| Citation: |
Shunpeng Lu, Jiangxiao Bai, Hongbo Li, Ke Jiang, Jianwei Ben, Shanli Zhang, Zi-Hui Zhang, Xiaojuan Sun, Dabing Li. 240 nm AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet micro-LEDs: size effect versus edge effect[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(1): 012504. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/1/012504
S P Lu, J X Bai, H B Li, K Jiang, J W Ben, S L Zhang, Z H Zhang, X J Sun, D B Li. 240 nm AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet micro-LEDs: size effect versus edge effect[J]. J. Semicond, 2024, 45(1): 012504. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/1/012504
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
240 nm AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet micro-LEDs: size effect versus edge effect
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/1/012504
More Information-
Abstract
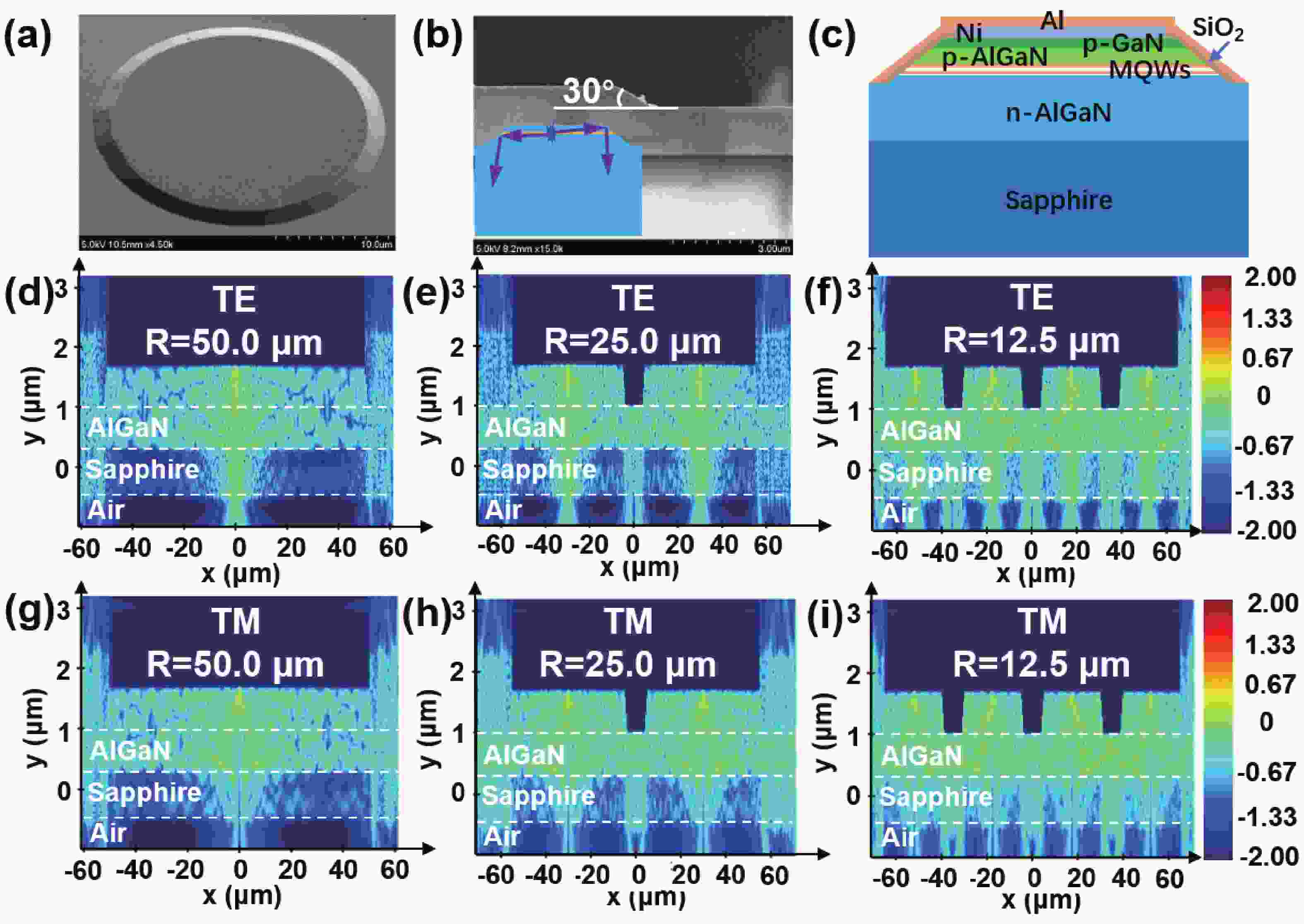
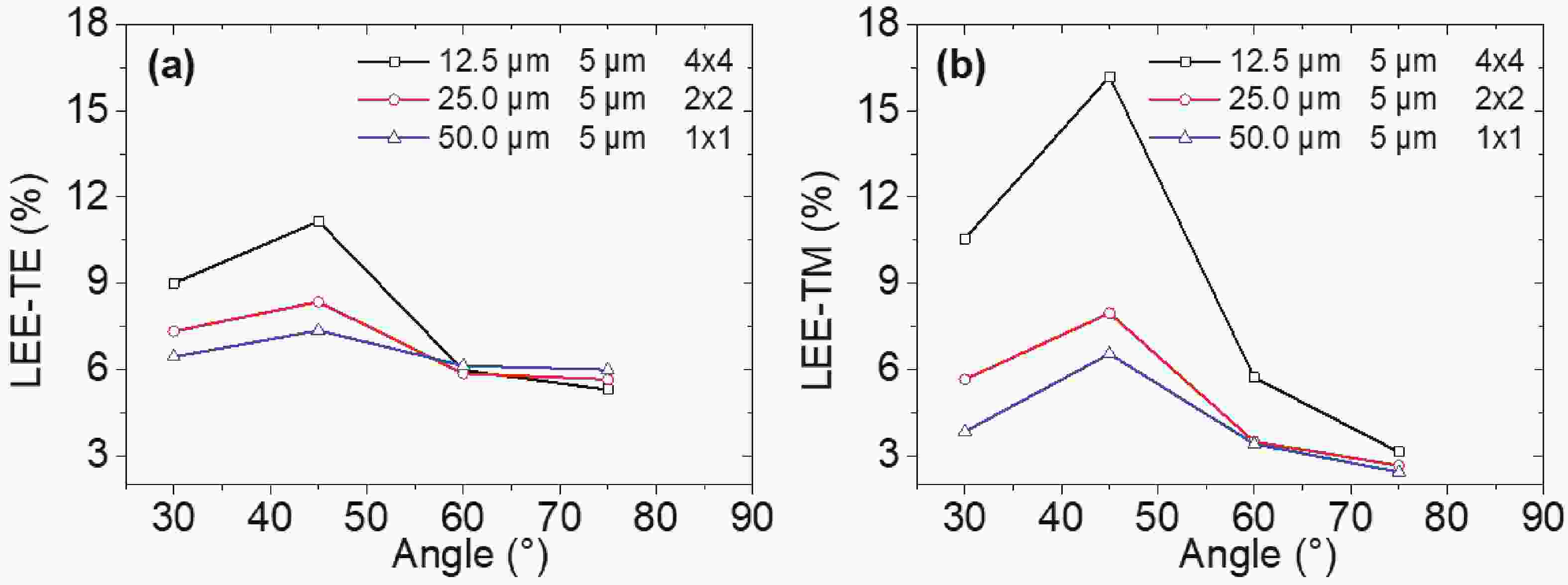
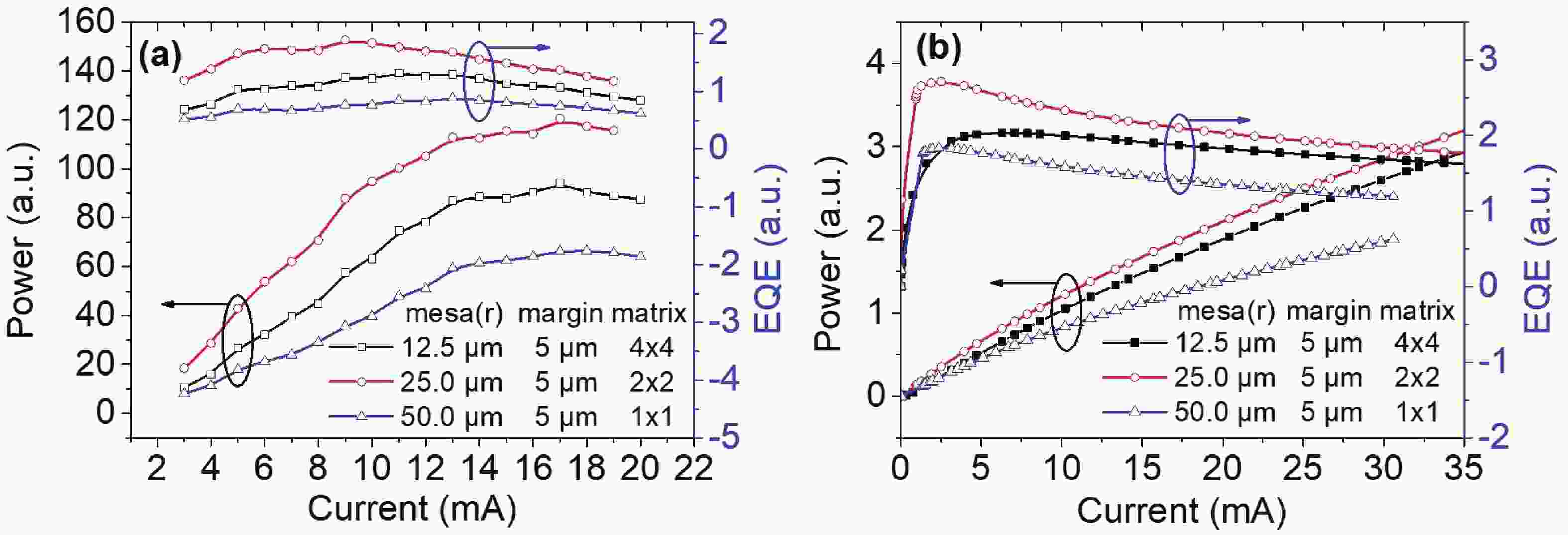
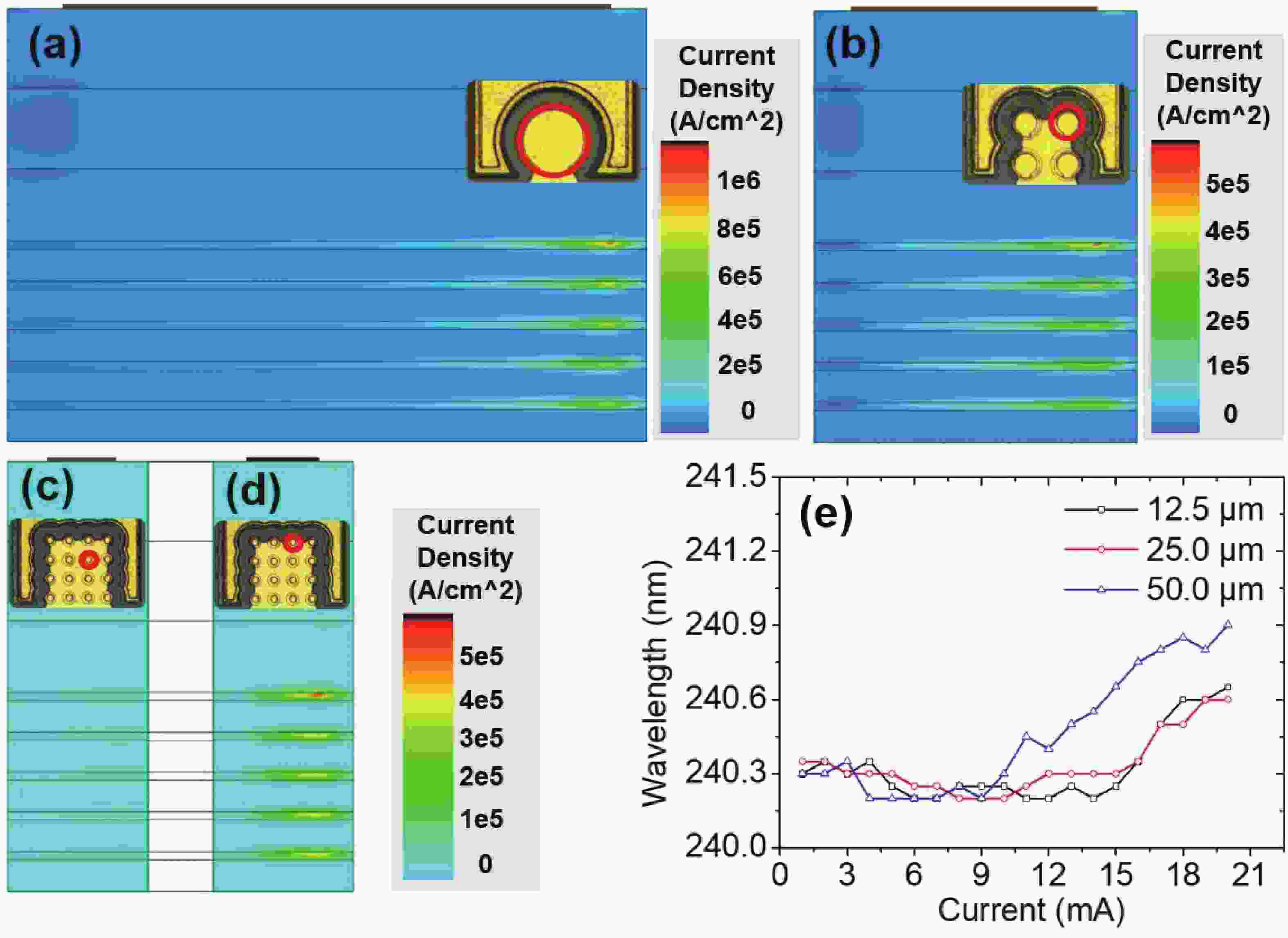
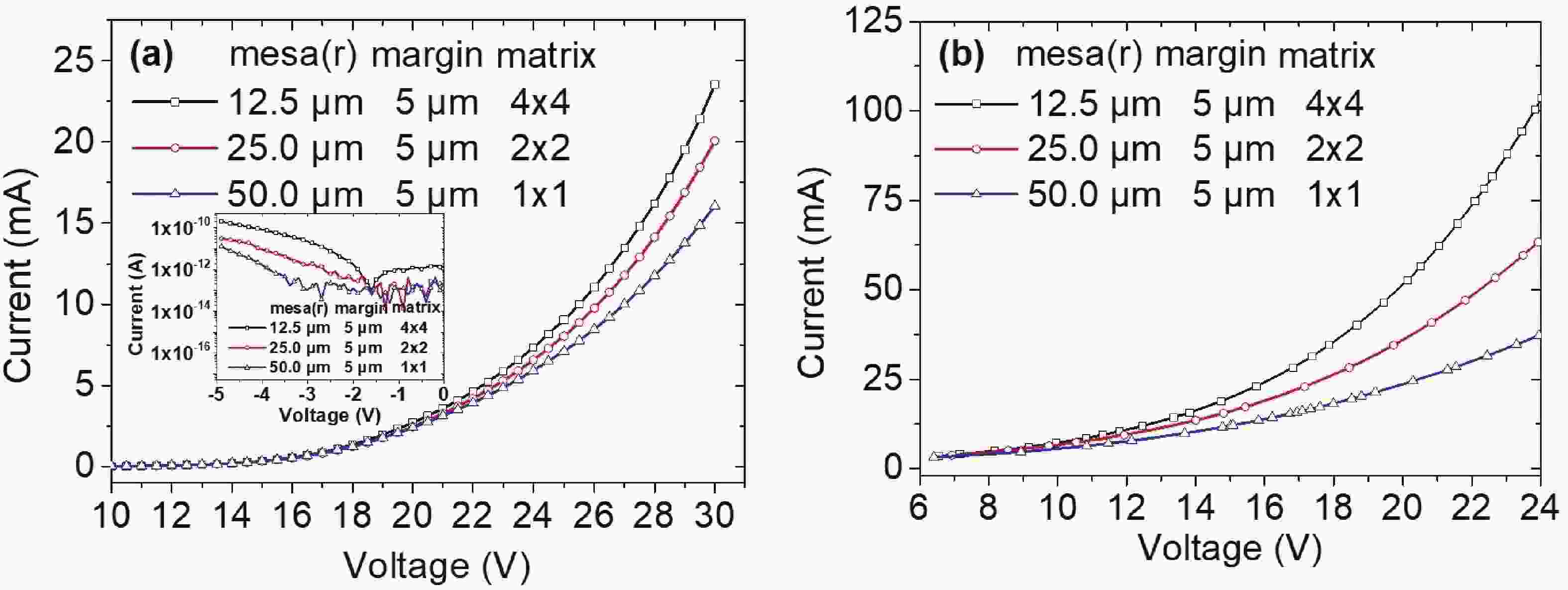
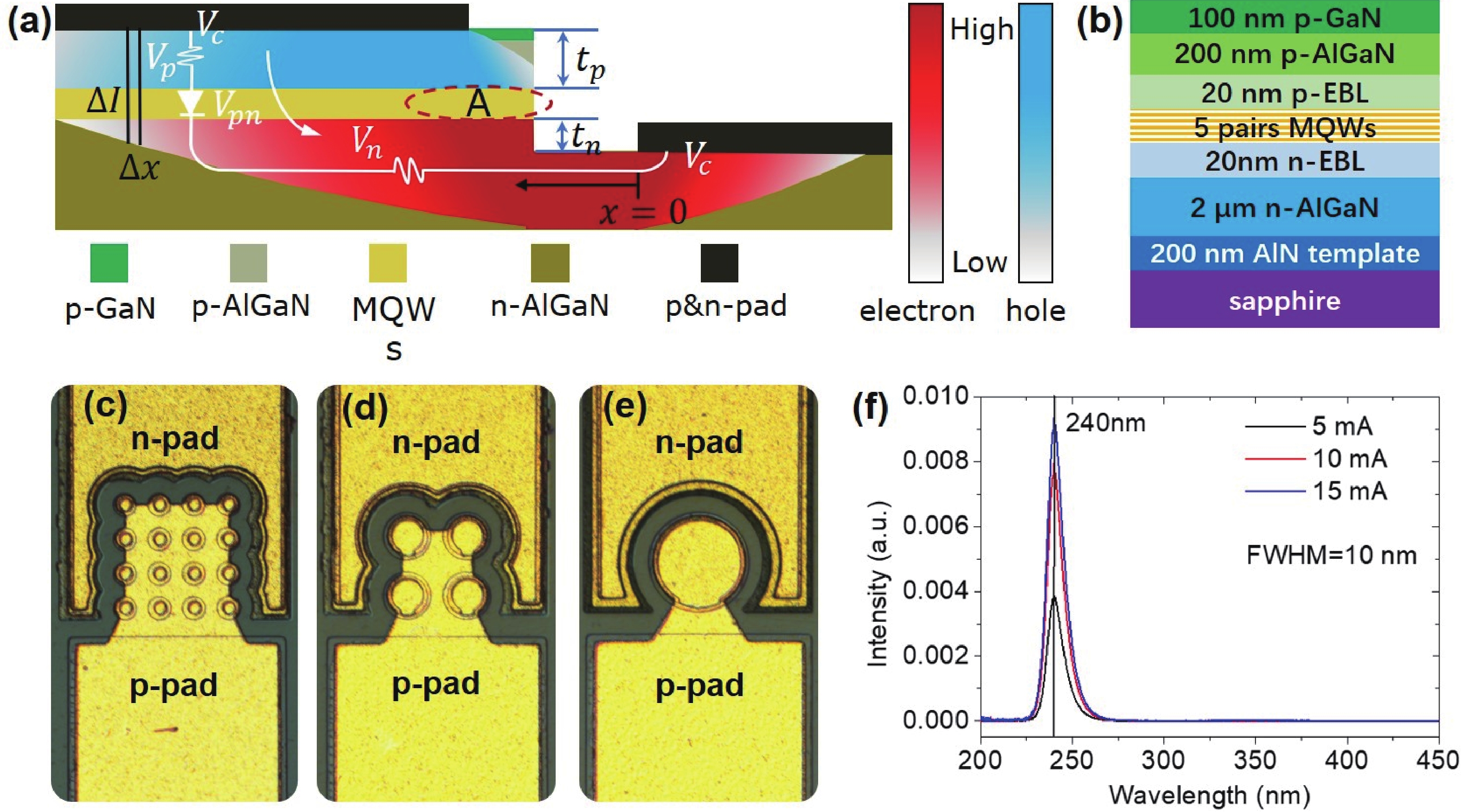
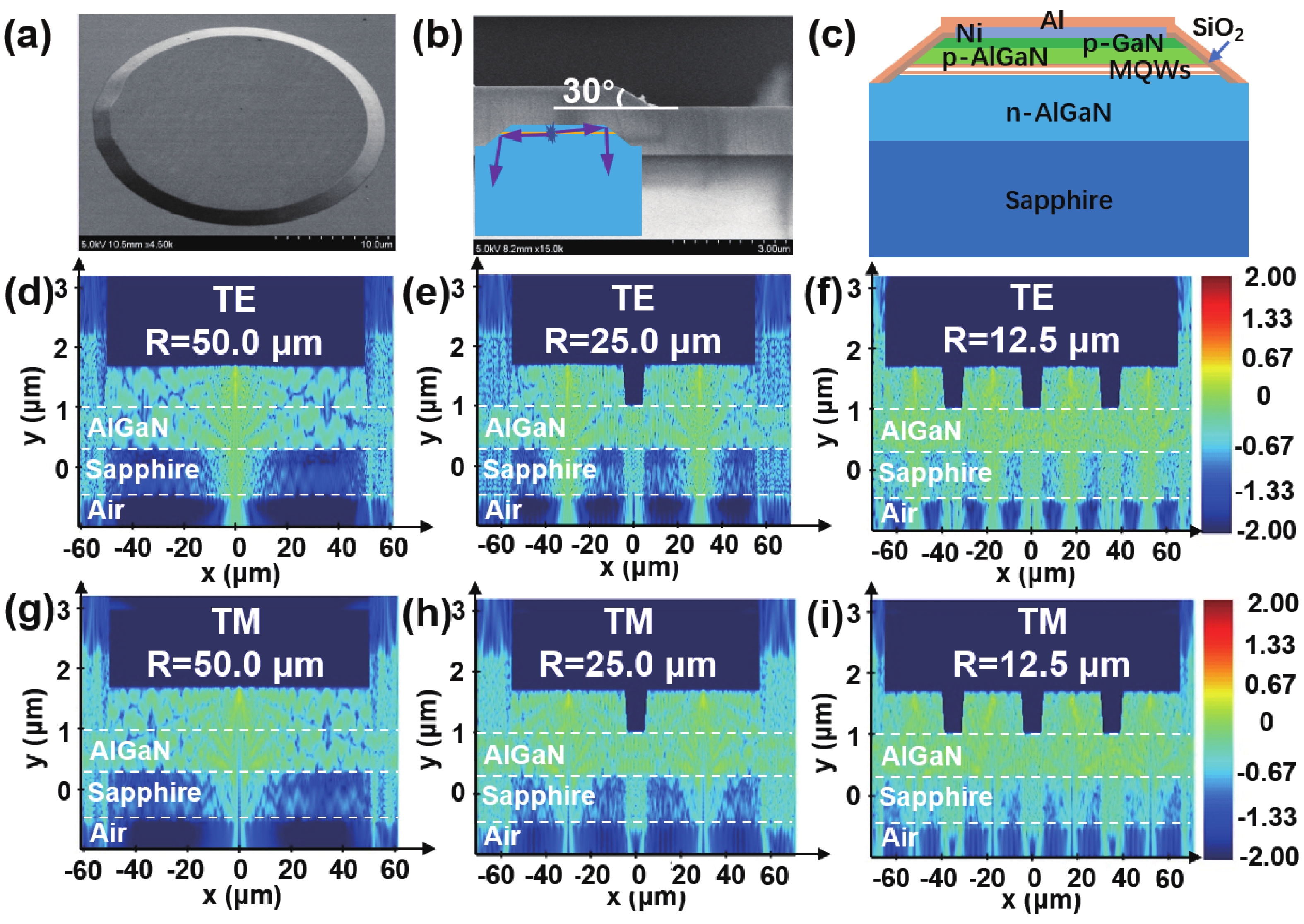
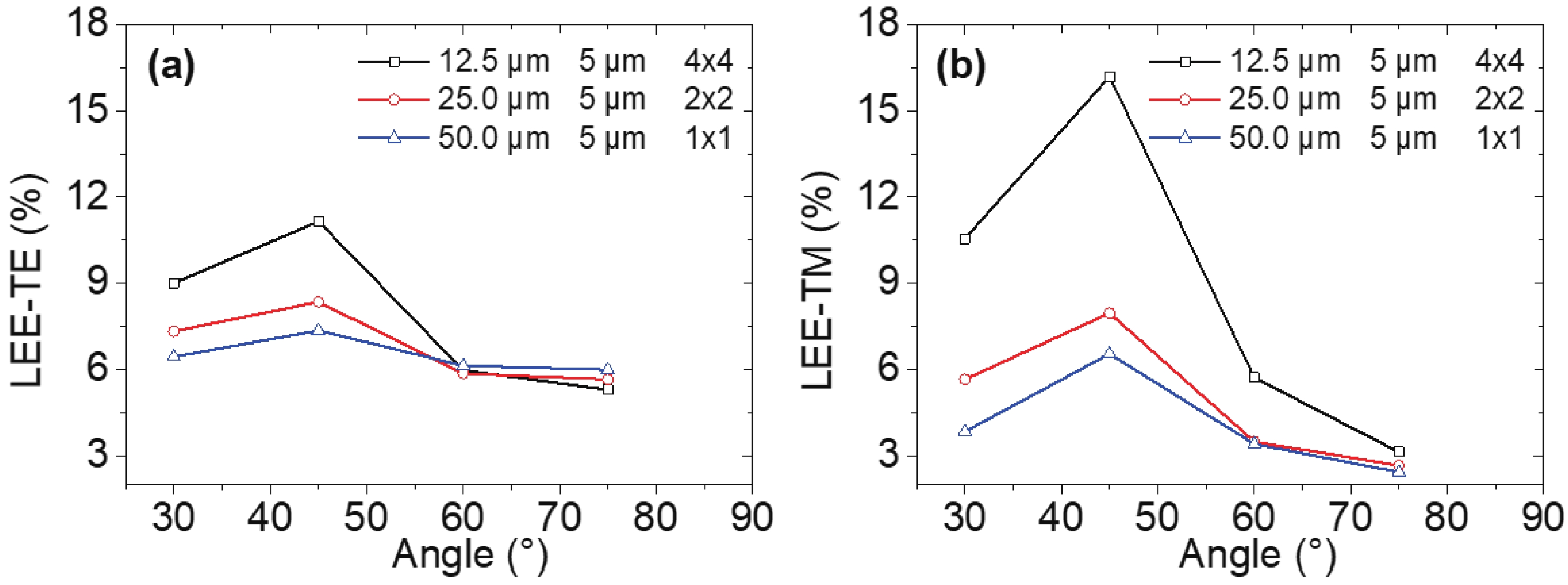
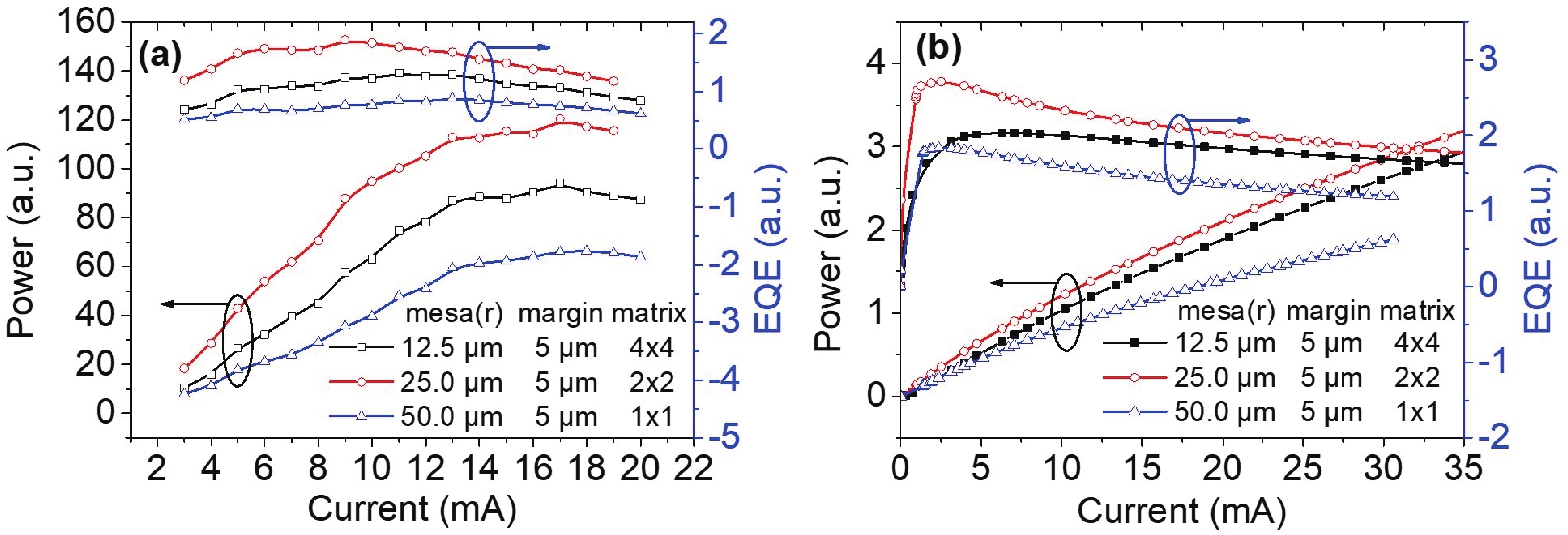
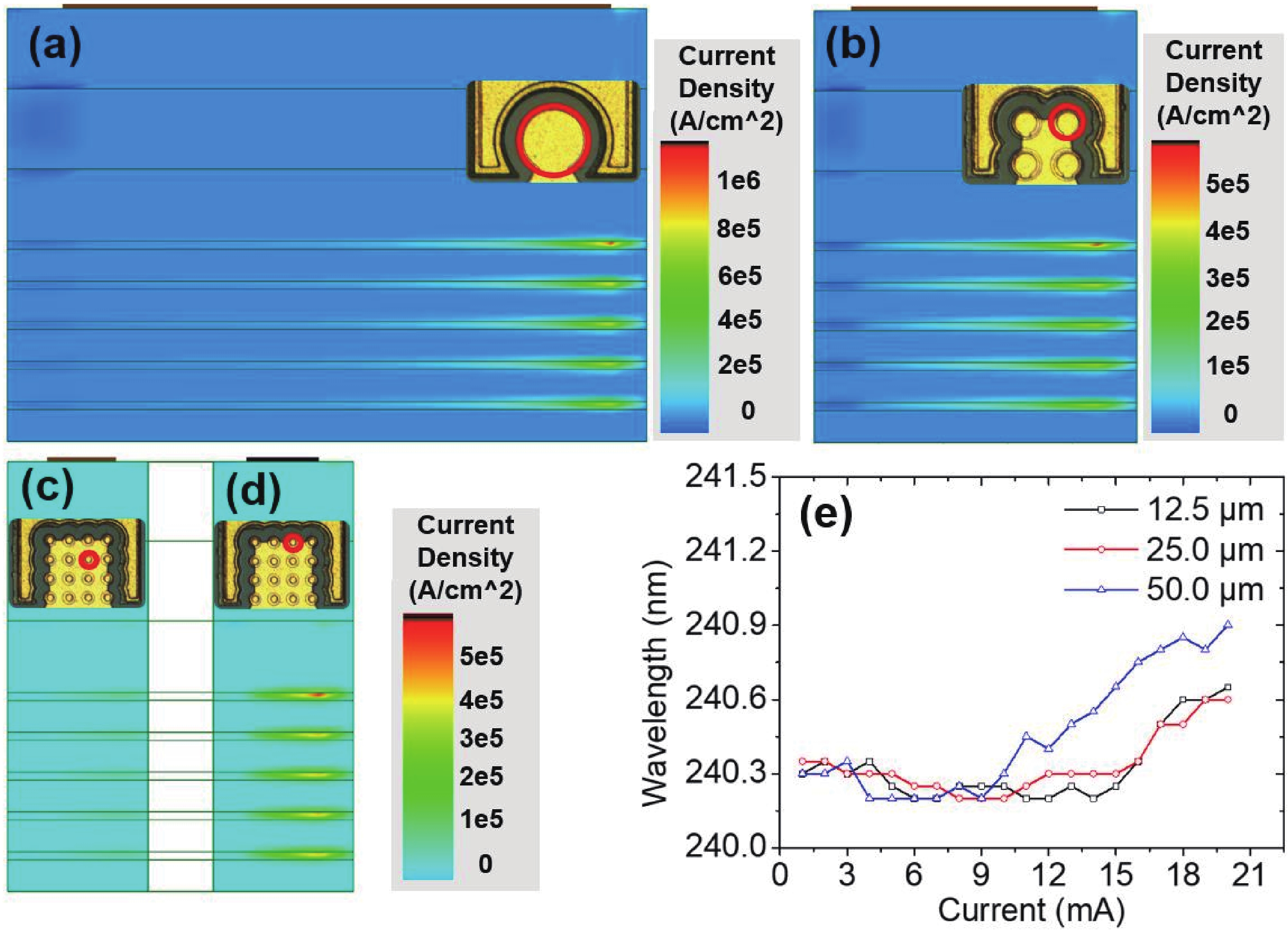
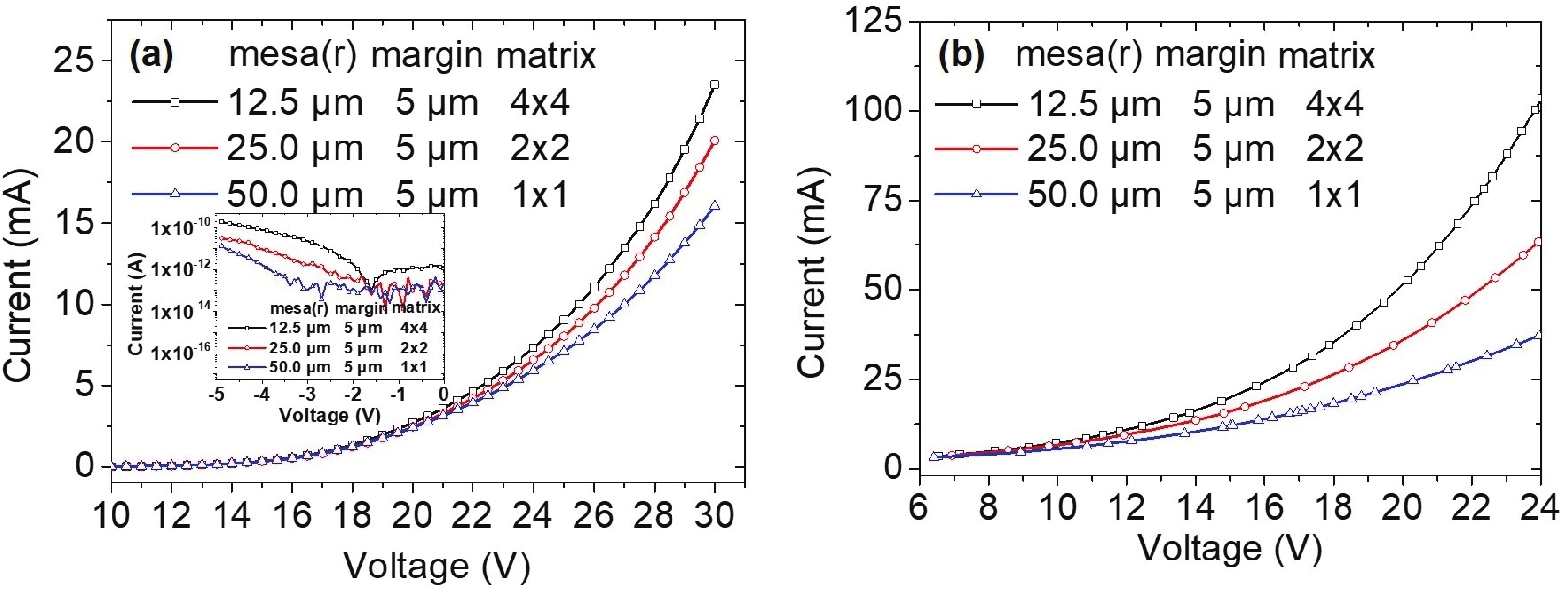
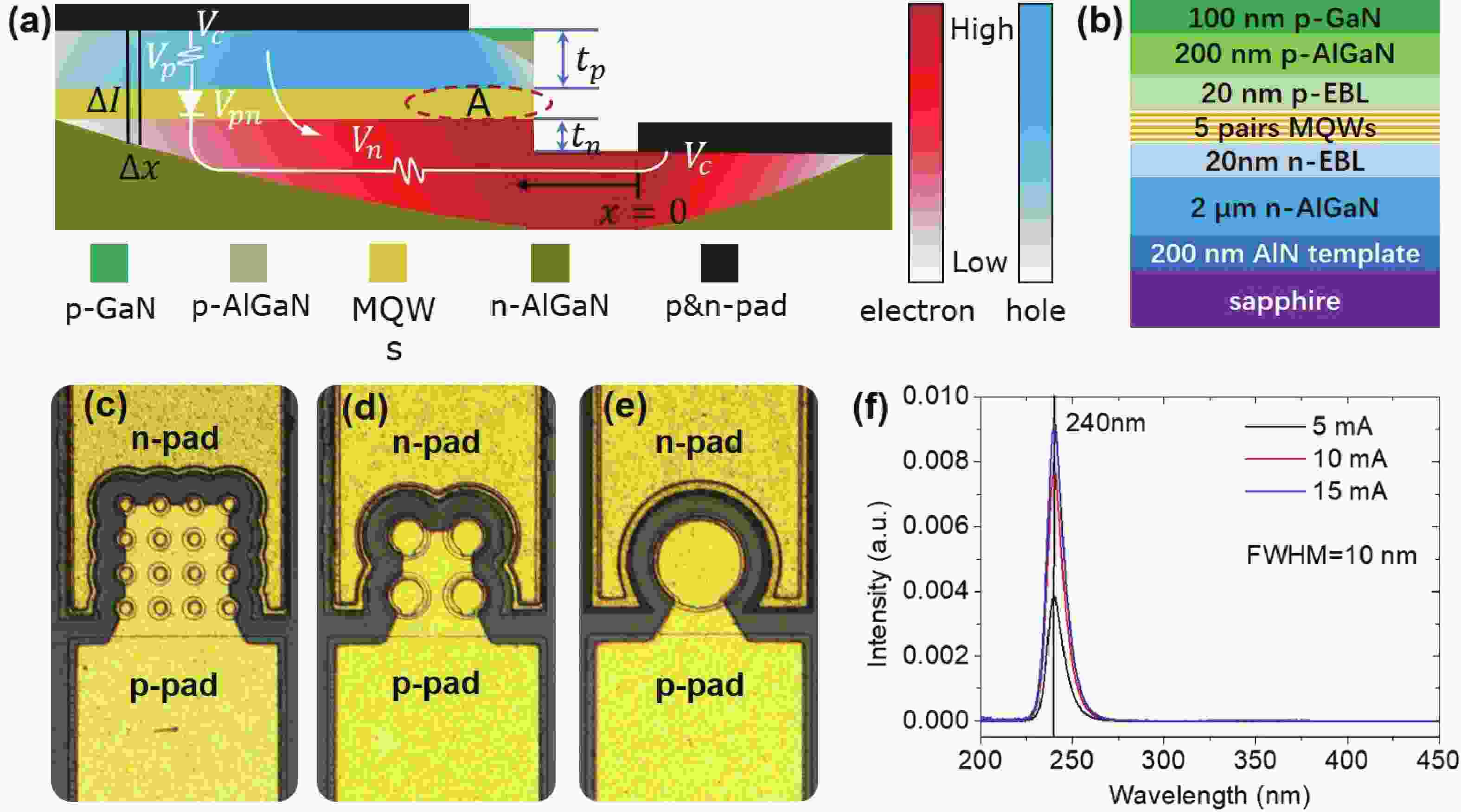
240 nm AlGaN-based micro-LEDs with different sizes are designed and fabricated. Then, the external quantum efficiency (EQE) and light extraction efficiency (LEE) are systematically investigated by comparing size and edge effects. Here, it is revealed that the peak optical output power increases by 81.83% with the size shrinking from 50.0 to 25.0 μm. Thereinto, the LEE increases by 26.21% and the LEE enhancement mainly comes from the sidewall light extraction. Most notably, transverse-magnetic (TM) mode light intensifies faster as the size shrinks due to the tilted mesa side-wall and Al reflector design. However, when it turns to 12.5 μm sized micro-LEDs, the output power is lower than 25.0 μm sized ones. The underlying mechanism is that even though protected by SiO2 passivation, the edge effect which leads to current leakage and Shockley-Read-Hall (SRH) recombination deteriorates rapidly with the size further shrinking. Moreover, the ratio of the p-contact area to mesa area is much lower, which deteriorates the p-type current spreading at the mesa edge. These findings show a role of thumb for the design of high efficiency micro-LEDs with wavelength below 250 nm, which will pave the way for wide applications of deep ultraviolet (DUV) micro-LEDs.-
Keywords:
- AlGaN,
- deep ultraviolet,
- micro-LEDs,
- light extraction efficiency,
- size effect,
- edge effect
-
References
[1] Jiang K, Sun X J, Shi Z M, et al. Quantum engineering of non-equilibrium efficient p-doping in ultra-wide band-gap nitrides. Light, 2021, 10, 69 doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00503-y[2] Khan A, Balakrishnan K, Katona T. Ultraviolet light-emitting diodes based on group three nitrides. Nat Photonics, 2008, 2, 77 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.293[3] Li D B, Jiang K, Sun X J, et al. AlGaN photonics: Recent advances in materials and ultraviolet devices. Adv Opt Photon, 2018, 10, 43 doi: 10.1364/AOP.10.000043[4] Kim D Y, Park J H, Lee J W, et al. Overcoming the fundamental light-extraction efficiency limitations of deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes by utilizing transverse-magnetic-dominant emission. Light, 2015, 4, e263 doi: 10.1038/lsa.2015.36[5] Wang P, Pandey A, Gim J, et al. Graphene-assisted molecular beam epitaxy of AlN for AlGaN deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2020, 116, 171905 doi: 10.1063/1.5144906[6] Yu H B, Memon M H, Jia H F, et al. A 10 × 10 deep ultraviolet light-emitting micro-LED array. J Semicond, 2022, 43, 062801 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/6/062801[7] Guo L A, Guo Y N, Wang J X, et al. Ultraviolet communication technique and its application. J Semicond, 2021, 42, 081801 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/8/081801[8] Luo W, Li T, Li Y D, et al. Watts-level ultraviolet-C LED integrated light sources for efficient surface and air sterilization. J Semicond, 2022, 43, 072301 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/43/7/072301[9] Buonanno M, Welch D, Shuryak I, et al. Far-UVC light (222 nm) efficiently and safely inactivates airborne human coronaviruses. Sci Rep, 2020, 10, 10285 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67211-2[10] Lobo-Ploch N, Mehnke F, Sulmoni L, et al. Milliwatt power 233 nm AlGaN-based deep UV-LEDs on sapphire substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2020, 117, 111102 doi: 10.1063/5.0015263[11] Raeiszadeh M, Adeli B. A critical review on ultraviolet disinfection systems against COVID-19 outbreak: Applicability, validation, and safety considerations. ACS Photonics, 2020, 7, 2941 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01245[12] Lu S P, Zhang Y P, Zhang Z H, et al. High-performance triangular miniaturized-LEDs for high current and power density applications. ACS Photonics, 2021, 8, 2304 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.1c00430[13] Hao G D, Taniguchi M, Tamari N, et al. Current crowding and self-heating effects in AlGaN-based flip-chip deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. J Phys D:Appl Phys, 2018, 51, 035103 doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa9e0e[14] McKendry J J D, Massoubre D, Zhang S L, et al. Visible-light communications using a CMOS-controlled micro-light- emitting-diode array. J Light Technol, 2012, 30, 61 doi: 10.1109/JLT.2011.2175090[15] Gong Z, Jin S R, Chen Y J, et al. Size-dependent light output, spectral shift, and self-heating of 400 nm InGaN light-emitting diodes. J Appl Phys, 2010, 107, 013103 doi: 10.1063/1.3276156[16] Xiao S D, Yu H B, Memon M H, et al. In-depth investigation of deep ultraviolet MicroLED geometry for enhanced performance. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2023, 44, 1520 doi: 10.1109/LED.2023.3294819[17] Yu H B, Memon M H, Wang D H, et al. AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet micro-LED emitting at 275 nm. Opt Lett, 2021, 46, 3271 doi: 10.1364/OL.431933[18] Shatalov M, Simin G, Adivarahan V, et al. Lateral Current crowding in deep UV light emitting diodes over sapphire substrates. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2002, 41, 5083 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.41.5083[19] Lin R H, Galan S V, Sun H D, et al. Tapering-induced enhancement of light extraction efficiency of nanowire deep ultraviolet LED by theoretical simulations. Photon Res, 2018, 6, 457 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.6.000457[20] Zhang G, Shao H, Zhang M Y, et al. Enhancing the light extraction efficiency for AlGaN-based DUV LEDs with a laterally over-etched p-GaN layer at the top of truncated cones. Opt Express, 2021, 29, 30532 doi: 10.1364/OE.435302[21] Zheng Y X, Zhang Y H, Zhang J, et al. Effects of meshed p-type contact structure on the light extraction effect for deep ultraviolet flip-chip light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2019, 14, 149 doi: 10.1186/s11671-019-2984-0[22] Tian M, Yu H B, Memon M H, et al. Enhanced light extraction of the deep-ultraviolet micro-LED via rational design of chip sidewall. Opt Lett, 2021, 46, 4809 doi: 10.1364/OL.441285[23] Chen Y F, Che J M, Chu C S, et al. Balanced resistivity in n-AlGaN layer to increase the current uniformity for AlGaN-based DUV LEDs. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2022, 34, 1065 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2022.3200460[24] Kuo Y K, Chang J Y, Chen F M, et al. Numerical investigation on the carrier transport characteristics of AlGaN deep-UV light-emitting diodes. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2016, 52, 1 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2016.2535252[25] Piprek J. Efficiency droop in nitride-based light-emitting diodes. Phys Stat Sol (a), 2010, 207, 2217 doi: 10.1002/pssa.201026149[26] Zhang M Y, Hang S, Chu C S, et al. A buried high k insulator for suppressing the surface recombination for GaN-based micro-light-emitting diodes. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2022, 69, 3213 doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3164638[27] Zhang Z H, Tian K K, Chu C S, et al. Establishment of the relationship between the electron energy and the electron injection for AlGaN based ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Opt Express, 2018, 26, 17977 doi: 10.1364/OE.26.017977[28] Zhang Z H, Huang Chen S W, Zhang Y H, et al. Hole transport manipulation to improve the hole injection for deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. ACS Photonics, 2017, 4, 1846 doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b00443[29] Ryu H Y, Choi I G, Choi H S, et al. Investigation of light extraction efficiency in AlGaN deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Express, 2013, 6, 062101 doi: 10.7567/APEX.6.062101[30] Vurgaftman I, Meyer J R. Band parameters for nitrogen-containing semiconductors. J Appl Phys, 2003, 94, 3675 doi: 10.1063/1.1600519[31] Guttmann M, Mehnke F, Belde B, et al. Optical light polarization and light extraction efficiency of AlGaN-based LEDs emitting between 264 and 220nm. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2019, 58, SCCB20 doi: 10.7567/1347-4065/ab0d09[32] Masui H, Sonoda J, Pfaff N, et al. Quantum-confined Stark effect on photoluminescence and electroluminescence characteristics of InGaN-based light-emitting diodes. J Phys D:Appl Phys, 2008, 41, 165105 doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/41/16/165105[33] Chhajed S, Xi Y, Gessmann T, et al. Junction temperature in light-emitting diodes assessed by different methods. Integrated Optoelectronic Devices 2005 (SPIE, 2005), 2005, 5739[34] Che J M, Chu C S, Tian K K, et al. On the p-AlGaN/n-AlGaN/p-AlGaN current spreading layer for AlGaN-based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2018, 13, 355 doi: 10.1186/s11671-018-2776-y[35] Wang W D, Chu C S, Che J M, et al. Is a thin p-GaN layer possible for making high-efficiency AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes? Opt Express, 2021, 29, 29651 doi: 10.1364/OE.434636[36] Zhang Y P, Zhang Z H, Liu W, et al. Nonradiative recombination—Critical in choosing quantum well number for InGaN/GaN light-emitting diodes. Opt Express, 2014, 23, A31 doi: 10.1364/OE.23.000A34[37] Lu S P, Liu W, Zhang Z H, et al. Low thermal-mass LEDs: Size effect and limits. Opt Express, 2014, 22, 32200 doi: 10.1364/OE.22.032200 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: