| Citation: |
Xue Wu, Wu Lu, Yiyuan Wang, Jialing Xu, Leqing Zhang, Jian Lu, Xin Yu, Xingyao Zhang, Tianle Hu. Total ionizing dose effects on a radiation-induced BiMOS analog-to-digital converter[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(1): 015006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/1/015006
****
X Wu, W Lu, Y Y Wang, J L Xu, L Q Zhang, J Lu, X Yu, X Y Zhang, T L Hu. Total ionizing dose effects on a radiation-induced BiMOS analog-to-digital converter[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(1): 015006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/1/015006.
|
Total ionizing dose effects on a radiation-induced BiMOS analog-to-digital converter
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/1/015006
More Information
-
Abstract
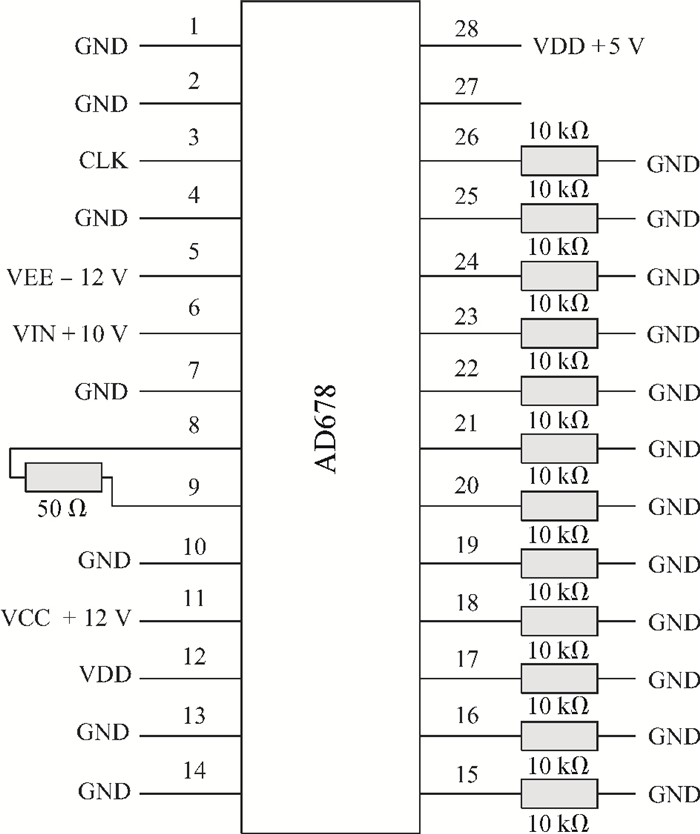
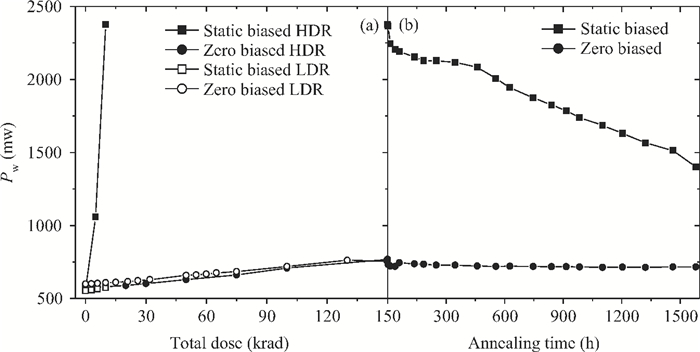
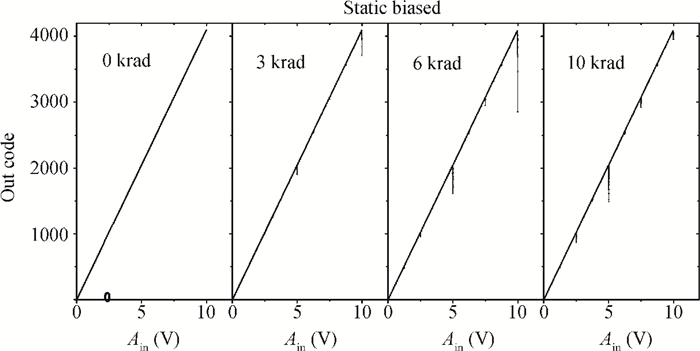
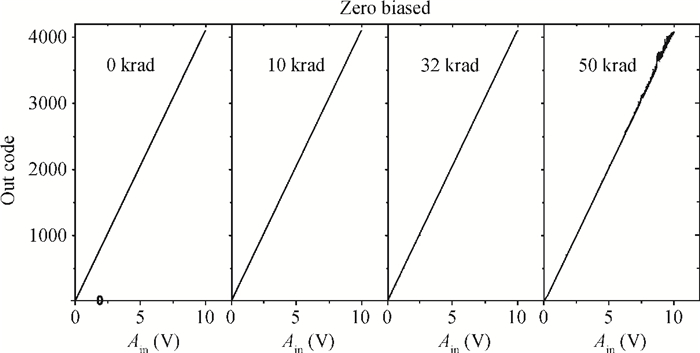
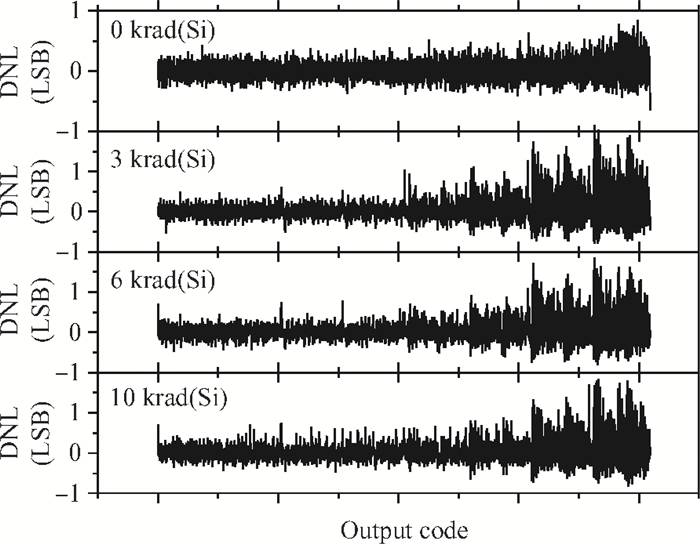
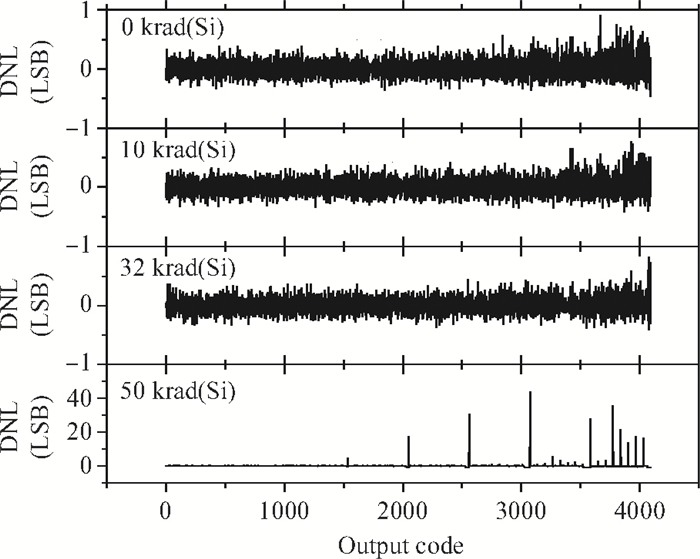
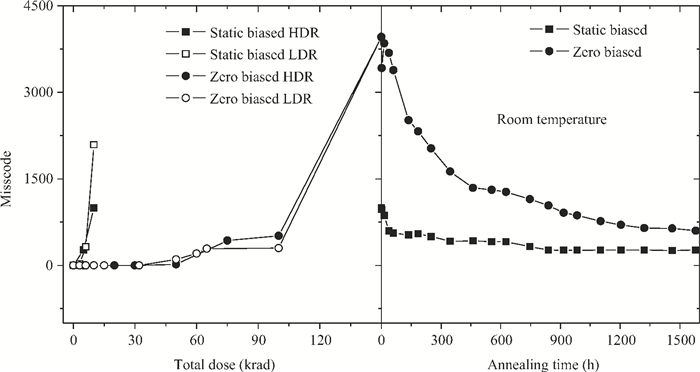
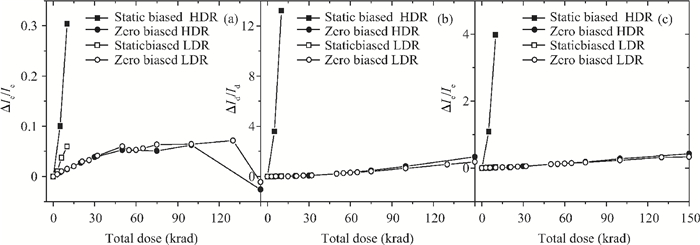
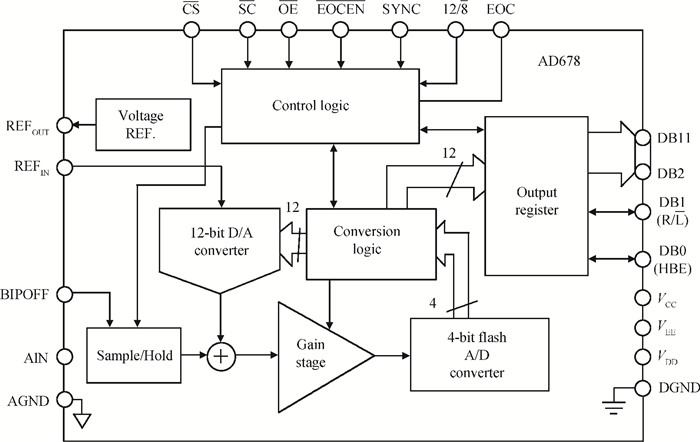
The total dose effect of an AD678 with a BiMOS process is studied. We investigate the performance degradation of the device in different bias states and at several dose rates. The results show that an AD678 can endure 3 krad(Si) at low dose rate and 5 krad(Si) at a high dose rate for static bias. The sensitive parameters to the bias states also differ distinctly. We find that the degradation is more serious on static bias. The underlying mechanisms are discussed in detail.-
Keywords:
- BiMOS,
- A/D converter,
- 60Co γ radiation,
- bias state,
- dose rate
-
References
[1] Lee C I, Rax B G, Johnston A H. Total ionizing dose effects in 12-bit successive-approximation analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop, Snowbird, Utah, 1993:112[2] Lee C I, Rax B G, Johnston A H. Total ionizing dose effects on high resolution (12/14-bit) analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1994, 41(6):2459 doi: 10.1109/23.340602[3] Lee C I, Rax B G, Johnston A H. Hardness assurance and testing techniques for high resolution (12 to 16 bit) analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1995, 42(6):1681 doi: 10.1109/23.488766[4] Youk G U. Dose rate effects of a bipolar AD converter. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop, Indian Wells, 1996:38 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/574186/keywords[5] Guo Q, Ren D, Fan L, et al. Ionizing radiation effect of analog to digital converters. Nucl Tech, 1997, 20(1):753[6] Xing K, Wang Y, Pan H. Radiation effect test on ADC/DAC and high density memory devices with 60Co γ-rays. J Radiati Res Radiat Processing, 2006, 24(4):253 https://www.researchgate.net/institution/Brookhaven_National_Laboratory/department/Instrumentation_Division/publications[7] Zheng Yuzhan, Lu Wu, Ren Diyuan, et al. Characteristics of high-and low-dose-rate damage for domestic npn transistors of various emitter areas. Acta Physica Sinic, 2009, 58(8):5572 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/1/015006/meta[8] Shaneyfelt M R, Dodd P E, Draper B L, et al. Challenges in hardening technologies using shallow-trench isolation. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1998, 45(6):2584 doi: 10.1109/23.736501[9] Enlow E W, Pease R L, Combs W, et al. Response of advanced bipolar processes to ionizing radiation. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1991, 49(6):1342 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/124115/?arnumber=124115[10] Lee C I, Johnston A H. Comparison of total dose responses on high resolution analog-to-digital converter technologies. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1998, 45(3):1444 doi: 10.1109/23.685221[11] Chavez R M, Rax B G, Scheick L Z, et al. Total ionizing dose effects in bipolar and BiCMOS devices. IEEE Radiation Effects Data Workshop, Seattle WA, 2005:144 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6522833/keywords[12] Fleetwood D M, Kosier S L, Nowlin R N, et al. Physical mechanisms contribution enhanced bipolar gain degradation at low dose rate. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 1994, 41(6):1871 doi: 10.1109/23.340519[13] Rashkeev S N, Cirba C R, Fleetwood D M, et al. Physical model for enhanced interface-trap formation at low dose rate. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2002, 38(6):2650 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1134199/authors[14] Hjalmarson H P, Pease R L, Witczak S C, et al. Mechanisms for radiation dose-rate sensitivity of bipolar transistors. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2003, 50(6):1901 doi: 10.1109/TNS.2003.821803 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: