| Citation: |
Zhi Deng, Hailong Wang, Qiqi Wei, Lei Liu, Hongli Sun, Dong Pan, Dahai Wei, Jianhua Zhao. Enhanced magnetic anisotropy and high hole mobility in magnetic semiconductor Ga1-x-yFexNiySb[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(1): 012101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/1/012101
Z Deng, H L Wang, Q Q Wei, L Liu, H L Sun, D Pan, D H Wei, J H Zhao. Enhanced magnetic anisotropy and high hole mobility in magnetic semiconductor Ga1-x-yFexNiySb[J]. J. Semicond, 2024, 45(1): 012101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/1/012101
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
Enhanced magnetic anisotropy and high hole mobility in magnetic semiconductor Ga1-x-yFexNiySb
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/1/012101
More Information-
Abstract
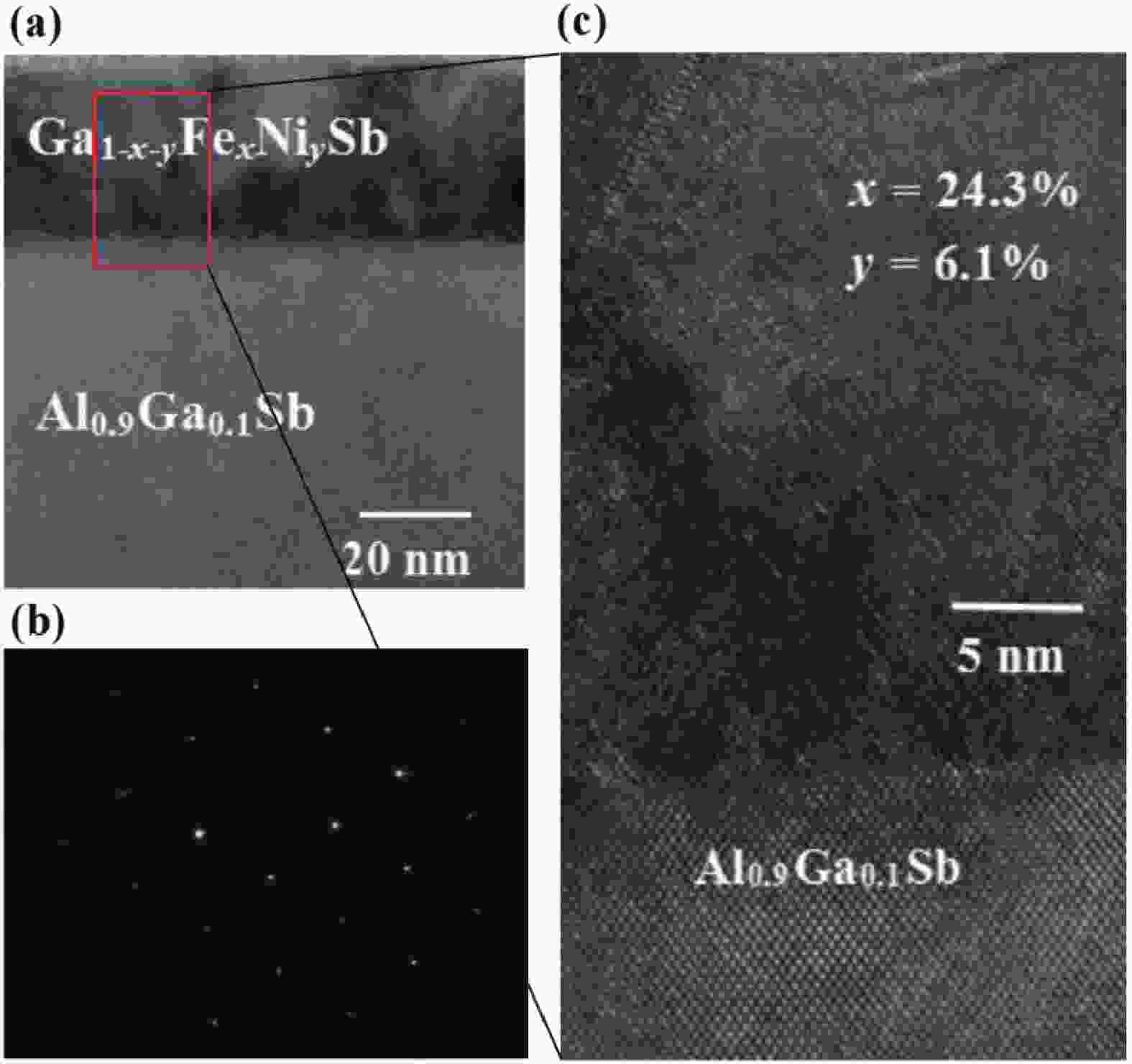
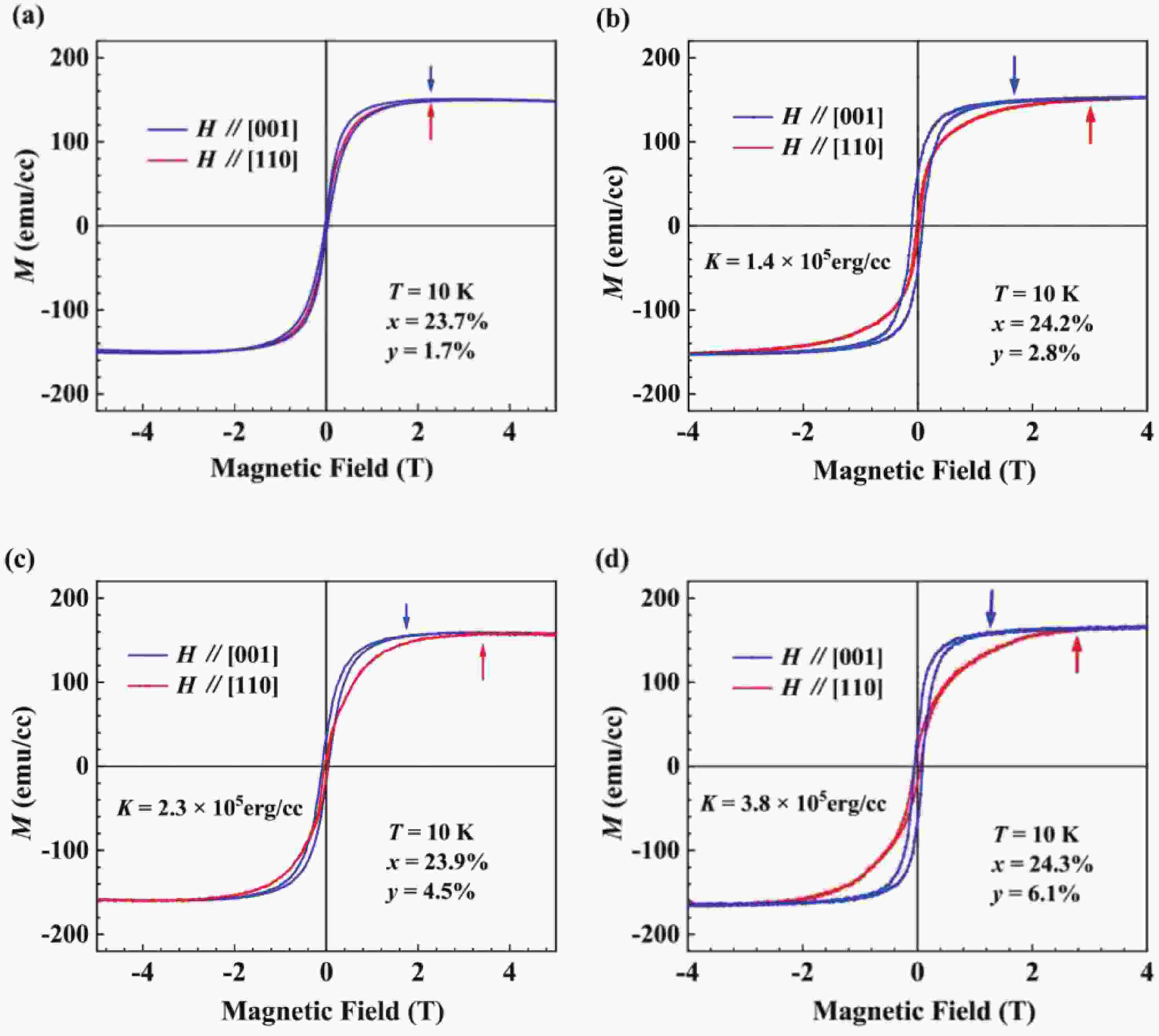
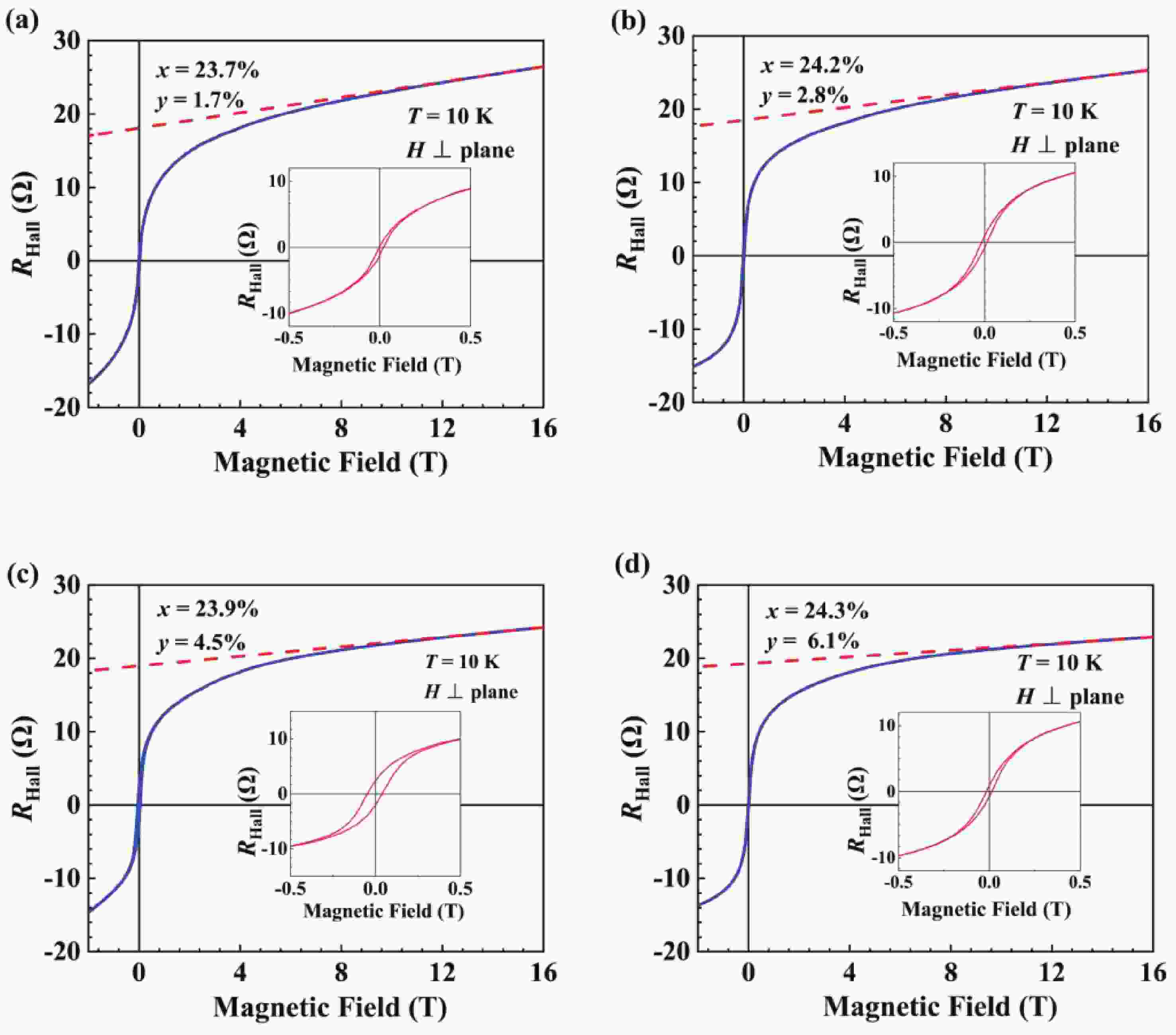
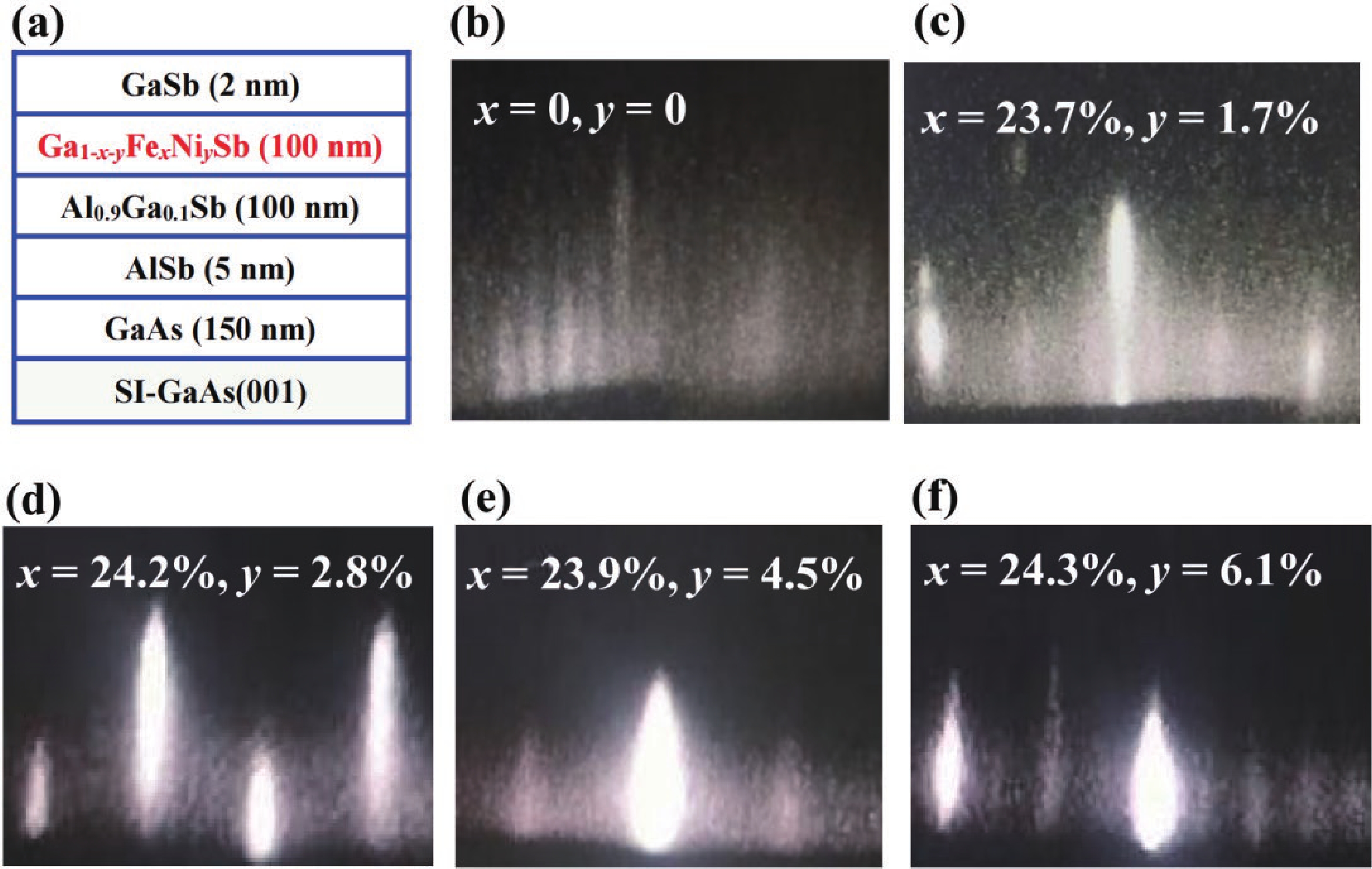
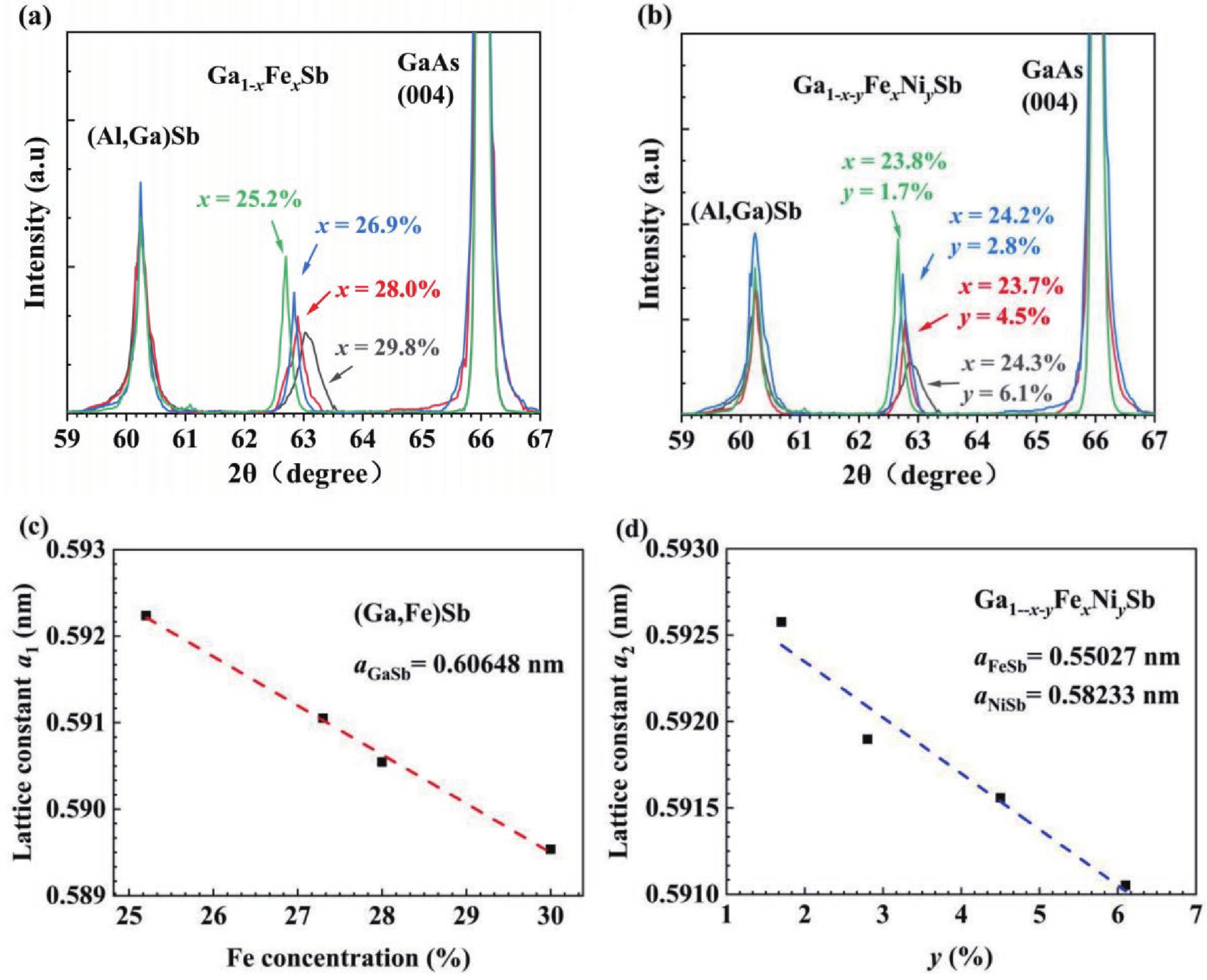
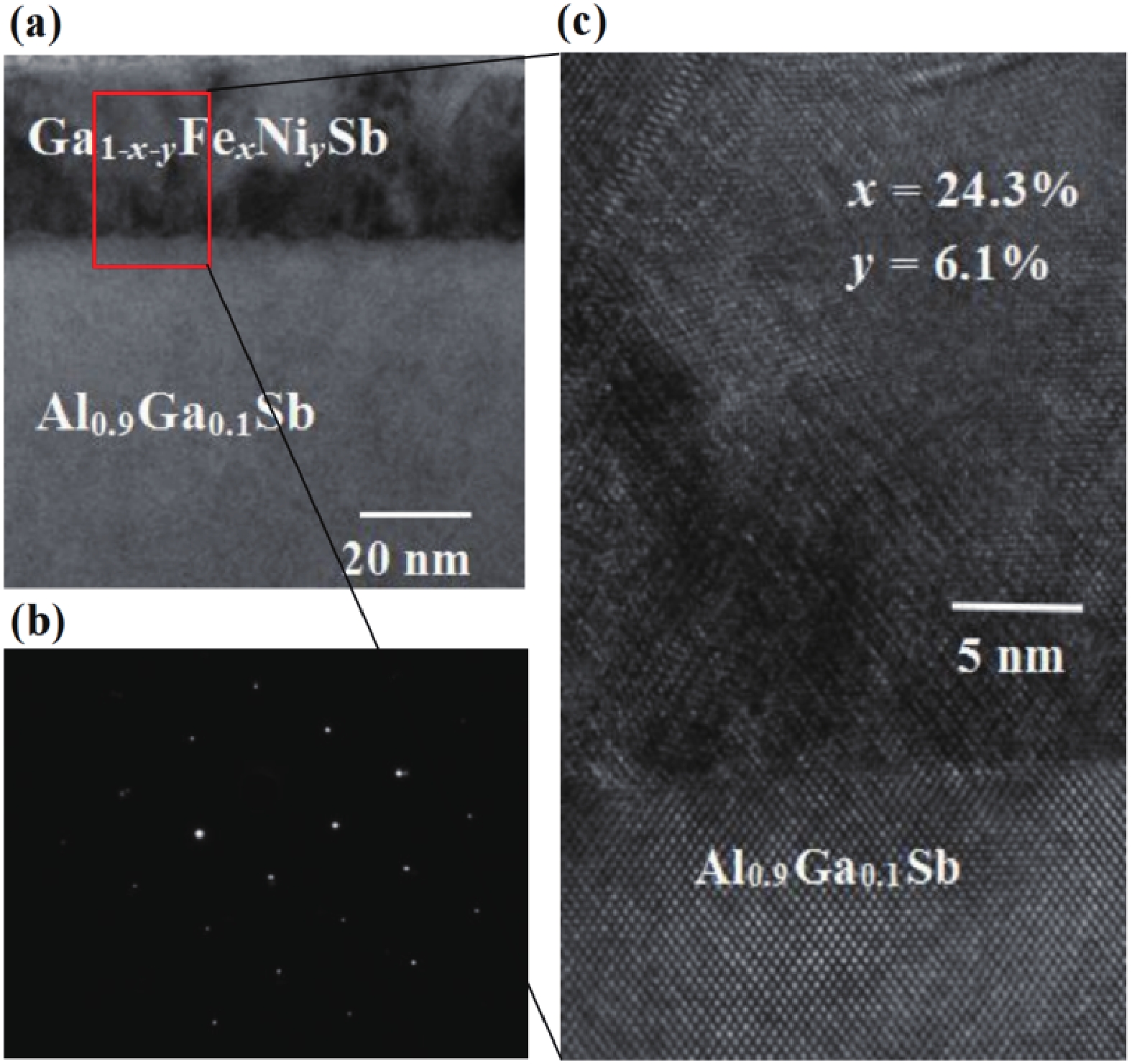
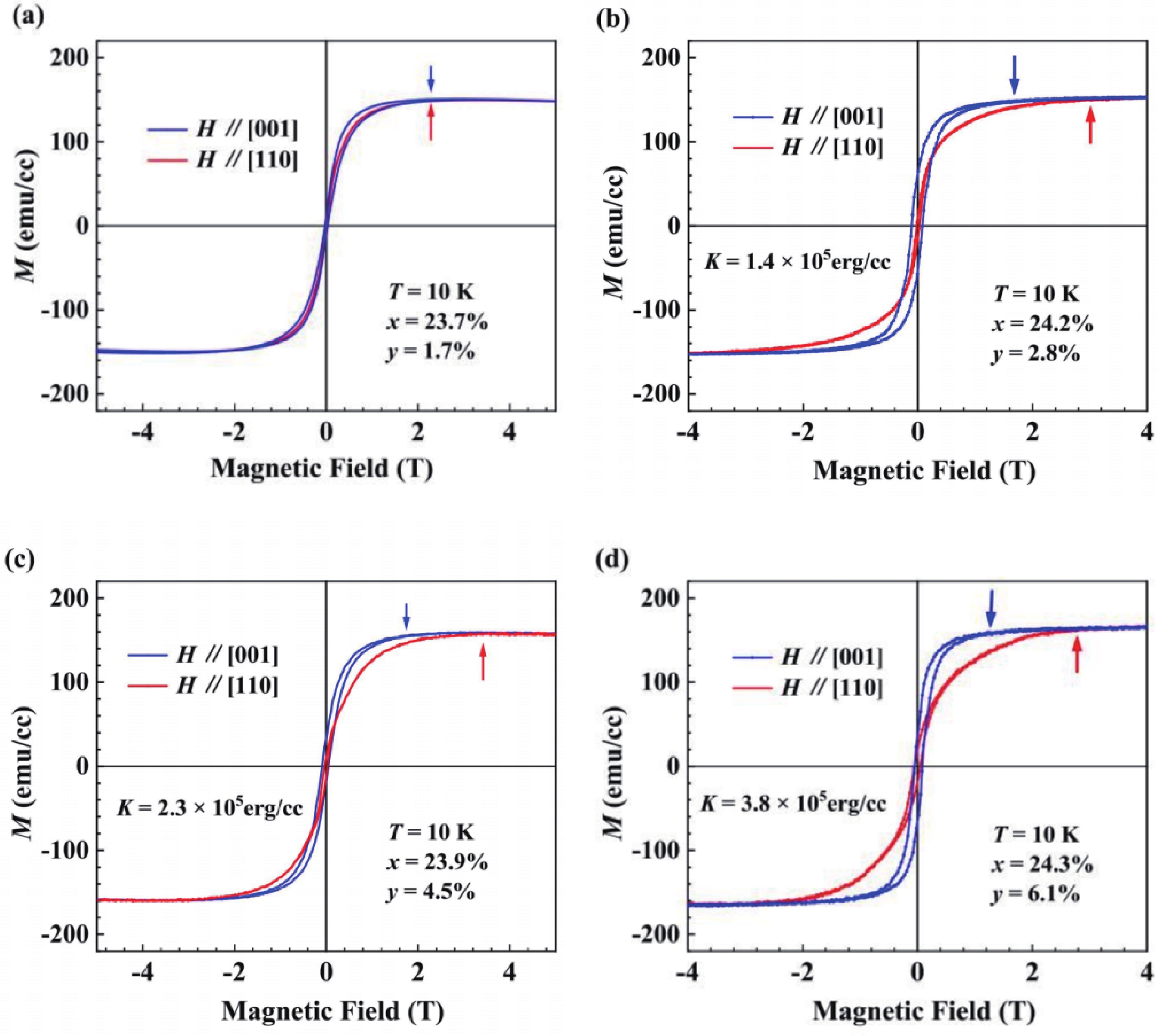
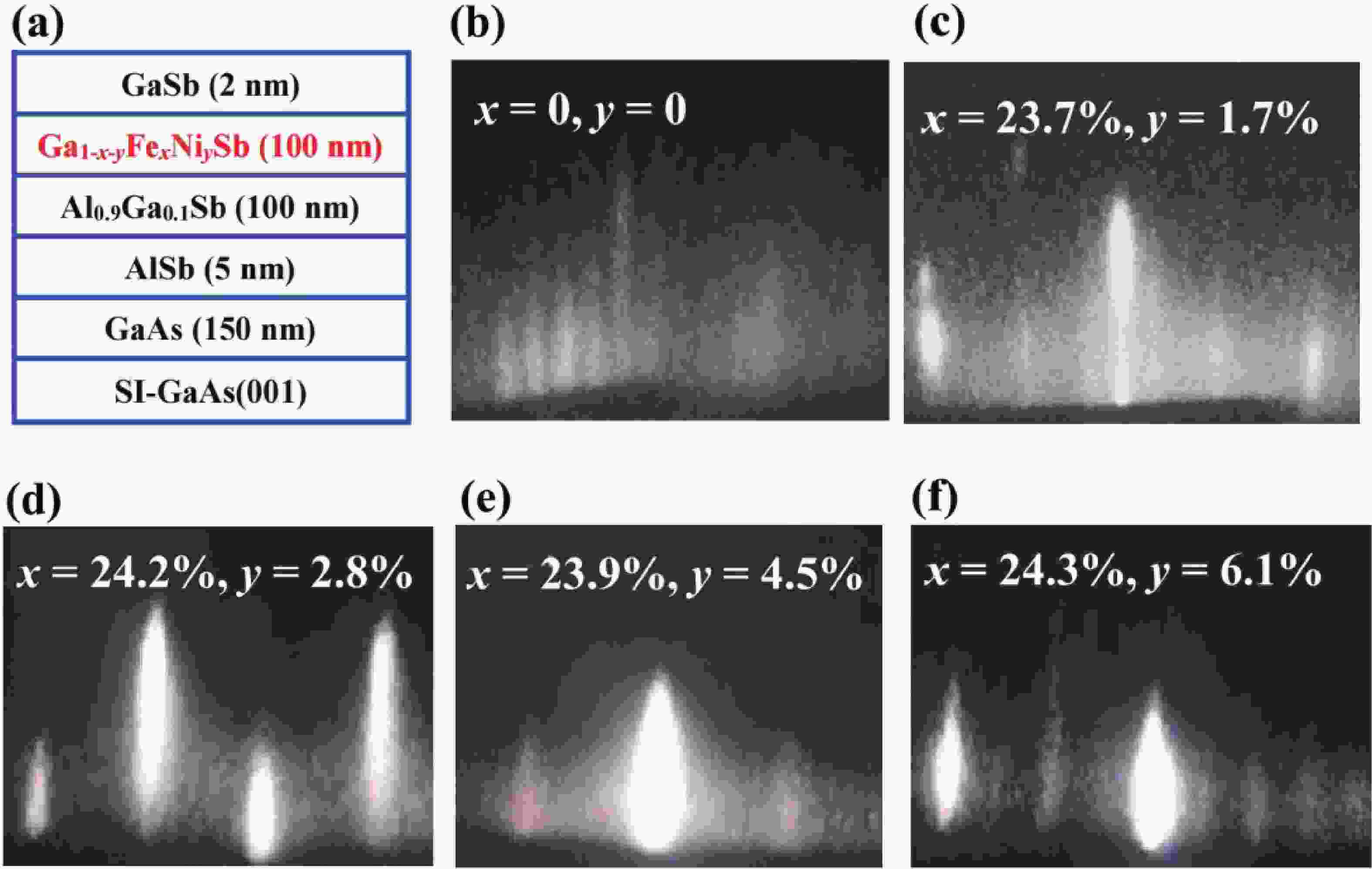
(Ga,Fe)Sb is a promising magnetic semiconductor (MS) for spintronic applications because its Curie temperature (TC) is above 300 K when the Fe concentration is higher than 20%. However, the anisotropy constant Ku of (Ga,Fe)Sb is below 7.6 × 103 erg/cm3 when Fe concentration is lower than 30%, which is one order of magnitude lower than that of (Ga,Mn)As. To address this issue, we grew Ga1-x-yFexNiySb films with almost the same x (≈24%) and different y to characterize their magnetic and electrical transport properties. We found that the magnetic anisotropy of Ga0.76-yFe0.24NiySb can be enhanced by increasing y, in which Ku is negligible at y = 1.7% but increases to 3.8 × 105 erg/cm3 at y = 6.1% (TC = 354 K). In addition, the hole mobility (µ) of Ga1-x-yFexNiySb reaches 31.3 cm2/(V∙s) at x = 23.7%, y = 1.7% (TC = 319 K), which is much higher than the mobility of Ga1-xFexSb at x = 25.2% (µ = 6.2 cm2/(V∙s)). Our results provide useful information for enhancing the magnetic anisotropy and hole mobility of (Ga,Fe)Sb by using Ni co-doping. -
References
[1] Ohno H. Making nonmagnetic semiconductors ferromagnetic. Science, 1998, 281, 951 doi: 10.1126/science.281.5379.951[2] Dietl T, Ohno H, Matsukura F, et al. Zener model description of ferromagnetism in zinc-blende magnetic semiconductors. Science, 2000, 287, 1019 doi: 10.1126/science.287.5455.1019[3] Chiba D, Sawicki M, Nishitani Y, et al. Magnetization vector manipulation by electric fields. Nature, 2008, 455, 515 doi: 10.1038/nature07318[4] Jungwirth T, Wunderlich J, Novák V, et al. Spin-dependent phenomena and device concepts explored in (Ga, Mn)As. Rev Mod Phys, 2014, 86, 855 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.86.855[5] Dietl T, Ohno H. Dilute ferromagnetic semiconductors: Physics and spintronic structures. Rev Mod Phys, 2014, 86, 187 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.86.187[6] Ohno H, Munekata H, Penney T, et al. Magnetotransport properties of p-type (In, Mn)As diluted magnetic III-V semiconductors. Phys Rev Lett, 1992, 68, 2664 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.68.2664[7] Koshihara S, Oiwa A, Hirasawa M, et al. Ferromagnetic order induced by photogenerated carriers in magnetic III-V semiconductor heterostructures of (In, Mn)As/GaSb. Phys Rev Lett, 1997, 78, 4617 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.4617[8] Akai H. Ferromagnetism and its stability in the diluted magnetic semiconductor (In, Mn)As. Phys Rev Lett, 1998, 81, 3002 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.81.3002[9] Oiwa A, Endo A, Katsumoto S, et al. Magnetic and transport properties of the ferromagnetic semiconductor heterostructures (In, Mn)As/(Ga, Al)Sb. Phys Rev B, 1999, 59, 5826 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.5826[10] Schallenberg T, Munekata H. Preparation of ferromagnetic (In, Mn)As with a high Curie temperature of 90K. Appl Phys Lett, 2006, 89, 042507 doi: 10.1063/1.2236210[11] Ohno H, Shen A, Matsukura F, et al. (Ga, Mn)As: A new diluted magnetic semiconductor based on GaAs. Appl Phys Lett, 1996, 69, 363 doi: 10.1063/1.118061[12] Matsukura F, Ohno H, Shen A, et al. Transport properties and origin of ferromagnetism in (Ga, Mn)As. Phys Rev B, 1998, 57, R2037 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.57.R2037[13] Chen L, Yang X, Yang F H, et al. Enhancing the curie temperature of ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga, Mn)As to 200 K via nanostructure engineering. Nano Lett, 2011, 11, 2584 doi: 10.1021/nl201187m[14] Wang H L, Ma J L, Zhao J H. Giant modulation of magnetism in (Ga, Mn)As ultrathin films via electric field. J Semicond, 2019, 40, 092501 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/9/092501[15] Wang H L, Ma J L, Wei Q Q, et al. Mn doping effects on the gate-tunable transport properties of Cd3As2 films epitaxied on GaAs. J Semicond, 2020, 41, 072903 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/7/072903[16] Tu N T, Hai P N, Anh L D, et al. (Ga, Fe)Sb: A p-type ferromagnetic semiconductor. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 105, 132402 doi: 10.1063/1.4896539[17] Tu N T, Hai P N, Anh L D, et al. Magnetic properties and intrinsic ferromagnetism in (Ga, Fe)Sb ferromagnetic semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 2015, 92, 144403 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.92.144403[18] Tu N T, Hai P N, Anh L D, et al. High-temperature ferromagnetism in heavily Fe-doped ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga, Fe)Sb. Appl Phys Lett, 2016, 108, 192401 doi: 10.1063/1.4948692[19] Goel S, Anh L D, Ohya S, et al. Ferromagnetic resonance and control of magnetic anisotropy by epitaxial strain in the ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga0.8, Fe0.2)Sb at room temperature. Phys Rev B, 2019, 99, 014431 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.99.014431[20] Goel S, Anh L D, Ohya S, et al. In-plane to perpendicular magnetic anisotropy switching in heavily-Fe-doped ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga, Fe)Sb with high Curie temperature. Phys Rev Materials , 2019, 084417 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevMaterials.3.084417[21] Tu N T, Hai P N, Anh L D, et al. High-temperature ferromagnetism in new n-type Fe-doped ferromagnetic semiconductor (In, Fe)Sb. Appl Phys Express, 2018, 11, 063005 doi: 10.7567/APEX.11.063005[22] Nguyen T T, Pham N, Le D, et al. Electrical control of ferromagnetism in the n-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In, Fe)Sb with high Curie temperature. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112, 122409 doi: 10.1063/1.5022828[23] Nguyen T T, Pham N H, Le D A, et al. Heavily Fe-doped n-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (In, Fe)Sb with high Curie temperature and large magnetic anisotropy. 2019 Compound Semiconductor Week (CSW), Nara, Japan, 2019, 1 doi: 10.1109/ICIPRM.2019.8819236[24] Sakamoto S, Tu N T, Takeda Y, et al. Electronic structure of the high-TC ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga, Fe)Sb: X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonance photoemission spectroscopy studies. Phys Rev B, 2019, 100, 035204 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.100.035204[25] Sriharsha K, Anh L D, Tu N T, et al. Magneto-optical spectra and the presence of an impurity band in p-type ferromagnetic semiconductor (Ga, Fe)Sb with high Curie temperature. APL Mater, 2019, 7, 021105 doi: 10.1063/1.5083175[26] Tanaka M. Recent progress in ferromagnetic semiconductors and spintronics devices. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2021, 60, 010101 doi: 10.35848/1347-4065/abcadc[27] Stefanowicz W, Śliwa C, Aleshkevych P, et al. Magnetic anisotropy of epitaxial (Ga, Mn)As on (113)A GaAs. Phys Rev B, 2010, 81, 155203 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.81.155203 -
Supplements
 Supplementary_Information-23080008.pdf
Supplementary_Information-23080008.pdf

-
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: