| Citation: |
Jihong Zhang, Xuefei Bai, Lu Huang. A wideband CMOS inductorless low noise amplifier employing noise cancellation for digital TV tuner applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(9): 095011. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095011
****
J H Zhang, X F Bai, L Huang. A wideband CMOS inductorless low noise amplifier employing noise cancellation for digital TV tuner applications[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(9): 095011. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095011.
|
A wideband CMOS inductorless low noise amplifier employing noise cancellation for digital TV tuner applications
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/9/095011
More Information
-
Abstract
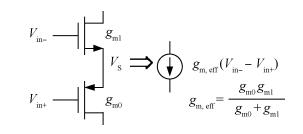
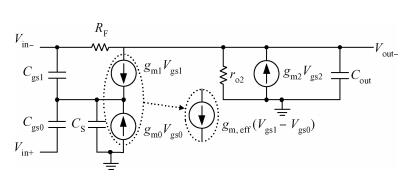
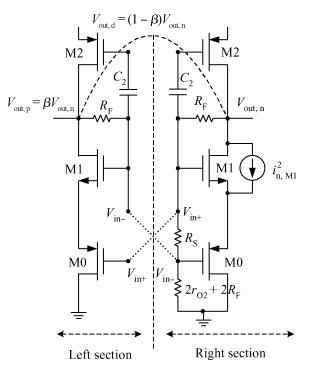
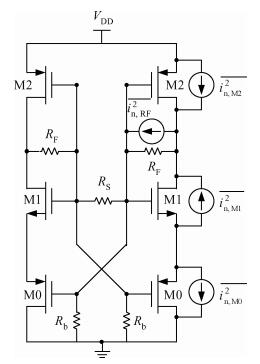
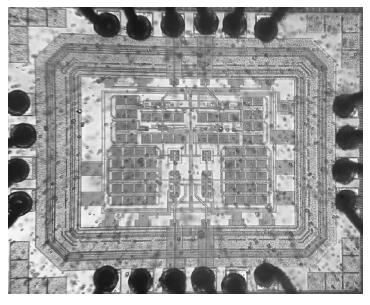
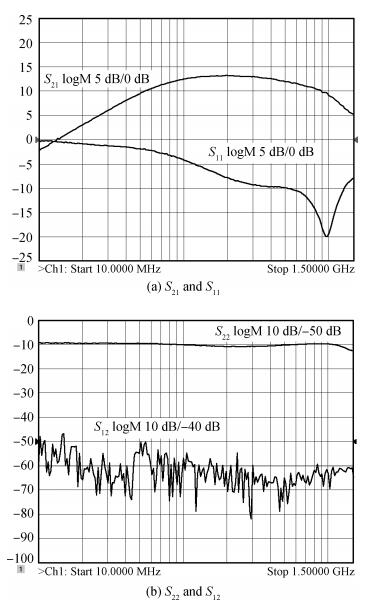
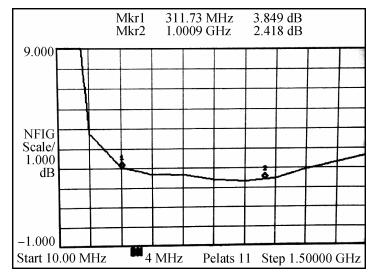
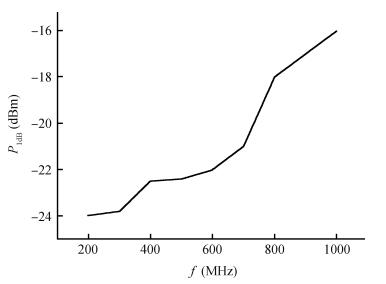
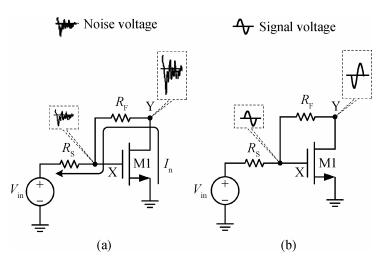
A wideband inductorless low noise amplifier for digital TV tuner applications is presented. The proposed LNA scheme uses a composite NMOS/PMOS cross-coupled transistor pair to provide partial cancellation of noise generated by the input transistors. The chip is implemented in SMIC 0.18 μm CMOS technology. Measurement shows that the proposed LNA achieves 12.2-15.2 dB voltage gain from 300 to 900 MHz, the noise figure is below 3.1 dB and has a minimum value of 2.3 dB, and the best input-referred 1-dB compression point (IP1dB) is -17 dBm at 900 MHz. The core consumes 7 mA current with a supply voltage of 1.8 V and occupies an area of 0.5×0.35 mm2.-
Keywords:
- LNA,
- noise cancellation,
- CMOS,
- wideband
-
References
[1] Yuan H Q, Lin F J, Fu Z Q, et al. A 0.18μm CMOS inductorless complementary-noise-canceling-LNA for TV tuner applications. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31(12):125006 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/12/125006[2] Bruccoleri F, Klumperink E A M, Nauta B. Wide-band CMOS low-noise amplifier exploiting thermal noise canceling. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(2):275 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.821786[3] Chen W H, Liu G, Zdravko B, et al. A highly linear broadband CMOS LNA employing noise and distortion cancellation. IEEE RFIC Symp, 2007:61 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4494645/[4] Blaakmeer S C, Klumperink E A M, Nauta B, et al. An inductorless wideband balun-LNA in 65 nm CMOS with balanced output. IEEE ESSCIRC, 2007:364 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4430319/[5] Woo S, Kim W, Lee C H, et al. A 3.6 mW differential common-gate CMOS LNA with positive-negative feedback. IEEE ISSCC, 2009:218 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4977386/?arnumber=4977386&searchWithin%3D60G%20power%20amplifier%26sortType%3Dasc_p_Sequence%26filter%3DAND(p_IS_Number:4977283)[6] Hampel S K, Schmitz O, Tiebout M, et al. Inductorless 1-10.5 GHz wideband LNA for multistandard applications. IEEE ASSCC, 2009:269[7] Kim J, Silva-Martinez J. Wideband inductorless balun-LNA employing feedback for low-power low-voltage applications. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2012, 60(9):2833 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2012.2206825[8] El-Nozahi M, Helmy A A, Sánchez-Sinencio E, et al. An inductor-less noise-cancelling broadband low noise amplifier with composite transistor pair in 90 nm CMOS Technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(5):1111 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2118310[9] Razavi B. RF microelectronics. 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2011, Chapter 5[10] Feng L S, Huang L, Bai X F, et al. A 0.18μm CMOS 3-5 GHz broadband flat gain low noise amplifier. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31(2):025003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/2/025003 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: