| Citation: |
Ruoshi Peng, Shengrui Xu, Xiaomeng Fan, Hongchang Tao, Huake Su, Yuan Gao, Jincheng Zhang, Yue Hao. Application of nano-patterned InGaN fabricated by self-assembled Ni nano-masks in green InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(4): 042801. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/4/042801
R S Peng, S R Xu, X M Fan, H C Tao, H K Su, Y Gao, J C Zhang, Y Hao. Application of nano-patterned InGaN fabricated by self-assembled Ni nano-masks in green InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(4): 042801. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/4/042801
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
Application of nano-patterned InGaN fabricated by self-assembled Ni nano-masks in green InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/4/042801
More Information-
Abstract
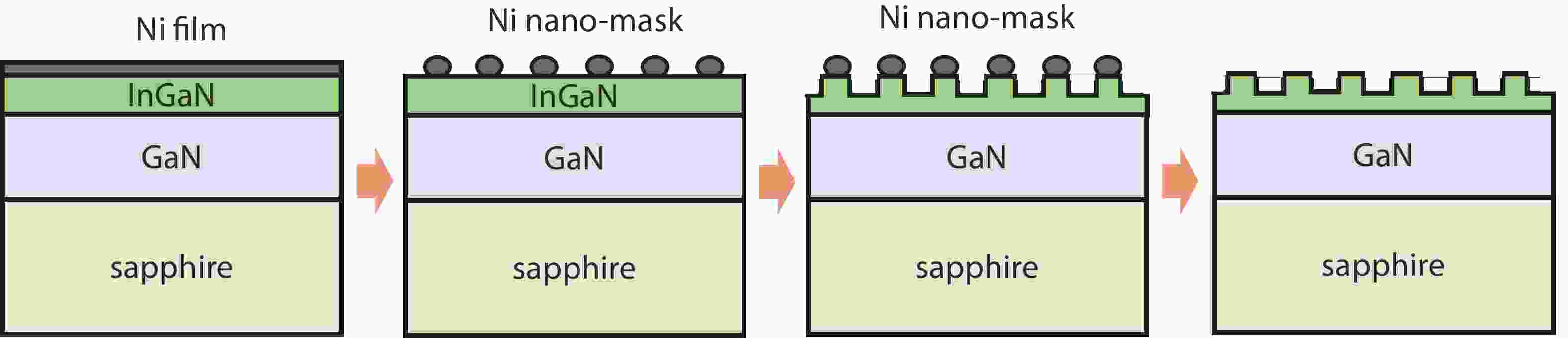
The nano-patterned InGaN film was used in green InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells (MQWs) structure, to relieve the unpleasantly existing mismatch between high indium content InGaN and GaN, as well as to enhance the light output. The different self-assembled nano-masks were formed on InGaN by annealing thin Ni layers of different thicknesses. Whereafter, the InGaN films were etched into nano-patterned films. Compared with the green MQWs structure grown on untreated InGaN film, which on nano-patterned InGaN had better luminous performance. Among them the MQWs performed best when 3 nm thick Ni film was used as mask, because that optimally balanced the effects of nano-patterned InGaN on the crystal quality and the light output.-
Keywords:
- GaN,
- InGaN,
- nano-mask,
- nano-patterned,
- MQWs
-
References
[1] Nakamura S, Mukai T, Senoh M. Candela-class high-brightness InGaN/AlGaN double-heterostructure blue-light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 1994, 64, 1687 doi: 10.1063/1.111832[2] Saito S, Hashimoto R, Hwang J, et al. InGaN light-emitting diodes on c-face sapphire substrates in green gap spectral range. Appl Phys Express, 2013, 6, 111004 doi: 10.7567/APEX.6.111004[3] Langer T, Kruse A, Ketzer F A, et al. Origin of the “green gap”: Increasing nonradiative recombination in indium-rich GaInN/GaN quantum well structures. Phys Status Solidi C, 2011, 8, 2170 doi: 10.1002/pssc.201001051[4] Kong J, Feng M X, Cai J, et al. GaN grown on nano-patterned sapphire substrates. J Semicond, 2015, 36, 043003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/043003[5] Yamaguchi S, Kariya M, Nitta S, et al. Structural properties of InN on GaN grown by metalorganic vapor-phase epitaxy. J Appl Phys, 1999, 85, 7682 doi: 10.1063/1.370571[6] Ho I H, Stringfellow G B. Solid phase immiscibility in GaInN. Appl Phys Lett, 1996, 69, 2701 doi: 10.1063/1.117683[7] Albrecht M, Strunk H P, Weyher J L, et al. Carrier recombination at single dislocations in GaN measured by cathodoluminescence in a transmission electron microscope. J Appl Phys, 2002, 92, 2000 doi: 10.1063/1.1490618[8] Huh C, Lee K S, Kang E J, et al. Improved light-output and electrical performance of InGaN-based light-emitting diode by microroughening of the p-GaN surface. J Appl Phys, 2003, 93, 9383 doi: 10.1063/1.1571962[9] Niu N H, Wang H B, Liu J P, et al. Improved quality of InGaN/GaN multiple quantum wells by a strain relief layer. J Cryst Growth, 2006, 286, 209 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.09.027[10] Wang J X, Wang L, Zhao W, et al. Study on internal quantum efficiency of blue InGaN multiple-quantum-well with an InGaN underneath layer. Sci China Technol Sci, 2010, 53, 306 doi: 10.1007/s11431-010-0062-z[11] Akasaka T, Gotoh H, Kobayashi Y, et al. InGaN quantum wells with small potential fluctuation grown on InGaN underlying layers. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89, 101110 doi: 10.1063/1.2347115[12] Wang J X, Wang L, Zhao W, et al. Understanding efficiency droop effect in InGaN/GaN multiple-quantum-well blue light-emitting diodes with different degree of carrier localization. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97, 201112 doi: 10.1063/1.3520139[13] Lin R M, Lu Y C, Yu S F, et al. Enhanced extraction and efficiency of blue light-emitting diodes prepared using two-step-etched patterned sapphire substrates. J Electrochem Soc, 2009, 156, H874 doi: 10.1149/1.3231502[14] Kim J Y, Kwon M K, Kim J P, et al. Enhanced light extraction from triangular GaN-based light-emitting diodes. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2007, 19, 1865 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2007.907644[15] Du J J, Xu S R, Peng R S, et al. Enhancement of optical characteristic of InGaN/GaN multiple quantum-well structures by self-growing air voids. Sci China Technol Sci, 2021, 64, 1583 doi: 10.1007/s11431-021-1868-7[16] Fujii T, Gao Y, Sharma R, et al. Increase in the extraction efficiency of GaN-based light-emitting diodes via surface roughening. Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 84, 855 doi: 10.1063/1.1645992[17] Wang R J, Liu D, Zuo Z Y, et al. Metal-assisted electroless fabrication of nanoporous p-GaN for increasing the light extraction efficiency of light emitting diodes. AIP Adv, 2012, 2, 012109 doi: 10.1063/1.3679150[18] Tao H C, Xu S R, Mao W, et al. Improved crystal quality of nonpolar a-plane GaN based on the nano pattern formed by the annealed thin Ni layer. Superlattices Microstruct, 2019, 130, 539 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2019.05.020[19] Carey J D, Ong L L, Silva S P. Formation of low-temperature self-organized nanoscale nickel metal Islands. Nanotechnology, 2003, 14, 1223 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/14/11/011[20] Chiu C H, Lo M H, Lu T C, et al. Nano-processing techniques applied in GaN-based light-emitting devices with self-assembly Ni nano-masks. J Lightwave Technol, 2008, 26, 1445 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2008.922157[21] Moram M A, Vickers M E. X-ray diffraction of III-nitrides. Rep Prog Phys, 2009, 72, 036502 doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/72/3/036502[22] Ashby C I H, Mitchell C C, Han J, et al. Low-dislocation-density GaN from a single growth on a textured substrate. Appl Phys Lett, 2000, 77, 3233 doi: 10.1063/1.1325394[23] He C G, Zhao W, Zhang K, et al. High-quality GaN epilayers achieved by facet-controlled epitaxial lateral overgrowth on sputtered AlN/PSS templates. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9, 43386 doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b14801[24] Oh M S, Kwon M K, Park I K, et al. Improvement of green LED by growing p-GaN on In0.25GaN/GaN MQWs at low temperature. J Cryst Growth, 2006, 289, 107 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.10.129[25] Schnitzer I, Yablonovitch E, Caneau C, et al. 30% external quantum efficiency from surface textured, thin-film light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 1993, 63, 2174 doi: 10.1063/1.110575 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:




























