| Citation: |
Liang Chen, Zhiqun Li, Jia Cao, Chenjian Wu, Meng Zhang. A new wideband LNA using a gm-boosting technique[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(1): 015002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015002
****
L Chen, Z Q Li, J Cao, C J Wu, M Zhang. A new wideband LNA using a gm-boosting technique[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(1): 015002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015002.
|
A new wideband LNA using a gm-boosting technique
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015002
More Information
-
Abstract
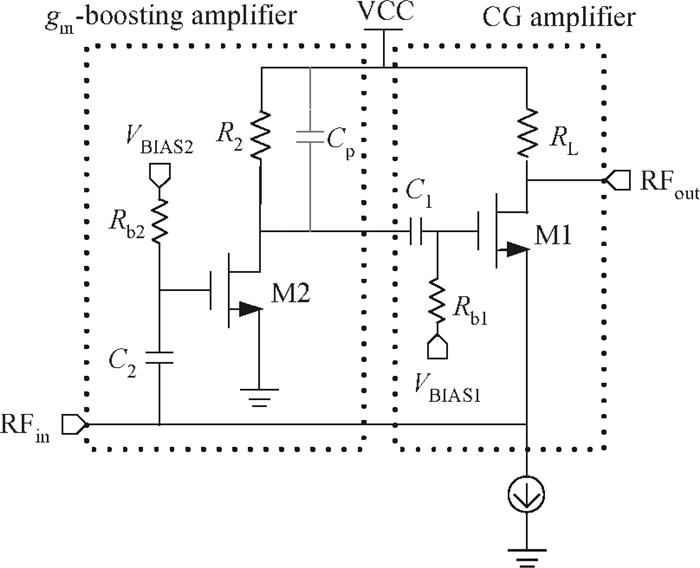
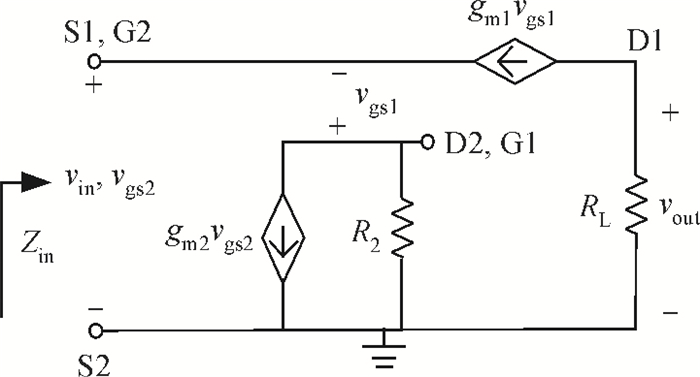
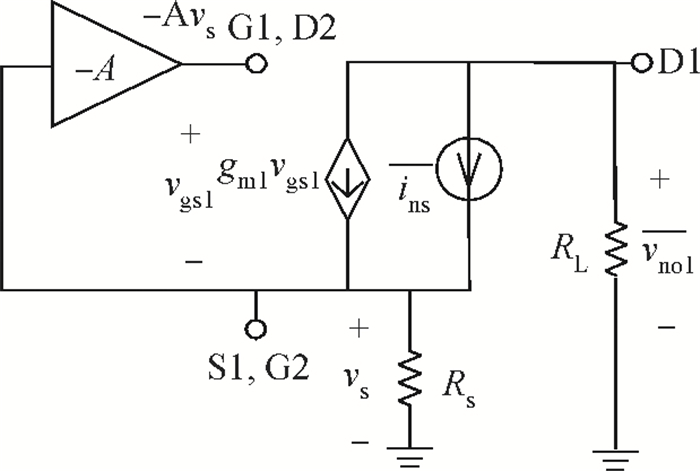
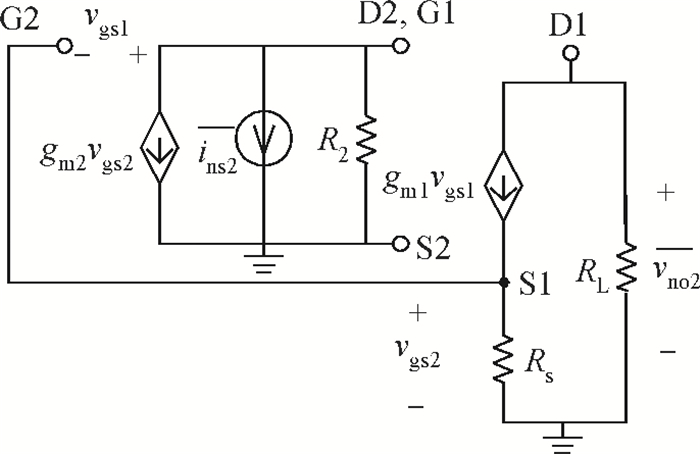
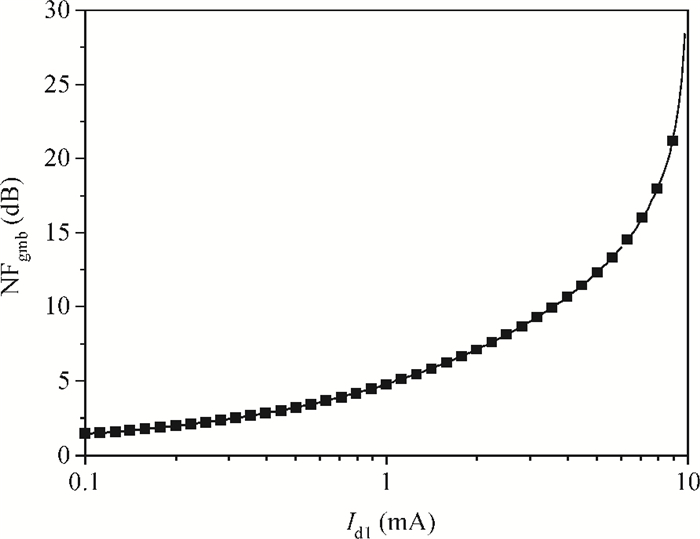
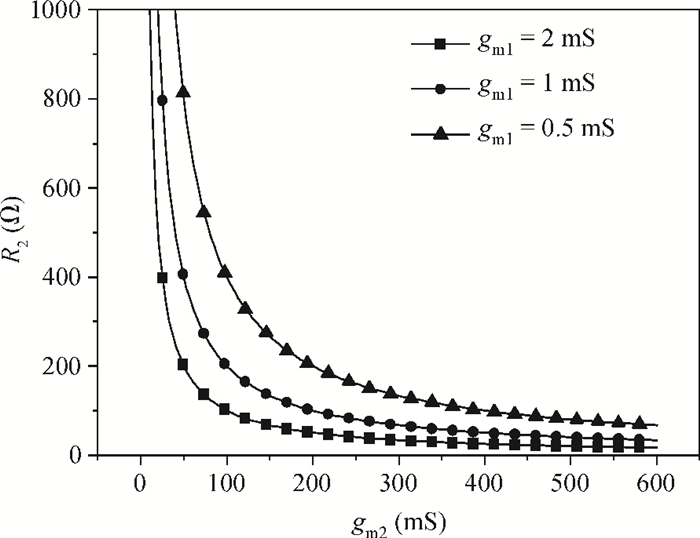
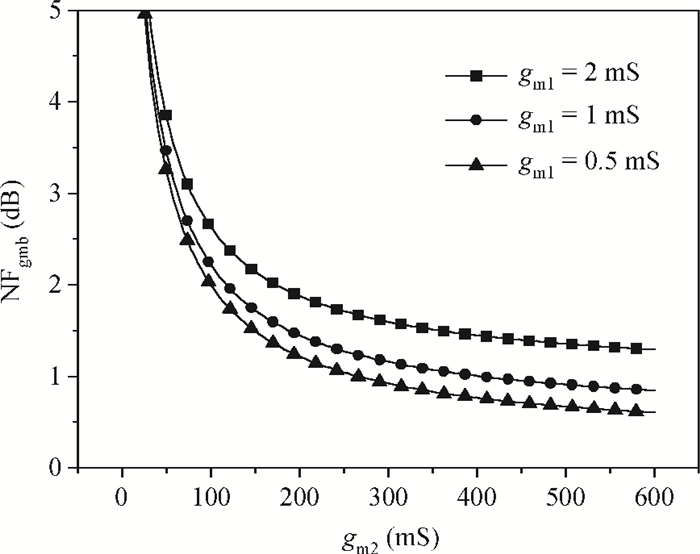
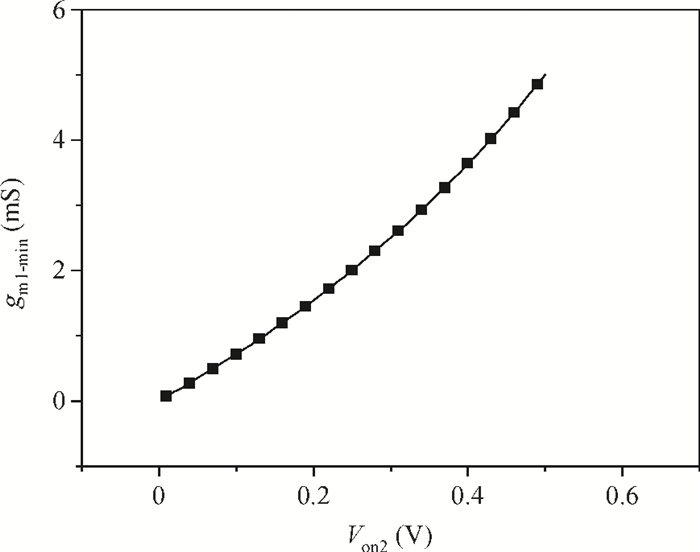
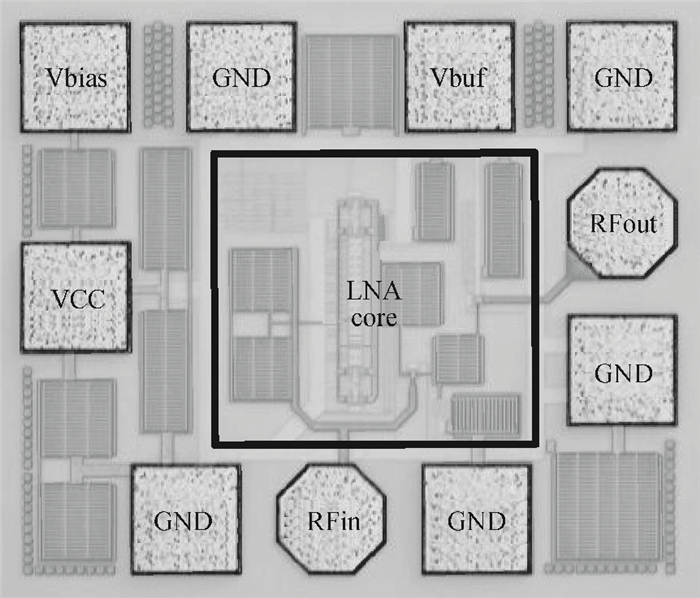
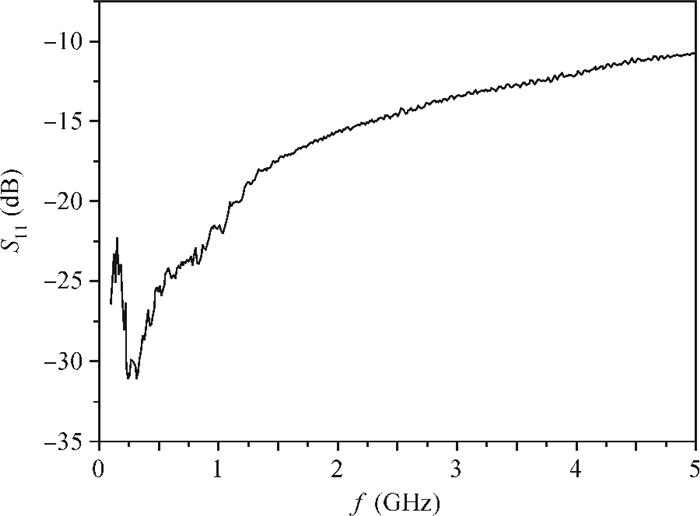
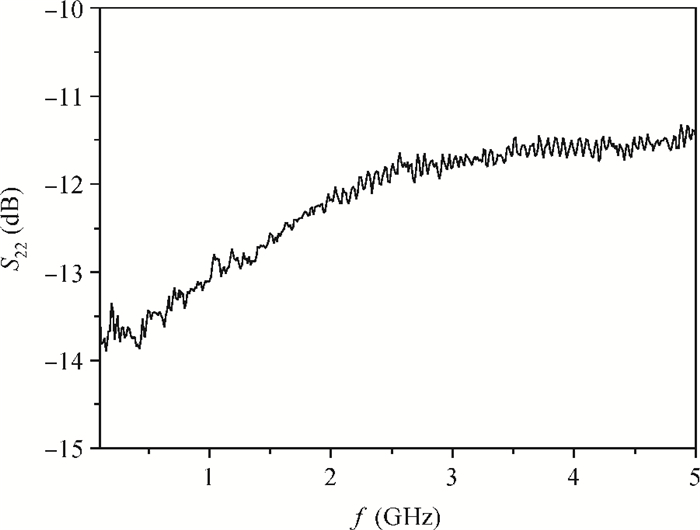
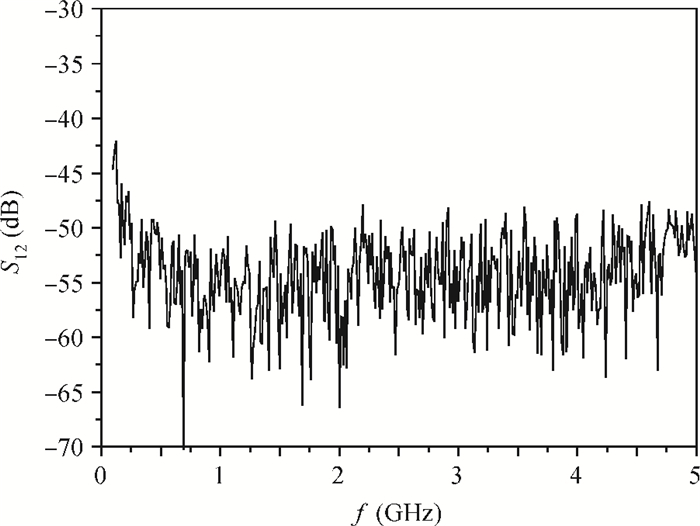
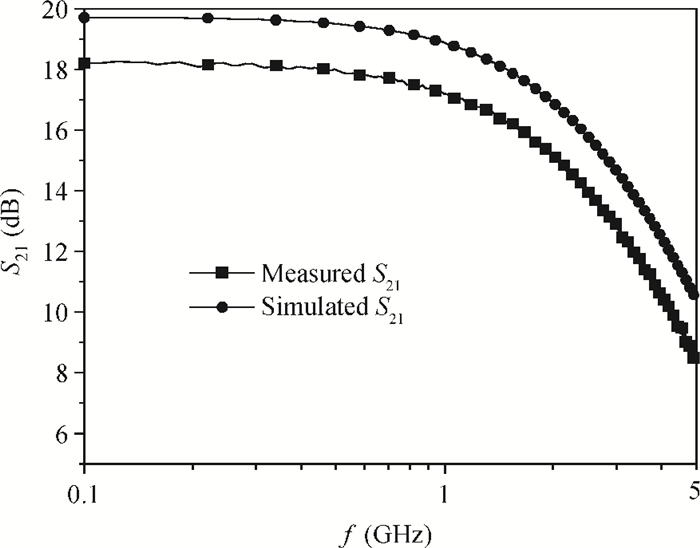
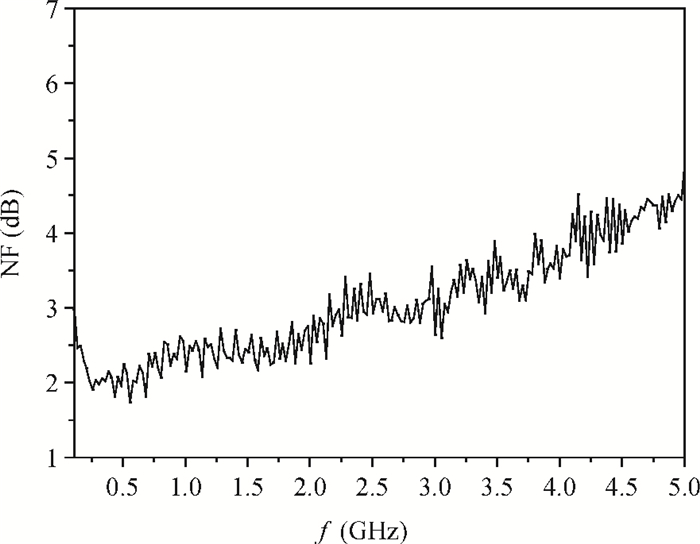
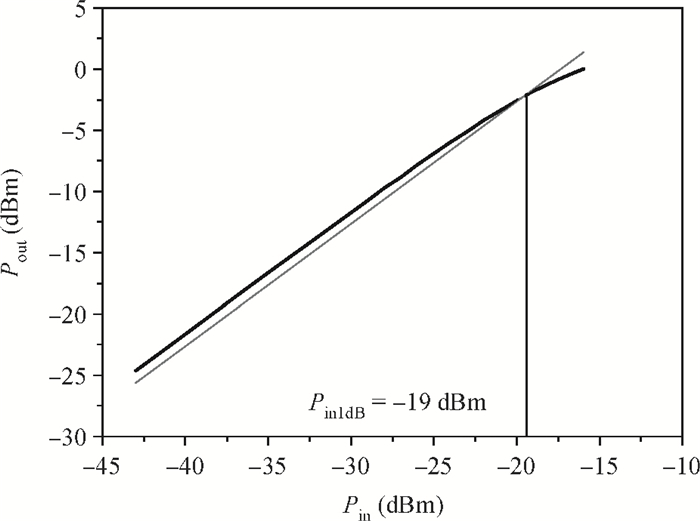
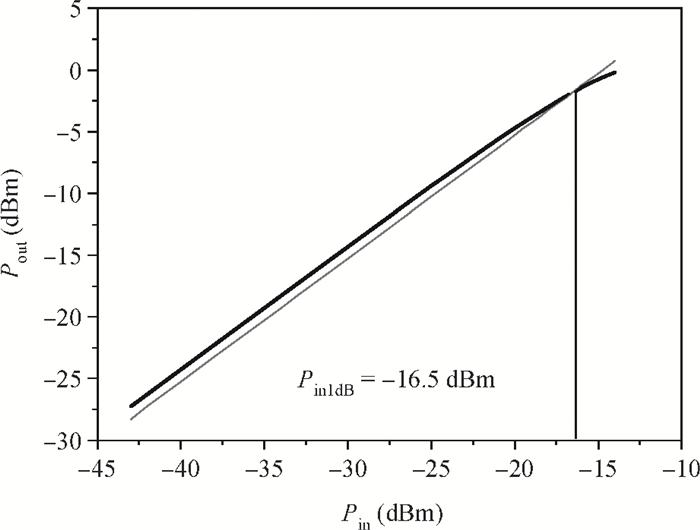
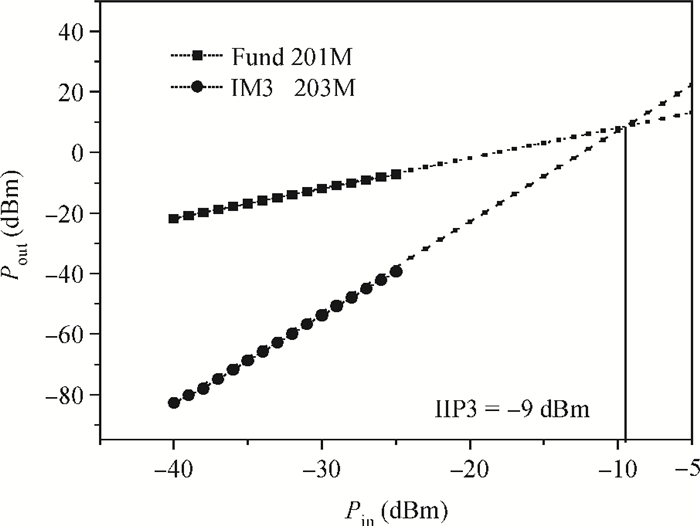
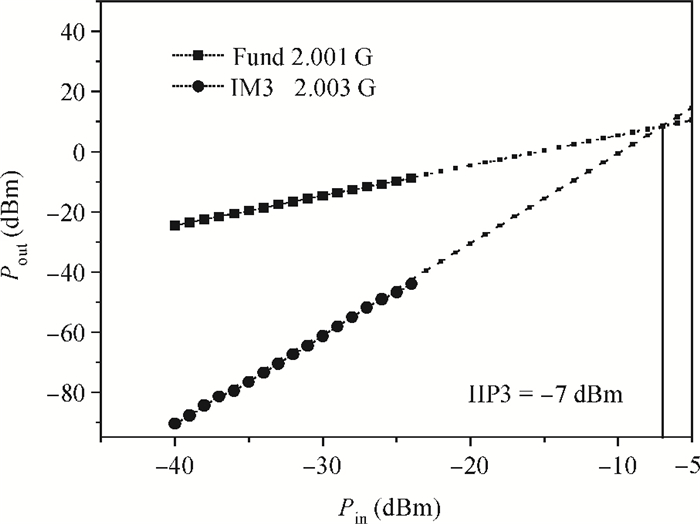
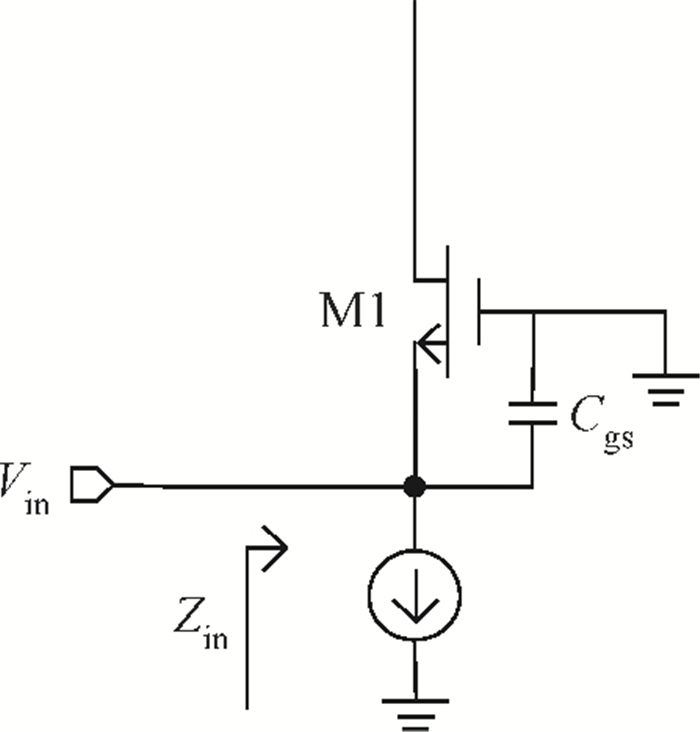
A new broadband low-noise amplifier (LNA) is proposed. The conventional common gate (CG) LNA exhibits a relatively high noise figure, so active gm-boosting technology is utilized to restrain the noise generated by the input transistors and reduce the noise figure. Theory, simulation and measurement are shown. An implemented prototype using 0.13 μm CMOS technology is evaluated using on-wafer probing. S11 and S22 are below -10 dB across 0.1-5 GHz. Measurements also show a gain of 18.3 dB with a 3 dB bandwidth from 100 MHz to 2.1 GHz and an ⅡP3 of -7 dBm at 2 GHz. The measured noise figure is better than 2.5 dB below 2.1 GHz, is better than 4.5 dB below 5 GHz, and at 500 MHz, it gets its minimum value 1.8 dB. The LNA consumes 9 mA from 1.5 V supply and occupies an area of 0.04 mm2.-
Keywords:
- broadband LNA,
- gm-boosting,
- CMOS
-
References
[1] Huang Q, Orsatti P, Piazza F. GSM transceiver front-end circuits in 0.25-μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1999:292 doi: 10.1007%2F0-306-47303-8_5[2] Zargari M, Terrovitis M, Jen S H M, et al. A single-chip dual-band tri-mode CMOS transceiver for IEEE 802.11a/b/g wireless LAN. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(12):2239 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.836349[3] Bao Kuan, Fan Xiangning, Zhang Li, et al. A wideband LNA employing gate-inductive-peaking and noise-canceling techniques in 0.18μm CMOS. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(1):015003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/1/015003[4] Perumana B G, Zhan J H C, Taylor S S, et al. A 0.5-6 GHz improved linearity, resistive feedback 90-nm CMOS LNA. Proc IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conf, 2006:263 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4197640/[5] Chen W H, Liu G, Zdravko B, et al. A highly linear broadband CMOS LNA employing noise and distortion cancellation. IEEE RFIC Symp Dig, 2007:61 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4494645/[6] El-Nozahi M, Helmy A A, Sanchez-Sinencio E, et al. An Inductor-less noise-cancelling broadband low noise amplifier with composite transistor pair in 90 nm CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2011, 46(5):1111 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2011.2118310[7] Zhuo W, Li X, Shekhar S, et al. a capacitor cross-coupled common-gate low-noise amplifier. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 2005, 52(12):875 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2005.853966[8] Meaamar A, Boon C C, Yeo K S, et al. A wideband low power low-noise amplifier in CMOS technology. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 2010, 57(4):773 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2009.2028592[9] Bruccoleri F, Klumperink E A M, Nauta B. Wide-band CMOS low-noise amplifier exploitingthermal noise canceling. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(2):275 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.821786[10] Gharpurey R. A broadband low-noise front-end amplifier for ultra wideband in 0.13-μm CMOS. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2005, 40(9):1983 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2005.848174[11] Blaakmeer S C, Klumperink E A M, Leenaerts D M W, et al. Wideband balun-LNA with simultaneous output balancing, noise-canceling and distortion-canceling. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(6):1341 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.922736[12] Kondou A, Ikebe M, Motohisa J, et al. A 0.6-4.5 GHz inductorless CMOS low noise amplifier with Gyrator-C network. 18th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), 2011:326 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6122279/?reload=true&arnumber=6122279&filter%3DAND%28p_IS_Number%3A6122192%29 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: