| Citation: |
Jinjing Huang, Jun Liu. A complete small-signal HBT model including AC current crowding effect[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2021, 42(5): 052401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/5/052401
J J Huang, J Liu, A complete small-signal HBT model including AC current crowding effect[J]. J. Semicond., 2021, 42(5): 052401. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/5/052401.
Export: BibTex EndNote
|
A complete small-signal HBT model including AC current crowding effect
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/5/052401
More Information-
Abstract
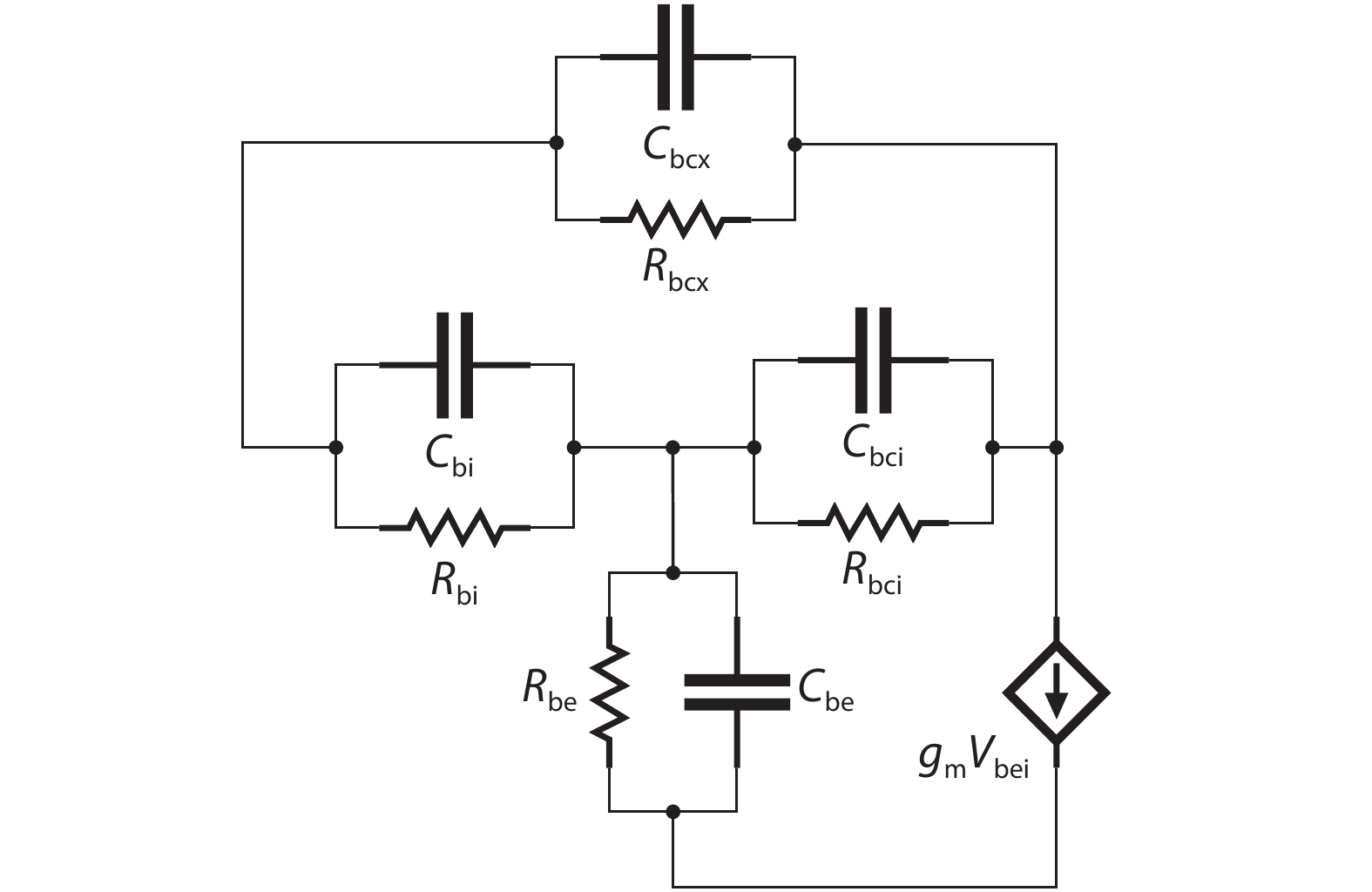
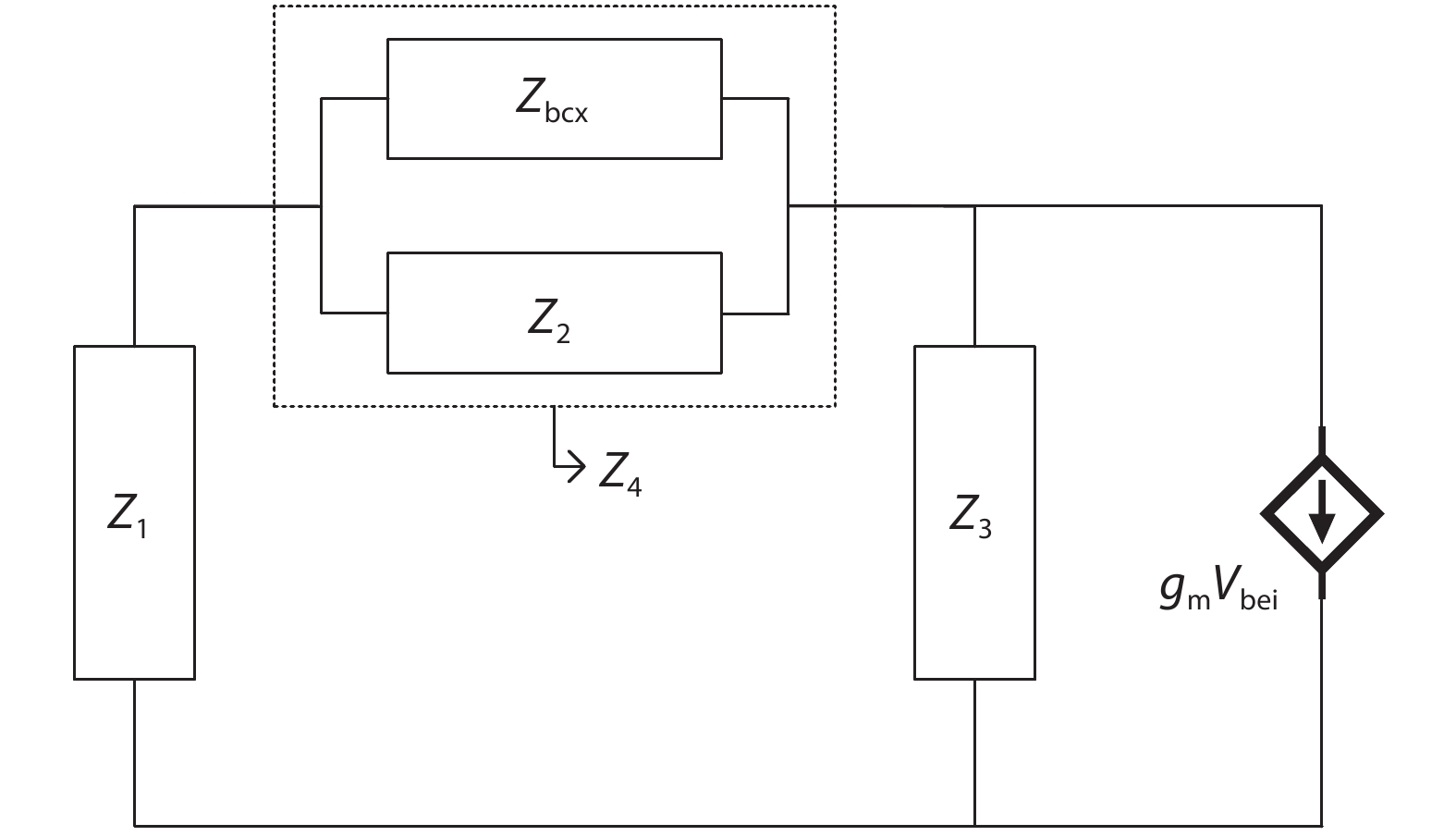
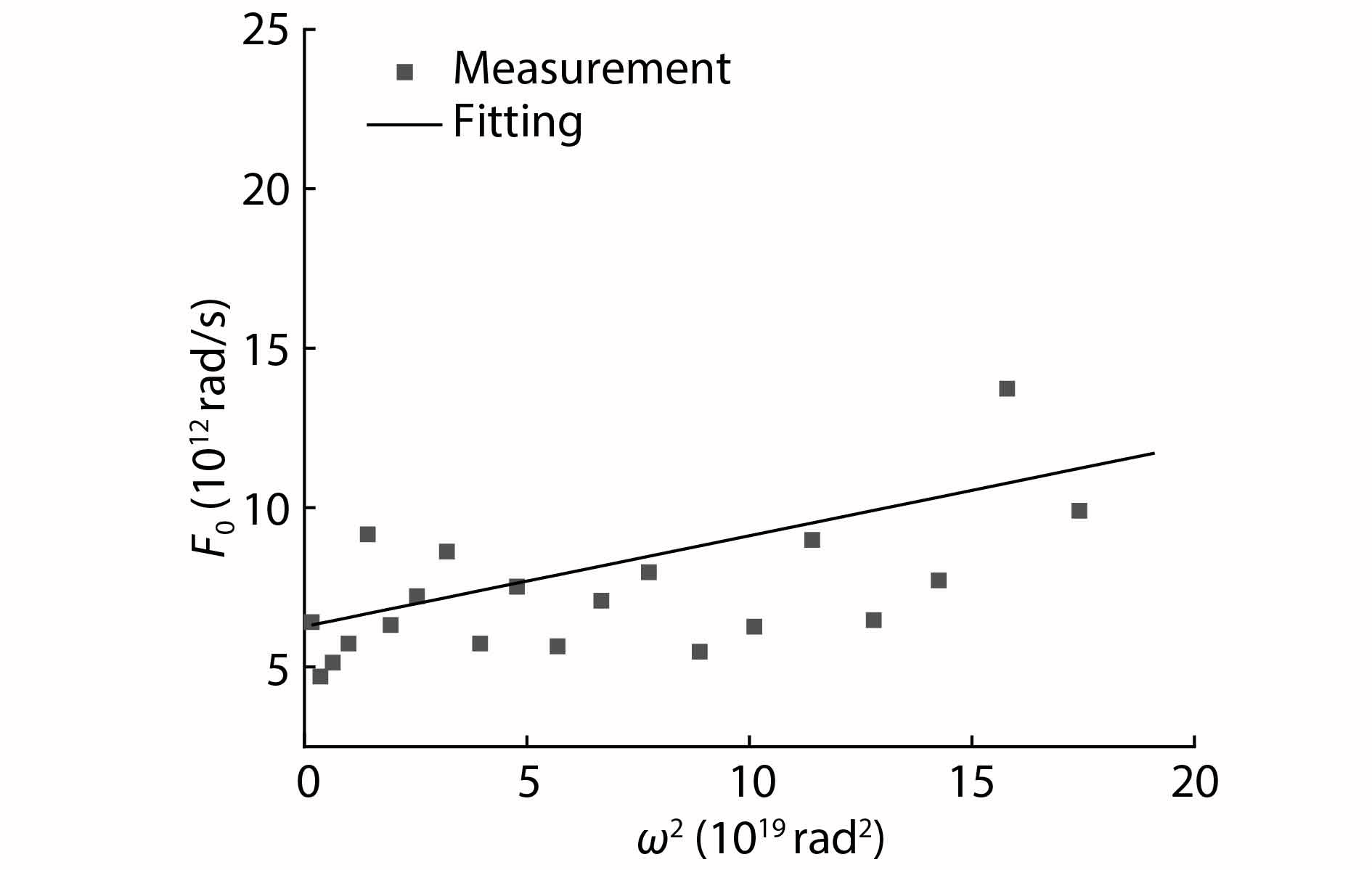
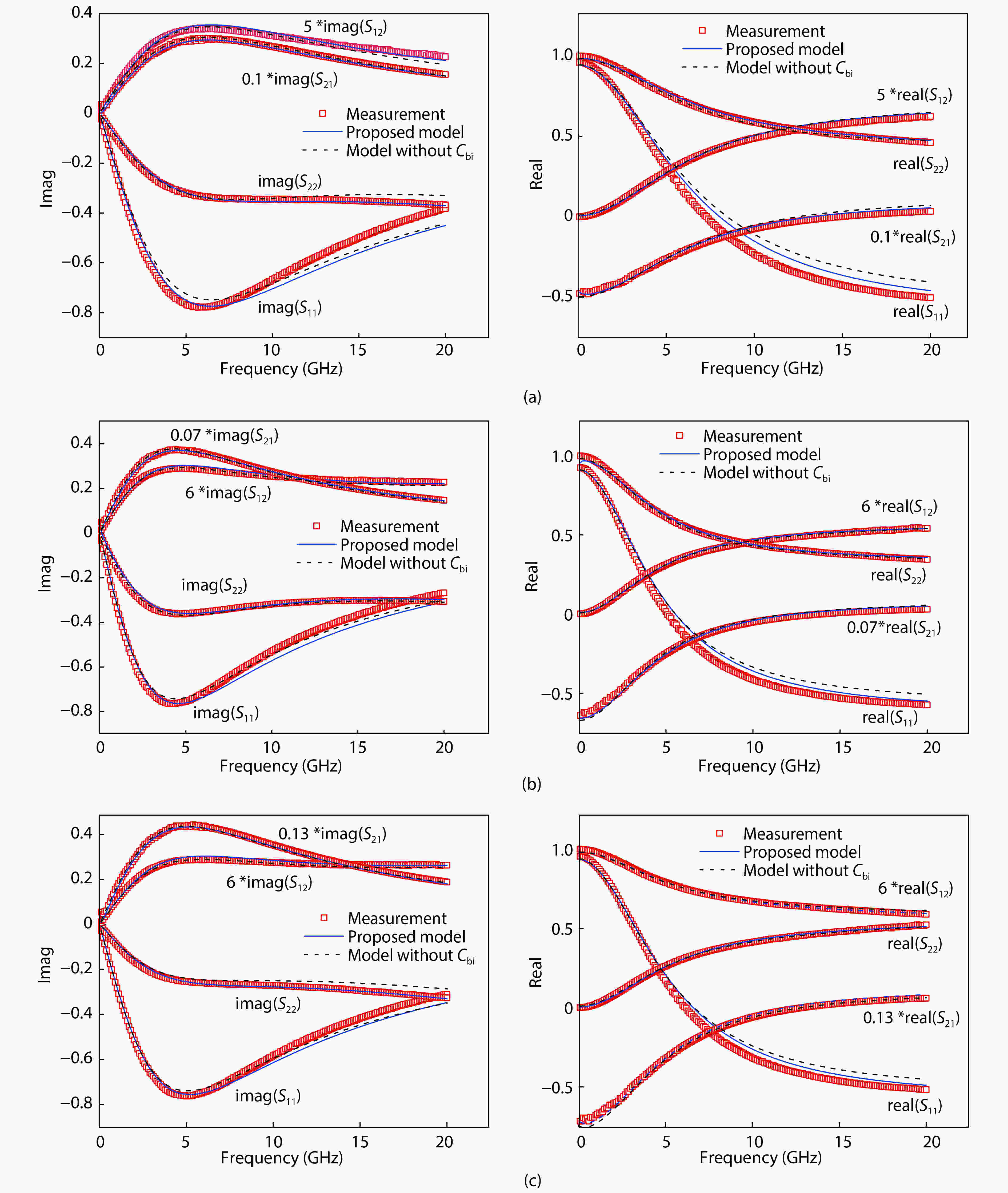
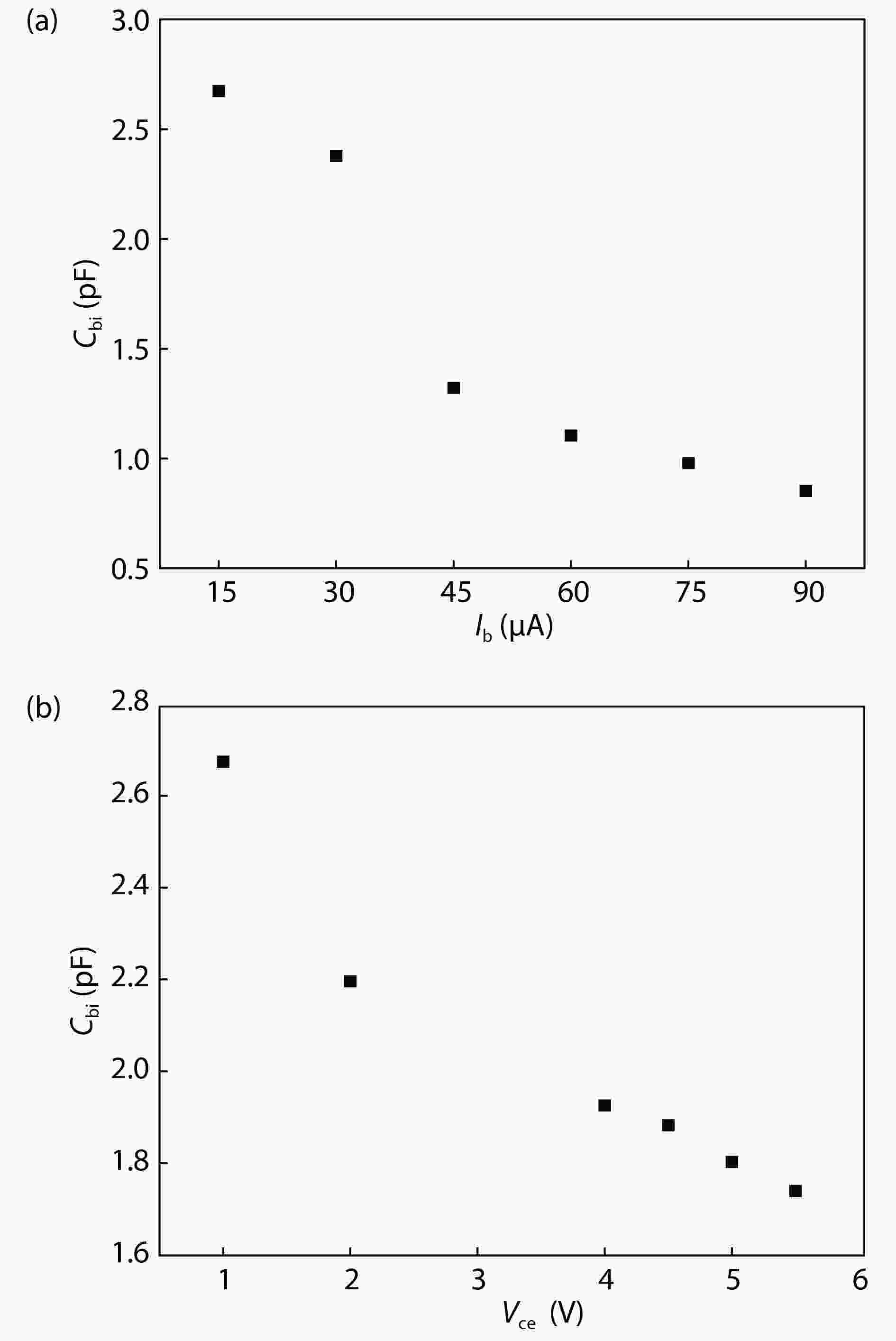
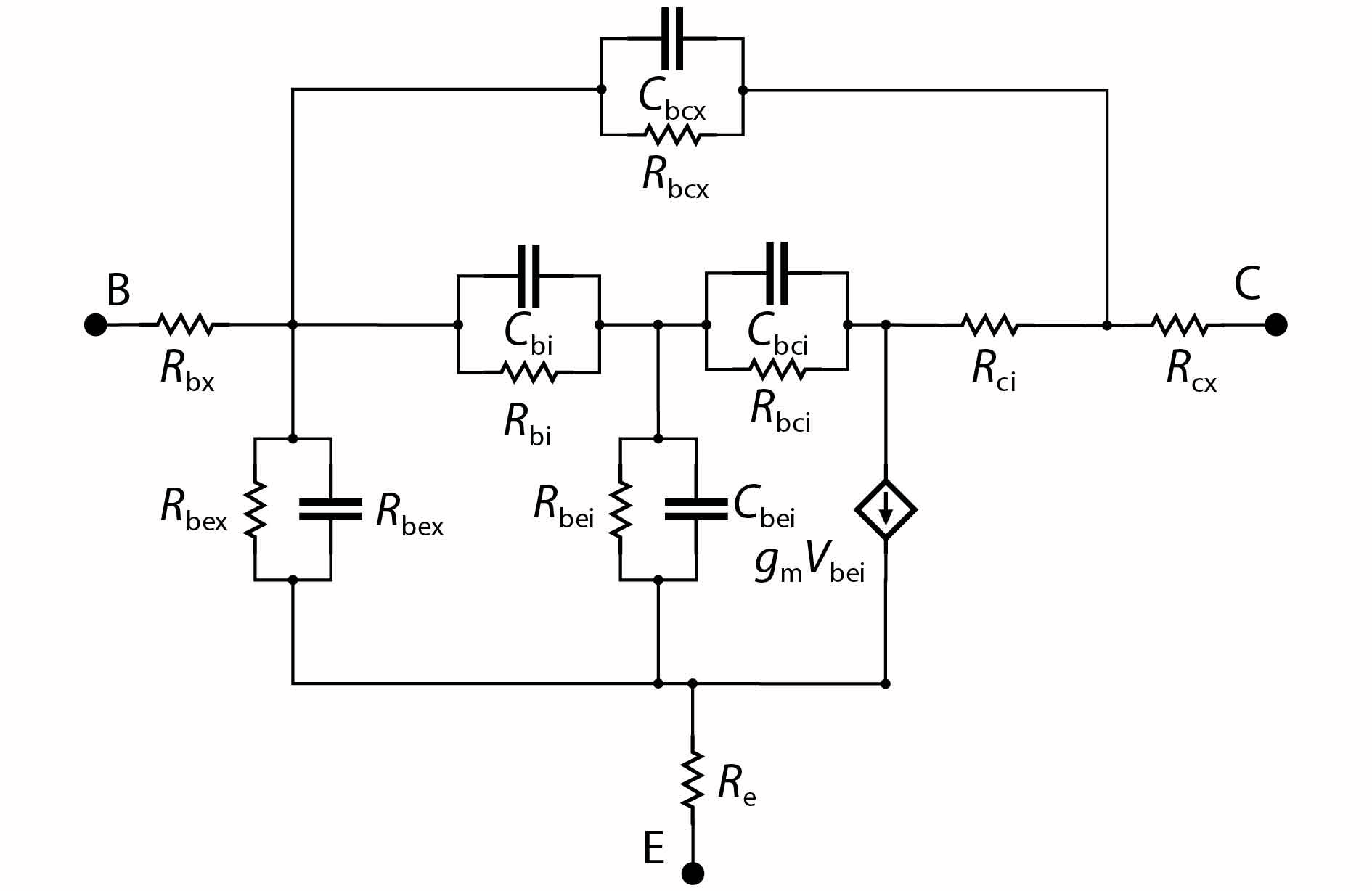
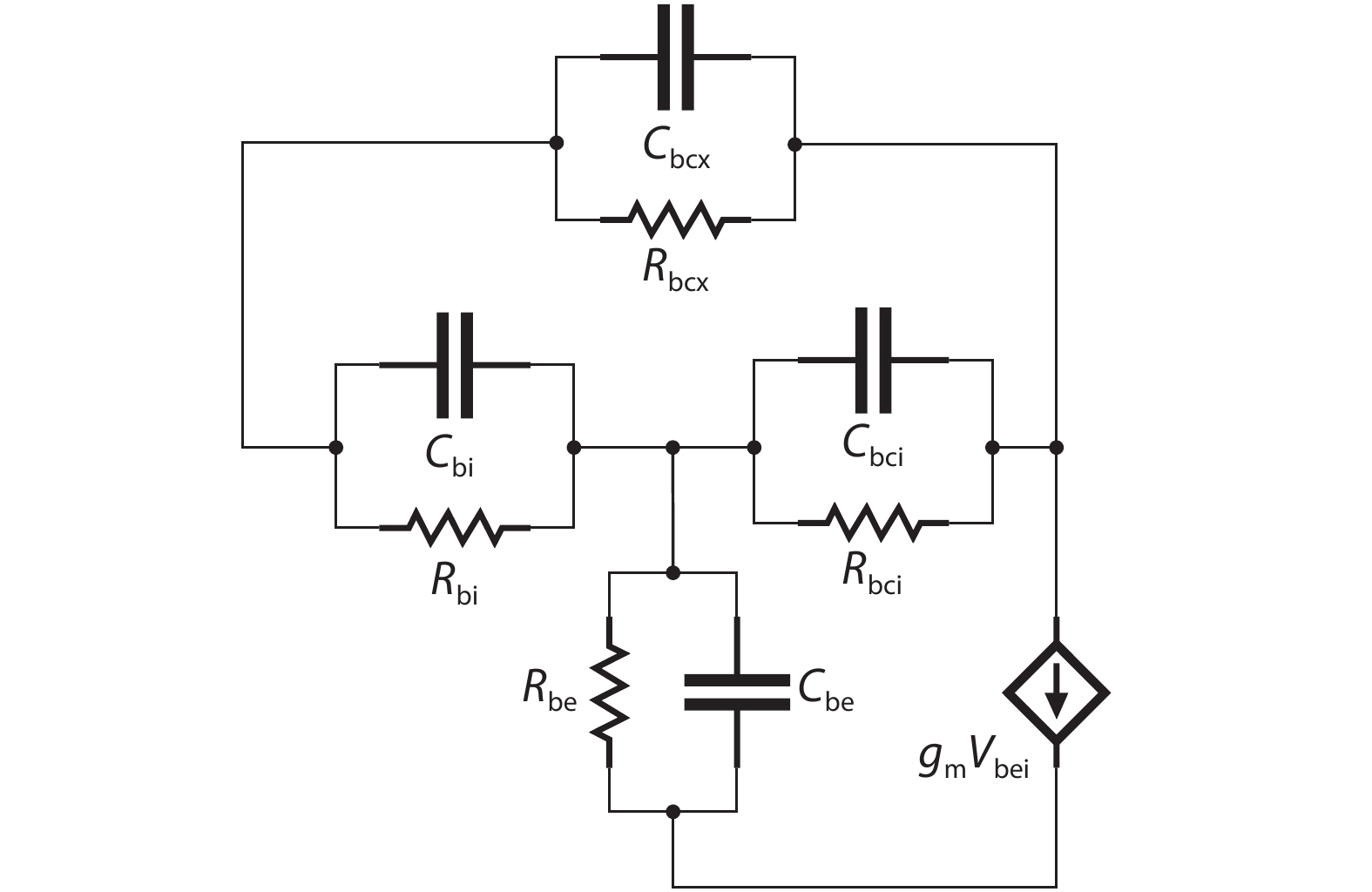
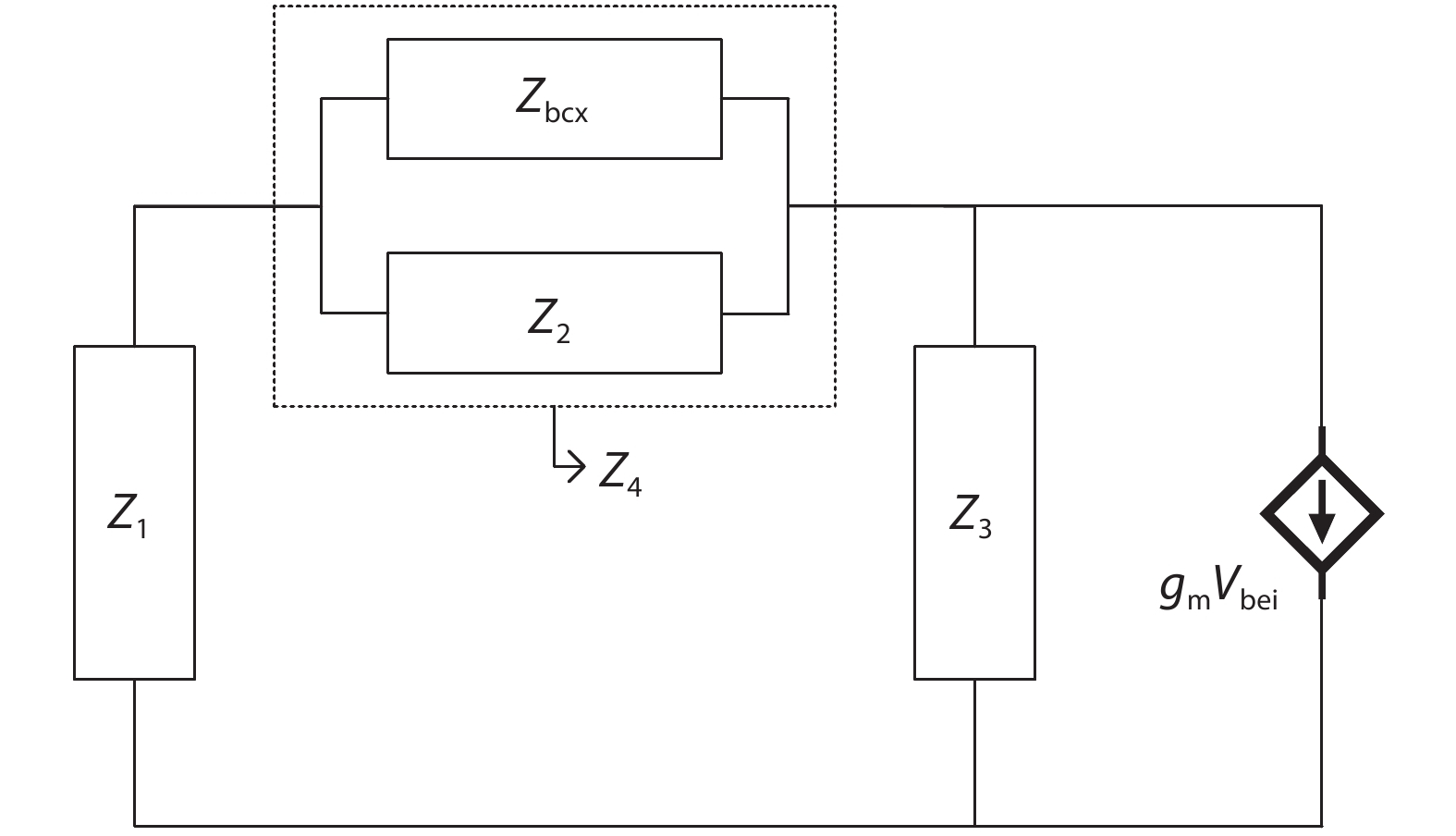
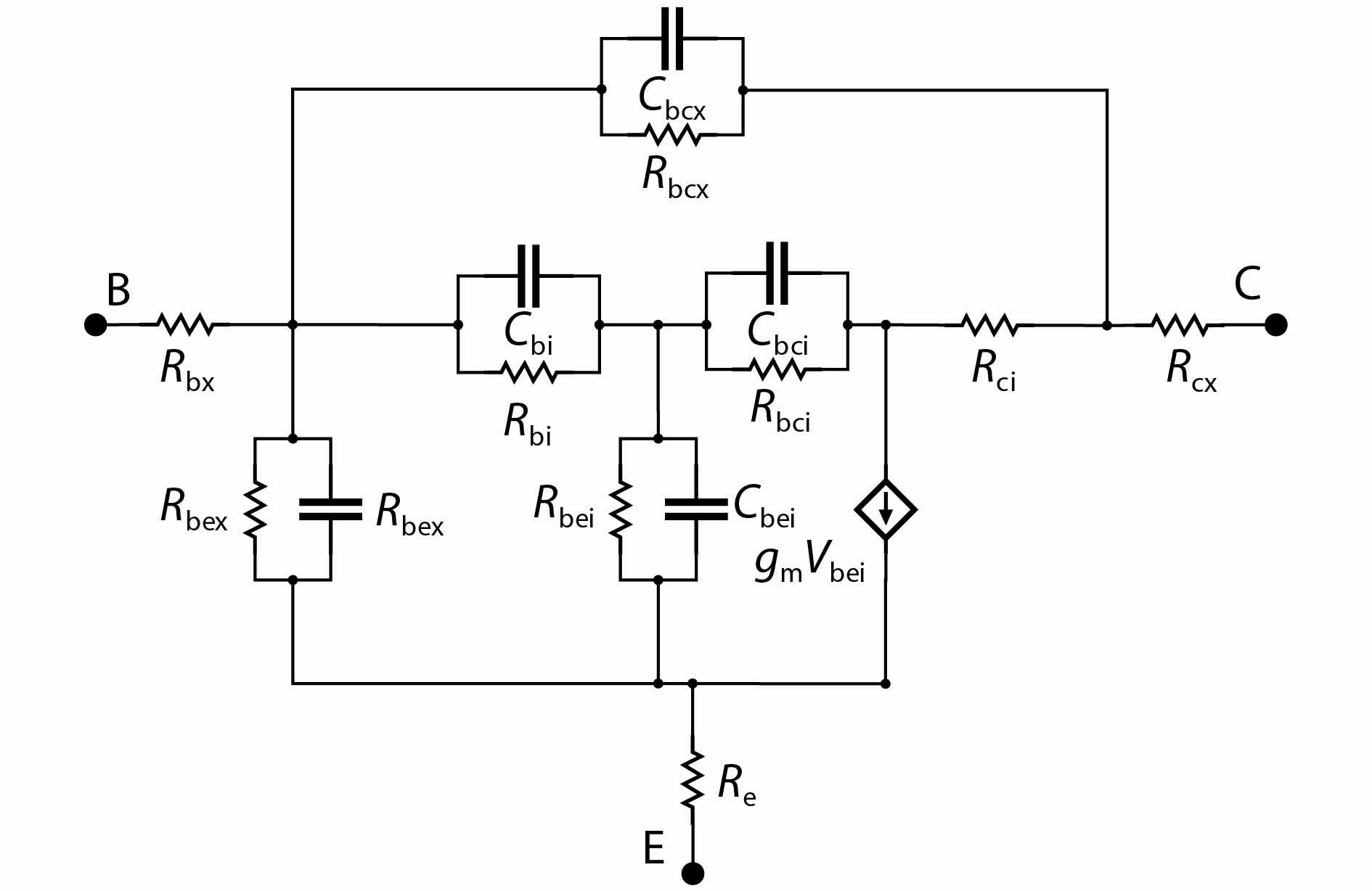
An improved small-signal equivalent circuit of HBT concerning the AC current crowding effect is proposed in this paper. AC current crowding effect is modeled as a parallel RC circuit composed of Cbi and Rbi, with distributed base-collector junction capacitance also taken into account. The intrinsic portion is taken as a whole and extracted directly from the measured S-parameters in the whole frequency range of operation without any special test structures. An HBT device with a 2 × 20 μm2 emitter-area under three different biases were used to demonstrate the extraction and verify the accuracy of the equivalent circuit.-
Keywords:
- small-signal model,
- HBT,
- AC current crowding effect
-
References
[1] Zhang J, Liu M, Wang J, et al. Modeling of InP HBTs with an improved keysight HBT model. Microw J, 2019, 62(7), 56[2] Shivan T, Weimann N, Hossain M, et al. A highly efficient ultrawideband traveling-wave amplifier in InP DHBT technology. IEEE Microw Wirel Compon Lett, 2018, 28(11), 1029 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2018.2871336[3] Griffith Z, Urteaga M, Rowell P. A 190-GHz high-gain, 3-dBm OP1dB low DC-power amplifier in 250-nm InP HBT. IEEE Microw Wirel Compon Lett, 2017, 27(12), 1128 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2017.2764739[4] Lin Q, Wu H, Chen Y J, et al. A 0.5 to 4.0 GHz low-cost broadband GaAs HBT low noise amplifier. 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium (IWS), 2019[5] Huang S C, Tang W B, Hsin Y M. High-frequency noise modeling of InGaP/GaAs HBT with base-contact capacitance and AC current crowding effect. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2009, 30(11), 1125 doi: 10.1109/LED.2009.2031132[6] Yadav S, Chakravorty A, Schroter M. Modeling of the lateral emitter-current crowding effect in SiGe HBTs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2016, 63(11), 4160 doi: 10.1109/TED.2016.2606652[7] Yapei C, Yong Z, Yuehang X, et al. Investigation of terahertz 3D EM simulation on device modeling and a new InP HBT dispersive inter-electrode impedance extraction method. IEEE Access, 2018, 6, 45772 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2865929[8] Gloria, Daniel, Danneville, et al. Small-signal characterization and modelling of 55 nm SiGe BiCMOS HBT up to 325 GHz. Solid State Electron, 2017, 129, 150 doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2016.11.012[9] Sun Y, Fu J, Wang Y, et al. Direct analytical parameter extraction for SiGe HBTs T-topology small-signal equivalent circuit. Superlattices Microstruct, 2016, 94, 223 doi: 10.1016/j.spmi.2016.03.046[10] Rhee H S, Lee S, Kim B R. D. c. and a. c. current crowding effects model analysis in bipolar junction transistors using a new extraction method. Solid-State Electron, 1995, 38(1), 31 doi: 10.1016/0038-1101(94)E0062-J[11] Tang W B, Wang C M, Hsin Y M. A new extraction technique for the complete small-signal equivalent-circuit model of InGaP/GaAs HBT including base contact impedance and AC current crowding effect. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2006, 54, 3641 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2006.882411[12] Lee K, Choi K, Kook S H, et al. Direct parameter extraction of SiGeHBTs for the VBIC bipolar compact model. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52(3), 375 doi: 10.1109/TED.2005.843906[13] Dousset D, Issaoun A, Ghannouchi F M, et al. Wideband closed-form expressions for direct extraction of HBT small-signal parameters for all amplifier bias classes. IEEE Proceedings - Circuits, Devices and Systems, 2005, 152(5), 441 doi: 10.1049/ip-cds:20045077[14] Johansen T K, Leblanc R, Poulain J, et al. Direct extraction of InP/GaAsSb/InP DHBT equivalent-circuit elements from S-parameters measured at cut-off and normal bias conditions. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2016, 64(1), 115 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2503769[15] Zhang J C, Liu B, Zhang L M, et al. A rigorous peeling algorithm for diret parameter extraction procedure of HBT small-signal equivalent circuit. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process, 2015, 85(3), 405 doi: 10.1007/s10470-015-0586-z[16] Bousnina S, Mandeville P, Kouki A B, et al. Direct parameter-extraction method for HBT small-signal model. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2002, 50(2), 529 doi: 10.1109/22.982232[17] Degachi L, Ghannouchi F M. Systematic and rigorous extraction method of HBT small-signal model parameters. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2006, 54(2), 682 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.862661[18] Degachi L, Ghannouchi F M. An augmented small-signal HBT model with its analytical based parameter extraction technique. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2008, 55(4), 968 doi: 10.1109/TED.2008.917539[19] Zhou W, Sun L, Liu J, et al. Extraction and verification of the small-signal model for InP DHBTs in the 0.2–325 GHz frequency range. ICE Electron Express, 2018, 15(13), 20180244 doi: 10.1587/elex.15.20180244[20] Zhang A, Gao J, Wang H. Direct parameter extraction method for InP heterojunction bipolar transistors based on the combination of T- and π-models up to 110 GHz. Semicond Sci Technol, 2019, 35(2), 025001 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/ab5917[21] Zhang A, Gao J. A direct extraction method to determine the extrinsic resistances for InP HBT device based on S-parameters measurement up to 110 GHz. Semicond Sci Technol, 2020, 35(7), 075025 doi: 10.1088/1361-6641/ab8b1e -
Proportional views
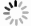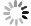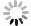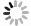




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: