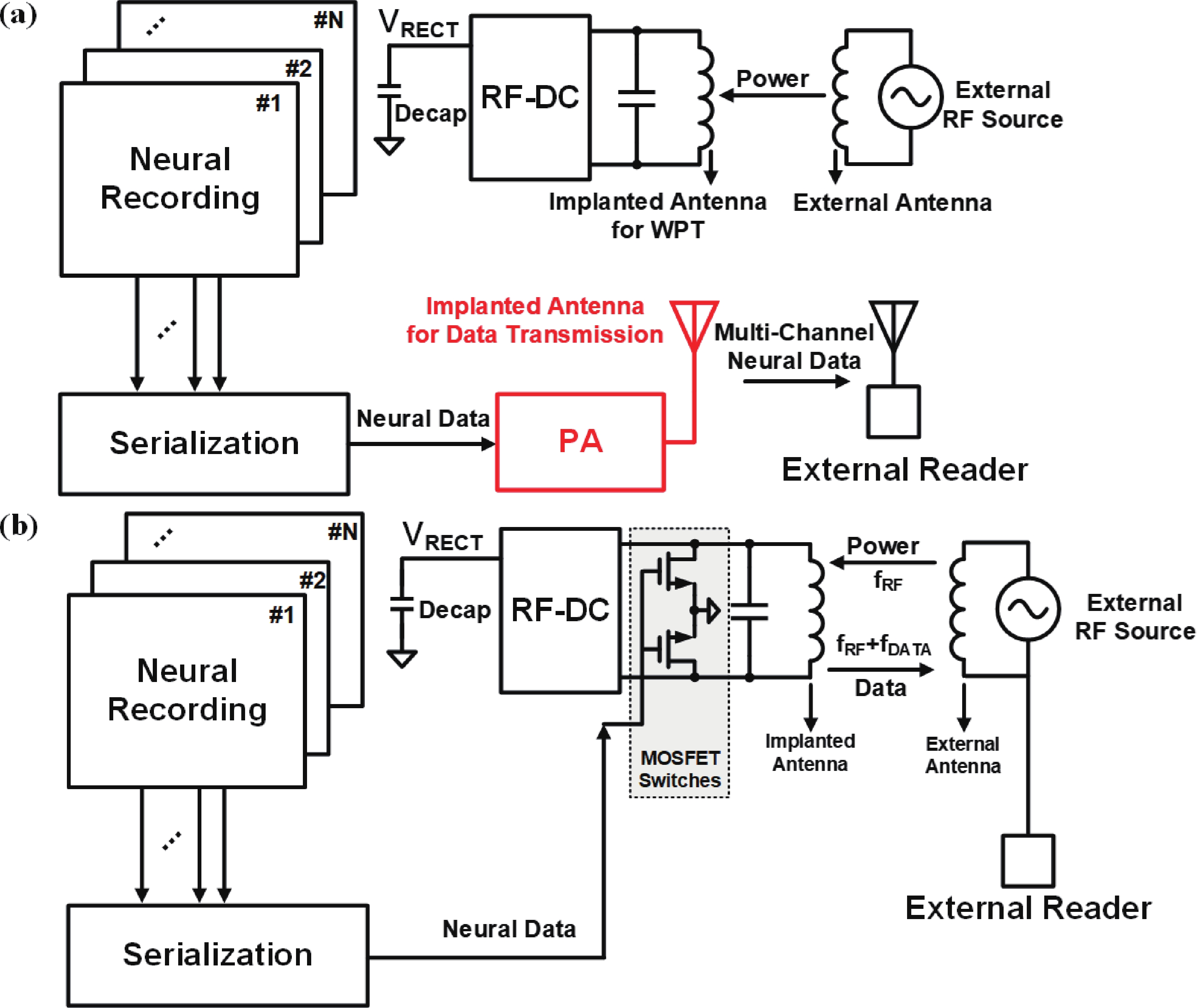
Battery-free radio systems utilizing wireless power transfer (WPT) further facilitate the miniaturization of neural implants. However, simultaneous monitoring of multiple neuronal activities is required to obtain high-fidelity neural signals. Consequently, the integration of numerous channels on a single chip and the wireless transmission of massive multi-channel data pose significant challenges for implantable battery-free neural interfaces. This work introduces dual overlapped on-chip antennas to eliminate the need for a battery in the neural implants and enable high-data-rate backscatter for transmitting the massive data acquired simultaneously from 72 channels. Additionally, an orthogonal coding and sampling technique is employed to reduce both power consumption and area per channel. Fabricated in a 65 nm CMOS process, the proposed chip integrates 72 neural recording channels within a 2 mm × 2 mm area and achieves a backscatter data rate of 18 Mbps.
Just Accepted manuscripts are peer-reviewed and accepted for publication. They are posted online prior to technical editing formatting for publication and author proofing.
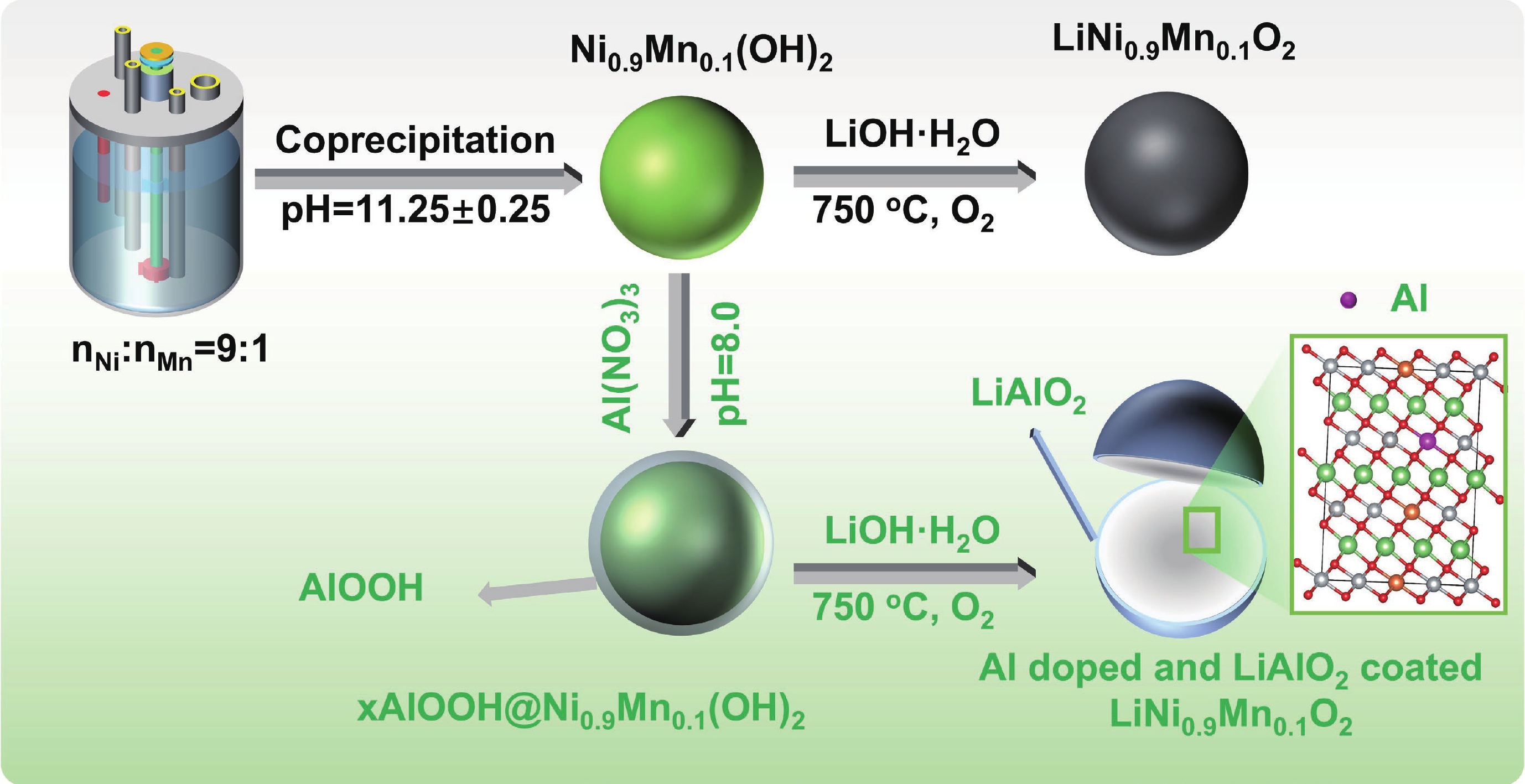
LiNi0.9Mn0.1O2 (LNM91) is a promising cobalt-free, high-energy cathode material for next-generation lithium-ion batteries, but its commercialization is challenged by rapid capacity fading resulting from bulk and interfacial structural degradation. Herein, an in-situ surface-to-bulk dual-modification strategy is developed to synthesize 6Al-LNM91 (6 mol% Al modified LNM91) via a one-step calcination process based on Al diffusion chemistry. This method concurrently constructs a protective LiAlO2 coating and incorporates Al3+ into the bulk lattice, effectively enhancing the structural integrity of the cathode during cycling. The optimized 6Al-LNM91 cathode delivers a remarkable rate capability of 165 mA∙h∙g−1 at 10 C and maintains 94.03% capacity retention after 120 cycles at 0.5 C (2.8 − 4.4 V), substantially outperforming the pristine material (76.82% of LNM91). This organic solvent-free, single-step modification approach offers a scalable and efficient route for improving high-nickel layered oxide cathodes.
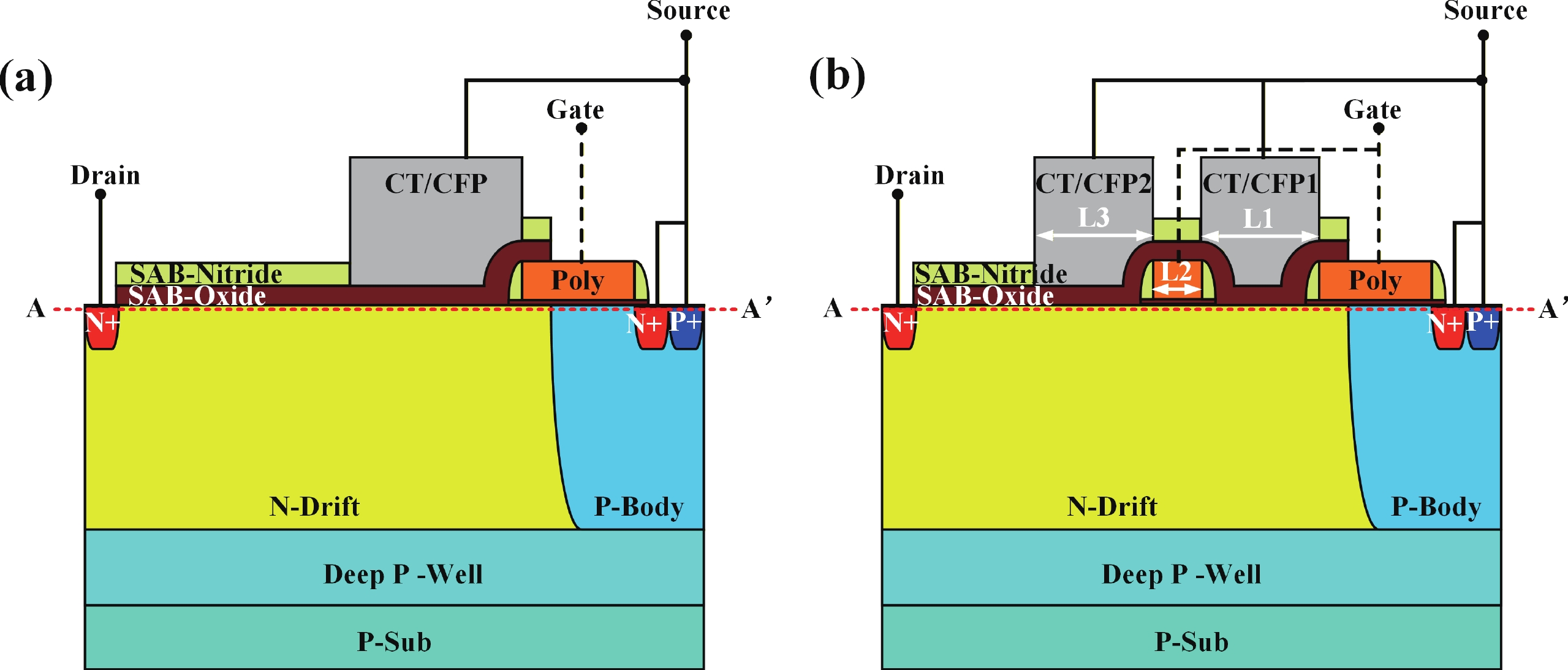
To improve the breakdown voltage (BV)−specific on-resistance (Ron,sp) trade-off and enhance manufacturability, this article proposes a novel lateral diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor (LDMOS) structure that features a split gate and split contact field plate (CFP). This novel structure requires no additional bias voltages, masks, or process steps, making it fully compatible with the bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) process flow. The physical mechanisms are elucidated through Technology computer-aided design (TCAD) simulations. In the on-state, the positively biased split gate forms an accumulation layer at the drift region surface, thereby reducing Ron,sp. In the off-state, both the split gate and split CFP introduce additional electric-field peaks that smooth the lateral electric field, thus preserving a high BV. Compared with the conventional CFP-LDMOS, the proposed CFP-LDMOS achieves an 8.52% reduction in Ron,sp without compromising BV, leading to an 8.07% improvement in the figure of merit (FOM). Notably, the proposed structure can be extended to LDMOS devices across different voltage levels within BCD platforms, demonstrating its broad applicability.
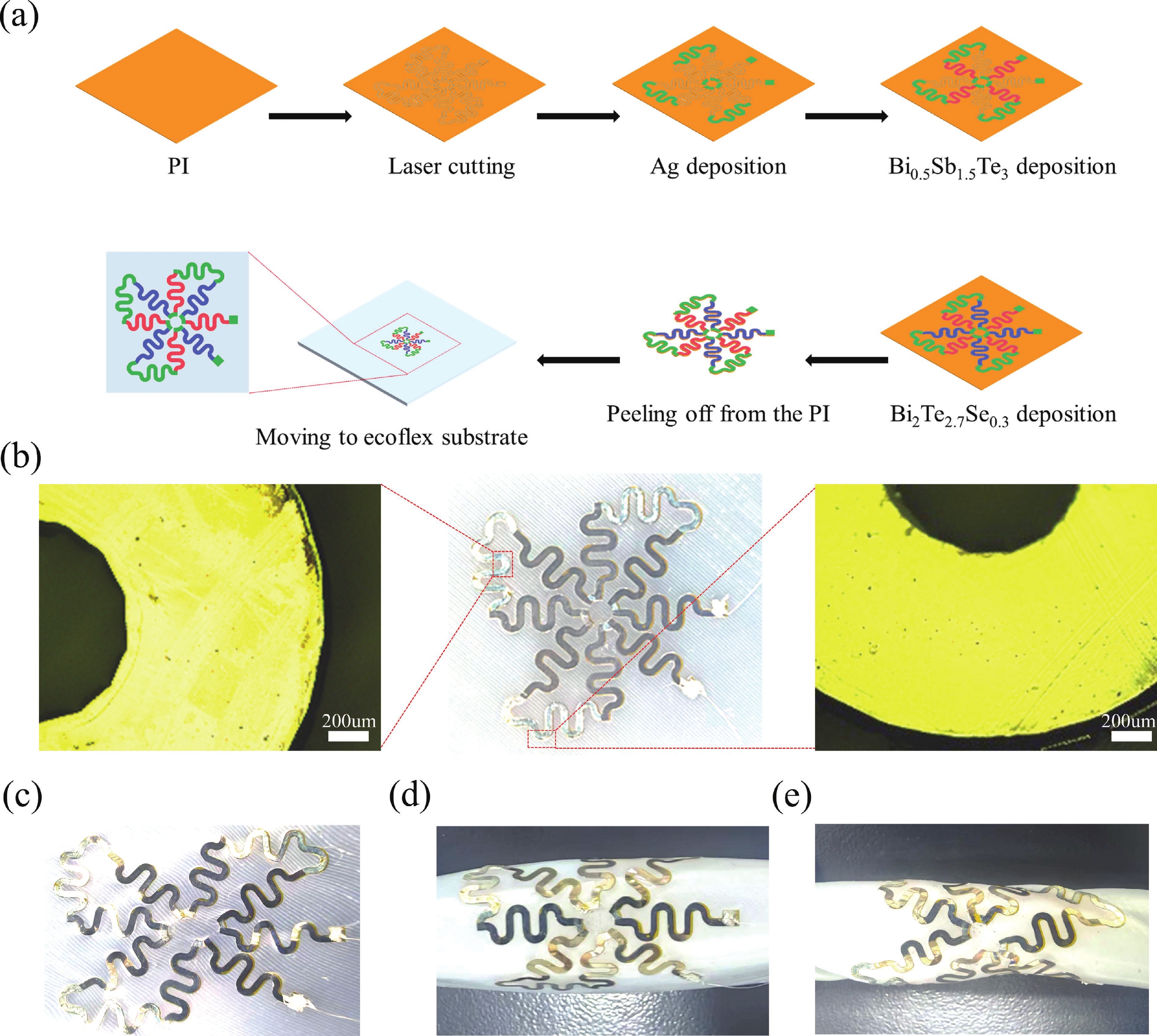
Thermoelectric power generation has attracted significant interest for its capability to directly convert thermal energy into electricity. Among various configurations, thin-film thermoelectric generators (TEGs) stand out due to their lightweight nature and facile integration, offering promising applications in waste heat recovery and wearable electronics. However, the performance of such devices under complex mechanical conditions, particularly under biaxial tensile strain, remains underexplored. In this work, we designed and fabricated a thin-film TEG insensitive to tensile strain and performed a parametric analysis using validated 3D numerical simulations to evaluate the effects of environmental conditions, material properties, and geometric parameters. Notably, the designed device maintained stable electrical performance under various biaxial tensile strains. Owing to its miniature and thin profile, variations in any component of the generator significantly affected its electrical performance. The results indicated that reduced thermal conductivity of the substrate and Ecoflex layer, as well as a thinner substrate, enhance the output voltage. Furthermore, longer thermoelectric legs within a certain range contributed to higher output voltage. Higher output voltage was more readily achieved when the inner radius length was close to the radius of the heat source. This work provides valuable insights for the development of high-performance compliant TEGs applicable in dynamic mechanical environments, such as complex stretching in the back and shoulder–elbow regions induced by human motion.
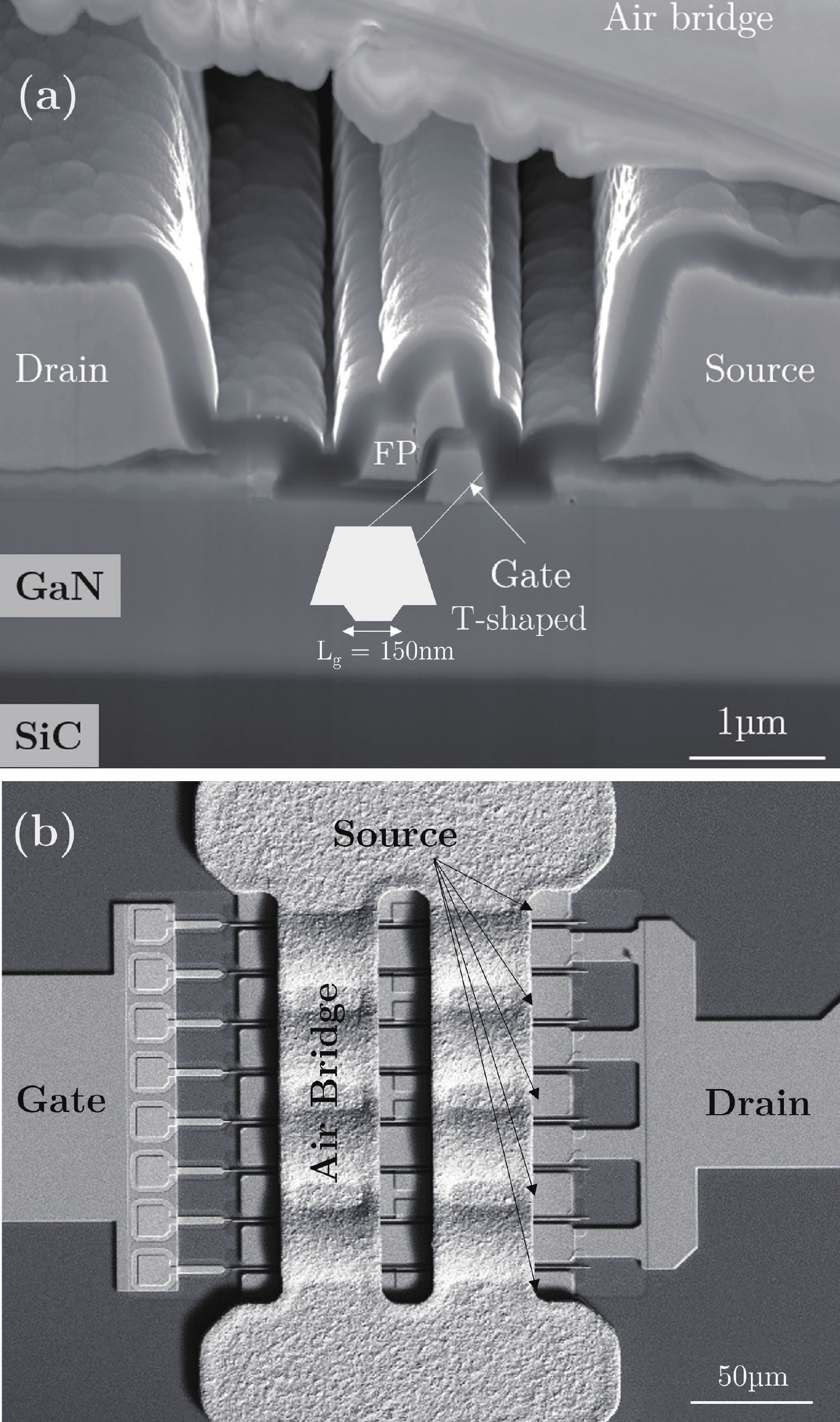
This work focuses on the early-life drift mechanisms in 150 nm AlGaN/GaN HEMTs on SiC under RF-HTOL stress at 9 GHz and 130 °C. Electrical measurements during the first hours of stress reveal significant shifts in threshold voltage, transconductance, and drain lag, indicating the activation of deep traps located in the buffer. A transient increase in gate leakage current is also observed under reverse gate bias, suggesting additional trapping or conduction paths at the AlGaN/SiN or cap/passivation interface. These electrical instabilities coincide with a progressive degradation of RF performance, notably in gain and power-added efficiency. Electroluminescence measurements further support the presence of electrically active defects, with distinct spatial patterns depending on the bias configuration.