| Citation: |
Wenbin Zuo, Qihang Zhu, Yuyang Fu, Yu Zhang, Tianqing Wan, Yi Li, Ming Xu, Xiangshui Miao. Volatile threshold switching memristor: An emerging enabler in the AIoT era[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(5): 053102. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/5/053102
****
W B Zuo, Q H Zhu, Y Y Fu, Y Zhang, T Q Wan, Y Li, M Xu, X S Miao. Volatile threshold switching memristor: An emerging enabler in the AIoT era[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(5): 053102. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/5/053102
|
Volatile threshold switching memristor: An emerging enabler in the AIoT era
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/5/053102
More Information
-
Abstract
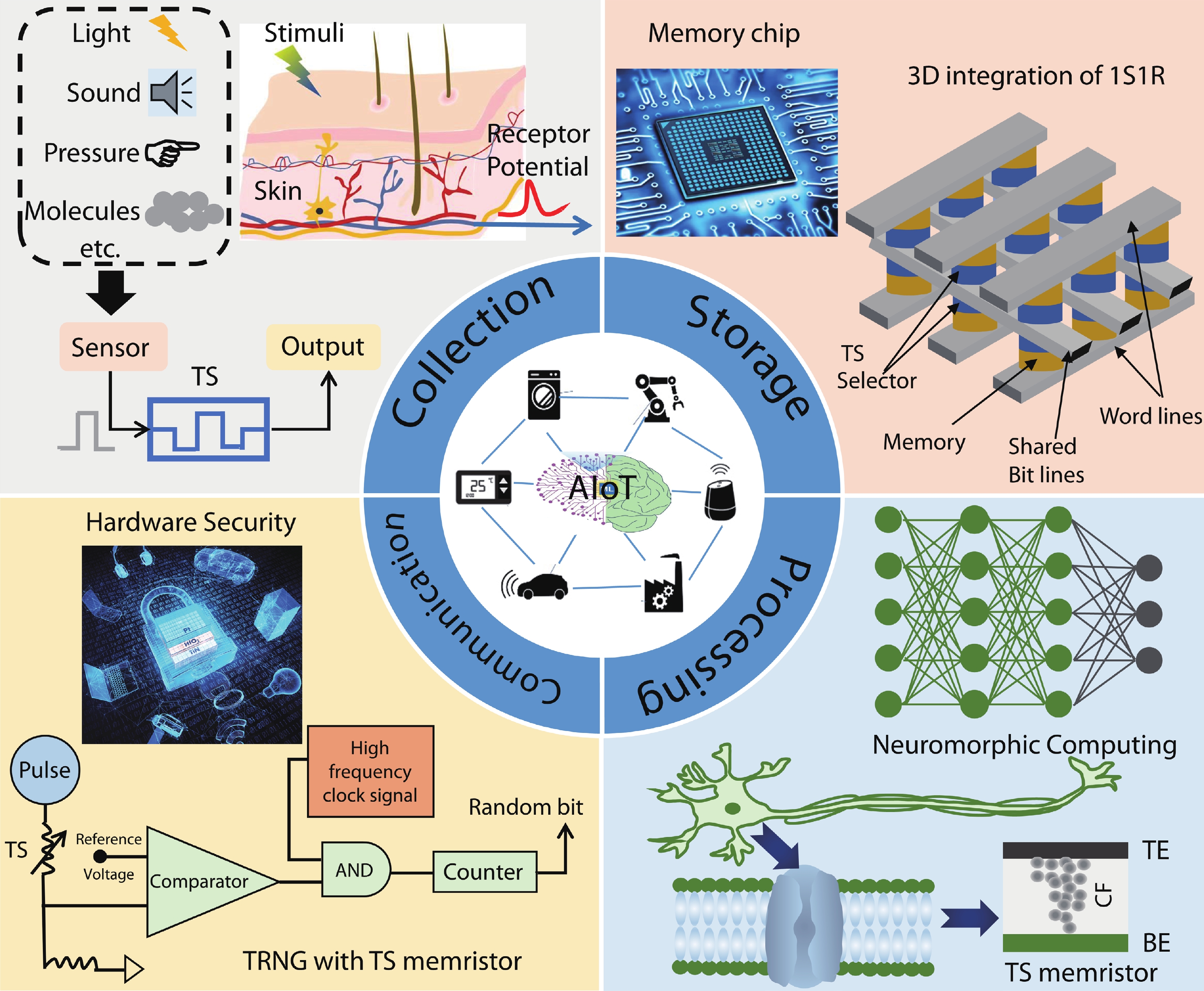
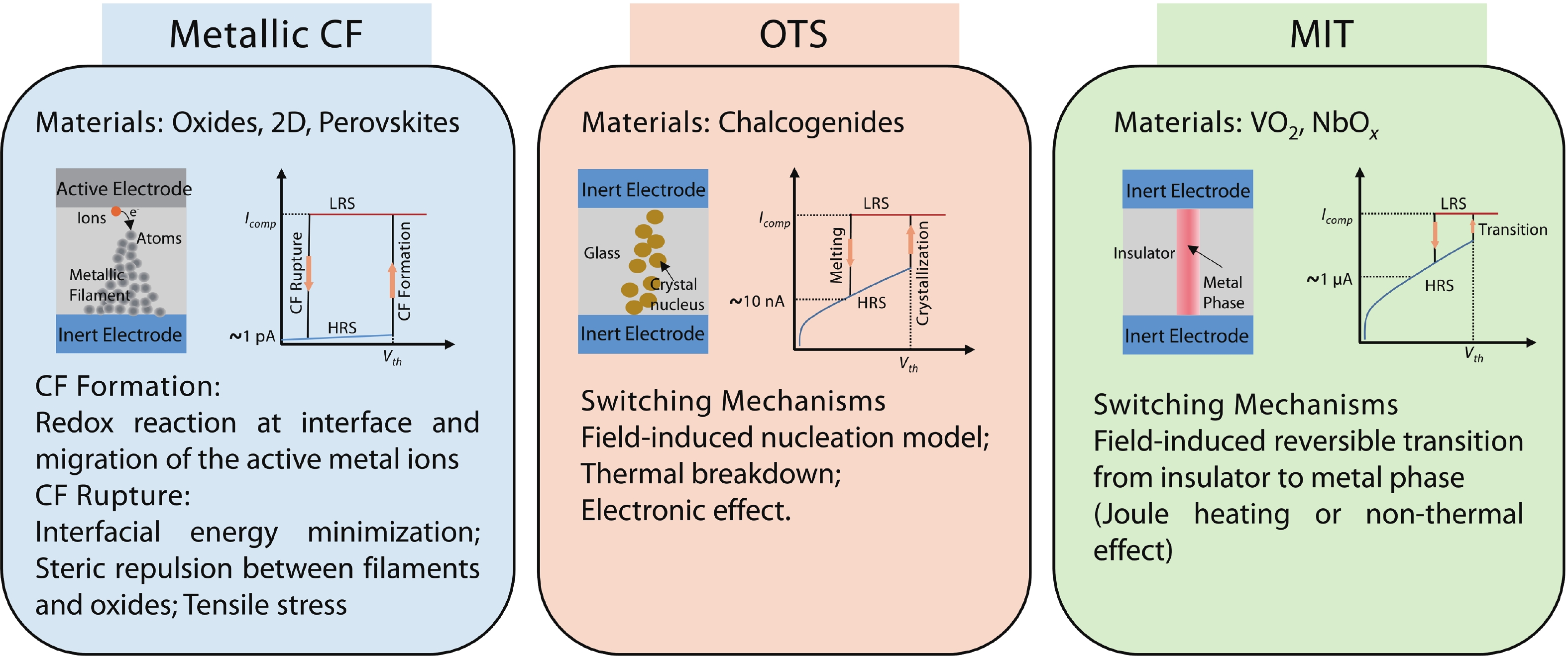
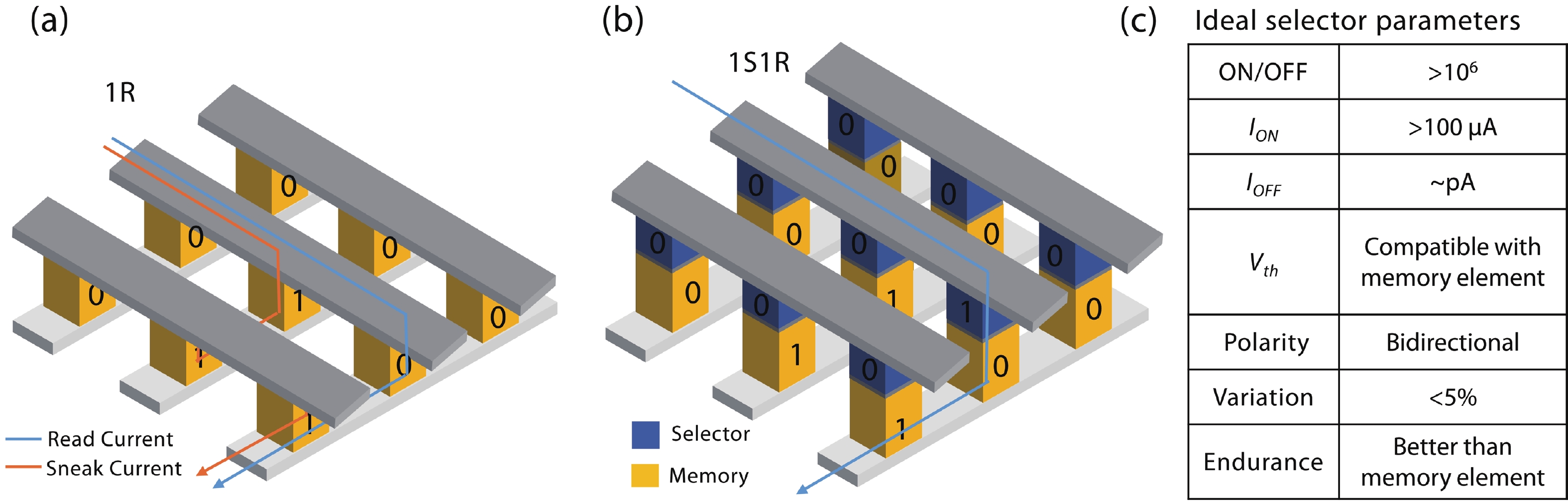
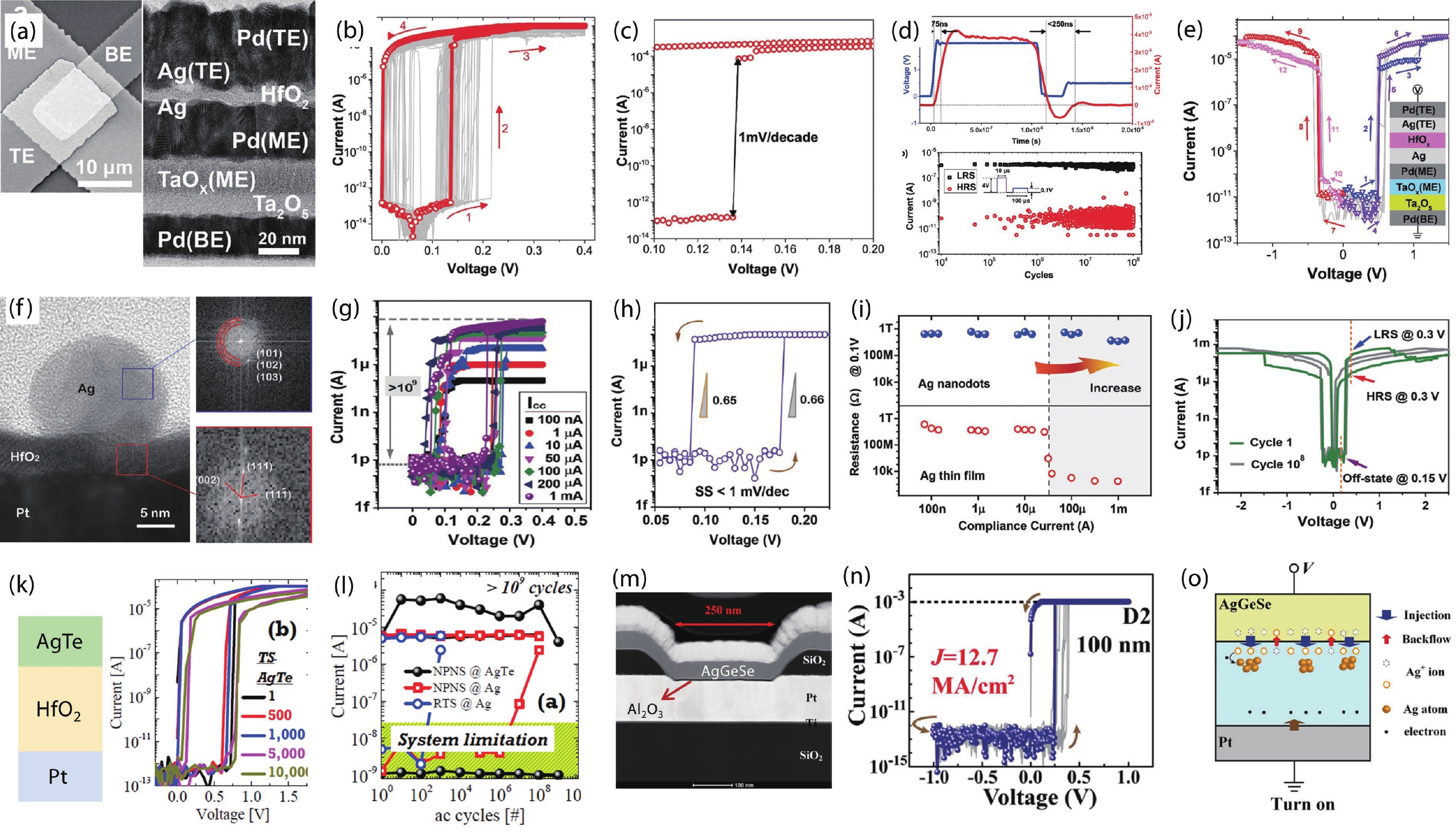
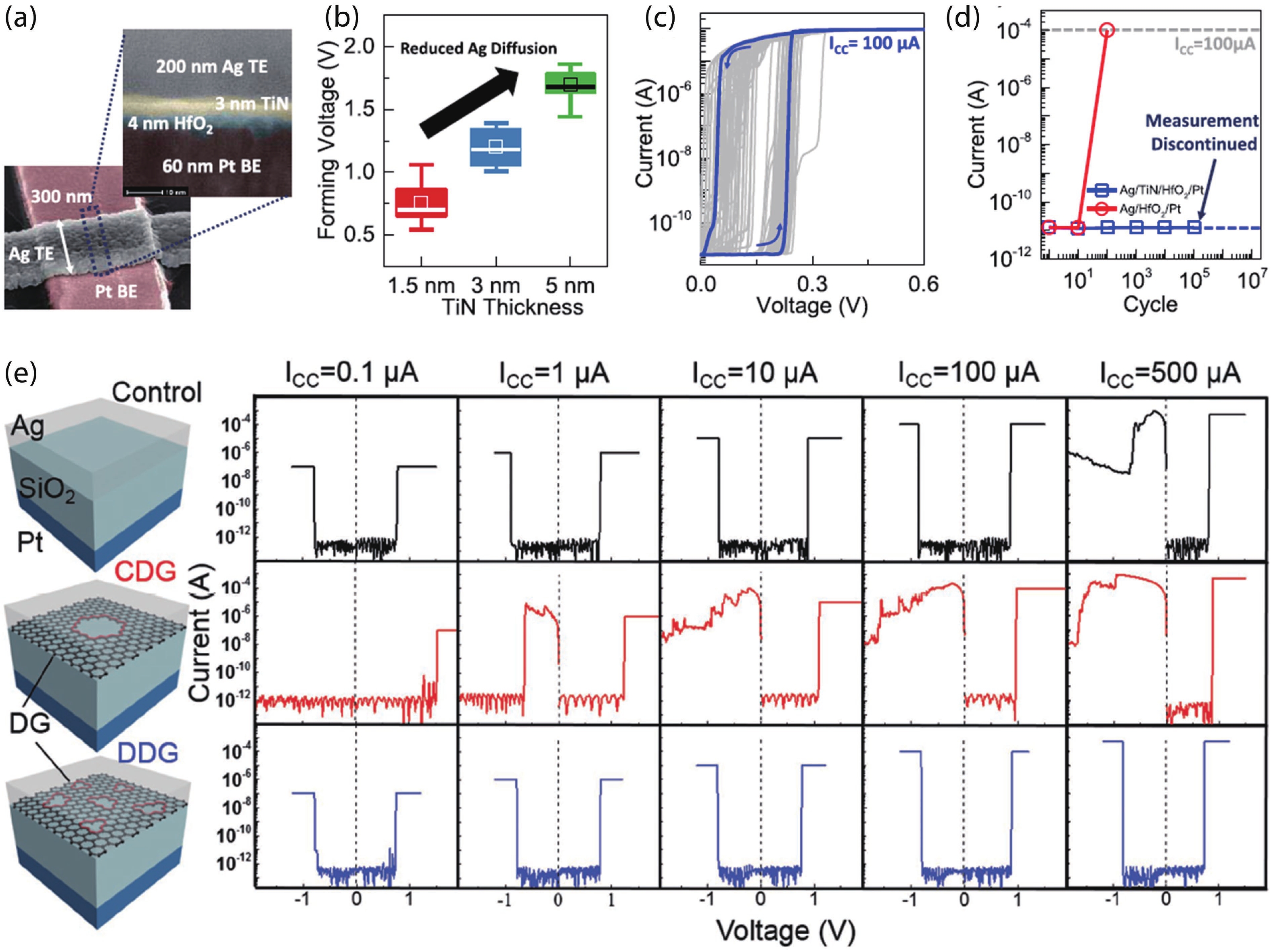
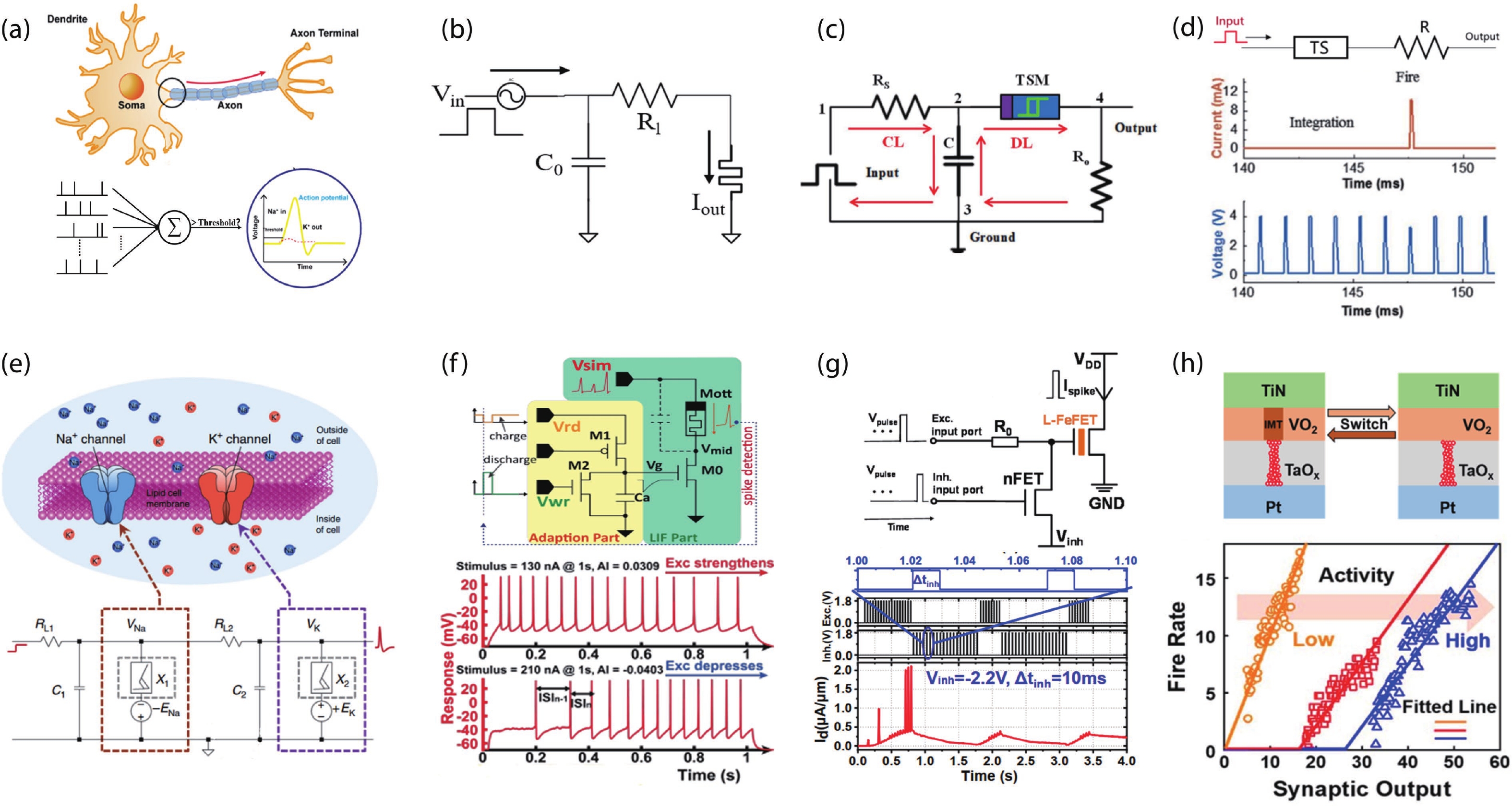
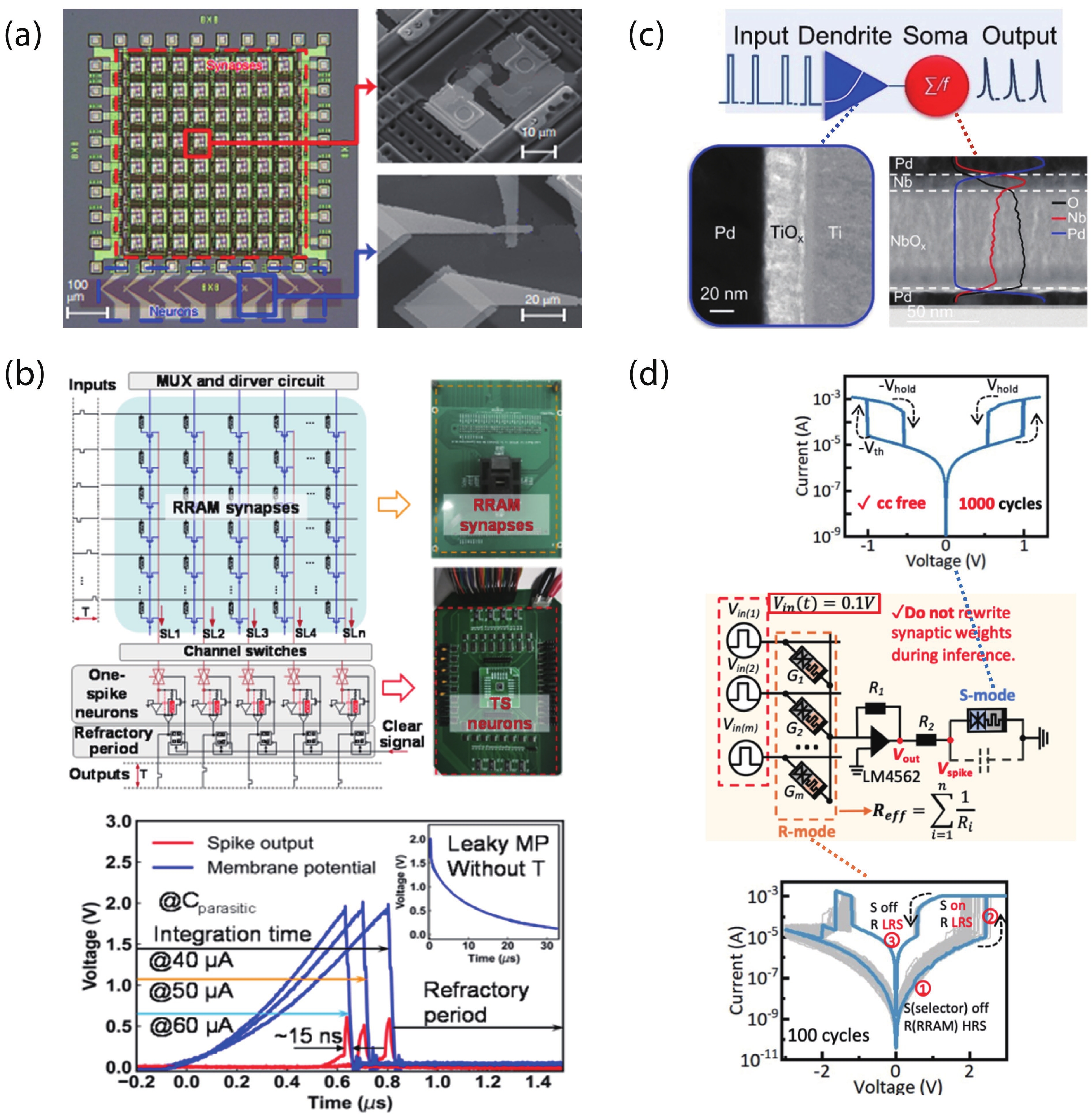
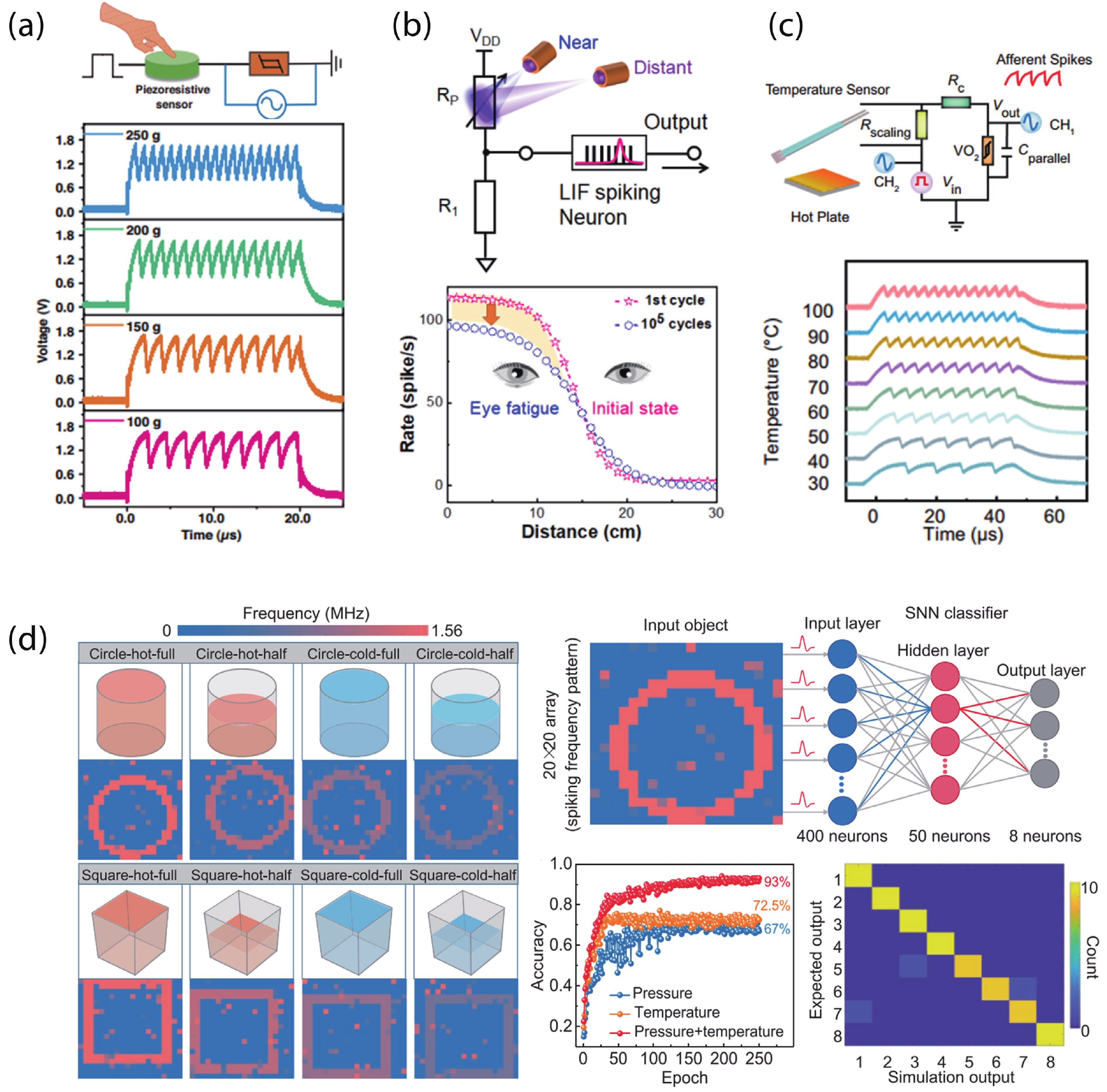
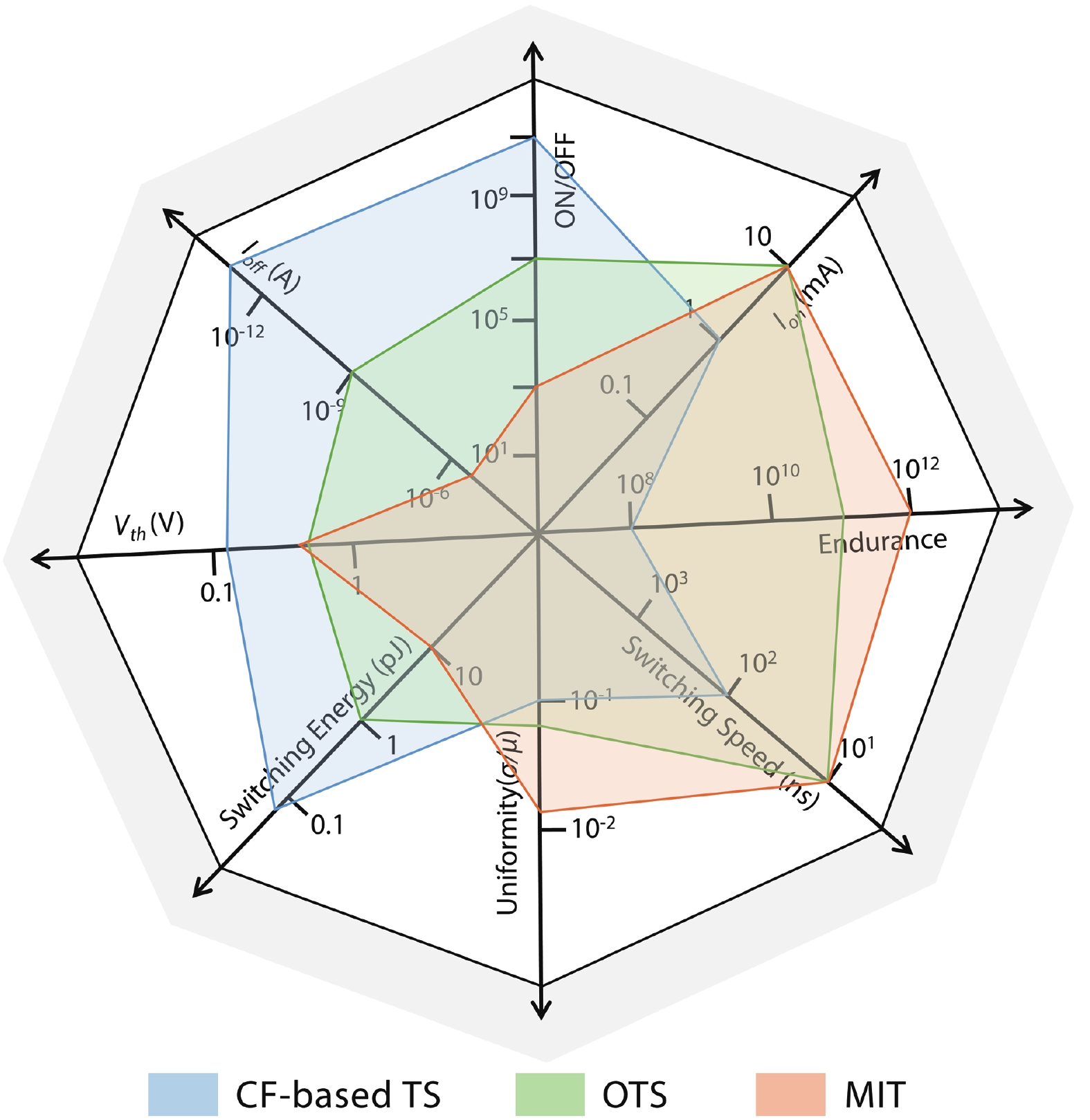
With rapid advancement and deep integration of artificial intelligence and the internet-of-things, artificial intelligence of things has emerged as a promising technology changing people’s daily life. Massive growth of data generated from the devices challenges the AIoT systems from information collection, storage, processing and communication. In the review, we introduce volatile threshold switching memristors, which can be roughly classified into three types: metallic conductive filament-based TS devices, amorphous chalcogenide-based ovonic threshold switching devices, and metal-insulator transition based TS devices. They play important roles in high-density storage, energy efficient computing and hardware security for AIoT systems. Firstly, a brief introduction is exhibited to describe the categories (materials and characteristics) of volatile TS devices. And then, switching mechanisms of the three types of TS devices are discussed and systematically summarized. After that, attention is focused on the applications in 3D cross-point memory technology with high storage-density, efficient neuromorphic computing, hardware security (true random number generators and physical unclonable functions), and others (steep subthreshold slope transistor, logic devices, etc.). Finally, the major challenges and future outlook of volatile threshold switching memristors are presented.-
Keywords:
- AIoT,
- threshold switching,
- memristor,
- selector,
- neuromorphic computing,
- hardware security
-
References
[1] Morteza R, Maryam S, Mostafa H K. Fog-based smart homes: A systematic review. J Netw Comput Appl, 2020, 153, 102531 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102531[2] Jose J, Peralta A, Christian W, et al. A systematic survey of internet of things frameworks for smart city applications. Sustain Cities Soc, 2022, 83, 103949 doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.103949[3] IBM. Smarter Planet. 2011-07-14[4] Zhang Z, Wen F, Sun Z, et al. Artificial intelligence-enabled sensing technologies in the 5G/internet of things era: from virtual reality/augmented reality to the digital twin. Adv Intell Syst, 2022, 4(7), 2100228 doi: 10.1002/aisy.202100228[5] Li J, Yang G. Network embedding enhanced intelligent recommendation for online social networks. Future Gener Comput Syst, 2021, 119, 68 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2021.01.017[6] Yang C, Chen H, Chang E, et al. Current advances and future challenges of AIoT applications in particulate matters (PM) monitoring and control. J Hazard Mater, 2021, 419, 126442 doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126442[7] Liao Y, Yu N, Zhou G, et al. A wireless multi-channel low-cost lab-on-chip algae culture monitor AIoT system for algae farm. Comput Electron Agr, 2022, 193, 106647 doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2021.106647[8] Caleb D, Albert C, Amos D. Artificial intelligence in green building. Automat Constr, 2022, 137, 104192 doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104192[9] Chiu M C, Yan W M, Showkat A B, et al. Development of smart aquaculture farm management system using IoT and AI-based surrogate models. J Agr Food Res, 2022, 9, 100357 doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100357[10] Jiang D, Li G, Tan C, et al. Semantic segmentation for multiscale target based on object recognition using the improved Faster-RCNN model. Future Gener Comput Syst, 2021, 123, 94 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2021.04.019[11] Betty P. Vertical 3D memory technologies. West Sussex: John Wiley and Sons Ltd, 2014.[12] Zhu J, Zhang T, Yang Y, et al. A comprehensive review on emerging artificial neuromorphic devices. Appl Phys Rev, 2020, 7, 011312 doi: 10.1063/1.5118217[13] Alqahtani F, Al-Makhadmeh Z, Tolba A, et al. TBM: A trust-based monitoring security scheme to improve the service authentication in the Internet of Things communications. Comput Commun, 2020, 150, 216 doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2019.11.030[14] Chua L O. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans Circuit Theory, 1971, 18(5), 507 doi: 10.1109/TCT.1971.1083337[15] Ge J, Zhang S, Liu Z, et al. Flexible artificial nociceptor using a biopolymer-based forming-free memristor. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(14), 6591 doi: 10.1039/C8NR08721K[16] Xu M, Mai X, Lin J, et al. Recent advances on neuromorphic devices based on chalcogenide phase-change materials. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30, 2003419 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202003419[17] Carboni R, Ielmini D. Stochastic memory devices for security and computing. Adv Electron Mater, 2019, 5, 1900198 doi: 10.1002/aelm.201900198[18] Rajendran G, Banerjee W, Anupam C. Application of resistive random-access memory in hardware security: A review. Adv Electron Mater, 2021, 7, 2100536 doi: 10.1002/aelm.202100536[19] Aluguri R, Tseng T Y. Memory technologies devices for 3D stackable cross point RRAM arrays. J Electron Dev Soc, 2016, 4(5), 294[20] Wang R, Yang J, Mao J, et al. Recent advances of volatile memristors: devices, mechanisms, and applications. Adv Intell Syst, 2020, 2, 2000055 doi: 10.1002/aisy.202000055[21] Chen W, Barnaby H J, Kozicki M N. Volatile and non-volatile switching in Cu-SiO2 programmable metallization cells. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2016, 37(5), 580 doi: 10.1109/LED.2016.2540361[22] Yoon J H, Wang Z, Kim K M, et al. An artificial nociceptor based on a diffusive memristor. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 417 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02572-3[23] Zhao X, Wang R, Xiao X, et al. Flexible cation-based threshold selector for resistive switching memory integration. Sci China Inform Sci, 2018, 61, 060413 doi: 10.1007/s11432-017-9352-0[24] Park Y, Han U B, Kim M K, et al. Solution-processed flexible threshold switch devices. Adv Electron Mater, 2018, 4, 1700521 doi: 10.1002/aelm.201700521[25] Saitoh S, Kinoshita K. Oxide-based selector with trap-filling-controlled threshold switching. Appl Phys Lett, 2020, 116, 112101 doi: 10.1063/1.5143631[26] Sung C, Lim S, Hwang H. Experimental determination of the tunable threshold voltage characteristics in a AgxTe1–x/Al2O3/TiO2-based hybrid memory device. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2020, 41(5), 713 doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.2979236[27] Lu Y F, Li H, Wan T, et al. Low-power artificial neurons based on Ag/TiN/HfAlOx/Pt threshold switching memristor for neuromorphic computing. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2020, 41(8), 1245 doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.3006581[28] Li H, Huang X, Yuan J, et al. Controlled memory and threshold switching behaviors in a heterogeneous memristor for neuromorphic computing. Adv Electron Mater, 2020, 6, 2000309 doi: 10.1002/aelm.202000309[29] Kumar M, Kim H S, Kim J. A highly transparent artificial photonic nociceptor. Adv Mater, 2019, 31, 1900021 doi: 10.1002/adma.201900021[30] Shi Y, Liang X, Yuan B, et al. Electronic synapses made of layered two-dimensional materials. Nat Electron, 2018, 1, 458 doi: 10.1038/s41928-018-0118-9[31] Wang M, Cai S, Pan C, et al. Robust memristors based on layered two-dimensional materials. Nat Electron, 2018, 1, 130 doi: 10.1038/s41928-018-0021-4[32] Dev D, Krishnaprasad A, Shawkat M S, et al. 2D MoS2-based threshold switching memristor for artificial neuron. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2020, 41(6), 936 doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.2988247[33] Yang J, Wang R, Wang Z, et al. Leaky integrate-and-fire neurons based on perovskite memristor for spiking neural networks. Nano Energy, 2020, 74, 104828 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104828[34] Wang L, Cai W, He D, et al. Performance improvement of GeTex-based Ovonic threshold switching selector by C doping. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2021, 42(5), 688 doi: 10.1109/LED.2021.3064857[35] Ambrosi E, Wu C, Lee H Y, et al. Reliable low voltage selector device technology based on robust SiNGeCTe arsenic-free chalcogenide. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2022, 43(10), 1673 doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3203146[36] Kim J, Kang M, Kim W, et al. Impact of Ag doping on subthreshold conduction in amorphous Ga2Te3 with threshold switching. J Alloy Comp, 2022, 913, 165176 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.165176[37] Bian J, Tao Y, Wang Z, et al. A stacked memristive device enabling both analog and threshold switching behaviors for artificial leaky integrate and fire neuron. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2022, 43(9), 1436 doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3188786[38] Huang H, Yang R, Tan Z H, et al. Quasi-Hodgkin-Huxley Neurons with leaky integrate-and-fire functions physically realized with memristive devices. Adv Mater, 2019, 31, 1803849 doi: 10.1002/adma.201803849[39] Zhang C, Shang J, Xue W, et al. Convertible resistive switching characteristics between memory switching and threshold switching in a single ferritin-based memristor. Chem Commun, 2016, 52, 4828 doi: 10.1039/C6CC00989A[40] Kim D, Jeon B, Lee Y, et al. Prospects and applications of volatile memristors. Appl Phys Lett, 2022, 121, 010501 doi: 10.1063/5.0093964[41] Sun Y, Song C, Yin S, et al. Design of a controllable redox-diffusive threshold switching memristor. Adv Electron Mater, 2020, 6, 2000695 doi: 10.1002/aelm.202000695[42] Yang Y, Gao P, Gaba S, et al. Observation of conducting filament growth in nanoscale resistive memories. Nat Commun, 2012, 3, 732 doi: 10.1038/ncomms1737[43] Yang Y, Gao P, Li L, et al. Electrochemical dynamics of nanoscale metallic inclusions in dielectrics. Nat Commun, 2014, 5, 4232 doi: 10.1038/ncomms5232[44] Yoo J, Park J, Song J, et al. Field-induced nucleation in threshold switching characteristics of electrochemical metallization devices. Appl Phys Lett, 2017, 111, 063109 doi: 10.1063/1.4985165[45] Wang Z, Joshi S, Sergey E S, et al. Memristors with diffusive dynamics as synaptic emulators for neuromorphic computing. Nat Mater, 2017, 16, 101 doi: 10.1038/nmat4756[46] Oh S, Lee S, Hwang H. Improved turn-off speed and uniformity of atomic threshold switch device by AgSe electrode and bipolar pulse forming. J Electron Dev Soc, 2021, 9, 864 doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2021.3115520[47] Ye F, Kiani F, Huang Y, et al. Diffusive memristors with unifor and tunable relaxation time for spike generation in event-based pattern recognition. Adv Mater, 2022, 34, 2204778 doi: 10.1002/adma.202204778[48] Chekol S A, Menzel S, Ahmad R W, et al. Effect of the threshold kinetics on the filament relaxation behaviour of Ag-based diffusive memristors. Adv Funct Mater, 2022, 32, 2111242 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202111242[49] Stoneham A M. Systematics of metal-insulator interfacial energies: A new rule for wetting and strong catalyst-support interactions. Application Surf Sci, 1983, 14, 249 doi: 10.1016/0378-5963(83)90040-5[50] Song J, Woo J, Prakash A, et al. Threshold selector with high selectivity and steep slope for cross-point memory array. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2015, 36(7), 681 doi: 10.1109/LED.2015.2430332[51] Ambrogio S, Balatti S, Choi S, et al. Impact of the Mechanical stress on switching characteristics of electrochemical resistive memory. Adv Mater, 2014, 26, 3885 doi: 10.1002/adma.201306250[52] Ovshinsky S R. Reversible electrical switching phenomena in disordered structures. Phys Rev Lett, 1968, 21(20), 1450 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.21.1450[53] Nardone M, Karpov V G, Jackson D C S, et al. A unified model of nucleation switching. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94, 103509 doi: 10.1063/1.3100779[54] Zhang W, Mazzarello R, Wuttig M, et al. Designing crystallization in phase-change materials for universal memory and neuro-inspired computing. Nat Rev Mater, 2019, 4, 150 doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0076-x[55] Ielmini D, Lacaita A L, Mantegazza D. Recovery and drift dynamics of resistance and threshold voltages in phase-change memories. IEEE Transaction Electron Dev, 2007, 54(2), 308 doi: 10.1109/TED.2006.888752[56] Guo Y R, Dong F, Qiao C, et al. Structural signature and transition dynamics of Sb2Te3 melt upon fast cooling. Phys Chem Chem Phys, 2018, 20(17), 11768 doi: 10.1039/C8CP00142A[57] Raty J Y, Noé P. Ovonic threshold switching in Se-rich GexSe1−x glasses from an atomistic point of view: The crucial role of the metavalent bonding mechanism. Phys Status Solidi-R, 2020, 14(5), 1900581 doi: 10.1002/pssr.201900581[58] Wuttig M, Deringer V L, Gonze X, et al. Incipient metals: functional materials with a unique bonding mechanism. Adv Mater, 2018, 30, 1803777 doi: 10.1002/adma.201803777[59] Zhu M, Cojocaru-Mirédin O, Mio A M, et al. Unique bond breaking in crystalline phase change materials and the quest for metavalent bonding. Adv Mater, 2018, 30(18), 1706735 doi: 10.1002/adma.201706735[60] Imada M, Fujimori A, Tokura Y. Metal-insulator transitions. Rev Modern Phys, 1998, 70, 1039 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.70.1039[61] Wentzcovitch R M, Schulz W W, Allen P B. VO2: Peierls or Mott-Hubbard? A view from band theory. Phys Rev Lett, 1994, 72, 3389 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.72.3389[62] Rice T M, Launois H, Pouget J P. Comment on "VO2: Peierls or Mott-Hubbard? A view from band theory". Phys Rev Lett, 1994, 73, 3042 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.73.3042[63] Schulz W W, Wentzcovitch R M. Electronic band structure and bonding in Nb3O3. Phys Rev B, 1993, 48(23), 16986 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.48.16986[64] Lee D, Chung B, Shi Y, et al. Isostructural metal-insulator transition in VO2. Science, 2018, 362, 1037 doi: 10.1126/science.aam9189[65] Morrison V R, Chatelain R P, Tiwari K L, et al. A photoinduced metal-like phase of monoclinic VO2 revealed by ultrafast electron diffraction. Science, 2014, 346, 445 doi: 10.1126/science.1253779[66] Biermann S, Poteryaev A, Lichtenstein A I, et al. Dynamical singlets and correlation-assisted Peierls transition in VO2. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 94, 026404 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.026404[67] Haverkort M W, Hu Z, Tanaka A, et al. Orbital-assisted metal-insulator transition in VO2. Phys Rev Lett, 2005, 95, 196404 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.196404[68] Zimmers A, Aigouy L, Mortier M, et al. Role of thermal heating on the voltage induced insulator-metal transition in VO2. Phys Rev Lett, 2013, 110, 056601 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.056601[69] Cheng S, Lee M, Li X, et al. Operando characterization of conductive filaments during resistive switching in Mott VO2. Pro National Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(9), e2013676118 doi: 10.1073/pnas.2013676118[70] Kumar S, Wang Z, Davila N, et al. Physical origins of current and temperature controlled negative differential resistances in NbO2. Nat Commun, 2017, 8, 658 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00773-4[71] Kalcheim Y, Camjayi A, Valle J D, et al. Non-thermal resistive switching in Mott insulator nanowires. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 2985 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16752-1[72] Valle J D, Vargas N M, Rocco R, et al. Spatiotemporal characterization of the field-induced insulator-to-metal transition. Science, 2021, 373, 907 doi: 10.1126/science.abd9088[73] Li C, Hu M, Li Y, et al. Analogue signal and image processing with large memristor crossbars. Nat electron, 2018, 1(1), 52-59 doi: 10.1038/s41928-017-0002-z[74] Li X, Wu H, Gao B, et al. Electrode-induced digital-to-analog resistive switching in TaOx-based RRAM devices. Nanotechnology, 2016, 27(30), 305201 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/27/30/305201[75] Midya R, Wang Z, Zhang J, et al. Anatomy of Ag/Hafnia-based selectors with 1010 nonlinearity. Adv Mater, 2017, 29(12), 1604457 doi: 10.1002/adma.201604457[76] Hua Q, Wu H, Gao B, et al. A threshold switching selector based on highly ordered Ag nanodots for X-point memory applications. Adv Sci, 2019, 6(10), 1900024 doi: 10.1002/advs.201900024[77] Li Y, Tang J, Gao B, et al. High-uniformity threshold switching HfO2-based selectors with patterned Ag nanodots. Adv Sci, 2020, 7(22), 2002251 doi: 10.1002/advs.202002251[78] Goux L, Opsomer K, Degraeve R, et al. Influence of the Cu-Te composition and microstructure on the resistive switching of Cu-Te/Al2O3/Si cells. Appl Phy Letts, 2011, 99(5), 053502 doi: 10.1063/1.3621835[79] Woo K S, Kim J, Han J, et al. A high-speed true random number generator based on a CuxTe1−x diffusive memristor. Adv Intelligent Syst, 2021, 3(7), 2100062 doi: 10.1002/aisy.202100062[80] Banerjee W, Karpov I V, Agrawal A, et al. Highly-stable (<3% fluctuation) Ag-based threshold switch with extreme-low OFF current of 0.1 pA, extreme-high selectivity of 109 and high endurance of 109 cycles. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2020, 28.4.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM13553.2020.9371960[81] Wan T Q, Lu Y F, Yuan J H, et al. 12.7 MA/cm2 on-current density and high uniformity realized in AgGeSe/Al2O3 selectors. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2021, 42(4), 613 doi: 10.1109/LED.2021.3061620[82] Grisafe B, Jerry M, Smith J A, et al. Performance enhancement of Ag/HfO2 metal ion threshold switch cross-point selectors. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2019, 40(10), 1602 doi: 10.1109/LED.2019.2936104[83] Zhao X, Ma J, Xiao X, et al. Breaking the current-retention dilemma in cation-based resistive switching devices utilizing graphene with controlled defects. Adv mater, 2018, 30(14), 1705193 doi: 10.1002/adma.201705193[84] Sahota A, Kim H S, Mohan J, et al. Highly reliable selection behavior with controlled Ag doping of nano-polycrystalline ZnO Layer for 3D X-Point framework. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2021, 43(1), 21 doi: 10.1109/LED.2021.3130828[85] Luo Q, Xu X, Liu H, et al. Cu BEOL compatible selector with high selectivity (> 107), extremely low off-current (~pA) and high endurance (>1010). IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2015, 10.4. 1. doi: 10.1109/IEDM.2015.7409669[86] Lu Y F, Li H Y, Li Y, et al. A High-performance Ag/TiN/HfOx/HfOy/HfOx/Pt diffusive memristor for calibration-free true random number generator. Adv Electron Mater, 2022, 2200202 doi: 10.1002/aelm.202200202[87] Yin J, Zeng F, Wan Q, et al. Self-modulating interfacial cation migration induced threshold switching in bilayer oxide memristive device. J Phys Chem C, 2018, 123(1), 878 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b09793[88] Czubatyj W, Hudgens S J. Thin-film Ovonic threshold switch: Its operation and application in modern integrated circuits. Electron Mater Lett, 2012, 8(2), 157 doi: 10.1007/s13391-012-2040-z[89] Zhu M, Ren K, Song Z. Ovonic threshold switching selectors for three-dimensional stackable phase-change memory. MRS Bull, 2019, 44, 715 doi: 10.1557/mrs.2019.206[90] Govoreanu B, Donadio G L, Opsomer K, et al. Thermally stable integrated Se-based OTS selectors with >20 MA/cm2 current drive, > 3.103 half-bias nonlinearity, tunable threshold voltage and excellent endurance. Symposium on VLSI Technology, 2017, T92 doi: 10.23919/VLSIT.2017.7998207[91] Navarro G, Verdy A, Castellani N, et al. Innovative PCM+OTS device with high sub-threshold non-linearity for non-switching reading operations and higher endurance performance. Symposium on VLSI Technology, 2017, T94 doi: 10.23919/VLSIT.2017.7998208[92] Avasarala N S, Donadio G L, Witters T, et al. Half-threshold bias Ioff reduction down to nA range of thermally and electrically stable high-performance integrated OTS selector obtained by Se enrichment and N-doping of thin GeSe layers. IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, 2018, 209 doi: 10.1109/VLSIT.2018.8510680[93] Liu G, Li T, Wu L, et al. Increasing trapped carrier density in nanoscale GeSeAs Films by As ion Implantation for selector devices in 3D-Stacking Memory. ACS Appl Nano Mater, 2019, 2(9), 5373 doi: 10.1021/acsanm.9b00734[94] Verdy A, Navarro G, Bernard M, et al. Carbon electrode for Ge-Se-Sb based OTS selector for ultra low leakage current and outstanding endurance. IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, 2018, 6D.4-1 doi: 10.1109/IRPS.2018.8353635[95] Verdy A, Bernard M, Garrione J, et al. Optimized reading window for crossbar arrays thanks to Ge-Se-Sb-N-based OTS selectors. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2018, 37.4.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM.2018.8614686[96] Cyrille M C, Verdy A, Navarro G, et al. OTS selector devices: Material engineering for switching performance. International Conference on IC Design & Technology, 2018, 113 doi: 10.1109/ICICDT.2018.8399769[97] Anbarasu M, Wimmer M, Bruns G, et al. Nanosecond threshold switching of GeTe6 cells and their potential as selector devices. Appl Phy Lett, 2012, 100(14), 143505 doi: 10.1063/1.3700743[98] Verdy A, Bernard M, Castellani N, et al. Tunable performances in OTS selectors thanks to Ge3Se7-As2Te3. IEEE 11th International Memory Workshop, 2019, 1 doi: 10.1109/IMW.2019.8739706[99] Lee M J, Lee D, Cho S H, et al. A plasma-treated chalcogenide switch device for stackable scalable 3D nanoscale memory. Nat Commun, 2013, 4(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/NCOMMS3629[100] Cheng H Y, Chien W C, Kuo I T, et al. An ultra high endurance and thermally stable selector based on TeAsGeSiSe chalcogenides compatible with BEOL IC Integration for cross-point PCM. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2017, 2.2.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM.2017.8268310[101] Chien W C, Yeh C W, Bruce R L, et al. A study on OTS-PCM pillar cell for 3-D stackable memory. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2018, 65(11), 5172 doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2871197[102] Koo Y, Lee S, Park S, et al. Simple binary ovonic threshold switching material SiTe and its excellent selector performance for high-density memory array application. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2017, 38(5), 568 doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2685435[103] Ho Lee J, Hwan Kim G, Bae Ahn Y, et al. Threshold switching in Si-As-Te thin film for the selector device of crossbar resistive memory. Appl Phy Lett, 2012, 100(12), 123505 doi: 10.1063/1.3696077[104] Chekol S A, Yoo J, Hwang H. Thermally stable Te-based binary OTS device for selector application. Non-Volatile Memory Technology Symposium, 2018, 1 doi: 10.1109/NVMTS.2018.8603103[105] Yoo J, Lee D, Park J, et al. Steep slope field-effect transistors with B–Te-based ovonic threshold switch device. IEEE J Electron Dev Soc, 2018, 6, 821 doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2018.2856853[106] Koo Y, Hwang H. Zn1−xTex Ovonic threshold switching device performance and its correlation to material parameters. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30207-0[107] Yoo J, Koo Y, Chekol S A, et al. Te-based binary OTS selectors with excellent selectivity (>105), endurance (>108) and thermal stability (>450°C). IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology, 2018, 207 doi: 10.1109/VLSIT.2018.8510681[108] Adinolfi V, Cheng L, Laudato M, et al. Composition-controlled atomic layer deposition of phase-change memories and ovonic threshold switches with high performance. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9), 10440 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b04233[109] Chekol S A, Yoo J, Park J, et al. AC–Te-based binary OTS device exhibiting excellent performance and high thermal stability for selector application. Nanotechnology, 2018, 29(34), 345202 doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aac9f5[110] Shen J, Jia S, Shi N, et al. Elemental electrical switch enabling phase segregation-free operation. Science, 2021, 374(6573), 1390 doi: 10.1126/science.abi6332[111] Vaziri S, Datye I M, Ambrosi E, et al. First Fire-free, Low-voltage (~1.2 V), and Low Off-current (~3 nA) SiOxTey Selectors. IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, 2022, 324-325 doi: 10.1109/VLSITechnologyandCir46769.2022.9830395[112] Jacob K T, Shekhar C, Vinay M, et al. Thermodynamic properties of niobium oxides. J Chem Eng Data, 2010, 55(11), 4854 doi: 10.1021/je1004609[113] Chen A, Fu Y, Ma G, et al. The co-improvement of selectivity and uniformity on NbOx-based selector by Al-doping. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2022, 43(6), 870 doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3165789[114] Jeon D S, Dongale T D, Kim T G. Low power Ti-doped NbO2-based selector device with high selectivity and low OFF current. J Alloy Compd, 2021, 884, 161041 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.161041[115] Chen D, Chen A, Yu Z, et al. Forming-free, ultra-high on-state current, and self-compliance selector based on titanium-doped NbOx thin films. Ceram Int, 2021, 47(16), 22677 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.04.282[116] Luo Q, Yu J, Zhang X, et al. Nb1–xO2 based universal selector with ultra-high endurance (>1012), high speed (10 ns) and excellent Vth Stability. Symposium on VLSI Technology, 2019, T236 doi: 10.23919/VLSIT.2019.8776546[117] Chen P, Zhang X, Wu Z, et al. High-yield and uniform NbOx-based threshold switching devices for neuron applications. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2022, 69(5), 2391 doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3161614[118] Kandel E R, Schwarts J H, Jessell T M. Principles of neural science. New York: McGraw-hill, 2000.[119] Abbott L F. Lapicque’s introduction of the integrate-and-fire model neuron. Brain Res Bull, 1999, 50(5), 303 doi: 10.1016/S0361-9230(99)00161-6[120] Hodgkin A L, Huxley A F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiology, 1952, 117(4), 500 doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764[121] Kadetotad D, Xu Z, Mohanty A, et al. Parallel architecture with resistive crosspoint array for dictionary learning acceleration. IEEE J Em Sel Top C, 2015, 5(2), 194 doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2015.2426495[122] Lin J, Sonde S, Chen C, et al. Low-voltage artificial neuron using feedback engineered insulator-to-metal-transition devices. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2016, 34.5.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM.2016.7838541[123] Zhang X, Wang W, Liu Q, et al. An artificial neuron based on a threshold switching memristor. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2017, 39(2), 308 doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2782752[124] Zhang Y, He W, Wu Y, et al. Highly compact artificial memristive neuron with low energy consumption. Small, 2018, 14(51), 1802188 doi: 10.1002/smll.201802188[125] Cao R, Zhang X, Liu S, et al. Compact artificial neuron based on anti-ferroelectric transistor. Nat Commun, 2022, 13, 7018 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34774-9[126] Pickett M D, Medeiros-Ribeiro G, Williams R S. A scalable neuristor built with Mott memristors. Nat Mater, 2013, 12(2), 114 doi: 10.1038/nmat3510[127] Yi W, Tsang K K, Lam S K, et al. Biological plausibility and stochasticity in scalable VO2 active memristor neurons. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02088-w[128] Liu H, Wu T, Yan X, et al. A tantalum disulfide charge-density-wave stochastic artificial neuron for emulating neural statistical properties. Nano Lett, 2021, 21(8), 3465 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c00108[129] Wei Q, Tang J, Li X, et al. Artificial neuron with spike frequency adaptation based on mott memristor. 5th IEEE Electron Devices Technology & Manufacturing Conference, 2021, 1 doi: 10.1109/EDTM50988.2021.9421014[130] Luo J, Yu L, Liu T, et al. Capacitor-less stochastic leaky-FeFET neuron of both excitatory and inhibitory connections for SNN with reduced hardware cost. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2019, 6.4.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM19573.2019.8993535[131] Wu L, Wang Z, Bao L, et al. Implementation of neuronal intrinsic plasticity by oscillatory device in spiking neural network. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2022, 69(4), 1830 doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3152468[132] Wang Y, Xu H, Wang W, et al. A configurable artificial neuron based on a threshold-tunable TiN/NbOₓ/Pt Memristor. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2022, 43(4), 631 doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3150034[133] Indiveri G, Linares-Barranco B, Legenstein R, et al. Integration of nanoscale memristor synapses in neuromorphic computing architectures. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(38), 384010 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/38/384010[134] Prezioso M, Merrikh-Bayat F, Hoskins B D, et al. Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors. Nature, 2015, 521(7550), 61 doi: 10.1038/nature14441[135] Sheridan P M, Cai F, Du C, et al. Sparse coding with memristor networks. Nat Nanotechnology, 2017, 12(8), 784 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2017.83[136] Yao P, Wu H, Gao B, et al. Fully hardware-implemented memristor convolutional neural network. Nature, 2020, 577(7792), 641 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1942-4[137] Wan W, Kubendran R, Schaefer C, et al. A compute-in-memory chip based on resistive random-access memory. Nature, 2022, 608(7923), 504 doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04992-8[138] Wang Z, Joshi S, Savel’ev S, et al. Fully memristive neural networks for pattern classification with unsupervised learning. Nature Electron, 2018, 1(2), 137 doi: 10.1038/s41928-018-0023-2[139] Duan Q, Jing Z, Zou X, et al. Spiking neurons with spatiotemporal dynamics and gain modulation for monolithically integrated memristive neural networks. Nat commu, 2020, 11(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17215-3[140] Li X, Tang J, Zhang Q, et al. Power-efficient neural network with artificial dendrites. Nat Nanotech, 2020, 15(9), 776 doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-0722-5[141] Zhang X, Wu Z, Lu J, et al. Fully memristive SNNs with temporal coding for fast and low-power edge computing. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2020, 29.6.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM13553.2020.9371937[142] Wang Z, Zheng Q, Kang J, et al. Self-activation neural network based on self-selective memory device with rectified multilevel states. IEEE Trans on Electron Dev, 2020, 67(10), 4166 doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.3014566[143] Li X, Zhong Y, Chen H, et al. A memristors-based dendritic neuron for high-efficiency spatial-temporal information processing. Adv Mater, 2023, 2203684 doi: 10.1002/adma.202203684[144] Fu Y, Zhou Y, Huang X, et al. Reconfigurable synaptic and neuronal functions in a V/VOx/HfWOx/Pt memristor for nonpolar spiking convolutional neural network. Adv Func Mater, 2022, 2111996 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202111996[145] Yu J, Zeng F, Wan Q, et al. Memristive structure of Nb/HfOx/Pd with controllable switching mechanisms to perform featured actions in neuromorphic networks. Nano Res, 2022, 15(9), 8410 doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4416-1[146] Mennel L, Symonowicz J, Wachter S, et al. Ultrafast machine vision with 2D material neural network image sensors. Nature, 2020, 579(7797), 62 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2038-x[147] Wang C Y, Liang S J, Wang S, et al. Gate-tunable van der Waals heterostructure for reconfigurable neural network vision sensor. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(26), 6173 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba6173[148] Zhou F, Chai Y. Near-sensor and in-sensor computing. Nat Electron, 2020, 3(11), 664 doi: 10.1038/s41928-020-00501-9[149] Dev D, Shawkat M S, Krishnaprasad A, et al. Artificial nociceptor using 2D MoS2 threshold switching memristor. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2020, 41(9), 1440 doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.3012831[150] Zhu J, Zhang X, Wang M, et al. An artificial spiking nociceptor integrating pressure sensors and memristors. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2022, 43(6), 962 doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3167421[151] Han C Y, Han Z R, Fang S L, et al. Characterization and modelling of flexible VO2 Mott memristor for the artificial spiking warm receptor. Adv Mater Int, 2022, 9, 2200394 doi: 10.1002/admi.202200394[152] Chen C, He Y, Mao H, et al. A photoelectric spiking neuron for visual depth perception. Adv Mater, 2022, 34, 2201895 doi: 10.1002/adma.202201895[153] Wang Y, Gong Y, Huang S, et al. Memristor-based biomimetic compound eye for real-time collision detection. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1), 5979 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26314-8[154] Duan Q, Zhang T, Liu C, et al. Artificial multisensory neurons with fused haptic and temperature perception for multimodal in‐sensor computing. Adv Intell Syst, 2022, 4, 2200039 doi: 10.1002/aisy.202200039[155] Song Y G, Suh J M, Park J Y, et al. Artificial adaptive and maladaptive sensory receptors based on a surface-dominated diffusive memristor. Adv Sci, 2022, 9(4), 2103484 doi: 10.1002/advs.202103484[156] Zhang X, Zhuo Y, Luo Q, et al. An artificial spiking afferent nerve based on Mott memristors for neurorobotics. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1), 51 doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13827-6[157] Yuan R, Duan Q, Tiw P J, et al. A calibratable sensory neuron based on epitaxial VO2 for spike-based neuromorphic multisensory system. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27699-2[158] Zhu J, Zhang X, Wang R, et al. A heterogeneously integrated spiking neuron array for multimode-fused Perception and object classification. Adv Mater, 2022, 34, 2200481 doi: 10.1002/adma.202200481[159] Chai Z, Shao W, Zhang W, et al. GeSe-based ovonic threshold switching volatile true random number generator. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2019, 41(2), 228 doi: 10.1109/LED.2019.2960947[160] Jiang H, Belkin D, Savel’ev S E, et al. A novel true random number generator based on a stochastic diffusive memristor. Nat Commu, 2017, 8(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/s41467-016-0009-6[161] Woo K S, Wang Y, Kim J, et al. A true random number generator using threshold-switching-based memristors in an efficient circuit design. Adv Electron Mater, 2019, 5, 1800543 doi: 10.1002/aelm.201800543[162] Woo K S, Wang Y, Kim Y, et al. A combination of a volatile-memristor-based true random number generator and a nonlinear-feedback shift register for high-speed encryption. Adv Electron Mater, 2020, 6, 1901117 doi: 10.1002/aelm.201901117[163] Kim G, In J H, Kim Y S, et al. Self-clocking fast and variation tolerant true random number generator based on a stochastic Mott memristor. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1), 2906 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23184-y[164] Ding Q, Jiang H, Li J, et al. Unified 0.75 pJ/Bit TRNG and attack resilient 2F 2/Bit PUF for robust hardware security solutions with 4-layer stacking 3D NbOx threshold switching array. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2021, 39.2.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM19574.2021.9720641[165] Shin J, Ko E, Park J, et al. Super steep-switching (SS~2 mV/decade) phase-FinFET with Pb(Zr0.52Ti048)O3 threshold switching device. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 113, 102104 doi: 10.1063/1.5030966[166] Lee C, Ko E, Shin C, et al. Steep slope silicon-on-insulator feedback field-effect transistor: design and performance analysis. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2019, 66(1), 286 doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2879653[167] Ko E, Lee J W, Shin C, et al. Negative capacitance FinFET with sub-20-mV/decade subthreshold slope and minimal hysteresis of 0.48 V. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2017, 38(4), 418 doi: 10.1109/LED.2017.2672967[168] hukla N, Thathachary A V, Agrawal A, et al. A steep-slope transistor based on abrupt electronic phase transition. Nat Commun, 2015(6), 7812 doi: 10.1038/ncomms8812[169] Song J, Park J, Moon K, et al. Monolithic integration of AgTe/TiO2 based threshold switching device with TiN liner for steep slope field-effect transistors. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2016, 25.3.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM.2016.7838478[170] Lim S, Yoo J, Song J, et al. CMOS compatible low-power volatile atomic switch for steep-slope FET devices. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 113, 033501 doi: 10.1063/1.5039898[171] Shukla N, Grisafe B, Ghosh R K, et al. Ag/HfO2 based threshold switch with extreme non-linearity for unipolar cross-point memory and steep-slope phase-FETs. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2016, 34.6.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM.2016.7838542[172] Jeong S, Han S, Lee H J, et al. Abruptly-switching MoS2-channel atomic-threshold-switching field-effect transistor with AgTi/HfO2-based threshold switching device. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 116953 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3106331[173] Park J H, Kim S H, Kim S G, et al. Nitrogen-induced filament confinement technique for a highly reliable hafnium-based electrochemical metallization threshold switch and its application to flexible logic circuits. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11(9), 9182 doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b18970[174] Lanza M, Waser R, Ielmini D, et al. Standards for the characterization of endurance in resistive switching devices. ACS Nano, 2021, 15(3), 17214 doi: 10.1021/ACSNANO.1C06980[175] Du G, Wang C, Li H, et al. Bidirectional threshold switching characteristics in Ag/ZrO2/Pt electrochemical metallization cells. AIP Adv, 2016, 6, 085316 doi: 10.1063/1.4961709[176] Song B, Xu H, Liu S, et al. Threshold switching behavior of Ag-SiTe-based selector device and annealing effect on its characteristics. IEEE J Electron Dev Soc, 2018, 6, 674 doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2018.2836400[177] Song J, Prakash A, Lee D, et al. Bidirectional threshold switching in engineered multilayer (Cu2O/Ag: Cu2O/Cu2O) stack for cross-point selector application. Appl Phys Lett, 2015, 107, 113504 doi: 10.1063/1.4931136[178] Sun Y, Zhao X, Song C, et al. Performance-enhancing selector via symmetrical multilayer design. Adv Funct Mater, 2019, 29, 1808376 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201808376[179] Ambrosi E, Wu C H, Lee H Y, et al. Low variability high endurance and low voltage arsenic-free selectors based on GeCTe. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2021, 28.5.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM19574.2021.9720628[180] Jia S, Li H, Gotoh T, et al. Ultrahigh drive current and large selectivity in GeS selector. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1), 1 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18382-z[181] Lee J, Kim S, Lee S, et al. Improving the SiGeAsTe Ovonic Threshold Switching (OTS) Characteristics by Microwave Annealing for Excellent Endurance (> 1011) and Low Drift Characteristics. IEEE Symposium on VLSI Technology and Circuits, 2022, 320-321 doi: 10.1109/VLSITechnologyandCir46769.2022.9830179[182] Wang Z, Kang J, Bai G, et al. Self-selective resistive device with hybrid switching mode for passive crossbar memory application. IEEE Electron Dev Lett, 2020, 41(7), 1009 doi: 10.1109/LED.2020.2992680[183] Yeh T H, Chen P H, Lin C Y, et al. Enhancing threshold switching characteristics and stability of vanadium oxide-based selector with vanadium electrode. IEEE Trans on Electron Dev, 2020, 67(11), 5059 doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.3019773[184] Kang D Y, Rani A, Yoo K J, et al. Improved threshold switching characteristics of vanadium oxide/oxynitride-based multilayer selector in a cross-point array. J Alloy Compd, 2022, 922, 166192 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166192[185] Zhao X, Chen A, Ji J, et al. Ultrahigh Uniformity and Stability in NbOx-Based Selector for 3-D Memory by Using Ru Electrode. IEEE Trans Electron Dev, 2021, 68(5), 2255 doi: 10.1109/TED.2021.3063327[186] Pickett M D, Williams R S. Sub-100 fJ and sub-nanosecond thermally driven threshold switching in niobium oxide crosspoint nanodevices. Nanotech, 2012, 23(21), 215202 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/21/215202[187] Hennen T, Bedau D, Rupp J A J, et al. Forming-free Mott-oxide threshold selector nanodevice showing s-type NDR with high endurance (> 1012 cycles), excellent Vth stability (5%), fast (< 10 ns) switching, and promising scaling properties. IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2018, 37.5.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM.2018.8614618[188] Fu Y, Zhou Y, Huang X, et al. Forming-free and Annealing-free V/VOx/HfWOx/Pt Device Exhibiting Reconfigurable Threshold and Resistive switching with high speed (< 30ns) and high endurance (> 1012/> 1010). IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, 2021, 12.6.1 doi: 10.1109/IEDM19574.2021.9720551[189] Chen A, He Y, Ma G, et al. Improved uniformity and threshold voltage in NbOx-ZrO2 selectors. Appl Phys Lett, 2021, 119(7), 073503 doi: 10.1063/5.0045257 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:












 Wenbin Zuo:is currently a postdoctoral researcher in School of Integrated Circuits in Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He received his PhD degree from Wuhan University in 2021. His research interests focus on metal oxides thin films and devices, as well as nonvolatile memory technology
Wenbin Zuo:is currently a postdoctoral researcher in School of Integrated Circuits in Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He received his PhD degree from Wuhan University in 2021. His research interests focus on metal oxides thin films and devices, as well as nonvolatile memory technology Qihang Zhu:is currently a postgraduate student in School of Integrated Circuits at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He received his Bachelor degree in Huazhong University of Science and Technology in 2021. His research interests mainly focus on memristive neural networks
Qihang Zhu:is currently a postgraduate student in School of Integrated Circuits at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He received his Bachelor degree in Huazhong University of Science and Technology in 2021. His research interests mainly focus on memristive neural networks Yi Li:is currently an associate professor at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). He received his PhD degree in microelectronics from HUST in 2014. His major research interests focus on memristors and their applications in neuromorphic computing and in-memory computing
Yi Li:is currently an associate professor at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). He received his PhD degree in microelectronics from HUST in 2014. His major research interests focus on memristors and their applications in neuromorphic computing and in-memory computing



