| Citation: |
Dong Yan, Luhong Mao, Qiujie Su, Sheng Xie, Shilin Zhang. A millimeter wave linear superposition oscillator in 0.18 μm CMOS technology[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(1): 015006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015006
****
D Yan, L H Mao, Q J Su, S Xie, S L Zhang. A millimeter wave linear superposition oscillator in 0.18 μm CMOS technology[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(1): 015006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015006.
|
A millimeter wave linear superposition oscillator in 0.18 μm CMOS technology
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/1/015006
More Information
-
Abstract
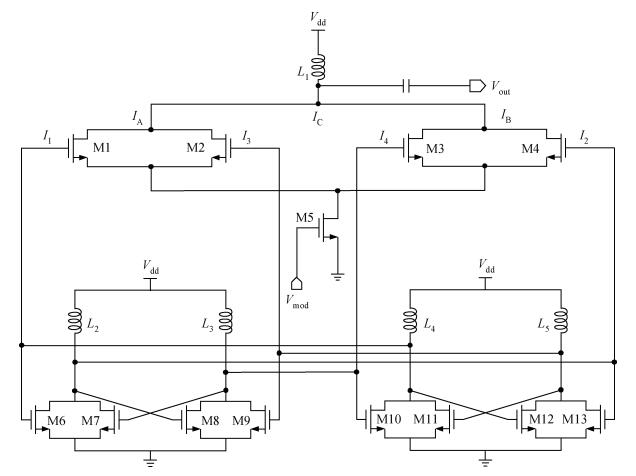
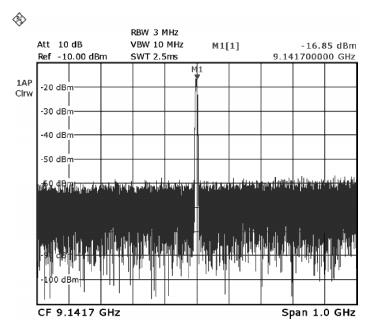
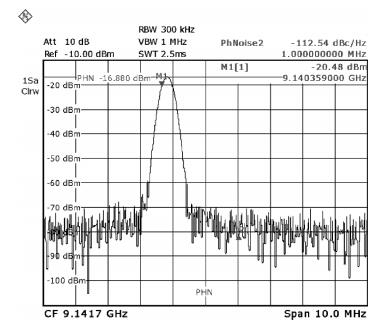
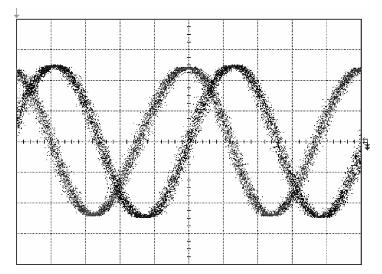
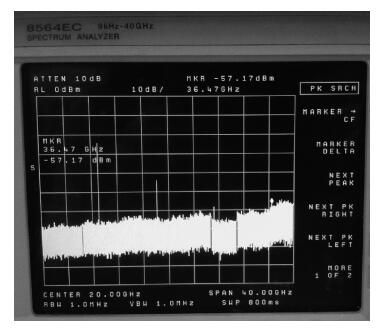
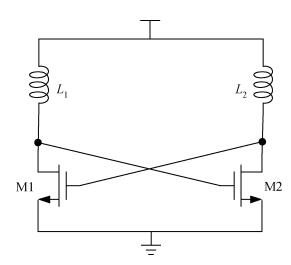
This paper presents a millimeter wave (mm-wave) oscillator that generates signal at 36.56 GHz. The mm-wave oscillator is realized in a UMC 0.18 μm CMOS process. The linear superposition (LS) technique breaks through the limit of cut-off frequency (fT), and realizes a much higher oscillation than fT. Measurement results show that the LS oscillator produces a calibrated -37.17 dBm output power when biased at 1.8 V; the output power of fundamental signal is -10.85 dBm after calibration. The measured phase noise at 1 MHz frequency offset is -112.54 dBc/Hz at the frequency of 9.14 GHz. This circuit can be properly applied to mm-wave communication systems with advantages of low cost and high integration density. -
References
[1] Lee J, Li Y A, Hung M H, et al. A fully-integrated 77-GHz FMCW radar transceiver in 65-nm CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 45(12):2746 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2010.2075250[2] Tiebout M, Wohlmuth H D, Knapp H, et al. Low power wideband receiver and transmitter chipset for mm-wave imaging in SiGe bipolar technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2012, 47(5):1175 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2012.2185570[3] Lu X, Lee C M, Wu S Y, et al. GaN-based S0-wave sensors on silicon for chemical and biological sensing in liquid environments. IEEE Sensors J, 2013, 13(4):1245 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2012.2231958[4] Pi Z, Khan F, et al. An introduction to millimeter-wave mobile broadband systems. IEEE Commun Mag, 2011, 49(6):101 doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2011.5783993[5] Huang Yinkun, Wu Danyu, Zhou Lei, et al. A 23 GHz low power VCO in SiGe BiCMOS technology. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(4):045003 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/4/045003[6] Cheng Wei, Wang Yuan, Zhao Yan, et al. A THz InGaAs/InP double heterojunction bipolar transistor with fmax=325 GHz and BVCBO=10.6 V. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(5):054006 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/5/054006[7] Liu J, Chien H C, Fan S H, et al. Efficient optical millimeter-wave generation using a frequency-tripling Fabry-Perot laser with sideband injection and synchronization. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett, 2011, 23(18):1325 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2011.2159834[8] Cao C, Seok E, K K O. 192 GHz push-push VCO in 0.13μm CMOS. Electron Lett, 2006, 42(4):208 doi: 10.1049/el:20064159[9] Li X, Yu J, Dong Z, et al. Photonics millimeter-wave generation in the E-band and bidirectional transmission. IEEE Photonics J, 2013, 5(1):7900107 doi: 10.1109/JPHOT.2013.2241419[10] Razavi B. Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits. Singapore:McGraw-Hill, 2001[11] Huang D, LaRocca T R, Chang M C F, et al. Terahertz CMOS frequency generator using linear superposition technique. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(12):2730 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2004868[12] Shang Y, Yu H, Cai D, et al. Design of high-Q millimeter-wave oscillator by differential transmission line loaded with metamaterial resonator in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2013, 61(5):1892 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2253489[13] Kim D D, Kim J, Plouchart J O, et al. A 70 GHz manufacturable complementary LC-VCO with 6.14 GHz tuning range in 65 nm SOI CMOS. IEEE ISSCC, 2007:540 doi: 10.1007%2Fs10470-011-9747-x.pdf[14] Cao C, Kenneth K O. A 140-GHz fundamental mode voltage-controlled oscillator in 90-nm CMOS technology. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2006, 16(10):555 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2006.882385[15] Yang J, Kim C Y, Kim D W, et al. Design of a 24-GHz CMOS VCO with an asymmetric-width transformer. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst, 2010, 57(3):173 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2010.2043381[16] Choi T Y, Lee H, Katehi L P B, et al. A low phase noise 10 GHz VCO in 0.18μm CMOS process. The European Conference on Wireless Technology, 2005:273 https://engineering.purdue.edu/~saeedm/CC40.pdf[17] Ko S, Kim J G, Song T, et al. 20GHz integrated CMOS frequency sources with a quadrature VCO using transformers. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, 2004:269 https://engineering.purdue.edu/~saeedm/CC40.pdf[18] Liu R C, Chang H Y, Wang C H, et al. A 63 GHz VCO using a standard 0.25μm CMOS process. IEEE ISSCC, 2004:446[19] Wang Huan, Wang Zhigong, Feng Jun, et al. A 10GHz LC voltage-controlled oscillator in 0.25μm CMOS. Journal of Semiconductors, 2008, 29(3):484 http://www.jos.ac.cn/bdtxbcn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=07081101&flag=1 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: