusion. IEEE Sens J, 2021, 21, 19186 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3090062[122] Mahmoodian N, Boese A, Friebe M, et al. Epileptic seizure detection using cross-bispectrum of electroencephalogram signal. Seizure, 2019, 66, 4 doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2019.02.001[123] Lu X, Zhang J, Huang S, et al. Detection and classification of epileptic EEG signals by the methods of nonlinear dynamics. Chaos Solitons & Fractals, 2021, 151, 111032 doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2021.111032[124] Solaija M S J, Saleem S, Khurshid K, et al. Dynamic mode decomposition based epileptic seizure detection from scalp EEG. IEEE Access, 2018, 6, 38683 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853125[125] Faust O, Acharya U R, Adeli H, et al. Wavelet-based EEG processing for computer-aided seizure detection and epilepsy diagnosis. Seizure, 2015, 26, 56 doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2015.01.012[126] Zhang Y L, Zhou W D, Yuan S S, et al. Seizure detection method based on fractal dimension and gradient boosting. Epilepsy Behav, 2015, 43, 30 doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2014.11.025[127] Alexandros T, Markos G, Dimitrios G, et al. Automated epileptic seizure detection methods: A review study. Epilepsy–Histological, Electroencephalographic and Psychological Aspects, 2012, 2027 doi: 10.5772/31597[128] Salam M T, Sawan M, Nguyen D K. Epileptic seizure onset detection prior to clinical manifestation. 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, 2010, 6210 doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5627732[129] Gotman J, Wang L Y. State-dependent spike detection: Concepts and preliminary results. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol, 1991, 79, 11 doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(91)90151-S[130] Zhang T, Chen W Z, Li M Y. Automatic seizure detection of electroencephalogram signals based on frequency slice wavelet transform and SVM. Acta Phys Sin, 2016, 65, 038703 doi: 10.7498/aps.65.038703[131] Shoeb A H. Application of machine learning to epileptic seizure onset detection and treatment. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2009[132] Tiwari A K, Pachori R B, Kanhangad V, et al. Automated diagnosis of epilepsy using key-point-based local binary pattern of EEG signals. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2017, 21, 888 doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2016.2589971[133] Vicnesh J, Hagiwara Y. Accurate detection of seizure using nonlinear parameters extracted from eeg signals. J Mech Med Biol, 2019, 19, 1940004 doi: 10.1142/S0219519419400049[134] Wang Y F, Li Z C, Feng L C, et al. Automatic detection of epilepsy and seizure using multiclass sparse extreme learning machine classification. Comput Math Methods Med, 2017, 2017, 1 doi: 10.1155/2017/6849360[135] Sharma M, Pachori R B, Rajendra Acharya U. A new approach to characterize epileptic seizures using analytic time-frequency flexible wavelet transform and fractal dimension. Pattern Recognit Lett, 2017, 94, 172 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2017.03.023[136] Chen D, Wan S R, Xiang J, et al. A high-performance seizure detection algorithm based on Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and EEG. PLoS One, 2017, 12, e0173138 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173138[137] Selvakumari R S, Mahalakshmi M, Prashalee P. Patient-specific seizure detection method using hybrid classifier with optimized electrodes. J Med Syst, 2019, 43, 121 doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1234-4[138] Parvez M Z, Paul M. Epileptic seizure detection by analyzing EEG signals using different transformation techniques. Neurocomputing, 2014, 145, 190 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2014.05.044[139] Guo L, Rivero D, Dorado J, et al. Automatic epileptic seizure detection in EEGs based on line length feature and artificial neural networks. J Neurosci Methods, 2010, 191, 101 doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.05.020[140] Yuan Q, Zhou W D, Zhang L R, et al. Epileptic seizure detection based on imbalanced classification and wavelet packet transform. Seizure, 2017, 50, 99 doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2017.05.018[141] Raghu S, Sriraam N. Classification of focal and non-focal EEG signals using neighborhood component analysis and machine learning algorithms. Expert Syst Appl, 2018, 113, 18 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.06.031[142] Fasil O K, Rajesh R. Time-domain exponential energy for epileptic EEG signal classification. Neurosci Lett, 2019, 694, 1 doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.10.062[143] Alickovic E, Kevric J, Subasi A. Performance evaluation of empirical mode decomposition, discrete wavelet transform, and wavelet packed decomposition for automated epileptic seizure detection and prediction. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2018, 39, 94 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2017.07.022[144] Tzimourta K D, Tzallas A T, Giannakeas N, et al. A robust methodology for classification of epileptic seizures in EEG signals. Health Technol, 2019, 9, 135 doi: 10.1007/s12553-018-0265-z[145] Birjandtalab J, Jarmale V N, Nourani M, et al. Imbalance learning using neural networks for seizure detection. 2018 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), 2018, 1 doi: 10.1109/BIOCAS.2018.8584683[146] Wang X S, Gong G H, Li N, et al. Detection analysis of epileptic EEG using a novel random forest model combined with grid search optimization. Front Hum Neurosci, 2019, 13, 52 doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00052[147] Yan A Y, Zhou W D, Yuan Q, et al. Automatic seizure detection using Stockwell transform and boosting algorithm for long-term EEG. Epilepsy Behav, 2015, 45, 8 doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2015.02.012[148] Mursalin M, Islam S S, Noman M K, et al. Epileptic seizure classification using statistical sampling and a novel feature selection algorithm. 2019: arXiv: 1902.09962.[149] Siddiqui M K, Islam M Z, Kabir M A. Analyzing performance of classification techniques in detecting epileptic seizure. International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications. ADMA 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, Cham, 2017, 10604, 386 doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-69179-4_27[150] Mursalin M, Zhang Y, Chen Y H, et al. Automated epileptic seizure detection using improved correlation-based feature selection with random forest classifier. Neurocomputing, 2017, 241, 204 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.053[151] Rajaguru H, Prabhakar S K. Multilayer autoencoders and EM-PCA with genetic algorithm for epilepsy classification from EEG. 2018 Second International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), 2018, 353 doi: 10.1109/ICECA.2018.8474658[152] Ji S W, Xu W, Yang M, et al. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2013, 35, 221 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.59[153] Jana G C, Sharma R, Agrawal A. A 1D-CNN-spectrogram based approach for seizure detection from EEG signal. Procedia Comput Sci, 2020, 167, 403 doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.248[154] Avcu M T, Zhang Z, Shih Chan D W. Seizure detection using least eeg channels by deep convolutional neural network. ICASSP 2019 - 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2019, 1120 doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8683229[155] Bizopoulos P, Lambrou G I, Koutsouris D. Signal2Image modules in deep neural networks for EEG classification. 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2019, 702 doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2019.8856620[156] Thara D K, PremaSudha B G, Xiong F. Epileptic seizure detection and prediction using stacked bidirectional long short term memory. Pattern Recognit Lett, 2019, 128, 529 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.10.034[157] Roy S, Kiral-Kornek I, Harrer S. ChronoNet: A deep recurrent neural network for abnormal EEG identification. Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Medicine in Europe. Springer, 2019, 47[158] Tsiouris K M, Pezoulas V C, Zervakis M, et al. A Long Short-Term Memory deep learning network for the prediction of epileptic seizures using EEG signals. Comput Biol Med, 2018, 99, 24 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.05.019[159] Akut R. Wavelet based deep learning approach for epilepsy detection. Health Inf Sci Syst, 2019, 7, 1 doi: 10.1007/s13755-018-0062-0[160] Gabr R H, Shahin A I, Sharawi A A, et al. A deep learning identification system for different epileptic seizure disease stages. J Eng Appl Sci, 2020, 67, 925[161] Zhang B C, Wang W N, Xiao Y T, et al. Cross-subject seizure detection in EEGs using deep transfer learning. Comput Math Methods Med, 2020, 2020, 1 doi: 10.1155/2020/7902072[162] Akbarian B, Erfanian A. A framework for seizure detection using effective connectivity, graph theory, and multi-level modular network. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2020, 59, 101878 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101878[163] Hadiyoso S, Wijayanto I, Humairani A. Signal dynamics analysis for epileptic seizure classification on EEG signals. Traitement Du Signal, 2021, 38, 73 doi: 10.18280/ts.380107[164] Zhao Y N, Dong C X, Zhang G B, et al. EEG-Based Seizure detection using linear graph convolution network with focal loss. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2021, 208, 106277 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106277[165] Jang S W, Lee S H. Detection of epileptic seizures using wavelet transform, peak extraction and PSR from EEG signals. Symmetry, 2020, 12, 1239 doi: 10.3390/sym12081239[166] Ma M N, Cheng Y L, Wei X H, et al. Research on epileptic EEG recognition based on improved residual networks of 1-D CNN and indRNN. BMC Med Informat Decis Making, 2021, 21, 1 doi: 10.1186/s12911-020-01362-0[167] Nogay H S, Adeli H. Detection of epileptic seizure using pretrained deep convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Eur Neurol, 2021, 83, 602 doi: 10.1159/000512985[168] Yildiz A, Zan H S, Said S. Classification and analysis of epileptic EEG recordings using convolutional neural network and class activation mapping. Biomed Signal Process Control, 2021, 68, 102720 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102720[169] Sui L F, Zhao X Y, Zhao Q B, et al. Localization of epileptic foci by using convolutional neural network based on iEEG. Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations, Hersonissos, Crete, 2019 doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-19823-7_27[170] Bin Altaf M A, Zhang C, Yoo J. A 16-channel patient-specific seizure onset and termination detection SoC with impedance-adaptive transcranial electrical stimulator. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2015, 50, 2728 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2015.2482498[171] Bin Altaf M A, Yoo J. A 1.83-J/classification, 8-channel, patient-specific epileptic seizure classification SoC using a non-linear support vector machine. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2016, 10, 49 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2014.2386891[172] Lin S K, Istiqomah, Wang L C, et al. An ultra-low power smart headband for real-time epileptic seizure detection. IEEE J Transl Eng Heath Med, 2018, 6, 1 doi: 10.1109/JTEHM.2018.2861882[173] Huang S A, Chang K C, Liou H H, et al. A 1.9-mW SVM processor with on-chip active learning for epileptic seizure control. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2020, 55, 452 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2019.2954775[174] Liu J H, Zhu Z, Zhou Y, et al. 4.5 BioAIP: A reconfigurable biomedical AI processor with adaptive learning for versatile intelligent health monitoring. 2021 IEEE International Solid- State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2021, 62 doi: 10.1109/ISSCC42613.2021.9365996[175] Zhang M L, Zhang L, Tsai C W, et al. A patient-specific closed-loop epilepsy management SoC with one-shot learning and online tuning. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2022, 57, 1049 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2022.3144460[176] Zhu L S, Liu D S, Li X H, et al. An Efficient Hardware Architecture for Epileptic Seizure Detection using EEG Signals based on 1D-CNN. 2021 IEEE 14th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), 2021, 1 doi: 10.1109/ASICON52560.2021.9620467[177] Chua A, Jordan M I, Muller R. SOUL: An energy-efficient unsupervised online learning seizure detection classifier. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2022, 57, 2532 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2022.3172231[178] Li C Q, Lammie C, Dong X N, et al. Seizure detection and prediction by parallel memristive convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst, 2022, 16, 609 doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2022.3185584[179] Goldenholz D M, Kuhn A, Austermuehle A, et al. Long-term monitoring of cardiorespiratory patterns in drug-resistant epilepsy. Epilepsia, 2017, 58, 77 doi: 10.1111/epi.13606 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: