| Citation: |
Rui He, Jianfei Xu, Na Yan, Jie Sun, Liqian Bian, Hao Min. Design and analysis of 20 Gb/s inductorless limiting amplifier in 65 nm CMOS technology[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(10): 105002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105002
****
R He, J F Xu, N Yan, J Sun, L Q Bian, H Min. Design and analysis of 20 Gb/s inductorless limiting amplifier in 65 nm CMOS technology[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(10): 105002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105002.
|
Design and analysis of 20 Gb/s inductorless limiting amplifier in 65 nm CMOS technology
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/105002
More Information
-
Abstract
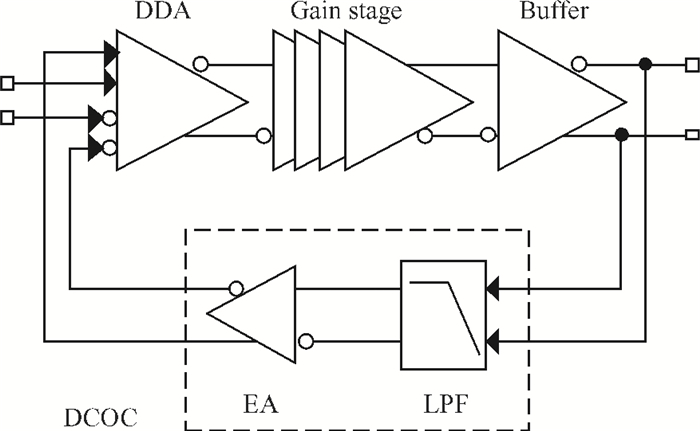
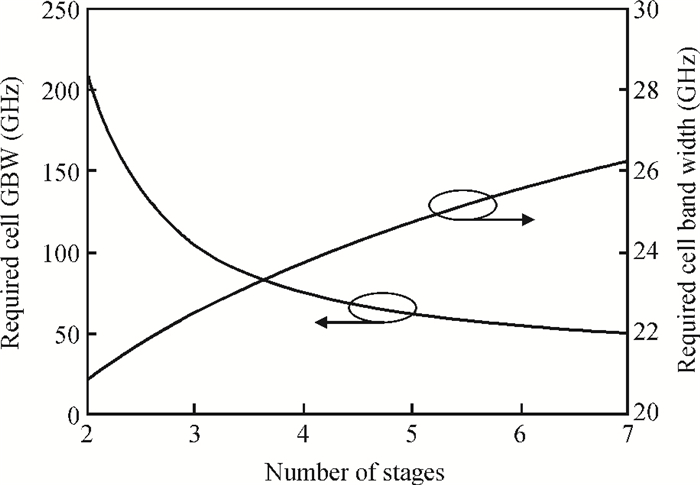
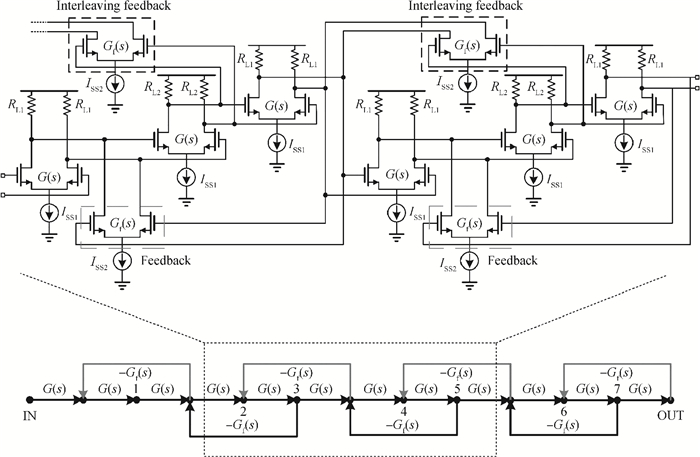
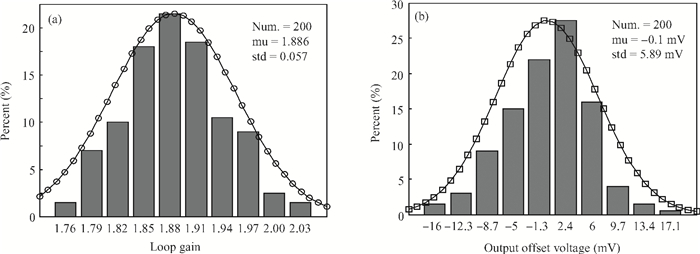
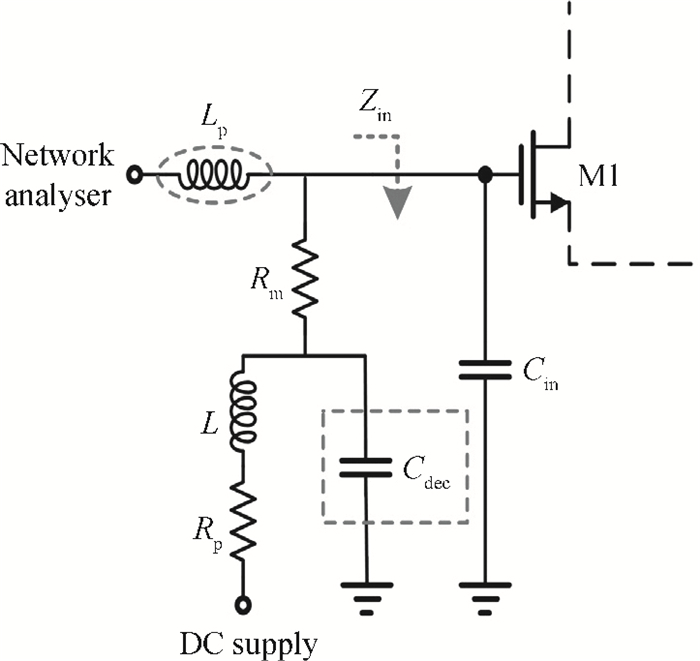
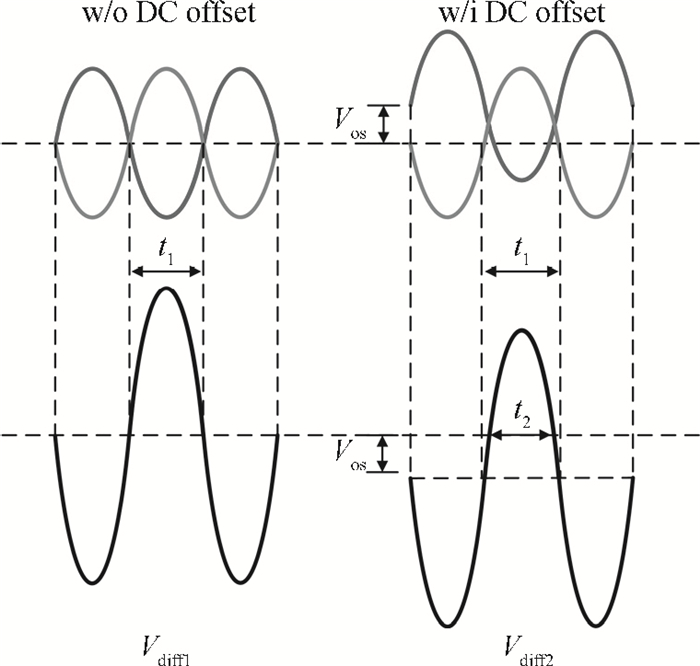
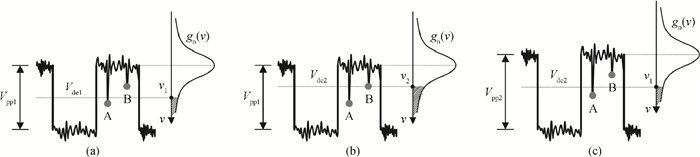
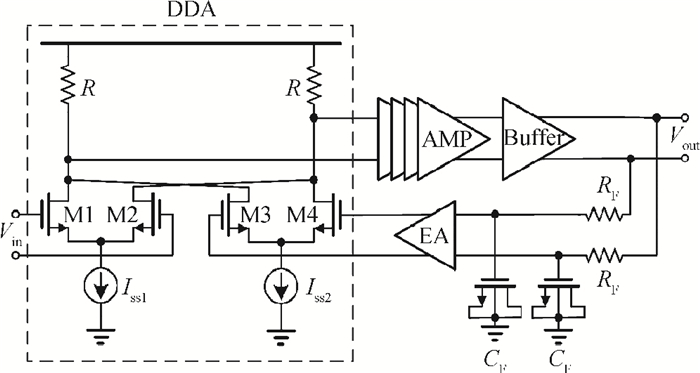
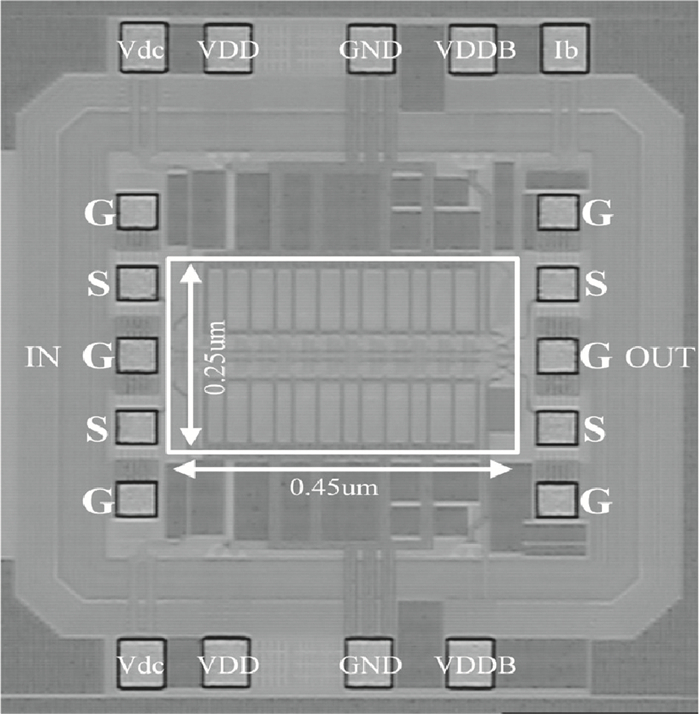
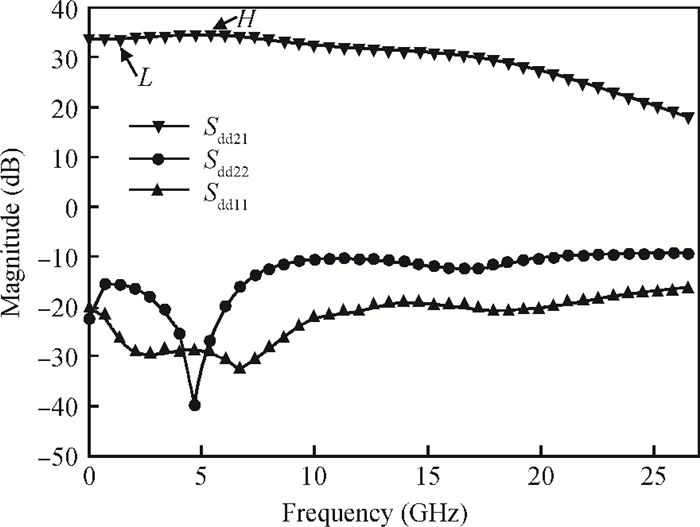
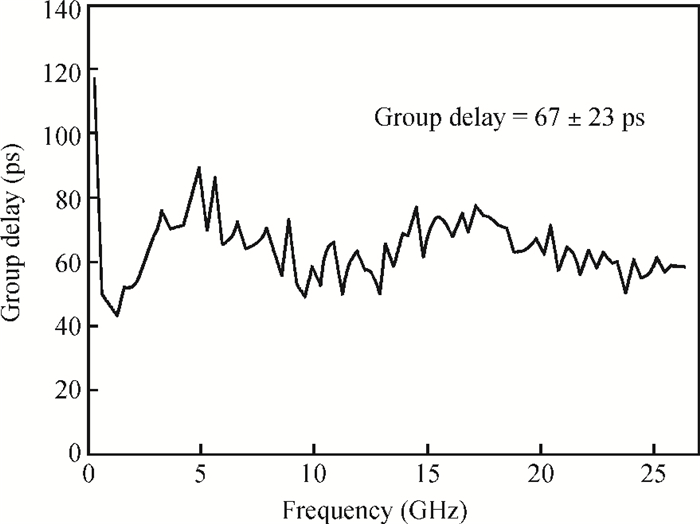
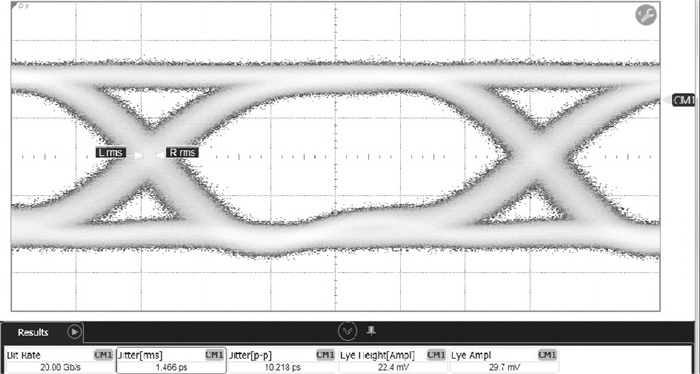
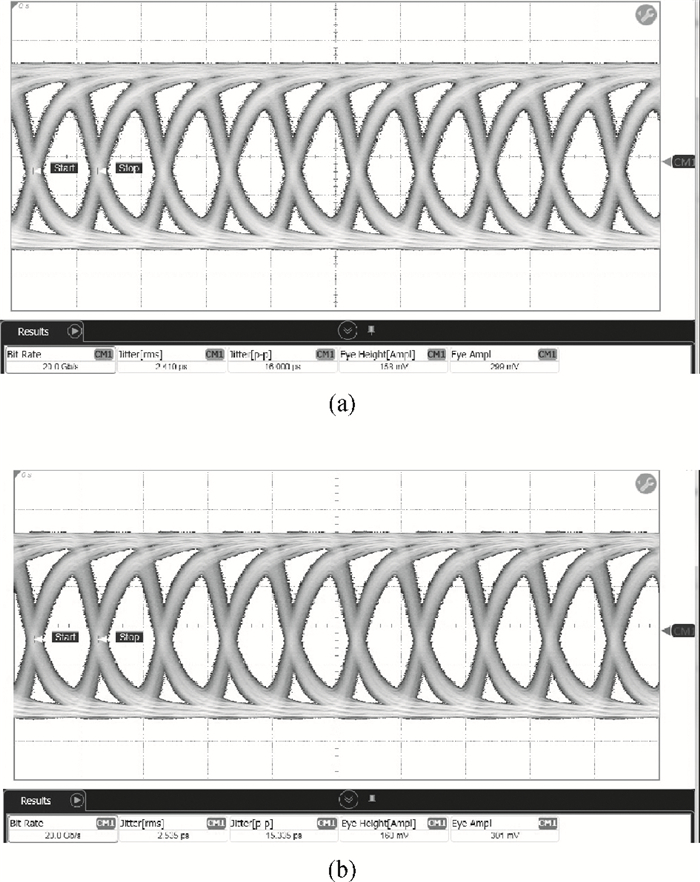
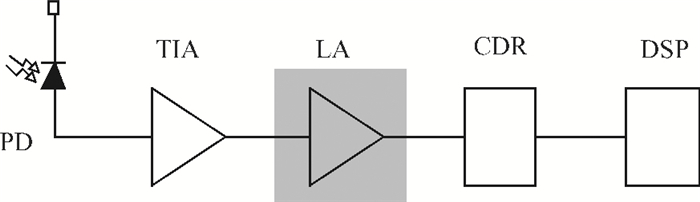
A high speed inductorless limiting amplifier (LA) in an optical communication receiver with the working speed up to 20 Gb/s is presented. The LA includes an input matching network, a four-stage 3rd order amplifier core, an output buffer for the test and a DC offset cancellation (DCOC). It uses the active interleaving feedback technique both to broaden the bandwidth and achieve the flatness response. Based on our careful analysis of the DCOC and stability, an error amplifier is added to the DCOC loop in order to keep the offset voltage reasonable. Fabricated in the 65 nm CMOS technology, the LA only occupies an area of 0.45×0.25 mm2 (without PAD). The measurement results show that the LA achieves a differential voltage gain of 37 dB, and a 3-dB bandwidth of 16.5 GHz. Up to 26.5 GHz, the Sdd11 and Sdd22 are less than -16 dB and -9 dB. The chip excluding buffer is supplied by 1.2 V VDD and draws a current of 50 mA. -
References
[1] Säckinger E. Broadband circuits for optical fiber communication. Wiley-Interscience, 2005[2] Razavi B. Design of integrated circuits for optical communications. Wiley, 2012[3] Sackinger E, Fischer W C. A 3-GHz 32-dB CMOS limiting amplifier for SONET OC-48 receivers. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2000, 35(12):1884 doi: 10.1109/4.890301[4] Galal S, Razavi B. 10-Gb/s limiting amplifier and laser/modulator driver in 0.18-μm CMOS technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(12):2138 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.818567[5] Huang H Y, Chien J C, Lu L H. A 10-Gb/s inductorless CMOS limiting amplifier with third-order interleaving active feedback. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(5):1111 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.894819[6] Sansen W M C. Analog design essentials. Springer, 2006[7] Tavernier F, Steyaert M. A low power, area efficient limiting amplifier in 90 nm CMOS. ESSCIRC, 2009: 128[8] Daneshgar S, Griffith Z, Rodwell M J W. A DC-100 GHz bandwidth and 20. 5 dB gain limiting amplifier in 0. 25μm InP DHBT technology. Compound Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Symposium (CSICS), 2013: 1[9] Hou Z X, Wang Y P, Pan Q, et al. A 25-Gb/s 32. 1-dB CMOS limiting amplifier for integrated optical receivers. The 10th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), 2013: 1[10] Chou S T, Huang S H, Hong Z H, et al. A 40 Gbps optical receiver analog front-end in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), 2012: 1736[11] Akita I, Tsubouchi Y, Itakura T, et al. A 6 Gbps 3 mW optical receiver with DCOC-combined ATC in 65 nm CMOS. ESSCIRC, 2011: 343 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: