| Citation: |
Jiaming Wang, Fujun Xu, Lisheng Zhang, Jing Lang, Xuzhou Fang, Ziyao Zhang, Xueqi Guo, Chen Ji, Chengzhi Ji, Fuyun Tan, Xuelin Yang, Xiangning Kang, Zhixin Qin, Ning Tang, Xinqiang Wang, Weikun Ge, Bo Shen. Progress in efficient doping of Al-rich AlGaN[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(2): 021501. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/2/021501
J M Wang, F J Xu, L S Zhang, J Lang, X Z Fang, Z Y Zhang, X Q Guo, C Ji, C Z Ji, F Y Tan, X L Yang, X N Kang, Z X Qin, N Tang, X Q Wang, W K Ge, B Shen. Progress in efficient doping of Al-rich AlGaN[J]. J. Semicond, 2024, 45(2): 021501. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/2/021501
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
-
Abstract
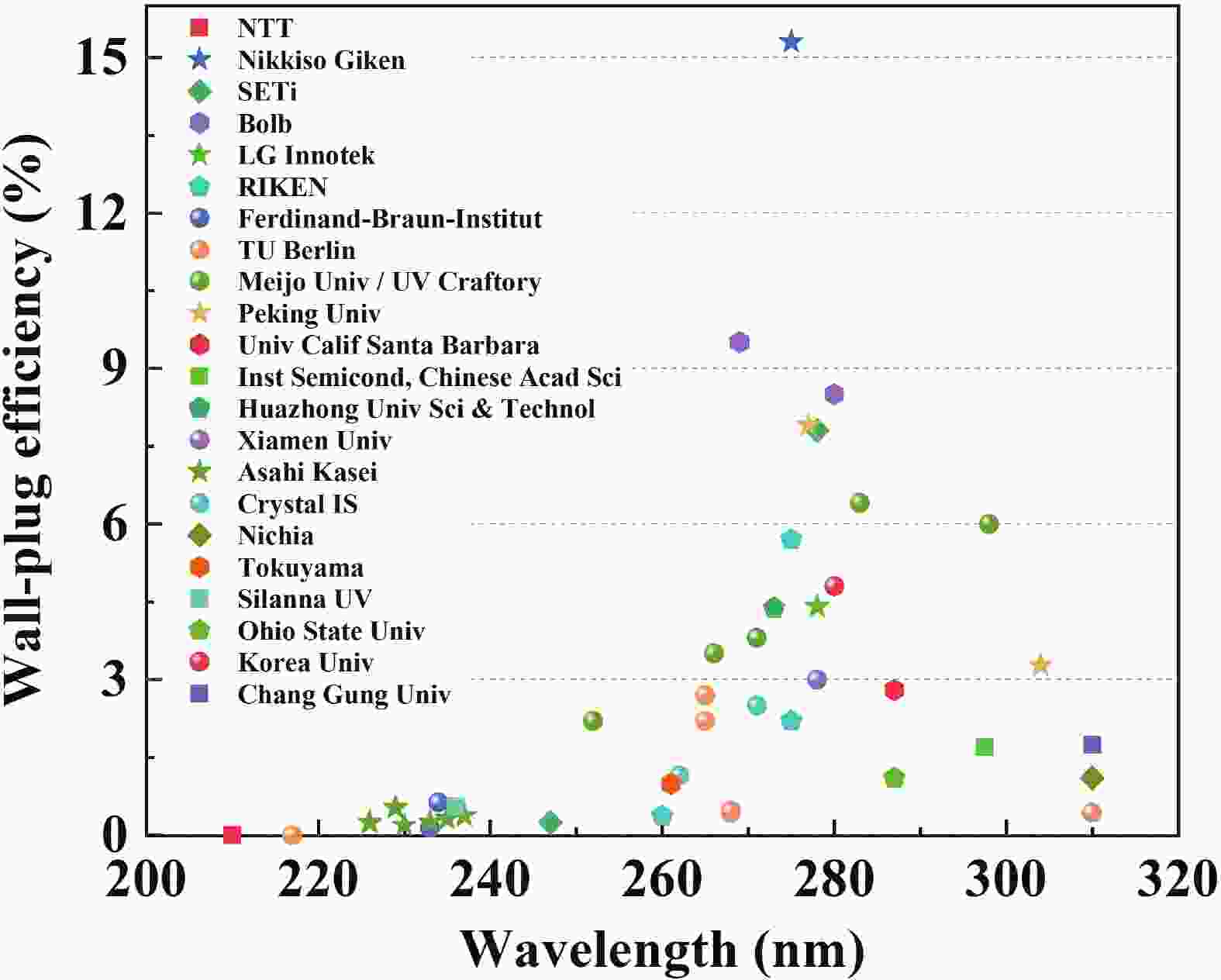
The development of semiconductors is always accompanied by the progress in controllable doping techniques. Taking AlGaN-based ultraviolet (UV) emitters as an example, despite a peak wall-plug efficiency of 15.3% at the wavelength of 275 nm, there is still a huge gap in comparison with GaN-based visible light-emitting diodes (LEDs), mainly attributed to the inefficient doping of AlGaN with increase of the Al composition. First, p-doping of Al-rich AlGaN is a long-standing challenge and the low hole concentration seriously restricts the carrier injection efficiency. Although p-GaN cladding layers are widely adopted as a compromise, the high injection barrier of holes as well as the inevitable loss of light extraction cannot be neglected. While in terms of n-doping the main issue is the degradation of the electrical property when the Al composition exceeds 80%, resulting in a low electrical efficiency in sub-250 nm UV-LEDs. This review summarizes the recent advances and outlines the major challenges in the efficient doping of Al-rich AlGaN, meanwhile the corresponding approaches pursued to overcome the doping issues are discussed in detail.-
Keywords:
- AlGaN-based UV-LEDs,
- Al-rich AlGaN,
- doping
-
References
[1] Nakamura S, Mukai T, Senoh M. Candela-class high-brightness InGaN/AlGaN double-heterostructure blue-light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 1994, 64, 1687 doi: 10.1063/1.111832[2] Ponce F A, Bour D P. Nitride-based semiconductors for blue and green light-emitting devices. Nature, 1997, 386, 351 doi: 10.1038/386351a0[3] Nakamura S, Senoh M, Nagahama S I, et al. InGaN-based multi-quantum-well-structure laser diodes. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1996, 35, L74 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.35.L74[4] Sun Y, Zhou K, Sun Q, et al. Room-temperature continuous-wave electrically injected InGaN-based laser directly grown on Si. Nat Photonics, 2016, 10, 595 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.158[5] Michel J, Liu J F, Kimerling L C. High-performance Ge-on-Si photodetectors. Nat Photonics, 2010, 4, 527 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.157[6] Parish G, Keller S, Kozodoy P, et al. High-performance (Al, Ga)N-based solar-blind ultraviolet p–i–n detectors on laterally epitaxially overgrown GaN. Appl Phys Lett, 1999, 75, 247 doi: 10.1063/1.124337[7] Amano H, Kito M, Hiramatsu K, et al. P-type conduction in Mg-doped GaN treated with low-energy electron beam irradiation (LEEBI). Jpn J Appl Phys, 1989, 28, L2112 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.28.L2112[8] Nakamura S, Mukai T, Senoh M, et al. Thermal annealing effects on P-type Mg-doped GaN films. Jpn J Appl Phys, 1992, 31, L139 doi: 10.1143/JJAP.31.L139[9] Taniyasu Y, Kasu M, Makimoto T. An aluminium nitride light-emitting diode with a wavelength of 210 nanometres. Nature, 2006, 441, 325 doi: 10.1038/nature04760[10] Khan A, Balakrishnan K, Katona T. Ultraviolet light-emitting diodes based on group three nitrides. Nat Photonics, 2008, 2, 77 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2007.293[11] Kneissl M, Seong T Y, Han J, et al. The emergence and prospects of deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diode technologies. Nat Photonics, 2019, 13, 233 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0359-9[12] Zollner C J, DenBaars S P, Speck J S, et al. Germicidal ultraviolet LEDs: A review of applications and semiconductor technologies. Semicond Sci Technol, 2021, 36, 123001 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/ac27e7[13] Li D B, Jiang K, Sun X J, et al. AlGaN photonics: Recent advances in materials and ultraviolet devices. Adv Opt Photon, 2018, 10, 43 doi: 10.1364/AOP.10.000043[14] Yole Développement. UV LEDs and UV lamps–market and technology trends, 2021[15] United Nations. The Minamata Convention on Mercury, 2013[16] Matsukura Y, Inazu T, Pernot C, et al. Improving light output power of AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes by optimizing the optical thickness of p-layers. Appl Phys Express, 2021, 14, 084004 doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ac154c[17] Zhang J P, Gao Y, Zhou L, et al. Transparent deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes with a p-type AlN ohmic contact layer. Light-Emitting Devices, Materials, and Applications, San Francisco, USA, 2019, 10940 doi: 10.1117/12.2506918[18] Zhang J P, Gao Y, Zhou L, et al. Surface hole gas enabled transparent deep ultraviolet light-emitting diode. Semicond Sci Technol, 2018, 33, 07LT01 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/aac7c1[19] Takano T, Mino T, Jun S K, et al. Deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency higher than 20% at 275 nm achieved by improving light-extraction efficiency. Appl Phys Express, 2017, 10, 031002 doi: 10.7567/APEX.10.031002[20] Mino T, Hirayama H, Takano T, et al. Highly-uniform 260 nm-band AlGaN-based deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes developed by 2-inch × 3 MOVPE system. Phys Status Solidi C, 2012, 9, 749 doi: 10.1002/pssc.201100358[21] Shatalov M, Sun W H, Lunev A, et al. 278 nm deep ultraviolet LEDs with 11% external quantum efficiency. 70th Device Research Conference, University Park, PA, USA, 2012, 255 doi: 10.1109/DRC.2012.6257013[22] Shatalov M, Sun W H, Bilenko Y, et al. Large chip high power deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Express, 2010, 3, 062101 doi: 10.1143/APEX.3.062101[23] Lobo-Ploch N, Mehnke F, Sulmoni L, et al. Milliwatt power 233 nm AlGaN-based deep UV-LEDs on sapphire substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2020, 117, 111102 doi: 10.1063/5.0015263[24] Kolbe T, Knauer A, Rass J, et al. 234 nm far-ultraviolet-C light-emitting diodes with polarization-doped hole injection layer. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122, 191101 doi: 10.1063/5.0143661[25] Susilo N, Ziffer E, Hagedorn S, et al. Improved performance of UVC-LEDs by combination of high-temperature annealing and epitaxially laterally overgrown AlN/sapphire. Photon Res, 2020, 8, 589 doi: 10.1364/PRJ.385275[26] Mehnke F, Sulmoni L, Guttmann M, et al. Influence of light absorption on the performance characteristics of UV LEDs with emission between 239 and 217 nm. Appl Phys Express, 2019, 12, 012008 doi: 10.7567/1882-0786/aaf788[27] Susilo N, Hagedorn S, Jaeger D, et al. AlGaN-based deep UV LEDs grown on sputtered and high temperature annealed AlN/sapphire. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112, 041110 doi: 10.1063/1.5010265[28] Höpfner J, Gupta P, Guttmann M, et al. Temperature-dependent electroluminescence of stressed and unstressed InAlGaN multi-quantum well UVB LEDs. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122, 151104 doi: 10.1063/5.0139200[29] Sung Y J, Kim M S, Kim H, et al. Light extraction enhancement of AlGaN-based vertical type deep-ultraviolet light-emitting-diodes by using highly reflective ITO/Al electrode and surface roughening. Opt Express, 2019, 27, 29930 doi: 10.1364/OE.27.029930[30] Pernot C, Kim M, Fukahori S, et al. Improved efficiency of 255–280 nm AlGaN-based light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Express, 2010, 3, 061004 doi: 10.1143/APEX.3.061004[31] Kaneda M, Pernot C, Nagasawa Y, et al. Uneven AlGaN multiple quantum well for deep-ultraviolet LEDs grown on macrosteps and impact on electroluminescence spectral output. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2017, 56, 061002 doi: 10.7567/JJAP.56.061002[32] Zollner C J, Almogbel A S, Yao Y F, et al. Superlattice hole injection layers for UV LEDs grown on SiC. Opt Mater Express, 2020, 10, 2171 doi: 10.1364/OME.398146[33] Wang J M, Xie N, Xu F J, et al. Group-III nitride heteroepitaxial films approaching bulk-class quality. Nat Mater, 2023, 22, 853 doi: 10.1038/s41563-023-01573-6[34] Li T, Luo W, Liu S F, et al. Paving the way for high-performance UVB-LEDs through substrate-dominated strain-modulation. Adv Funct Materials, 2023, 33, 2208171 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202208171[35] Grandusky J R, Gibb S R, Mendrick M C, et al. High output power from 260 nm pseudomorphic ultraviolet light-emitting diodes with improved thermal performance. Appl Phys Express, 2011, 4, 082101 doi: 10.1143/APEX.4.082101[36] Grandusky J R, Chen J F, Gibb S R, et al. 270 nm pseudomorphic ultraviolet light-emitting diodes with over 60 mW continuous wave output power. Appl Phys Express, 2013, 6, 032101 doi: 10.7567/APEX.6.032101[37] Ni R X, Chuo C C, Yang K, et al. AlGaN-based ultraviolet light-emitting diode on high-temperature annealed sputtered AlN template. J Alloys Compd, 2019, 794, 8 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.04.256[38] Zheng Z H, Chen Q, Dai J N, et al. Enhanced light extraction efficiency via double nano-pattern arrays for high-efficiency deep UV LEDs. Opt Laser Technol, 2021, 143, 107360 doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107360[39] Yoshikawa A, Hasegawa R, Morishita T, et al. Improve efficiency and long lifetime UVC LEDs with wavelengths between 230 and 237 nm. Appl Phys Express, 2020, 13, 022001 doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ab65fb[40] Kobayashi H, Sato K, Okuaki Y, et al. Milliwatt-power sub-230-nm AlGaN LEDs with >1500 h lifetime on a single-crystal AlN substrate with many quantum wells for effective carrier injection. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122, 101103 doi: 10.1063/5.0139970[41] Fujioka A, Asada K, Yamada H, et al. High-output-power 255/280/310 nm deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes and their lifetime characteristics. Semicond Sci Technol, 2014, 29, 084005 doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/29/8/084005[42] Zhang Y W, Jamal-Eddine Z, Akyol F, et al. Tunnel-injected sub 290 nm ultra-violet light emitting diodes with 2.8% external quantum efficiency. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112, 071107 doi: 10.1063/1.5017045[43] Kinoshita T, Obata T, Nagashima T, et al. Performance and reliability of deep-ultraviolet light-emitting diodes fabricated on AlN substrates prepared by hydride vapor phase epitaxy. Appl Phys Express, 2013, 6, 092103 doi: 10.7567/APEX.6.092103[44] Huang Z X, Zhong Z B, Wang H C, et al. Enhanced emission of deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes through using work function tunable Cu nanowires as the top transparent electrode. J Phys Chem Lett, 2020, 11, 2559 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c00653[45] Lee T H, Park T H, Shin H W, et al. Smart wide-bandgap omnidirectional reflector as an effective hole-injection electrode for deep-UV light-emitting diodes. Adv Opt Mater, 2020, 8, 1901430 doi: 10.1002/adom.201901430[46] Liu T Y, Huang S M, Lai M J, et al. Narrow-band AlGaN-based UVB light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl Electron Mater, 2021, 3, 4121 doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.1c00593[47] Nicholls J, Anderson L, Lee W, et al. High performance and high yield sub-240 nm AlN: GaN short period superlattice LEDs grown by MBE on 6 in. sapphire substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 123, 051105 doi: 10.1063/5.0160177[48] Collazo R, Mita S, Xie J Q, et al. Progress on n-type doping of AlGaN alloys on AlN single crystal substrates for UV optoelectronic applications. Phys Status Solidi C, 2011, 8, 2031 doi: 10.1002/pssc.201000964[49] Armstrong A M, Moseley M W, Allerman A A, et al. Growth temperature dependence of Si doping efficiency and compensating deep level defect incorporation in Al0.7Ga0.3N. J Appl Phys, 2015, 117, 185704 doi: 10.1063/1.4920926[50] Kakanakova-Georgieva A, Sahonta S L, Nilsson D, et al. N-Type conductivity bound by the growth temperature: The case of Al0.72Ga0.28N highly doped by silicon. J Mater Chem C, 2016, 4, 8291 doi: 10.1039/C6TC02825J[51] Ikenaga K, Mishima A, Yano Y, et al. Growth of silicon-doped Al0.6Ga0.4N with low carbon concentration at high growth rate using high-flow-rate metal organic vapor phase epitaxy reactor. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2016, 55, 05FE04 doi: 10.7567/JJAP.55.05FE04[52] Washiyama S, Reddy P, Sarkar B, et al. The role of chemical potential in compensation control in Si: AlGaN. J Appl Phys, 2020, 127, 105702 doi: 10.1063/1.5132953[53] Nagata K, Makino H, Yamamoto T, et al. Low resistivity of highly Si-doped n-type Al0.62Ga0.38N layer by suppressing self-compensation. Appl Phys Express, 2020, 13, 025504 doi: 10.7567/1882-0786/ab65cb[54] Yang J, Zhang Y H, Zhao D G, et al. Realization low resistivity of high AlN mole fraction Si-doped AlGaN by suppressing the formation native vacancies. J Cryst Growth, 2021, 570, 126245 doi: 10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2021.126245[55] Almogbel A S, Zollner C J, Saifaddin B K, et al. Growth of highly conductive Al-rich AlGaN: Si with low group-III vacancy concentration. AIP Adv, 2021, 11, 095119 doi: 10.1063/5.0066652[56] Cantu P, Keller S, Mishra U K, et al. Metalorganic chemical vapor deposition of highly conductive Al0.65Ga0.35N films. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82, 3683 doi: 10.1063/1.1577410[57] Liu B Y, Xu F J, Wang J M, et al. Correlation between electrical properties and growth dynamics for Si-doped Al-rich AlGaN grown by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition. Micro Nanostruct, 2022, 163, 107141 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2021.107141[58] Wang J M, Xu F J, Lang J, et al. Regulation of surface kinetics: Rapid growth of n-AlGaN with high conductivity for deep-ultraviolet light emitters. CrystEngComm, 2022, 24, 4251 doi: 10.1039/D2CE00362G[59] Bryan I, Bryan Z, Washiyama S, et al. Doping and compensation in Al-rich AlGaN grown on single crystal AlN and sapphire by MOCVD. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112, 062102 doi: 10.1063/1.5011984[60] Zollner C J, Yao Y F, Wang M, et al. Highly conductive n-Al0.65Ga0.35N grown by MOCVD using low V/III ratio. Crystals, 2021, 11, 1006 doi: 10.3390/cryst11081006[61] Nishikawa Y, Ueno K, Kobayashi A, et al. Preparation of degenerate n-type AlxGa1–xN (0 < x ≤ 0.81) with record low resistivity by pulsed sputtering deposition. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122, 062102 doi: 10.1063/5.0144418[62] Borisov B, Kuryatkov V, Kudryavtsev Y, et al. Si-doped Al x Ga1– x N (0.56 ≤ × ≤ 1) layers grown by molecular beam epitaxy with ammonia. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 87, 132106 doi: 10.1063/1.2061856[63] Lee K, Page R, Protasenko V, et al. MBE growth and donor doping of coherent ultrawide bandgap AlGaN alloy layers on single-crystal AlN substrates. Appl Phys Lett, 2021, 118, 092101 doi: 10.1063/5.0037079[64] Nakarmi M L, Kim K H, Zhu K, et al. Transport properties of highly conductive n-type Al-rich Al x Ga1– x N (x ≥ 0.7). Appl Phys Lett, 2004, 85, 3769 doi: 10.1063/1.1809272[65] Mehnke F, Wernicke T, Pingel H, et al. Highly conductive n-Al x Ga1–xN layers with aluminum mole fractions above 80%. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 103, 212109 doi: 10.1063/1.4833247[66] Mehnke F, Trinh X T, Pingel H, et al. Electronic properties of Si-doped Al x Ga1– x N with aluminum mole fractions above 80%. J Appl Phys, 2016, 120, 145702 doi: 10.1063/1.4964442[67] Taniyasu Y, Kasu M, Kobayashi N. Intentional control of n-type conduction for Si-doped AlN and Al x Ga1– x N (0.42 ≤ x < 1). Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 81, 1255 doi: 10.1063/1.1499738[68] Zhang C Y, Jiang K, Sun X J, et al. Recent progress on AlGaN based deep ultraviolet light-emitting diodes below 250 nm. Crystals, 2022, 12, 1812 doi: 10.3390/cryst12121812[69] Buonanno M, Welch D, Shuryak I, et al. Far-UVC light (222 nm) efficiently and safely inactivates airborne human coronaviruses. Sci Rep, 2020, 10, 10285 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67211-2[70] Mattila T, Nieminen R M. Ab initio study of oxygen point defects in GaAs, GaN, and AlN. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54, 16676 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.16676[71] Kataoka K, Narita T, Yagi Y, et al. Comprehensive study of electron conduction and its compensation for degenerate Si-doped AlN-rich AlGaN. Physica Rapid Research Ltrs, 2023, 2300055 doi: 10.1002/pssr.202300055[72] Zeisel R, Bayerl M W, Goennenwein S T B, et al. DX-behavior of Si in AlN. Phys Rev B, 2000, 61, R16283 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.61.R16283[73] Trinh X T, Nilsson D, Ivanov I G, et al. Stable and metastable Si negative-U centers in AlGaN and AlN. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 105, 162106 doi: 10.1063/1.4900409[74] Liang Y H, Towe E. Progress in efficient doping of high aluminum-containing group III-nitrides. Appl Phys Rev, 2018, 5, 011107 doi: 10.1063/1.5009349[75] Breckenridge M H, Bagheri P, Guo Q A, et al. High n-type conductivity and carrier concentration in Si-implanted homoepitaxial AlN. Appl Phys Lett, 2021, 118, 112104 doi: 10.1063/5.0042857[76] Bagheri P, Quiñones-Garcia C, Khachariya D, et al. High conductivity in Ge-doped AlN achieved by a non-equilibrium process. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122, 142108 doi: 10.1063/5.0146439[77] Ahmad H, Engel Z, Matthews C M, et al. Realization of homojunction PN AlN diodes. J Appl Phys, 2022, 131, 175701 doi: 10.1063/5.0086314[78] Zhang S B, Wei S H, Zunger A. Overcoming doping bottlenecks in semiconductors and wide-gap materials. Phys B, 1999, 273/274, 976 doi: 10.1016/S0921-4526(99)00605-5[79] Simon J, Protasenko V, Lian C X, et al. Polarization-induced hole doping in wide–band-gap uniaxial semiconductor heterostructures. Science, 2010, 327, 60 doi: 10.1126/science.1183226[80] Tanaka T, Watanabe A, Amano H, et al. p-type conduction in Mg-doped GaN and Al0.08Ga0.92N grown by metalorganic vapor phase epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett, 1994, 65, 593 doi: 10.1063/1.112309[81] Nakarmi M L, Kim K H, Li J, et al. Enhanced p-type conduction in GaN and AlGaN by Mg-δ-doping. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 82, 3041 doi: 10.1063/1.1559444[82] Suzuki M, Nishio J, Onomura M, et al. Doping characteristics and electrical properties of Mg-doped AlGaN grown by atmospheric-pressure MOCVD. J Cryst Growth, 1998, 189/190, 511 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(98)00341-8[83] Li J, Oder T N, Nakarmi M L, et al. Optical and electrical properties of Mg-doped p-type Al x Ga1– x N. Appl Phys Lett, 2002, 80, 1210 doi: 10.1063/1.1450038[84] Chakraborty A, Moe C G, Wu Y A, et al. Electrical and structural characterization of Mg-doped p-type Al0.69Ga0.31N films on SiC substrate. J Appl Phys, 2007, 101, 053717 doi: 10.1063/1.2710303[85] Nakarmi M L, Kim K H, Khizar M, et al. Electrical and optical properties of Mg-doped Al0.7Ga0.3N alloys. Appl Phys Lett, 2005, 86, 092108 doi: 10.1063/1.1879098[86] Wang X, Wang W, Wang J L, et al. Experimental evidences for reducing Mg activation energy in high Al-content AlGaN alloy by MgGa δ doping in (AlN)m/(GaN)n superlattice. Sci Rep, 2017, 7, 44223 doi: 10.1038/srep44223[87] Nam K B, Nakarmi M L, Li J, et al. Mg acceptor level in AlN probed by deep ultraviolet photoluminescence. Appl Phys Lett, 2003, 83, 878 doi: 10.1063/1.1594833[88] Zheng T C, Lin W, Cai D J, et al. High Mg effective incorporation in Al-rich AlxGa1-xN by periodic repetition of ultimate V/III ratio conditions. Nanoscale Res Lett, 2014, 9, 40 doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-40[89] Stampfl C, Van de Walle C G. Doping of Al x Ga1– x N. Appl Phys Lett, 1998, 72, 459 doi: 10.1063/1.120803[90] Miceli G, Pasquarello A. Self-compensation due to point defects in Mg-doped GaN. Phys Rev B, 2016, 93, 165207 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.165207[91] Nakarmi M L, Nepal N, Lin J Y, et al. Photoluminescence studies of impurity transitions in Mg-doped AlGaN alloys. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94, 091903 doi: 10.1063/1.3094754[92] Kozodoy P, Smorchkova Y P, Hansen M, et al. Polarization-enhanced Mg doping of AlGaN/GaN superlattices. Appl Phys Lett, 1999, 75, 2444 doi: 10.1063/1.125042[93] Ebata K, Nishinaka J, Taniyasu Y, et al. High hole concentration in Mg-doped AlN/AlGaN superlattices with high Al content. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2018, 57, 04FH09 doi: 10.7567/JJAP.57.04FH09[94] Yao Y F, Zollner C J, Wang M, et al. Polarization-enhanced p-AlGaN superlattice optimization for GUV LED. IEEE J Quantum Electron, 2022, 58, 3300409 doi: 10.1109/JQE.2022.3159821[95] Simon J, Cao Y, Jena D. Short-period AlN/GaN p-type superlattices: Hole transport use in p-n junctions. Phys Status Solidi C, 2010, 7, 2386 doi: 10.1002/pssc.200983868[96] Wang J M, Wang M X, Xu F J, et al. Sub-nanometer ultrathin epitaxy of AlGaN and its application in efficient doping. Light, 2022, 11, 71 doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-00753-4[97] Jiang K, Sun X J, Shi Z M, et al. Quantum engineering of non-equilibrium efficient p-doping in ultra-wide band-gap nitrides. Light, 2021, 10, 69 doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00503-y[98] Ambacher O, Smart J, Shealy J R, et al. Two-dimensional electron gases induced by spontaneous and piezoelectric polarization charges in N- and Ga-face AlGaN/GaN heterostructures. J Appl Phys, 1999, 85, 3222 doi: 10.1063/1.369664[99] Li S B, Zhang T, Wu J A, et al. Polarization induced hole doping in graded AlxGa1–xN ( x = 0.7 ~ 1) layer grown by molecular beam epitaxy. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102, 3300409 doi: 10.1063/1.4792685[100] Rathkanthiwar S, Reddy P, Moody B, et al. High p-conductivity in AlGaN enabled by polarization field engineering. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122, 152105 doi: 10.1063/5.0143427[101] Zhang Z Y, Kushimoto M, Sakai T, et al. A 271.8 nm deep-ultraviolet laser diode for room temperature operation. Appl Phys Express, 2019, 12, 124003 doi: 10.7567/1882-0786/ab50e0[102] Omori T, Ishizuka S, Tanaka S, et al. Internal loss of AlGaN-based ultraviolet-B band laser diodes with p-type AlGaN cladding layer using polarization doping. Appl Phys Express, 2020, 13, 071008 doi: 10.35848/1882-0786/ab9e4a[103] Tanaka S, Ogino Y, Yamada K, et al. AlGaN-based UV-B laser diode with a high optical confinement factor. Appl Phys Lett, 2021, 118, 163504 doi: 10.1063/5.0046224[104] Ahmad H, Lindemuth J, Engel Z, et al. Substantial P-type conductivity of AlN achieved via beryllium doping. Adv Mater, 2021, 33, 2104497 doi: 10.1002/adma.202104497[105] Tersoff J. Enhanced solubility of impurities and enhanced diffusion near crystal surfaces. Phys Rev Lett, 1995, 74, 5080 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.5080[106] Chen Y D, Wu H L, Han E Z, et al. High hole concentration in p-type AlGaN by indium-surfactant-assisted Mg-delta doping. Appl Phys Lett, 2015, 106, 162102 doi: 10.1063/1.4919005[107] Qiu X J, Chen Y D, Han E Z, et al. High doping efficiency in p-type Al-rich AlGaN by modifying the Mg doping planes. Mater Adv, 2020, 1, 77 doi: 10.1039/D0MA00026D[108] Kinoshita T, Obata T, Yanagi H, et al. High p-type conduction in high-Al content Mg-doped AlGaN. Appl Phys Lett, 2013, 102, 012105 doi: 10.1063/1.4773594[109] Bagheri P, Klump A, Washiyama S, et al. Doping and compensation in heavily Mg doped Al-rich AlGaN films. Appl Phys Lett, 2022, 120, 082102 doi: 10.1063/5.0082992[110] Chung S J, Senthil Kumar M, Lee Y S, et al. Characteristics of Mg-doped and In–Mg co-doped p-type GaN epitaxial layers grown by metal organic chemical vapour deposition. J Phys D:Appl Phys, 2010, 43, 185101 doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/43/18/185101 -
Proportional views




 DownLoad:
DownLoad:
































