| Citation: |
Jingting Sun, Junyan Ren, Yuting Xiong, Yiting Cheng, Huize Tang, Hongfei Wu, Wangying Xu, Lingyan Liang, Hongtao Cao. Boosted IGZO optoelectronic synaptic performance by mitigating photolithography-induced surface effects[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, In Press. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25080023
****
J T Sun, J Y Ren, Y T Xiong, Y T Cheng, H Z Tang, H F Wu, W Y Xu, L Y Liang, and H T Cao, Boosted IGZO optoelectronic synaptic performance by mitigating photolithography-induced surface effects[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, accepted doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25080023
|
Boosted IGZO optoelectronic synaptic performance by mitigating photolithography-induced surface effects
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/25080023
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.25080023
More Information-
Abstract
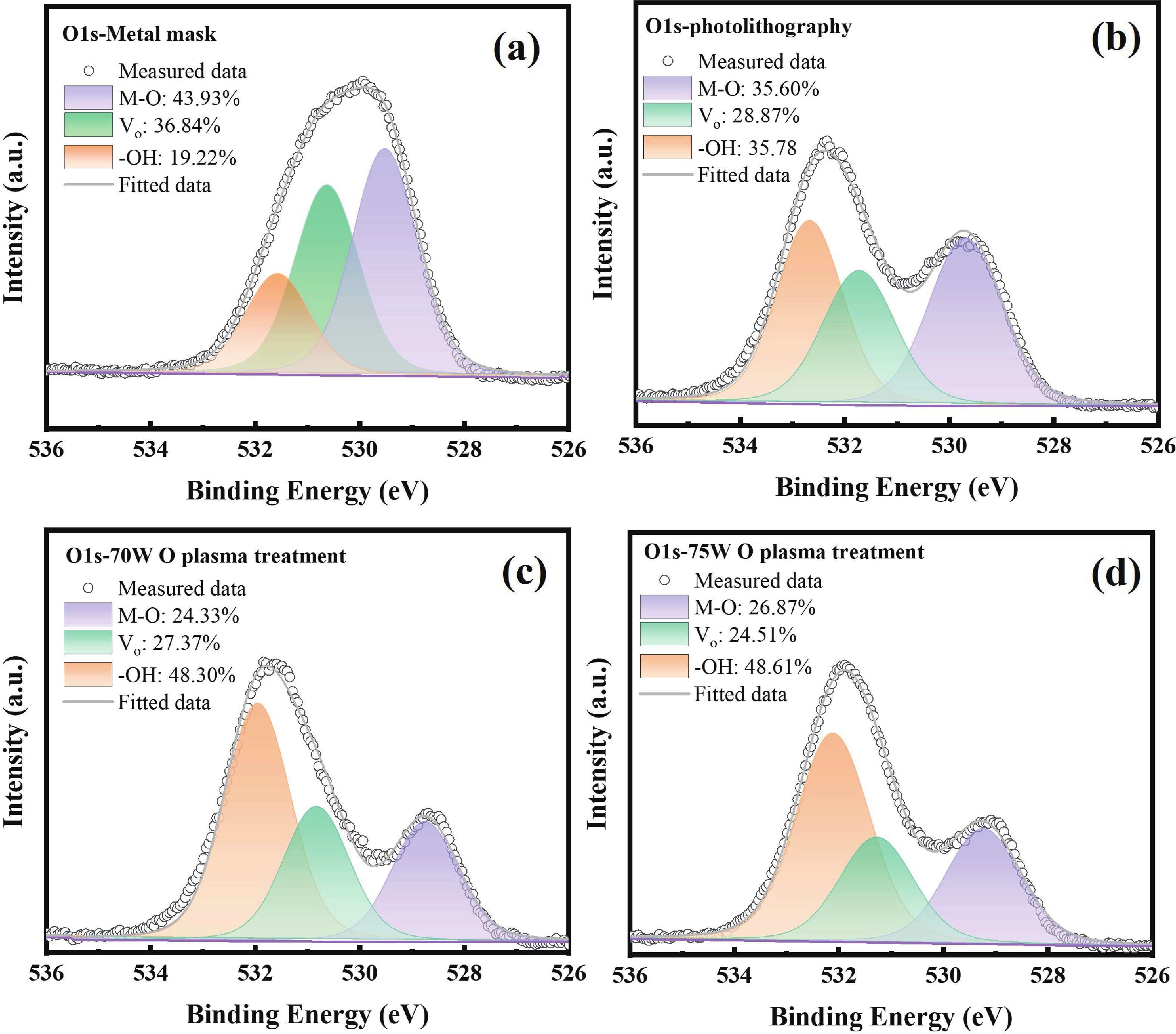
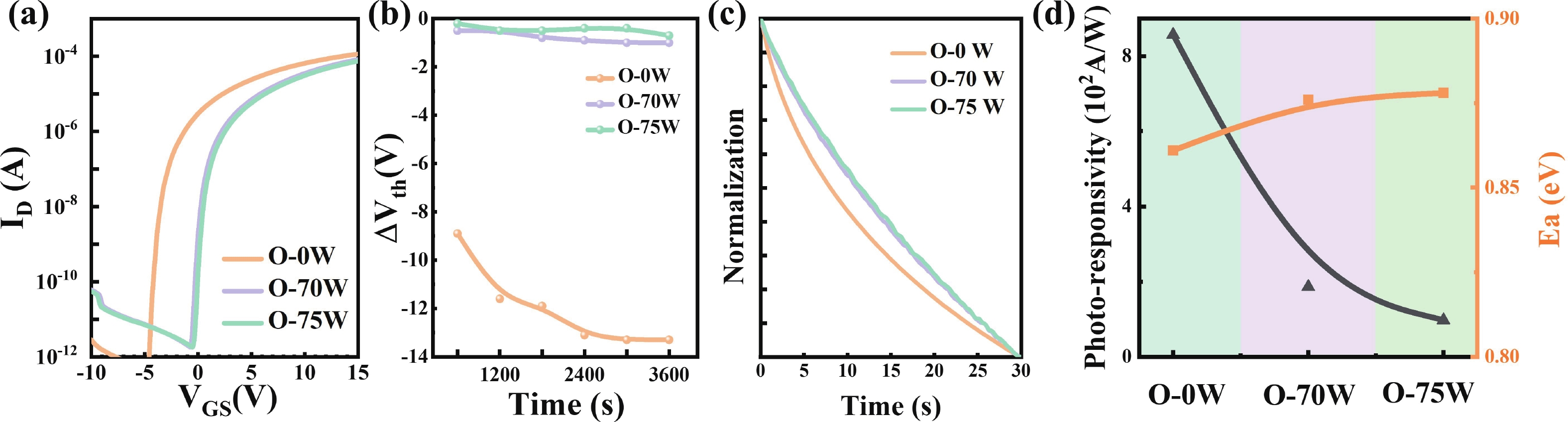
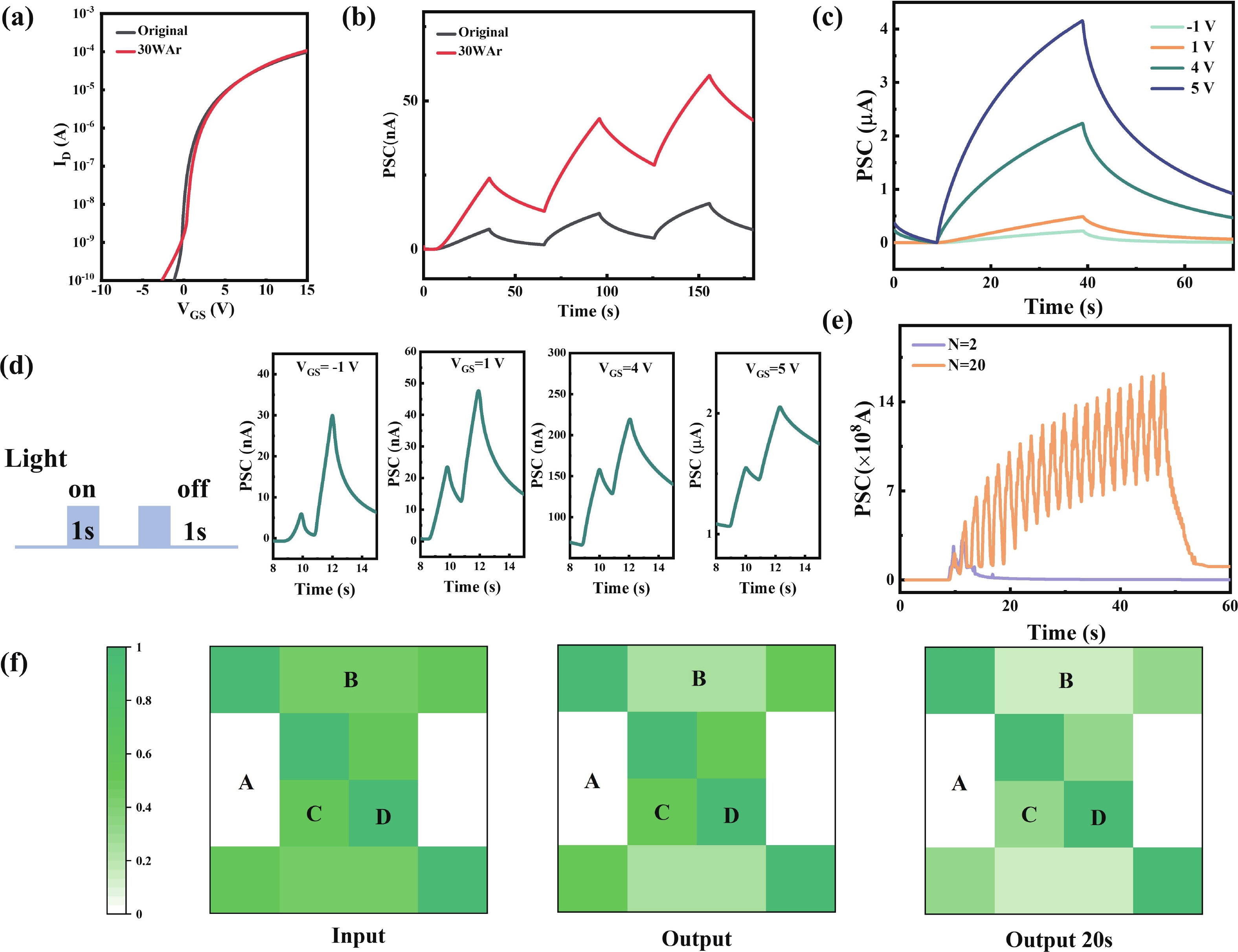
Oxide semiconductor-based neuromorphic devices hold great potential for visual information processing, yet their performance is critically limited by photolithography-induced organic residues. This work systematically investigates the effects of photoresist contaminants on In-Ga-Zn-O thin-film transistors (IGZO TFTs), revealing that these residues introduce deep-level trap states that degrade both photo-responsivity and carrier transport dynamics. Through optimized plasma-assisted surface treatments, these adverse effects would be effectively eliminated. Additionally, we show that gate-voltage modulation can precisely control the relaxation kinetics of photocarriers in these devices. By applying these strategies to IGZO-based synaptic arrays, we achieve enhanced image contrast through controlled optoelectronic response modulation. Overall, our findings highlight the critical impact of photolithography-induced organic residues in IGZO optoelectronic synaptic devices and demonstrate an effective approach for performance enhancement through surface plasma treatment and gate-voltage modulation. -
References
[1] Xiang B, Zou T Y, Wang Y, et al. Photovoltage-coupled dual-gate InGaZnO thin-film transistors operated at the subthreshold region for low-power photodetection. ACS Appl Electron Mater, 2020, 2(6), 1745 doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.0c00308[2] Oommen R, Ganapathi Mavuri D S, Jose K, et al. Tunable memory behavior in light stimulated artificial synapse based on ZnO thin film transistors. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2024, 57(46), 465102 doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ad6dff[3] Guo Y B, Zhu L Q. Recent progress in optoelectronic neuromorphic devices. Chin Phys B, 2020, 29(7), 078502 doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/ab99b6[4] Zhu X J, Lu W D. Optogenetics-inspired tunable synaptic functions in memristors. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(2), 1242 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07317[5] Zhou L, Mao J Y, Ren Y, et al. Biological spiking synapse constructed from solution processed bimetal core-shell nanoparticle based composites. Small, 2018, 14(28), e1800288 doi: 10.1002/smll.201800288[6] Shi Z W, Wang W S, Ai L, et al. Non-associative learning behavior in mixed proton and electron conductor hybrid pseudo-diode. J Mater Sci Technol, 2023, 160, 204 doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2023.02.061[7] Zhu J D, Yang Y C, Jia R D, et al. Ion gated synaptic transistors based on 2D van der waals crystals with tunable diffusive dynamics. Adv Mater, 2018, 30(21), e1800195 doi: 10.1002/adma.201800195[8] Yang R Q, Tian Y, Hu L X, et al. Dual-input optoelectronic synaptic transistor based on amorphous ZnAlSnO for multi-target neuromorphic simulation. Mater Today Nano, 2024, 26, 100480 doi: 10.1016/j.mtnano.2024.100480[9] Yang R Q, Hu D N, Chen Q J, et al. SnS-facilitated ZnAlSnO-based fully optically modulated artificial synaptic device for image processing. Adv Funct Materials, 2025, 35(4), 2414210 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202414210[10] Yang R Q, Wang Y, Li S Q, et al. All-optically controlled artificial synapse based on full oxides for low-power visible neural network computing. Adv Funct Materials, 2024, 34(10), 2312444 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202312444[11] Liang L Y, Zhang H B, Li T, et al. Addressing the conflict between mobility and stability in oxide thin-film transistors. Adv Sci, 2023, 10(14), e2300373. doi: 10.1002/advs.202300373[12] Shiah Y S, Sim K, Ueda S, et al. Unintended carbon-related impurity and negative bias instability in high-mobility oxide TFTs. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2021, 42(9), 1319 doi: 10.1109/LED.2021.3101654[13] Xiao P, Huang J H, Dong T, et al. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of the effect of photoresist passivation on InGaZnO thin-film transistors. Appl Surf Sci, 2019, 471, 403 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.211[14] Shiah Y S, Sim K, Shi Y H, et al. Mobility–stability trade-off in oxide thin-film transistors. Nat Electron, 2021, 4, 800 doi: 10.1038/s41928-021-00671-0[15] Liu J S, He L F, Xu Z, et al. Defect generation mechanism in magnetron sputtered metal films on PMMA substrates. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2019, 30(16), 14847 doi: 10.1007/s10854-019-01855-3[16] Lu J Q, Wang W H, Liang J X, et al. Contact resistance reduction of low temperature atomic layer deposition ZnO thin film transistor using Ar plasma surface treatment. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2022, 43(6), 890 doi: 10.1109/LED.2022.3169345[17] Lee G W, Shim J I, Shin D S. On the ideality factor of the radiative recombination current in semiconductor light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2016, 109(3), 031104 doi: 10.1063/1.4959081[18] Goudon T, Miljanović V, Schmeiser C. On the Shockley–read–hall model: Generation-recombination in semiconductors. SIAM J Appl Math, 2007, 67(4), 1183 doi: 10.1137/060650751[19] Gao Z X, Ju X, Zhang H Z, et al. InP quantum dots tailored oxide thin film phototransistor for bioinspired visual adaptation. Adv Funct Materials, 2023, 33(52), 2305959 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202305959[20] Chen H Y, Ren J Y, Sun J T, et al. Photoresponse design in metal oxide semiconductor TFTs toward diverse applications: Display drivers, photodetectors, and optoelectronic synapses. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2025, 17(5), 8727 doi: 10.1021/acsami.5c00152[21] Li T, Liu X H, Ren J Y, et al. High-mobility InSnZnO thin film transistors via introducing water vapor sputtering gas. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2024, 16(24), 31237 doi: 10.1021/acsami.3c17894 -
Proportional views




 Jingting Sun received her BS in Materials Science and Engineering in 2018 from Yangtze Normal University and her MS degree in Materials Physics & Chemistry in 2025 from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS). She is currently conducting research on thin-film transistors (TFTs).
Jingting Sun received her BS in Materials Science and Engineering in 2018 from Yangtze Normal University and her MS degree in Materials Physics & Chemistry in 2025 from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS). She is currently conducting research on thin-film transistors (TFTs). Junyan Ren received her BS in Materials Chemistry in 2020 from Yunnan University and her MS/PH.D degree in 2025 in Material Physics & Chemistry from Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). She is currently a postdoctoral researcher at NIMTE, CAS. Her current research focuses on amorphous and nano-crystalline oxide semiconductors and their devices for electronics/optoelectronics.
Junyan Ren received her BS in Materials Chemistry in 2020 from Yunnan University and her MS/PH.D degree in 2025 in Material Physics & Chemistry from Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). She is currently a postdoctoral researcher at NIMTE, CAS. Her current research focuses on amorphous and nano-crystalline oxide semiconductors and their devices for electronics/optoelectronics. Lingyan Liang received her BS in physics in 2003 from Nanjing University and her MS/Ph.D degree in 2008 in Material Physics & Chemistry from Institute of Semiconductor, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). She is currently a professor at Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering, CAS. Her current research focuses on amorphous and nano-crystalline oxide semiconductors and their devices for electronics/optoelectronics/bioelectronics.
Lingyan Liang received her BS in physics in 2003 from Nanjing University and her MS/Ph.D degree in 2008 in Material Physics & Chemistry from Institute of Semiconductor, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). She is currently a professor at Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering, CAS. Her current research focuses on amorphous and nano-crystalline oxide semiconductors and their devices for electronics/optoelectronics/bioelectronics.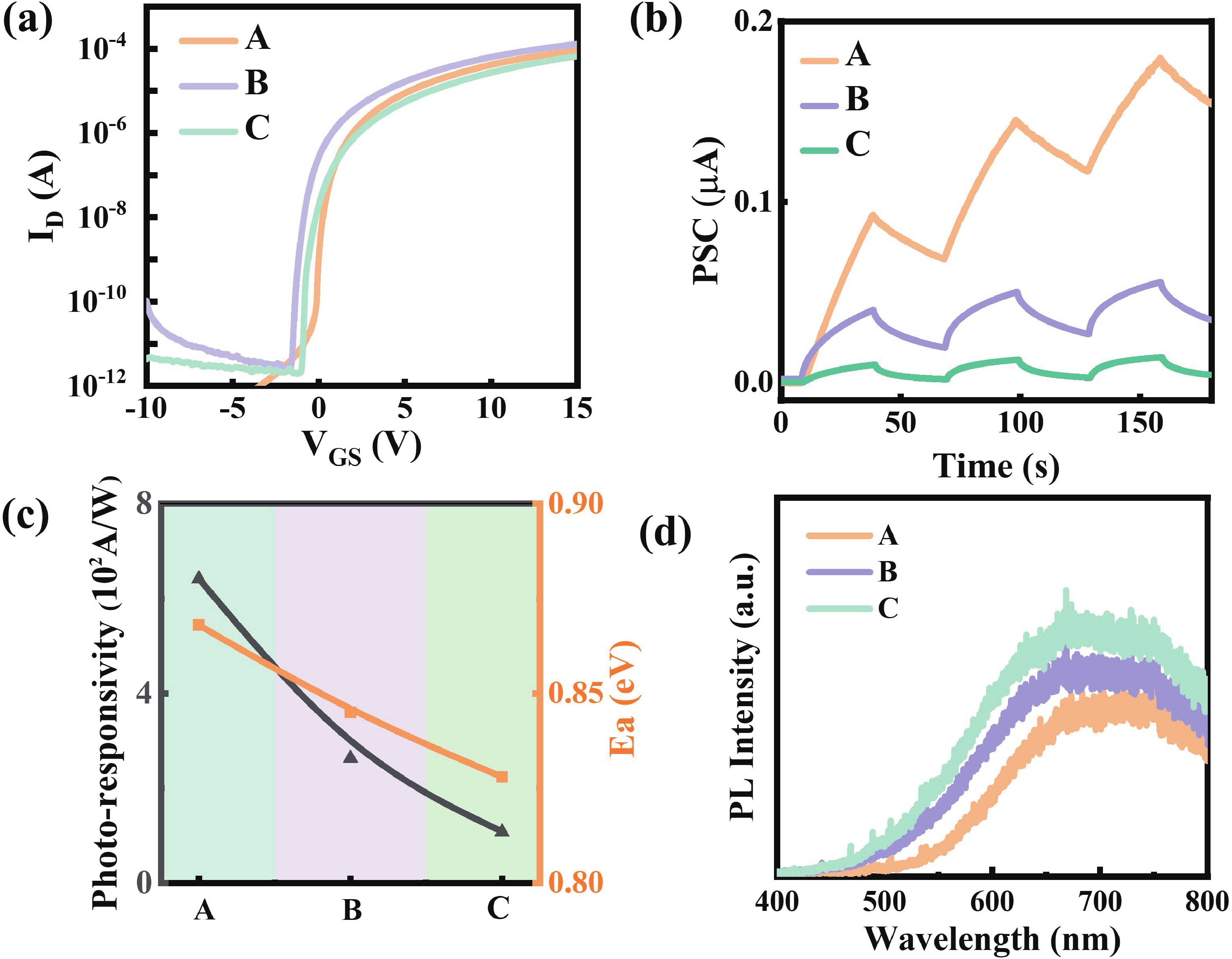
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: