| Citation: |
Guowei Wang, Wei Xiang, Yingqiang Xu, Liang Zhang, Zhenyu Peng, Yanqiu Lü, Junjie Si, Juan Wang, Junliang Xing, Zhengwei Ren, Zhichuan Niu. Growth and fabrication of a mid-wavelength infrared focal plane array based on type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb superlattices[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(11): 114012. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/114012
****
G W Wang, W Xiang, Y Q Xu, L Zhang, Z Y Peng, Y Lü, J J Si, J Wang, J L Xing, Z W Ren, Z C Niu. Growth and fabrication of a mid-wavelength infrared focal plane array based on type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb superlattices[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(11): 114012. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/114012.
|
Growth and fabrication of a mid-wavelength infrared focal plane array based on type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb superlattices
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/11/114012
More Information
-
Abstract
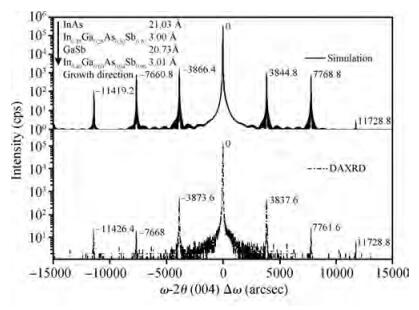
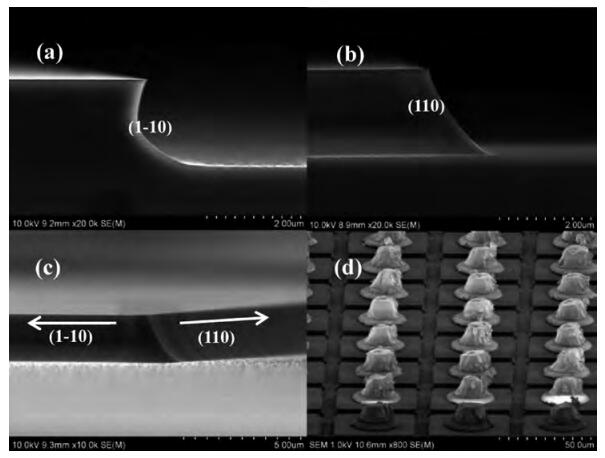
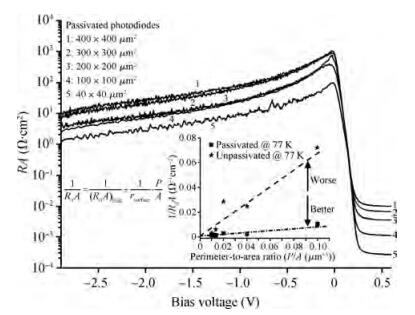
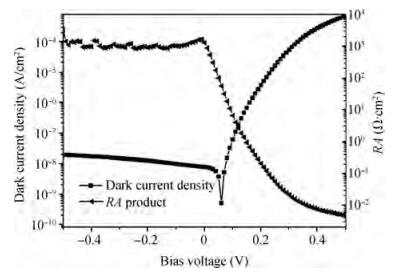
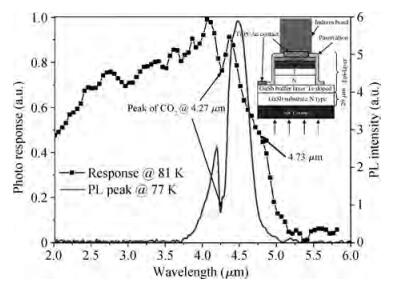
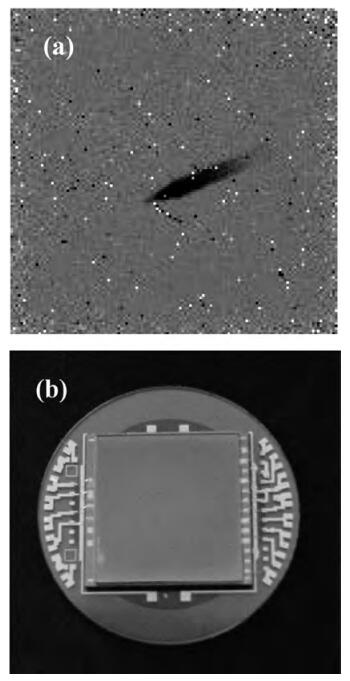
We present the fabrication of a mid-wavelength infrared focal plane array (FPA) based on type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb strain layer superlattices (SLs). The detectors contain a 400-period 8 ML InAs/8 ML GaSb SL active layer, which is grown by solid source molecular beam epitaxy on GaSb (100) N type substrates. Lattice mismatch between the superlattices and GaSb substrate achieves 148.9 ppm. The full width at half maximum of the first order satellite peak from X-ray diffraction was 28 arcsec. Single element detectors and FPA with a 128×128 pixels were fabricated using citric acid based solution wet chemical etching. Chemical and physical passivation effectively reduces the surface leakage and this process was characterized by Ⅰ-Ⅴ measurement. The devices showed a 50% cut-off wavelength of 4.73 μm at 77 K. The photodiode exhibited an R0A of 103 Ω· cm2. The FPA was characterized with an integration time of 0.5 ms and F/2.0 optics at 77 K and the average blackbody detectivity of the detectors is 2.01×109 cm·Hz1/2/W.-
Keywords:
- superlattices,
- GaSb,
- focal plane array,
- infrared detector
-
References
[1] Smith D L, Mailhiot C. Theory of semiconductor superlattice electronic structure. Rev Mod Phys, 1990, 62(1):173 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.62.173[2] Gautam N, Kim H S, Kutty M N, et al. Performance improvement of longwave infrared photodetector based on type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb superlattices using unipolar current blocking layers. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 96(23):231107 doi: 10.1063/1.3446967[3] Nguyen B M, Hoffman D, Huang E K W, et al. Background limited long wavelength infrared type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb superlattice photodiodes operating at 110 K. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 93(12):123502 doi: 10.1063/1.2978330[4] Delaunay P Y, Nguyen B M, Hoffman D, et al. Background limited performance of long wavelength infrared focal plane arrays fabricated from M-structure InAs-GaSb superlattices. IEEE J Quant Electron, 2009, 45(1/2):157[5] Huang E K W, Hoffman D, Nguyen B M, et al. Surface leakage reduction in narrow band gap type-Ⅱ antimonide-based superlattice photodiodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2009, 94(5):053506 doi: 10.1063/1.3078282[6] Hill C J, Soibel A, Keo S A, et al. Demonstration of large format mid-wavelength infrared focal plane arrays based on superlattice and BIRD detector structures. Infrared Phys Technol, 2009, 52(6):348 doi: 10.1016/j.infrared.2009.09.007[7] Cabanski W, Munzberg M, Rode W, et al. Third generation focal plane array IR detection modules and applications. Proc SPIE, 2005, 5783:340 doi: 10.1117/12.605818[8] Walther M, Rehm R, Fleissner J, et al. InAs/GaSb type-Ⅱ short-period superlattices for advanced single and dual-color focal plane arrays. Proc SPIE, 2007, 6542:654206 doi: 10.1117/12.719227[9] Lew A Y, Zuo S L, Yu E T, et al. Anisotropy and growth-sequence dependence of atomic-scale interface structure in InAs/Ga1-xInxSb superlattices. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 70(1):75 doi: 10.1063/1.119311[10] Rodriguez J B, Christol P, Cerutti L, et al. MBE growth and characterization of type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb superlattices for mid-infrared detection. J Cryst Growth, 2005, 274(1/2):6[11] Aifer E H, Jackson E M, Bennett B R, et al. Suppression of bulk defects in antimonide superlattice infrared photodiodes. In: Wehrspohn R B, Marz R, Noda S, et al. ed. Materials and devices for optoelectronics and microphotonics. Materials Research Society: Warrendale, 2002: 275[12] Szmulowicz F, Haugan H J, Brown G J, et al. Interfaces as design tools for short-period InAs/GaSb type-Ⅱ superlattices for mid-infrared detectors. Opto-Electronics Rev, 2006, 14(1):71[13] Sullivan G J, Ikhlassi A, Bergman J, et al. Molecular beam epitaxy growth of high quantum efficiency InAs/GaSb superlattice detectors. J Vac Sci Technol B, 2005, 23(3):1144 doi: 10.1116/1.1928238[14] Walther M, Rehm R, Schmitz J, et al. Defect density reduction in InAs/GaSb type Ⅱ superlattice focal plane array infrared detectors. Proc SPIE 2011:79451N[15] Bracker A S, Yang M J, Bennett B R, et al. Surface reconstruction phase diagrams for InAs, AlSb, and GaSb. J Cryst Growth, 2000, 220(4):384 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(00)00871-X[16] Chaghi R, Cervera C, Ait-Kaci H, et al. Wet etching and chemical polishing of InAs/GaSb superlattice photodiodes. Semicond Sci Technol, 2009, 24(6):065010 doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/24/6/065010[17] Kim H S, Plis E, Rodriguez J B, et al. Mid-IR focal plane array based on type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb strain layer superlattice detector with nBn design. Appl Phys Lett, 2008, 92(18):183502 doi: 10.1063/1.2920764[18] Kim H S, Plis E, Gautam N, et al. Reduction of surface leakage current in InAs/GaSb strained layer long wavelength superlattice detectors using SU-8 passivation. Appl Phys Lett, 2010, 97(14):143512 doi: 10.1063/1.3499290[19] Bogdanov S, Nguyen B M, Hoang A M, et al. Surface leakage current reduction in long wavelength infrared type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb superlattice photodiodes. Appl Phys Lett, 2011, 98(18):183501 doi: 10.1063/1.3584853[20] Walther M, Rehm R, Fuchs F, et al. 256×256 focal plane array midwavelength infrared camera based on InAs/GaSb short-period superlattices. J Electronic Materials, 2005, 34(6):722 doi: 10.1007/s11664-005-0010-z[21] Razeghi M, Pour S A, Huang E K, et al. Type-Ⅱ InAs/GaSb photodiodes and focal plane arrays aimed at high operating temperatures. Opto-Electronics Review, 2011, 19(3):261 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: