| Citation: |
Xin Gu, Wen-Long Fei, Bao-Quan Sun, Ya-Kun Wang, Liang-Sheng Liao. Wide-bandgap and heavy-metal-free quantum dots for blue light-emitting diodes[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2025, 46(4): 041101. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24100016
****
X Gu, W L Fei, B Q Sun, Y K Wang, and L S Liao, Wide-bandgap and heavy-metal-free quantum dots for blue light-emitting diodes[J]. J. Semicond., 2025, 46(4), 041101 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24100016
|
Wide-bandgap and heavy-metal-free quantum dots for blue light-emitting diodes
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24100016
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.24100016
More Information-
Abstract
Colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) are highly regarded for their outstanding photovoltaic characteristics, including excellent color purity, stability, high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY), narrow emission spectra, and ease of solution processing. Despite significant progress in quantum dot light-emitting diodes (QLEDs) technology since its inception in 1994, blue QLEDs still fall short in efficiency and lifespan compared to red and green versions. The toxicity concerns associated with Cd/Pb-based quantum dots (QDs) have spurred the development of heavy-metal-free alternatives, such as group Ⅱ−Ⅵ (e.g., ZnSe-based QDs), group Ⅲ−Ⅴ (e.g., InP, GaN QDs), and carbon dots (CDs). In this review, we discuss the key properties and development history of quantum dots (QDs), various synthesis approaches, the role of surface ligands, and important considerations in developing core/shell (C/S) structured QDs. Additionally, we provide an outlook on the challenges and future directions for blue QLEDs. -
References
[1] Pietryga J M, Park Y S, Lim J, et al. Spectroscopic and device aspects of nanocrystal quantum dots. Chem Rev, 2016, 116, 10513 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00169[2] Fei W L, Li S N, Xie J C, et al. X-type ligands effect on the operational stability of heavy-metal-free quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett, 2024, 24, 14066 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c04032[3] Wang A Q, Shen H B, Zang S P, et al. Bright, efficient, and color-stable violet ZnSe-based quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 2951. doi: 10.1039/C4NR06593J[4] Shtykov S N, Rusanova T Y. Nanomaterials and nanotechnologies in chemical and biochemical sensors: Capabilities and applications. Russ J Gen Chem, 2008, 78, 2521 doi: 10.1134/S1070363208120323[5] Chuang C H M, Brown P R, Bulović V, et al. Improved performance and stability in quantum dot solar cells through band alignment engineering. Nat Mater, 2014, 13, 796 doi: 10.1038/nmat3984[6] Chen Y J, Herrnsdorf J, Guilhabert B, et al. Laser action in a surface-structured free-standing membrane based on a π-conjugated polymer-composite. Org Electron, 2011, 12, 62 doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2010.09.021[7] Wei H Y, Wei Q, Fang F, et al. Blue lasing from heavy-metal-free colloidal quantum dots. Laser Photonics Rev, 2023, 17, 2200557 doi: 10.1002/lpor.202200557[8] Jia H R, Wang F Z, Tan Z A. Material and device engineering for high-performance blue quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale, 2020, 12, 13186 doi: 10.1039/D0NR02074E[9] Pan J L, Yu Y J, Wang Y K, et al. Lanthanide ion-doped perovskite nanocrystals in electroluminescent device. Adv Funct Mater, 2024, 34, 2401327 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202401327[10] Li H H, Wang Y K, Liao L S. Near-infrared luminescent materials incorporating rare earth/transition metal ions: From materials to applications. Adv Mater, 2024, 36, 2403076 doi: 10.1002/adma.202403076[11] Pan J L, Shen W S, Li S N, et al. Polarity-mediated antisolvent control enables efficient lanthanide-based near-infrared perovskite LEDs. Nano Lett, 2024, 24, 2765 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c04586[12] Duan H W, Zhao F, Li S N, et al. Bi-ligand synergy enables threshold low voltage and bandgap stable pure-red mix-halide perovskite LEDs. Adv Funct Mater, 2024, 34, 2310697 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202310697[13] Wang Y K, Wan H Y, Teale S, et al. Long-range order enabled stability in quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nature, 2024, 629, 586 doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07363-7[14] Zhao J Y, Chen L X, Li D Z, et al. Large-area patterning of full-color quantum dot arrays beyond 1000 pixels per inch by selective electrophoretic deposition. Nat Commun, 2021, 12, 4603 doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24931-x[15] Dai X L, Deng Y Z, Peng X G, et al. Quantum-dot light-emitting diodes for large-area displays: Towards the dawn of commercialization. Adv Mater, 2017, 29, 1607022 doi: 10.1002/adma.201607022[16] Yang Z W, Gao M Y, Wu W J, et al. Recent advances in quantum dot-based light-emitting devices: Challenges and possible solutions. Mater Today, 2019, 24, 69 doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2018.09.002[17] Zhang J F, Wang L, Zhang X Y, et al. Blue light-emitting diodes based on halide perovskites: Recent advances and strategies. Mater Today, 2021, 51, 222 doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2021.10.023[18] Li H Y, Bian Y Y, Zhang W J, et al. High performance InP-based quantum dot light-emitting diodes via the suppression of field-enhanced electron delocalization. Adv Funct Mater, 2022, 32, 2204529 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202204529[19] Chao W C, Chiang T H, Liu Y C, et al. High efficiency green InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes by balancing electron and hole mobility. Commun Mater, 2021, 2, 96 doi: 10.1038/s43246-021-00203-5[20] Mei G D, Tan Y Z, Sun J Y, et al. Light extraction employing optical tunneling in blue InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2022, 120, 091101 doi: 10.1063/5.0084416[21] Battaglia D, Peng X G. Formation of high quality InP and InAs nanocrystals in a noncoordinating solvent. Nano Lett, 2002, 2, 1027 doi: 10.1021/nl025687v[22] Qu L H, Peng X G. Control of photoluminescence properties of CdSe nanocrystals in growth. J Am Chem Soc, 2002, 124, 2049 doi: 10.1021/ja017002j[23] Wu Q Q, Gong X W, Zhao D W, et al. Efficient tandem quantum-dot LEDs enabled by an inorganic semiconductor-metal-dielectric interconnecting layer stack. Adv Mater, 2022, 34, 2108150. doi: 10.1002/adma.202108150[24] Li S N, Pan J L, Yu Y J, et al. Advances in solution-processed blue quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Nanomaterials, 2023, 13, 1695 doi: 10.3390/nano13101695[25] Qiu C H, Melton W, Leksono M W, et al. Photocurrent decay in n-type GaN thin films. Appl Phys Lett, 1996, 69, 1282 doi: 10.1063/1.117392[26] Morkoc H, Strite S, Gao G B, et al. Large-band-gap SiC, Ⅲ-Ⅴ nitride, and Ⅱ-Ⅵ ZnSe-based semiconductor device technologies. J Appl Phys, 1994, 76, 1363 doi: 10.1063/1.358463[27] Schmidt L C, Pertegás A, González-Carrero S, et al. Nontemplate synthesis of CH3NH3PbBr3 perovskite nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc, 2014, 136, 850 doi: 10.1021/ja4109209[28] Tan Z K, Moghaddam R S, Lai M L, et al. Bright light-emitting diodes based on organometal halide perovskite. Nat Nanotechnol, 2014, 9, 687 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.149[29] Brus L. Electronic wave-functions in semiconductor clusters: Experiment and theory. J Phys Chem, 1986, 90, 2555 doi: 10.1021/j100403a003[30] Tang X B, Yang F Q. Quantum dots: Synthesis, characterization, and applications. Handbook of Energy Materials. Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2022, 1 doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-4480-1_27-1[31] Alivisatos A P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science, 1996, 271, 933 doi: 10.1126/science.271.5251.933[32] Chen Z N, Li H T, Yuan C X, et al. Color revolution: Prospects and challenges of quantum-dot light-emitting diode display technologies. Small Meth, 2024, 8, 2300359 doi: 10.1002/smtd.202300359[33] Jang E, Jang H. Review: Quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Chem Rev, 2023, 123, 4663 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00695[34] Ekimov A I, Efros A L, Onushchenko A A. Quantum size effect in semiconductor microcrystals. Solid State Commun, 1985, 56, 921 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1098(85)80025-9[35] Ekimov A I, Onushchenko A A. Quantum size effect in three-dimensional microscopic semiconductor crystals. JETP Lett, 2023, 118, S15 doi: 10.1134/S0021364023130040[36] Ekimov A I, Onushchenko A A, Tsekhomskii V A. Exciton absorption by CuCl crystals in a glassy matrix. Fiz Khim Stekla, 1980, 6, 511[37] Efros A, Efros A. Interband absorption of light in a semiconductor sphere. SPIE Milest Ser, 2005, 180, 71[38] Rossetti R, Nakahara S, Brus L E. Quantum size effects in the redox potentials, resonance Raman spectra, and electronic spectra of CdS crystallites in aqueous solution. J Chem Phys, 1983, 79, 1086 doi: 10.1063/1.445834[39] Brus L E. Electron-electron and electron-hole interactions in small semiconductor crystallites: The size dependence of the lowest excited electronic state. J Chem Phys, 1984, 80, 4403 doi: 10.1063/1.447218[40] Efros A L, Brus L E. Nanocrystal quantum dots: From discovery to modern development. ACS Nano, 2021, 15, 6192 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c01399[41] Dhawan S, Dhawan T, Vedeshwar A G. Growth of Nb2O5 quantum dots by physical vapor deposition. Mater Lett, 2014, 126, 32 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.03.107[42] Bart N, Dangel C, Zajac P, et al. Wafer-scale epitaxial modulation of quantum dot density. Nat Commun, 2022, 13, 1633 doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29116-8[43] Reilly C E, Keller S, Nakamura S, et al. Metalorganic chemical vapor deposition of InN quantum dots and nanostructures. Light Sci Appl, 2021, 10, 150 doi: 10.1038/s41377-021-00593-8[44] Shariat M, Karimipour M, Molaei M. Synthesis of CdS quantum dots using direct plasma injection in liquid phase. Plasma Chem Plasma Process, 2017, 37, 1133 doi: 10.1007/s11090-017-9819-5[45] Murray C B, Norris D J, Bawendi M G. Synthesis and characterization of nearly monodisperse CdE (E = sulfur, selenium, tellurium) semiconductor nanocrystallites. J Am Chem Soc, 1993, 115, 8706 doi: 10.1021/ja00072a025[46] Ayyaril S S, Shanableh A, Bhattacharjee S, et al. Recent progress in micro and nano-encapsulation techniques for environmental applications: A review. Results Eng, 2023, 18, 101094 doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101094[47] Sohail M I, Waris A A, Ayub M A, et al. Environmental application of nanomaterials: A promise to sustainable future. Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019, 1 doi: 10.1016/bs.coac.2019.10.002[48] Joe S Y, Yoon B, Shin D, et al. Time-resolved mechanism of positive aging in InP quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2024, 16, 46486 doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c10646[49] Kim T, Kim K H, Kim S, et al. Efficient and stable blue quantum dot light-emitting diode. Nature, 2020, 586, 385 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2791-x[50] Yuan F, Wang Y K, Sharma G, et al. Bright high-colour-purity deep-blue carbon dot light-emitting diodes via efficient edge amination. Nat Photonics, 2019, 14, 171 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0557-5[51] Li S N, Kong F C, Yu Y J, et al. Electroluminescence from GaN-based quantum dots. Adv Optical Mater, 2024, 12, 2301427 doi: 10.1002/adom.202301427[52] Sun Y Z, Jiang Y B, Sun X W, et al. Beyond OLED: Efficient quantum dot light-emitting diodes for display and lighting application. Chem Rec, 2019, 19, 1729 doi: 10.1002/tcr.201800191[53] Colvin V L, Schlamp M C, Alivisatos A P. Light-emitting-diodes made from cadmium selenide nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. Nature, 1994, 370, 354 doi: 10.1038/370354a0[54] Dabbousi B O, Bawendi M G, Onitsuka O, et al. Electroluminescence from CdSe quantum-dot/polymer composites. Appl Phys Lett, 1995, 66, 1316 doi: 10.1063/1.113227[55] Schlamp M C, Peng X G, Alivisatos A P. Improved efficiencies in light emitting diodes made with CdSe(CdS) core/shell type nanocrystals and a semiconducting polymer. J Appl Phys, 1997, 82, 5837 doi: 10.1063/1.366452[56] Coe S, Woo W K, Bawendi M, et al. Electroluminescence from single monolayers of nanocrystals in molecular organic devices. Nature, 2002, 420, 800 doi: 10.1038/nature01217[57] García de Arquer F P, Talapin D V, Klimov V I, et al. Semiconductor quantum dots: Technological progress and future challenges. Science, 2021, 373, eaaz8541 doi: 10.1126/science.aaz8541[58] Anikeeva P O, Halpert J E, Bawendi M G, et al. Quantum dot light-emitting devices with electroluminescence tunable over the entire visible spectrum. Nano Lett, 2009, 9, 2532 doi: 10.1021/nl9002969[59] Yalcin S E, Yang B Q, Labastide J A, et al. Electrostatic force microscopy and spectral studies of electron attachment to single quantum dots on indium tin oxide substrates. J Phys Chem C, 2012, 116, 15847 doi: 10.1021/jp305857d[60] Song N H, Zhu H M, Liu Z, et al. Unraveling the exciton quenching mechanism of quantum dots on antimony-doped SnO2 films by transient absorption and single dot fluorescence spectroscopy. ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 1599 doi: 10.1021/nn3054494[61] Stouwdam J W, Janssen R A J. Red, green, and blue quantum dot LEDs with solution processable ZnO nanocrystal electron injection layers. J Mater Chem, 2008, 18, 1889 doi: 10.1039/b800028j[62] Cho K S, Lee E K, Joo W J, et al. High-performance crosslinked colloidal quantum-dot light-emitting diodes. Nat Photonics, 2009, 3, 341 doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2009.92[63] Kim H Y, Park Y J, Kim J, et al. Transparent InP quantum dot light-emitting diodes with ZrO2 electron transport layer and indium zinc oxide top electrode. Adv Funct Mater, 2016, 26, 3454 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201505549[64] Dai X L, Zhang Z X, Jin Y Z, et al. Solution-processed, high-performance light-emitting diodes based on quantum dots. Nature, 2014, 515, 96 doi: 10.1038/nature13829[65] Zhang Z X, Ye Y X, Pu C D, et al. High-performance, solution-processed, and insulating-layer-free light-emitting diodes based on colloidal quantum dots. Adv Mater, 2018, 30, 1801387 doi: 10.1002/adma.201801387[66] Shen H B, Gao Q, Zhang Y B, et al. Visible quantum dot light-emitting diodes with simultaneous high brightness and efficiency. Nat Photonics, 2019, 13, 192 doi: 10.1038/s41566-019-0364-z[67] Lamer V K, Dinegar R H. Theory, production and mechanism of formation of monodispersed hydrosols. J Am Chem Soc, 1950, 72, 4847 doi: 10.1021/ja01167a001[68] Deng X Z, Zhang F J, Zhang Y, et al. Heavy-metal-free blue-emitting ZnSe(Te) quantum dots: Synthesis and light-emitting applications. J Mater Chem C, 2023, 11, 14495 doi: 10.1039/D3TC02699J[69] Kwon S G, Hyeon T. Formation mechanisms of uniform nanocrystals via hot-injection and heat-up methods. Small, 2011, 7, 2685 doi: 10.1002/smll.201002022[70] Hines M A, Guyot-Sionnest P. Bright UV-blue luminescent colloidal ZnSe nanocrystals. J Phys Chem B, 1998, 102, 3655 doi: 10.1021/jp9810217[71] Reiss P, Quemard G, Carayon S, et al. Luminescent ZnSe nanocrystals of high color purity. Mater Chem Phys, 2004, 84, 10 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2003.11.002[72] Banski M, Afzaal M, Malik M A, et al. Special role for zinc stearate and octadecene in the synthesis of luminescent ZnSe nanocrystals. Chem Mater, 2015, 27, 3797 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b00347[73] Liu Y, Tang Y, Ning Y, et al. "One-pot" synthesis and shape control of ZnSe semiconductor nanocrystals in liquid paraffin. J Mater Chem, 2010, 20, 4451 doi: 10.1039/c0jm00115e[74] Chen H S, Lo B, Hwang J Y, et al. Colloidal ZnSe, ZnSe/ZnS, and ZnSe/ZnSeS quantum dots synthesized from ZnO. J Phys Chem B, 2004, 108, 19566 doi: 10.1021/jp040689k[75] Ippen C, Greco T, Kim Y, et al. ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots as emitting material in blue QD-LEDs with narrow emission peak and wavelength tunability. Org Electron, 2014, 15, 126 doi: 10.1016/j.orgel.2013.11.003[76] Micic O I, Sprague J R, Curtis C J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of InP, GaP, and GaInP2 quantum dots. J Phys Chem, 1995, 99, 7754 doi: 10.1021/j100019a063[77] Yoo D, Choi M J. Asymmetric metal-carboxylate complexes for synthesis of InGaP alloyed quantum dots with blue emission. ACS Nano, 2024, 18, 16051 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.4c05643[78] Reiss P, Carrière M, Lincheneau C, et al. Synthesis of semiconductor nanocrystals, focusing on nontoxic and earth-abundant materials. Chem Rev, 2016, 116, 10731 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00116[79] Lee Y J, Kim S, Lee J, et al. Crystallographic and photophysical analysis on facet-controlled defect-free blue-emitting quantum dots. Adv Mater, 2024, 36, 2311719 doi: 10.1002/adma.202311719[80] Peng Q, Dong Y J, Deng Z X, et al. Low-temperature elemental-direct-reaction route to Ⅱ−Ⅵ semiconductor nanocrystalline ZnSe and CdSe. Inorg Chem, 2001, 40, 3840 doi: 10.1021/ic0100424[81] Zhang J, Chen Q H, Zhang W L, et al. Microwave-assisted aqueous synthesis of transition metal ions doped ZnSe/ZnS core/shell quantum dots with tunable white-light emission. Appl Surf Sci, 2015, 351, 655 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.178[82] Yao D, Liu Y, Li J, et al. Advances in green colloidal synthesis of metal selenide and telluride quantum dots. Chin Chemical Lett, 2019, 30, 277 doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2018.07.012[83] Long Z W, Liu M R, Wu X G, et al. A reactivity-controlled epitaxial growth strategy for synthesizing large nanocrystals. Nat Synth, 2023, 2, 296 doi: 10.1038/s44160-022-00210-5[84] Gao M, Yang H W, Shen H B, et al. Bulk-like ZnSe quantum dots enabling efficient ultranarrow blue light-emitting diodes. Nano Lett, 2021, 21, 7252 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c02284[85] Yang Z W, Wu Q Q, Zhou X C, et al. A seed-mediated and double shell strategy to realize large-size ZnSe/ZnS/ZnS quantum dots for high color purity blue light-emitting diodes. Nanoscale, 2021, 13, 4562 doi: 10.1039/D0NR05025C[86] Park S, Son C, Kang S, et al. Development of highly efficient blue-emitting ZnSe xTe1− x/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots and their electroluminescence application. J Ind Eng Chem, 2020, 88, 348 doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2020.05.003[87] Bi Y H, Cao S, Yu P, et al. Reducing emission linewidth of pure-blue ZnSeTe quantum dots through shell engineering toward high color purity light-emitting diodes. Small, 2023, 19, 2303247 doi: 10.1002/smll.202303247[88] Imran M, Paritmongkol W, Mills H A, et al. Molecular-additive-assisted tellurium homogenization in ZnSeTe quantum dots. Adv Mater, 2023, 35, 2303528 doi: 10.1002/adma.202303528[89] Kim Y H, Yoon S Y, Yang H. Blue-emissive ZnSeTe quantum dots and their electroluminescent devices. J Phys Chem Lett, 2024, 15, 2142 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.4c00070[90] He L J, Cao S, Li Q Y, et al. Achieving near-unity quantum yield in blue ZnSeTe quantum dots through NH4F molecular-assisted synthesis for highly efficient light-emitting diodes. Chem Eng J, 2024, 489, 151347 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.151347[91] Jang E P, Han C Y, Lim S W, et al. Synthesis of alloyed ZnSeTe quantum dots as bright, color-pure blue emitters. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11, 46062 doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b14763[92] Lee S H, Song S W, Yoon S Y, et al. Heterostructural tailoring of blue ZnSeTe quantum dots toward high-color purity and high-efficiency electroluminescence. Chem Eng J, 2022, 429, 132464 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132464[93] Xiang C Y, Koo W, Chen S, et al. Solution processed multilayer cadmium-free blue/violet emitting quantum dots light emitting diodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2012, 101, 053303 doi: 10.1063/1.4738375[94] Ji W Y, Jing P T, Fan Y, et al. Cadmium-free quantum dot light emitting devices: Energy-transfer realizing pure blue emission. Opt Lett, 2013, 38, 7 doi: 10.1364/OL.38.000007[95] Han C Y, Lee S H, Song S W, et al. More than 9% efficient ZnSeTe quantum dot-based blue electroluminescent devices. ACS Energy Lett, 2020, 5, 1568 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.0c00638[96] Li L, Reiss P. One-pot synthesis of highly luminescent InP/ZnS nanocrystals without precursor injection. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130, 11588 doi: 10.1021/ja803687e[97] Nematpour A, Nikoufard M. Plasmonic thin film InP/graphene-based Schottky-junction solar cell using nanorods. J Adv Res, 2018, 10, 15 doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2018.01.008[98] Yang D, Wang D K, Fang X, et al. Research progress in surface modification engineering and application of PbSe quantum dots. Laser Optoelectron Prog, 2023, 60, 1500004 doi: 10.3788/LOP221857[99] Bai R X, Yang J H, Wei D H, et al. Research progress of low-dimensional semiconductor materials in field of nonlinear optics. Acta Phys Sin, 2020, 69, 184211 doi: 10.7498/aps.69.20200206[100] Jo J H, Jo D Y, Choi S W, et al. Highly bright, narrow emissivity of InP quantum dots synthesized by aminophosphine: Effects of double shelling scheme and Ga treatment. Adv Optical Mater, 2021, 9, 2100427 doi: 10.1002/adom.202100427[101] Zhang H, Hu N, Zeng Z P, et al. High-efficiency green InP quantum dot-based electroluminescent device comprising thick-shell quantum dots. Adv Optical Mater, 2019, 7, 1801602 doi: 10.1002/adom.201801602[102] Park J, Won Y H, Han Y, et al. Tuning hot carrier dynamics of InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots by shell morphology control. Small, 2022, 18, 2105492 doi: 10.1002/smll.202105492[103] Mićić O I, Curtis C J, Jones K M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of InP quantum dots. J Phys Chem, 1994, 98, 4966 doi: 10.1021/j100070a004[104] Guzelian A A, Katari J E B, Kadavanich A V, et al. Synthesis of size-selected, surface-passivated InP nanocrystals. J Phys Chem, 1996, 100, 7212 doi: 10.1021/jp953719f[105] Mićić O I, Cheong H M, Fu H, et al. Size-dependent spectroscopy of InP quantum dots. J Phys Chem B, 1997, 101, 4904 doi: 10.1021/jp9704731[106] Mićić O I, Ahrenkiel S P, Nozik A J. Synthesis of extremely small InP quantum dots and electronic coupling in their disordered solid films. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 78, 4022 doi: 10.1063/1.1379990[107] Talapin D V, Rogach A L, Mekis I, et al. Synthesis and surface modification of amino-stabilized CdSe, CdTe and InP nanocrystals. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects, 2002, 202, 145 doi: 10.1016/S0927-7757(01)01078-0[108] Jang E, Kim Y, Won Y H, et al. Environmentally friendly InP-based quantum dots for efficient wide color gamut displays. ACS Energy Lett, 2020, 5, 1316 doi: 10.1021/acsenergylett.9b02851[109] Cui Z J, Yang D, Qin S T, et al. Advances, challenges, and perspectives for heavy-metal-free blue-emitting indium phosphide quantum dot light-emitting diodes. Adv Optical Mater, 2023, 11, 2202036 doi: 10.1002/adom.202202036[110] Mićić O I, Smith B B, Nozik A J. Core-shell quantum dots of lattice-matched ZnCdSe2 shells on InP cores: Experiment and theory. J Phys Chem B, 2000, 104, 12149 doi: 10.1021/jp0021502[111] Hahm D, Chang J H, Jeong B G, et al. Design principle for bright, robust, and color-pure InP/ZnSe xS1− x/ZnS heterostructures. Chem Mater, 2019, 31, 3476 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.9b00740[112] Ryu E, Kim S, Jang E, et al. Step-wise synthesis of InP/ZnS core-shell quantum dots and the role of zinc acetate. Chem Mater, 2009, 21, 573 doi: 10.1021/cm803084p[113] Lim K, Jang H S, Woo K. Synthesis of blue emitting InP/ZnS quantum dots through control of competition between etching and growth. Nanotechnology, 2012, 23, 485609 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/23/48/485609[114] Haubold S, Haase M, Kornowski A, et al. Strongly luminescent InP/ZnS core-shell nanoparticles. Chemphyschem, 2001, 2, 331 doi: 10.1002/1439-7641(20010518)2:5<331::AID-CPHC331>3.0.CO;2-0[115] Lim J, Bae W K, Lee D G, et al. InP@ZnSeS, Core@Composition gradient shell quantum dots with enhanced stability. Chem Mater, 2011, 23, 4459 doi: 10.1021/cm201550w[116] Kim S, Kim T, Kang M, et al. Highly luminescent InP/GaP/ZnS nanocrystals and their application to white light-emitting diodes. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134, 3804 doi: 10.1021/ja210211z[117] Park J P, Lee J J, Kim S W. Highly luminescent InP/GaP/ZnS QDs emitting in the entire color range via a heating up process. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 30094 doi: 10.1038/srep30094[118] Xie R G, Peng X G. Synthesis of Cu-doped InP nanocrystals (d-dots) with ZnSe diffusion barrier as efficient and color-tunable NIR emitters. J Am Chem Soc, 2009, 131, 10645 doi: 10.1021/ja903558r[119] Zhang Z L, Liu D, Li D Z, et al. Dual emissive Cu: InP/ZnS/InP/ZnS nanocrystals: Single-source "greener" emitters with flexibly tunable emission from visible to near-infrared and their application in white light-emitting diodes. Chem Mater, 2015, 27, 1405 doi: 10.1021/cm5047269[120] Pietra F, Kirkwood N, De Trizio L, et al. Ga for Zn cation exchange allows for highly luminescent and photostable InZnP-based quantum dots. Chem Mater, 2017, 29, 5192 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00848[121] Mei S L, Wei X, Yang D, et al. Color-tunable optical properties of cadmium-free transition metal ions doped InP/ZnS quantum dots. J Lumin, 2019, 212, 264 doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2019.04.040[122] Wegner K D, Pouget S, Ling W L, et al. Gallium-a versatile element for tuning the photoluminescence properties of InP quantum dots. Chem Commun, 2019, 55, 1663 doi: 10.1039/C8CC09740B[123] Wei X, Mei S L, Yang B B, et al. Optical and morphological properties of single-phased and dual-emissive InP/ZnS quantum dots via transition metallic and inorganic ions. Langmuir, 2020, 36, 10244 doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c01788[124] Liu H, Shang G L, Ren C, et al. Photophysical properties of Mn-doped InP/ZnS nanocrystals. J Phys Chem C, 2021, 125, 21748 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.1c06858[125] Hughes K E, Stein J L, Friedfeld M R, et al. Effects of surface chemistry on the photophysics of colloidal InP nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 14198 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b07027[126] Shen W, Tang H Y, Yang X L, et al. Synthesis of highly fluorescent InP/ZnS small-core/thick-shell tetrahedral-shaped quantum dots for blue light-emitting diodes. J Mater Chem C, 2017, 5, 8243 doi: 10.1039/C7TC02927F[127] Zhang H, Ma X Y, Lin Q L, et al. High-brightness blue InP quantum dot-based electroluminescent devices: The role of shell thickness. J Phys Chem Lett, 2020, 11, 960 doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b03567[128] Zhang W D, Ding S H, Zhuang W D, et al. InP/ZnS/ZnS core/shell blue quantum dots for efficient light-emitting diodes. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30, 2005303 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202005303[129] Zhang W D, Tan Y Z, Duan X J, et al. High quantum yield blue InP/ZnS/ZnS quantum dots based on bromine passivation for efficient blue light-emitting diodes. Adv Optical Mater, 2022, 10, 2200685 doi: 10.1002/adom.202200685[130] Kim K H, Jo J H, Jo D Y, et al. Cation-exchange-derived InGaP alloy quantum dots toward blue emissivity. Chem Mater, 2020, 32, 3537 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c00551[131] Xu X Y, Ray R, Gu Y L, et al. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J Am Chem Soc, 2004, 126, 12736 doi: 10.1021/ja040082h[132] Yuan F L, Wang Z B, Li X H, et al. Bright multicolor bandgap fluorescent carbon quantum dots for electroluminescent light-emitting diodes. Adv Mater, 2024, 36, 2312060 doi: 10.1002/adma.202312060[133] Zhang T Y, Wang X, Wu Z Y, et al. Highly stable and bright blue light-emitting diodes based on carbon dots with a chemically inert surface. Nanoscale Adv, 2021, 3, 6949 doi: 10.1039/D1NA00576F[134] An Y L, Liu C, Li Y, et al. Preparation of multicolour solid fluorescent carbon dots for light-emitting diodes using phenylethylamine as a co-carbonization agent. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23, 11071 doi: 10.3390/ijms231911071[135] Zhang D Y, Wang J Y, Yin J X, et al. Bright blue light-emitting diodes based on well-modified carbon dots by designing co-host systems to balance carriers’ injection. Adv Optical Mater, 2023, 11, 2300075 doi: 10.1002/adom.202300075[136] Choi Y C, Kim H, Lee C, et al. Blue emission of α-GaN colloidal quantum dots via Zn doping. Chem Mater, 2019, 31, 5370 doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b05193[137] Xie Y, Qian Y, Wang W, et al. A benzene-thermal synthetic route to nanocrystalline GaN. Science, 1996, 272, 1926 doi: 10.1126/science.272.5270.1926[138] Dimos K, Jankovič L, Koutselas I B, et al. Low-temperature synthesis and characterization of gallium nitride quantum dots in ordered mesoporous silica. J Phys Chem C, 2012, 116, 1185 doi: 10.1021/jp208011y -
Proportional views




 Xin Gu received his B.E. degree from Soochow University in 2024. Currently, he is a master student at the Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University under the supervision of Professor Liang-Sheng Liao and Ya-Kun Wang. His research interests focus on blue light quantum dot materials and their optoelectronic applications.
Xin Gu received his B.E. degree from Soochow University in 2024. Currently, he is a master student at the Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University under the supervision of Professor Liang-Sheng Liao and Ya-Kun Wang. His research interests focus on blue light quantum dot materials and their optoelectronic applications. Wen-Long Fei received his B.E. degree from Henan Polytechnic University in 2023. Currently, he is a master student in Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University under the supervision of Prof. Liang-Sheng Liao and Prof. Ya-Kun Wang. His research interest focus on high-performance quantum dots light-emitting diodes in blue region.
Wen-Long Fei received his B.E. degree from Henan Polytechnic University in 2023. Currently, he is a master student in Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Soochow University under the supervision of Prof. Liang-Sheng Liao and Prof. Ya-Kun Wang. His research interest focus on high-performance quantum dots light-emitting diodes in blue region. Ya-Kun Wang obtained his Ph.D. in Chemistry from Soochow University (International Visiting Graduate Student (IVGS) in Edward Sargent group from 2018−2020). Following this, he served as a postdoctoral researcher at the Sargent Group at the University of Toronto and Soochow University. Since 2023, he has held the position of associate professor at Soochow University. His research focuses on leveraging emerging quantum dots (QDs) to develop high-performance light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in the shortwave IR region.
Ya-Kun Wang obtained his Ph.D. in Chemistry from Soochow University (International Visiting Graduate Student (IVGS) in Edward Sargent group from 2018−2020). Following this, he served as a postdoctoral researcher at the Sargent Group at the University of Toronto and Soochow University. Since 2023, he has held the position of associate professor at Soochow University. His research focuses on leveraging emerging quantum dots (QDs) to develop high-performance light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in the shortwave IR region. Liang-Sheng Liao received his Ph.D. degree in physics from Nanjing University, China. After working at Eastman Kodak Company as a senior research scientist from 2000 to 2009, he joined Soochow University as a full professor. He has over 30 years of research experience on organic optoelectronics. His current research interests include materials and architectures of organic light-emitting diodes, quantum light-emitting diodes, organic photonics, organic solar cells, and perovskite solar cells.
Liang-Sheng Liao received his Ph.D. degree in physics from Nanjing University, China. After working at Eastman Kodak Company as a senior research scientist from 2000 to 2009, he joined Soochow University as a full professor. He has over 30 years of research experience on organic optoelectronics. His current research interests include materials and architectures of organic light-emitting diodes, quantum light-emitting diodes, organic photonics, organic solar cells, and perovskite solar cells.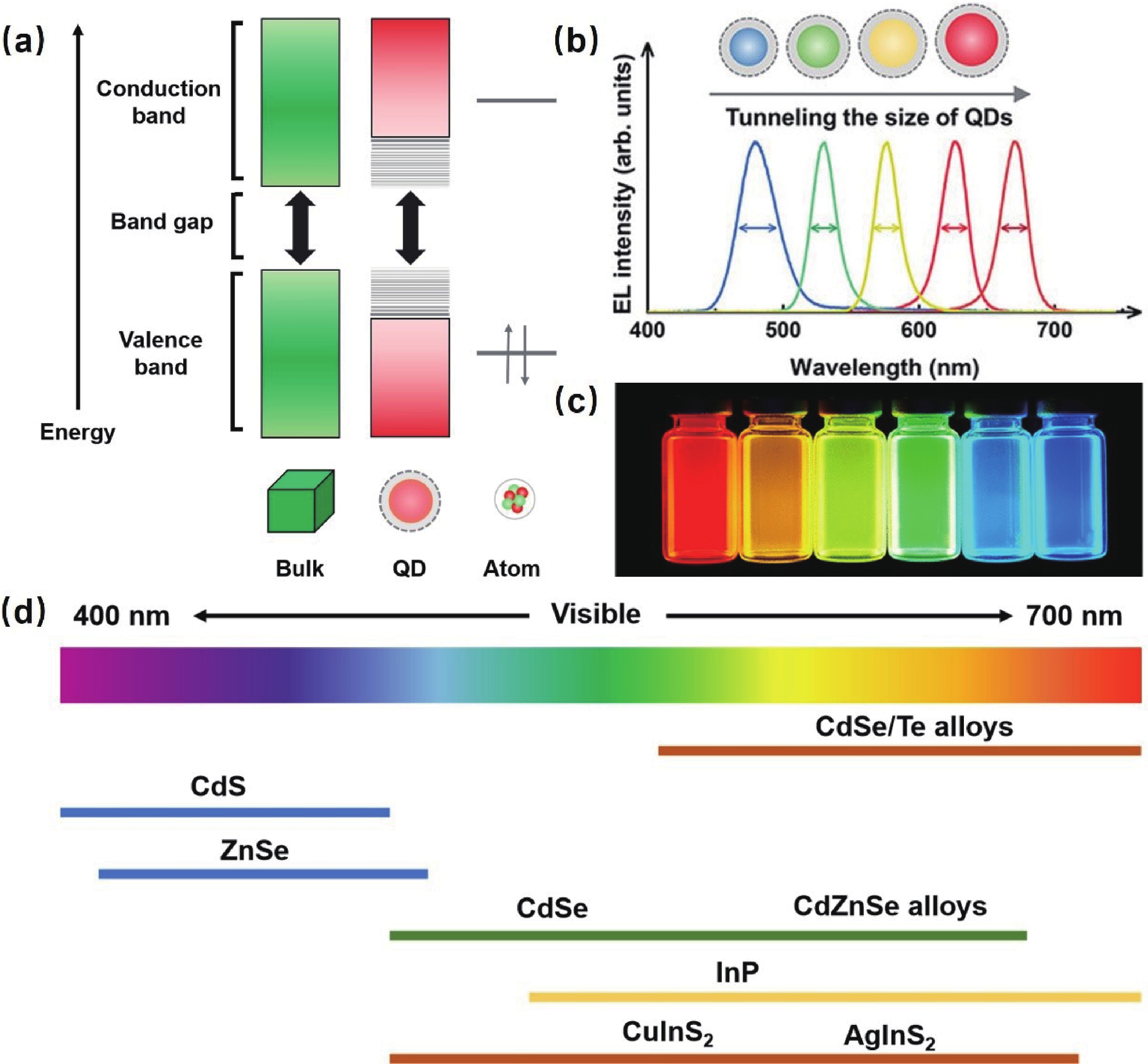
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: