| Citation: |
Sen Li, Jinguang Jiang, Xifeng Zhou, Jianghua Liu. A low phase noise and low spur PLL frequency synthesizer for GNSS receivers[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(1): 015004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015004
****
S Li, J G Jiang, X F Zhou, J H Liu. A low phase noise and low spur PLL frequency synthesizer for GNSS receivers[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(1): 015004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015004.
|
A low phase noise and low spur PLL frequency synthesizer for GNSS receivers
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015004
More Information
-
Abstract
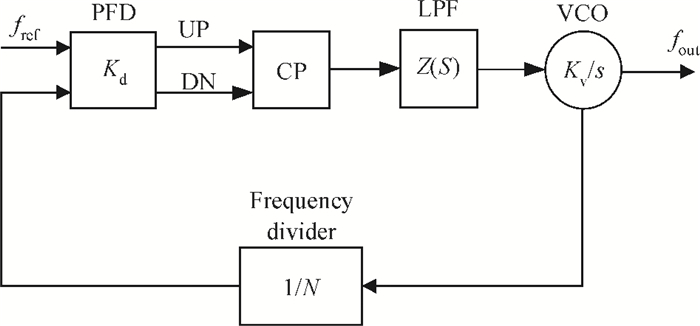
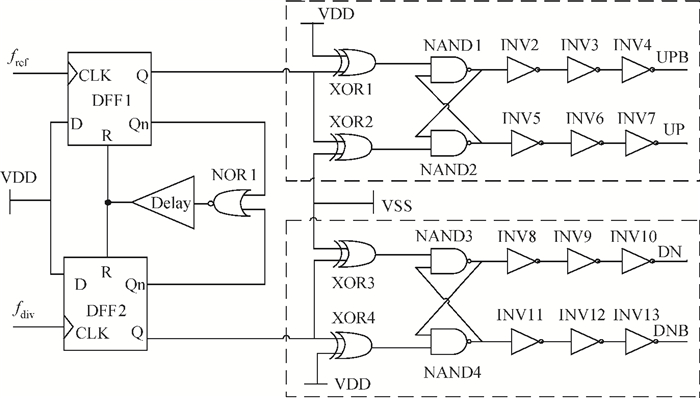
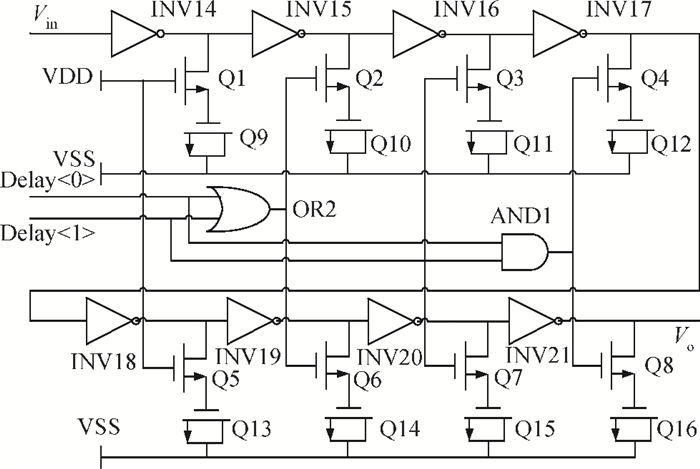
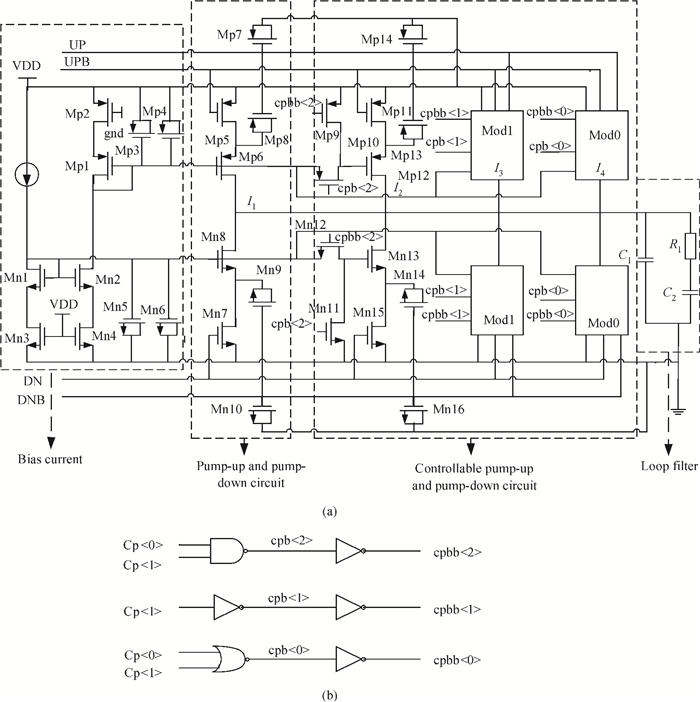
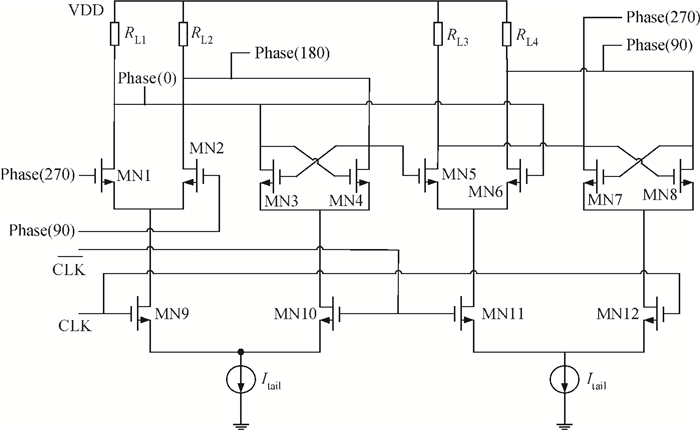
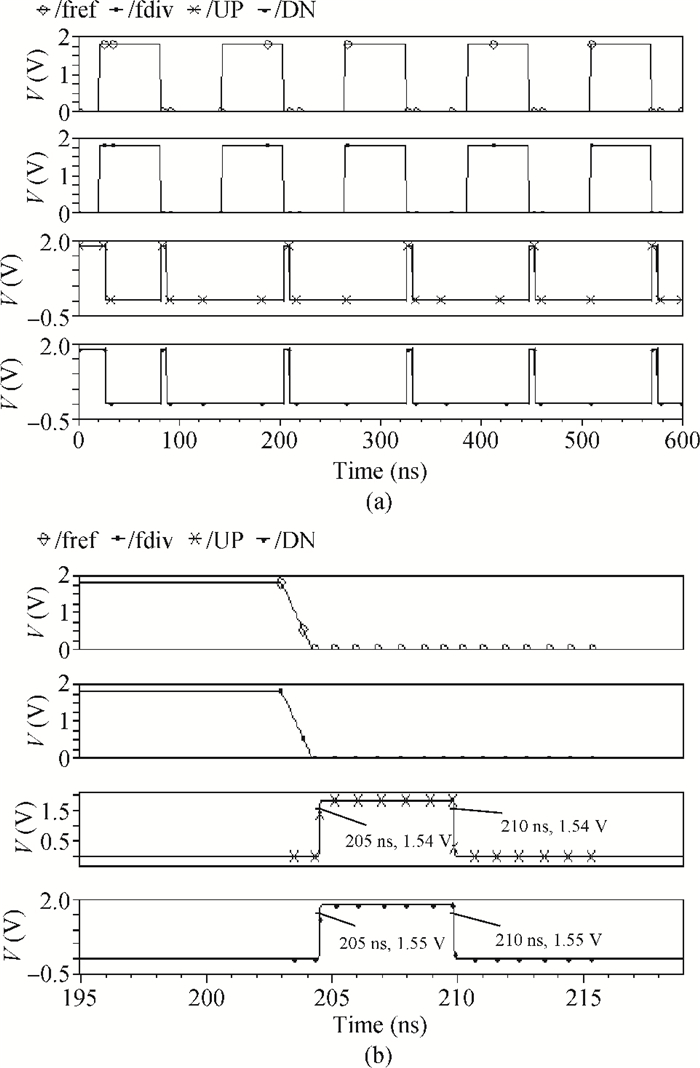
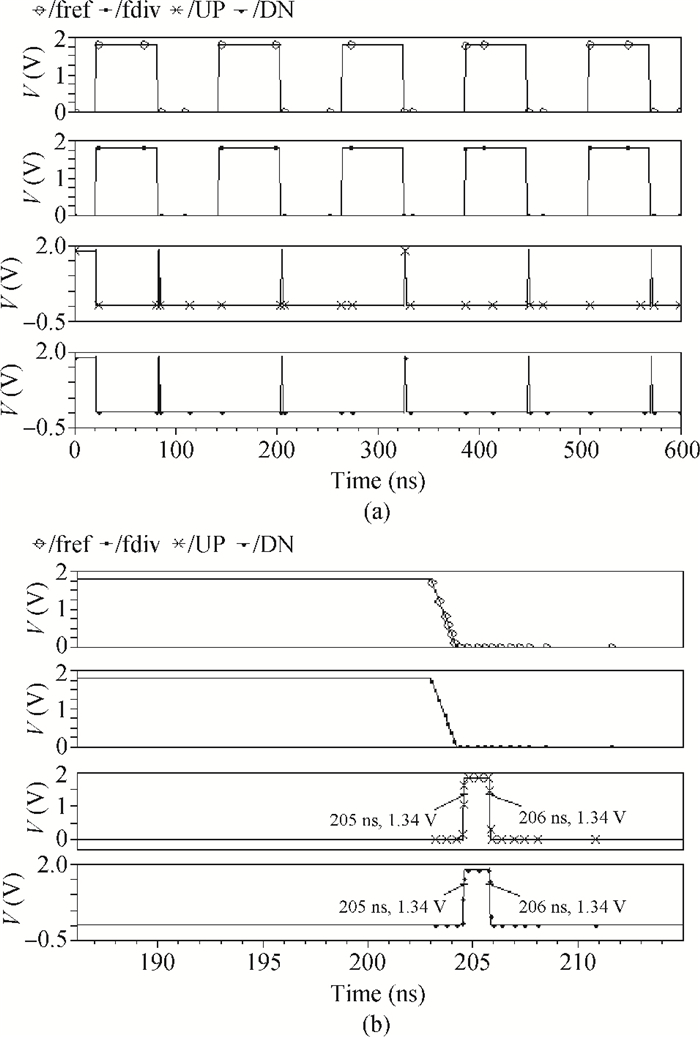
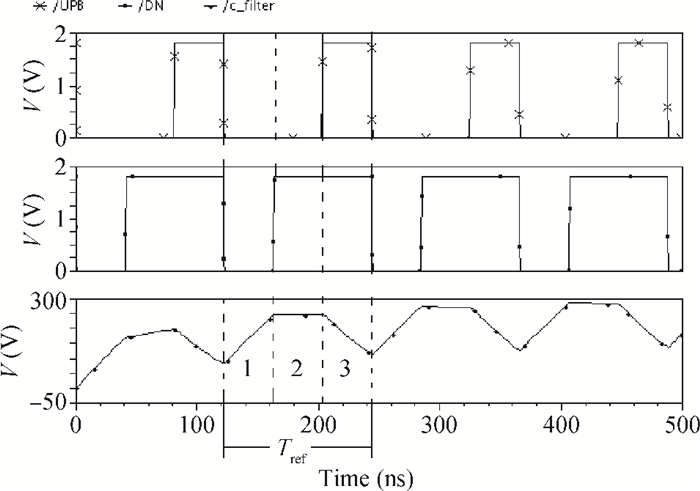
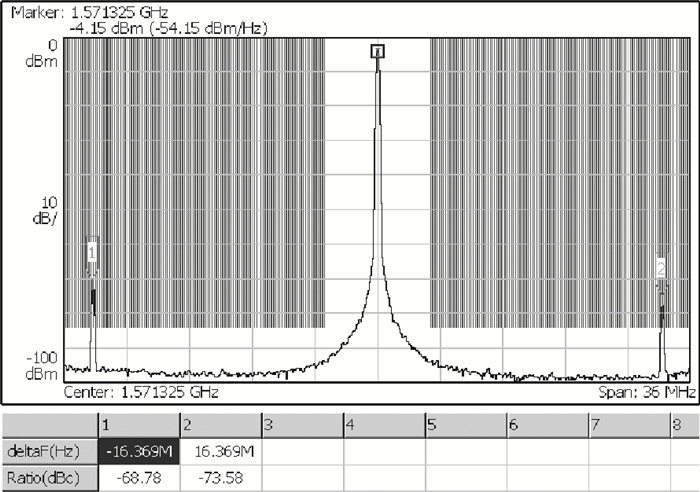
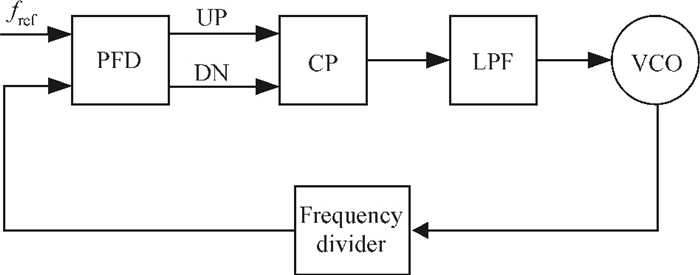
A low phase noise and low spur phase locked loop (PLL) frequency synthesizer for use in global navigation satellite system (GNSS) receivers is proposed. To get a low spur, the symmetrical structure of the phase frequency detector (PFD) produces four control signals, which can reach the charge pump (CP) simultaneously, and an improved CP is realized to minimize the charge sharing and the charge injection and make the current matched. Additionally, the delay is controllable owing to the programmable PFD, so the dead zone of the CP can be eliminated. The output frequency of the VCO can be adjusted continuously and precisely by using a programmable LC-TANK. The phase noise of the VCO is lowered by using appropriate MOS sizes. The proposed PLL frequency synthesizer is fabricated in a 0.18 μm mixed-signal CMOS process. The measured phase noise at 1 MHz offset from the center frequency is -127.65 dBc/Hz and the reference spur is -73.58 dBc.-
Keywords:
- PLL frequency synthesizer,
- phase noise,
- spur,
- PFD,
- CP,
- VCO
-
References
[1] Yin Xizhen, Xiao Shimao, Jin Yuhua, et al. A constant loop bandwidth fractional-N frequency synthesizer for GNSS receivers. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(4):045007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/4/045007[2] Chi Baoyong, Zhu Xiaolei, Wang Ziqiang, et al. Low phase noise quadrature oscillators using new injection locked technique. Chinese Journal of Semiconductors, 2005, 26(9):1705[3] Di F K. Dual reference frequencies for low spur and low phase noise fractional-N frequency phase locked loop. 7th International Conference on ASICON, 2007:1357 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/4415535/4415536/04415889.pdf[4] Yan D L, Khannur P B, Bin Z, et al. A UHF low-spur, low-phase noise fractional-N synthesizer in 0.18μm CMOS. IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology, 2009:124 https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.ieee-art-000005383704[5] Gierkink S L J. Low-spur, low-phase-noise clock multiplier based on a combination of PLL and recirculating DLL with dual-pulse ring oscillator and self-correcting charge pump. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(12):2967 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2006225[6] Shrestha B, Maharjan R K, Sungjin C, et al. A low phase noise oscillator using spur line resonator for I-band application. Microwave Conference Proceedings (APMC), 2010:469 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/abstractKeywords.jsp?reload=true&arnumber=5728661[7] Fouzar Y, Sawan M, Savaria Y. CMOS wide-swing differential VCO for fully integrated fast PLL. Proceedings of the 43rd IEEE Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2000, 2:948 doi: 10.1109/MWSCAS.2000.952910[8] Li Zhiqun, Zheng Shuangshuang, Hou Ningbing. Design of a high performance CMOS charge pump for phase-locked loop synthesizers. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(7):075007 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/7/075007[9] Yu Yunfeng, Yue Jianlian, Xiao Shimao, et al. A low-power frequency synthesizer for GPS receivers. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31(6):065012 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/6/065012[10] Jerng A, Sodini C G. The impact of device type and sizing on phase noise mechanisms. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2002, 37(12):360 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1388625/keywords[11] Yu Peng, Yan Jun, Shi Yin, et al. A dual-band frequency synthesizer for CMMB application with low phase noise. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31(9):095001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/9/095001[12] Andreani P, Bonfanti A, Romano L, et al. Analysis and design of a 1.8-GHz CMOS LC quadrature VCO. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2002, 37(12):1737 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2002.804352[13] Pamarti S, Janson L, Galton I. A wideband 2.4-GHz delta-sigma fractional-N PLL with 1-Mb/s in-loop modulation. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(1):49 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.820858[14] Yang C Y, Dehng G K, Hsu J M, et al. New dynamic flip-flops for high-speed dual-modulus prescaler. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1998, 33(10):1568 doi: 10.1109/4.720406[15] Lee T C, Lee W L. A spur suppression technique for phase-locked frequency synthesizers. IEEE International Solid-State Circuit Conference, 2006:2432 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1696307/[16] Fu Haipeng, Cai Deyun, Ren Junyan, et al. A low reference spur quadrature phase-locked loop for UWB systems. Journal of Semiconductors, 2011, 32(11):115012 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/32/11/115012[17] Chen Danfeng, Li Wei, Li Ning, et al. A low-spurious fast-hopping MB-OFDM UWB synthesizer. Journal of Semiconductors, 2010, 31(6):065003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/31/6/065003 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: