| Citation: |
Minchao Zhou, Danzhu Lü, Lin Cheng, BillYang Liu, Zhiliang Hong. A dual-path, current-sensing resistor-free boost LED driver with fast PWM dimming[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(4): 045005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045005
****
M C Zhou, D Lü, L Cheng, B Liu, Z L Hong. A dual-path, current-sensing resistor-free boost LED driver with fast PWM dimming[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(4): 045005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045005.
|
A dual-path, current-sensing resistor-free boost LED driver with fast PWM dimming
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045005
More Information
-
Abstract
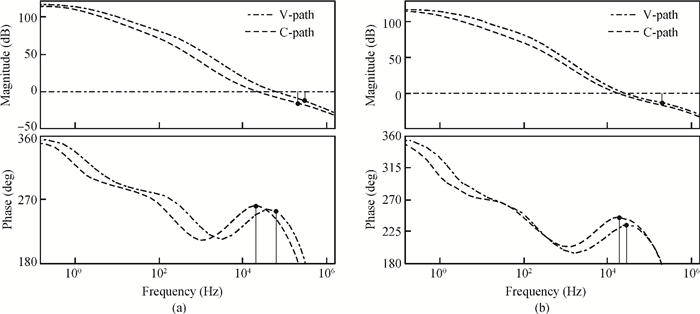
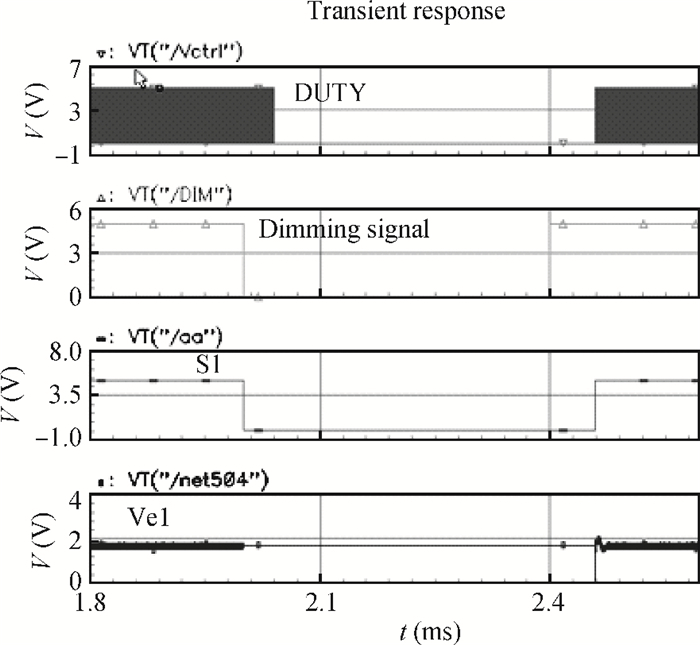
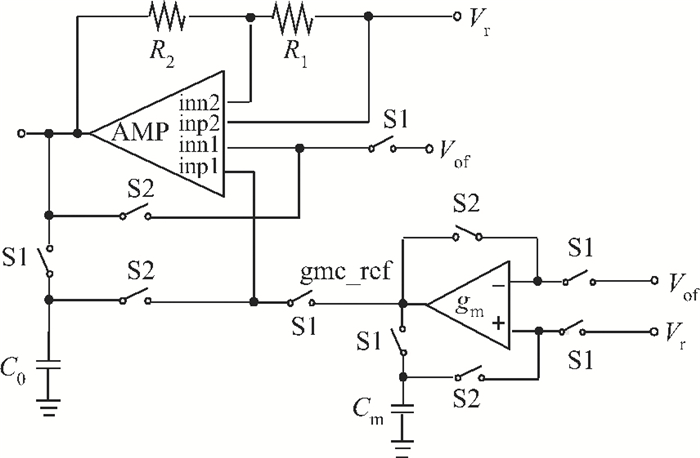
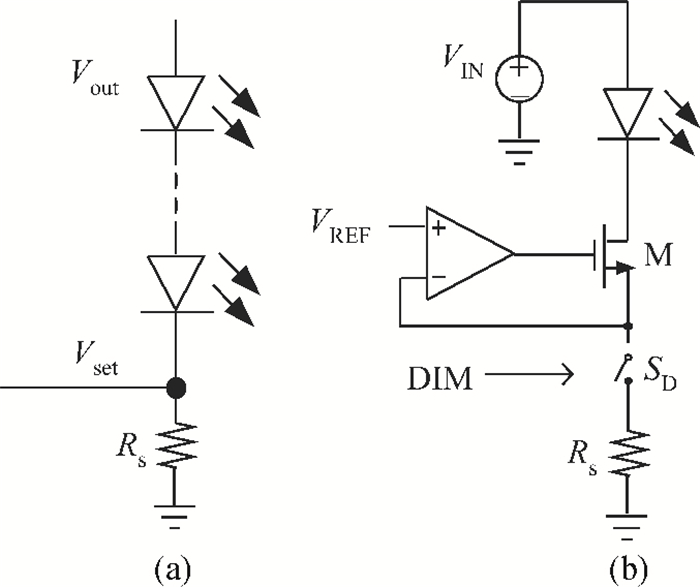
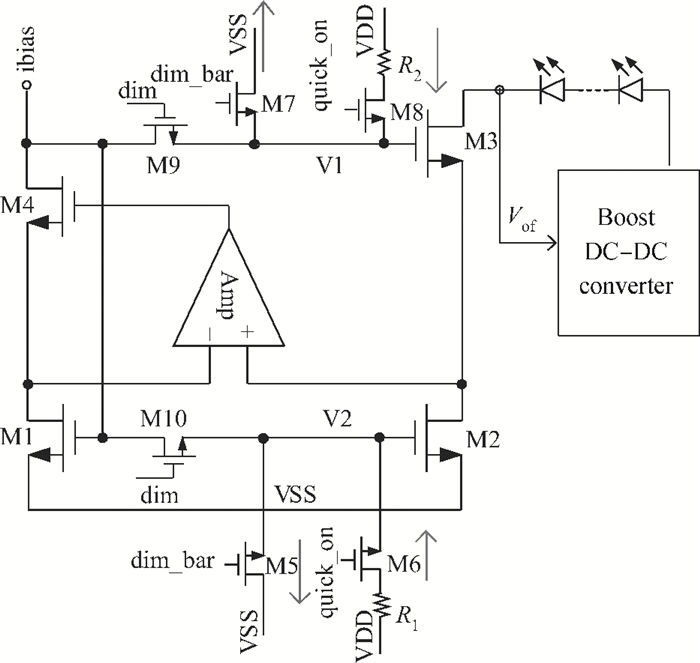
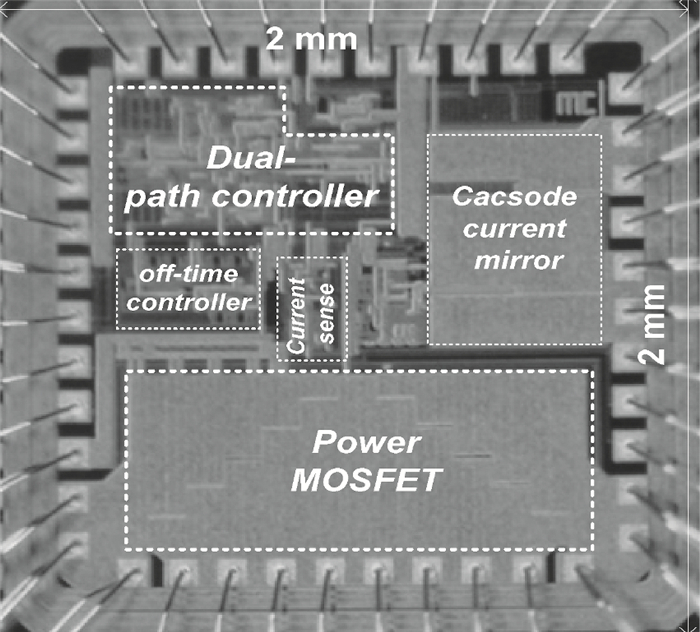
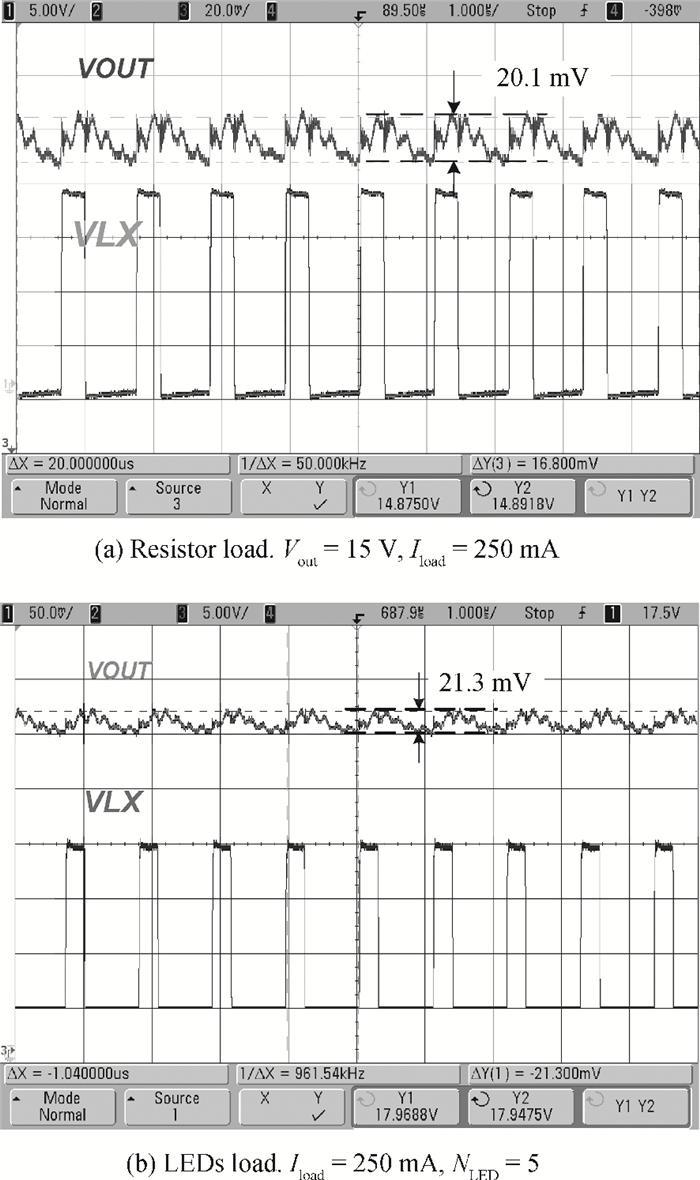
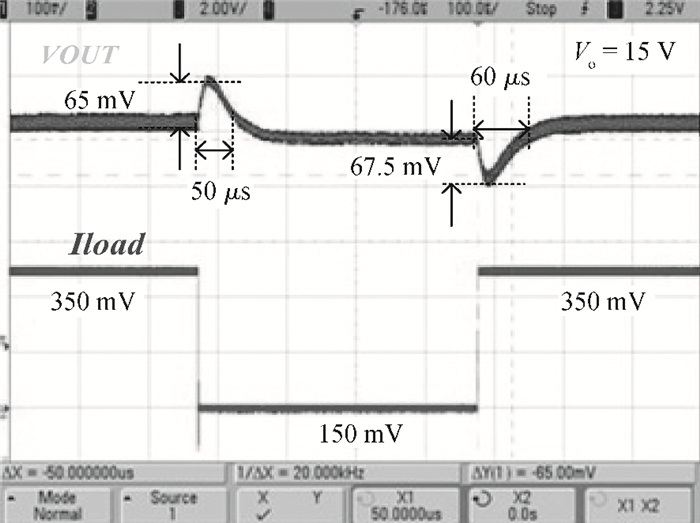
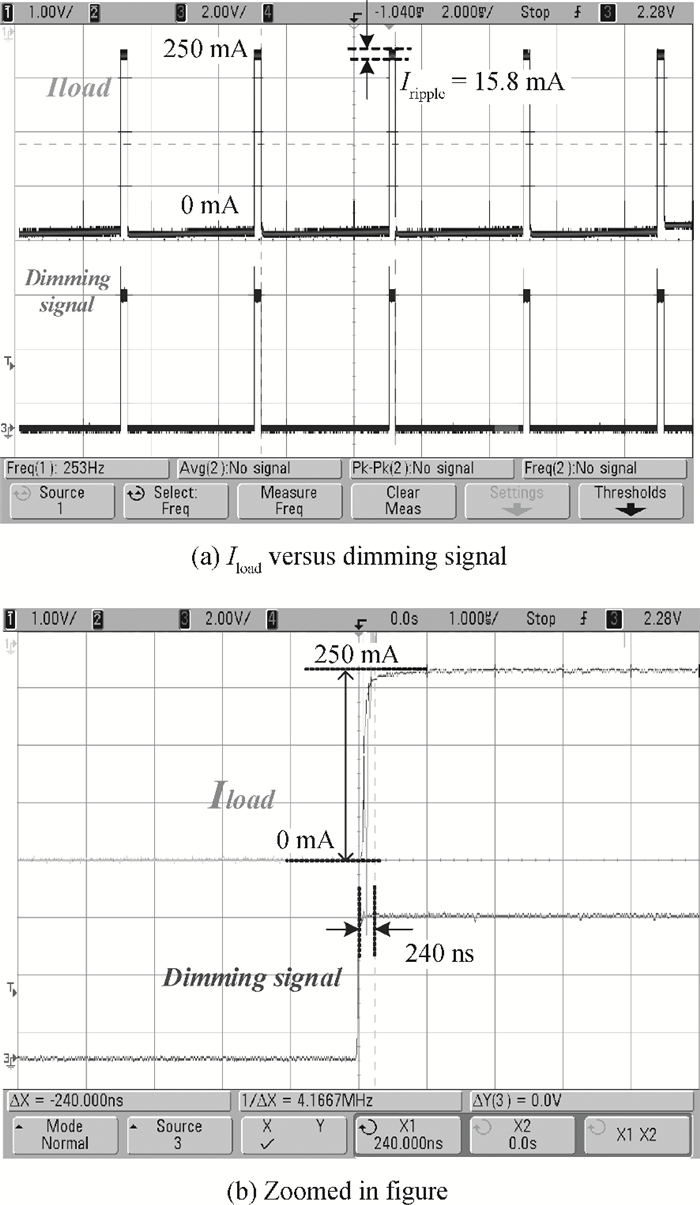
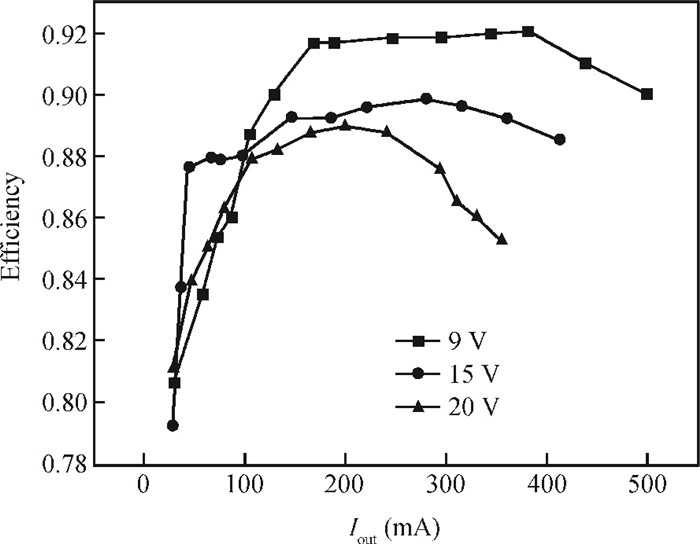
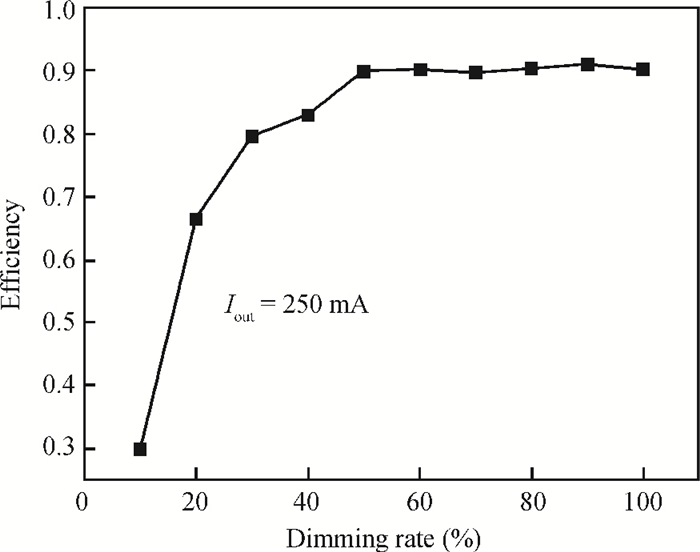
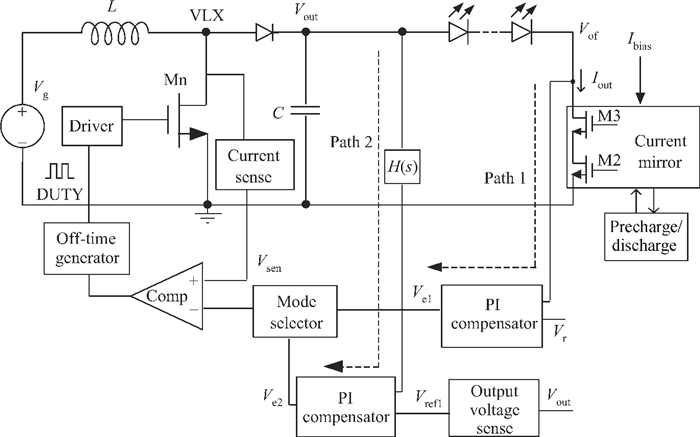
A boost LED driver featuring a high PWM dimming ratio and optimized efficiency is presented. This LED driver, which has a low dropout voltage and is able to drive 3-7 LEDs in series with constant output current and fast PWM dimming, provides an alternative technique for brightness adjustment. A dual-path control scheme with automatic switching and state maintenance is proposed. Meanwhile, a cascode current mirror structure is applied with the output transistor multiplexed as an LED PWM dimming transistor. Implemented in 0.5 μm 25 V BCD process, the measurement results show that a voltage conversion range of 5 V input to 6-24 V output with constant output current is obtained. With automatically switching dual-path control and an optimized current mirror, the response time during PWM dimming is reduced to as low as 240 ns and the efficiency keeps above 89% over a wide PWM dimming ratio@250 mA output current.-
Keywords:
- boost LED driver,
- constant current,
- fast PWM dimming,
- dual-path,
- multiplex,
- efficiency
-
References
[1] Doshi M, Zane R. Digital architecture for driving large LED arrays with dynamic bus voltage regulation and phase shifted PWM. Proc IEEE APEC, 2007:287 http://www.ee.bgu.ac.il/~pedesign/Graduate_problem_papers/papers2007/LED_Mux.pdf?origin=publication_detail[2] Dyble M, Narendran N, Bierman A, et al. Impact of dimming white LEDs:chromaticity shifts due to different dimming methods. Proceedings of the SPIE, 2005, 5941:280 doi: 10.1117/12.625924.full[3] Xu Xiaoru, Wu Xiaobo. High dimming ratio LED driver with fast transient boost converter. IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, PESC, 2008:4192 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4592613/authors[4] Hong S I, Han J W, Kim D H, et al. A double-loop control LED backlight driver IC for medium-sized LCDs. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2010:116[5] Rao S, Khan Q, Bang S, et al. A 1.2 A buck-boost LED driver with 13% efficiency improvement using error-averaged sense FET-based current sensing. IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2011:238 https://experts.illinois.edu/en/publications/a-12a-buck-boost-led-driver-with-13-efficiency-improvement-using-[6] Erickson R W, Maksimovic D. Fundamentals of power electronics. Secaucus, NJ, USA:Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2000:300 doi: 10.1007%2Fb100747[7] Zaitsu R. Voltage mode boost converter small signal control loop analysis using the TPS61030. 2009[8] Ridley R B. Analysis and interpretation of loop gain of multiloop-controlled switching regulators. IEEE Trans Power Electron, 1988, 3(4):489 doi: 10.1109/63.17971[9] Cheng L, Ni J H. A constant off-time controlled boost converter with adaptive current sensing technique. IEEE ESSCIRC, 2011:443 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6045002/keywords[10] Texas Instrument. Compensating and measuring the control loop of a high-power LED driver. 2008[11] ST Microelectronics, part number STCF06. 1. 5 A white LED driver with I2C interface. 2010[12] Charlon O, Redman-White Q. Ultra high-compliance CMOS current mirrors for low voltage charge pumps and references. IEEE ESSCIRC, 2004:227 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: