| Citation: |
Bo Duan, Jianwei Zhou, Yuling Liu, Chenwei Wang, Yufeng Zhang. Slurry components of TiO2 thin film in chemical mechanical polishing[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(10): 106003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/106003
****
B Duan, J W Zhou, Y L Liu, C W Wang, Y F Zhang. Slurry components of TiO2 thin film in chemical mechanical polishing[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(10): 106003. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/106003.
|
Slurry components of TiO2 thin film in chemical mechanical polishing
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/10/106003
More Information
-
Abstract
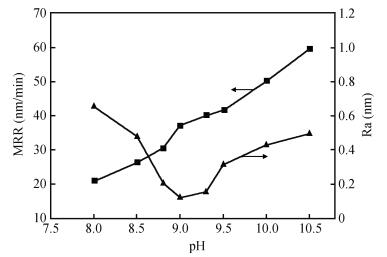
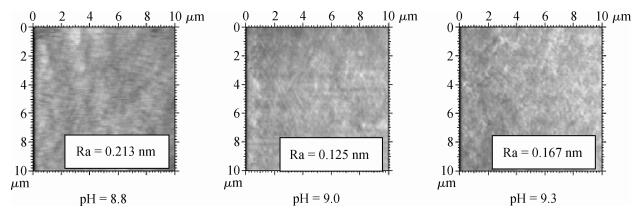
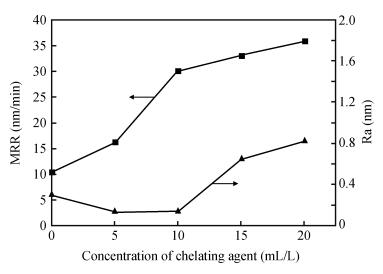
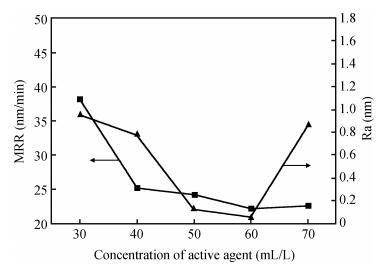
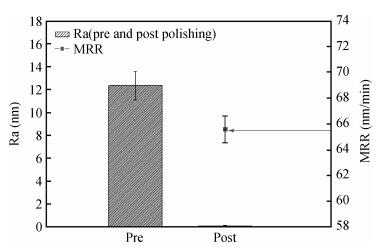
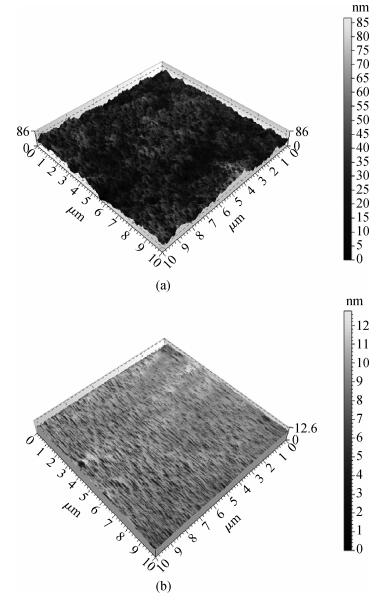
A chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) process was selected to smooth TiO2 thin film surface and improve the removal rate. Meanwhile, the optimal process conditions were used in TiO2 thin film CMP. The effects of silica sols concentration, slurry pH, chelating agent and active agent concentration on surface roughness and material removal rate were investigated. Our experimental results indicated that we got lower surface roughness (1.26 Å, the scanned area was 10×10 μm2) and higher polishing rate (65.6 nm/min), the optimal parameters were:silica sols concentration 8.0%, pH value 9.0, active agent concentration 50 mL/L, chelating agent concentration 10 mL/L, respectively.-
Keywords:
- TiO2 thin film,
- slurry components,
- surface roughness,
- removal rate
-
References
[1] Callback K, Sikora M, Kapusta C, et al. X-ray absorption and emission spectroscopy of TiO2 thin films with modified anionic sublattice. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2013, 93:40 doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.03.035[2] Shen H, Cheng B, Lu G, et al. Enhancement of optical nonlinearity in periodic gold nanoparticle arrays. Nanotechnology, 2006, 17:4274 doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/17/16/045[3] Wang Wuyu, Wang Xijing, Yang Taili. Review on optoelectronic properties and applications of TiO2 films. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2008, 32(6):781[4] Hocine D, Belkaid M S, Pasquinelli M, et al. Improved efficiency of multicrystalline silicon solar cells by TiO2 antireflection coatings derived by APCVD process. Mater Sci Semicond Processing, 2013, 16(1):113 doi: 10.1016/j.mssp.2012.06.004[5] Peng Xiao, Feng Yaqing, Meng Shuxian, et al. Preparation of hierarchical TiO2 films with uniformly or gradually changed pore size for use as photoelectrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 115:255 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.10.126[6] Weng K W, Huang Y P. Preparation of TiO2 thin films on glass surfaces with self-cleaning characteristics for solar concentrators. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2013, 231:201 doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2012.06.058[7] Wang T Q, Lu X C, Zhao D W, et al. Optimization of design of experiment for chemical mechanical polishing of a 12-inch wafer. Microelectron Eng, 2013, 112:5 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2013.05.010[8] Choi S, Doyle F M, Dornfeld D, et al. a model of material removal and post process surface topography for copper CMP. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 19:73 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.11.082[9] Choi G W, Lee K Y, Kim N H, et al. CMP characteristics and optical property of ITO thin film by using silica slurry with a variety of process parameters. Microelectron Eng, 2006, 83:2213 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2006.10.006[10] Liu Y L, Zhang K L, Wang F, et al. Investigation on the final polishing slurry and technique of silicon substrate in ULSI. Microelectron Eng, 2003, 66:438 doi: 10.1016/S0167-9317(02)00908-5[11] Seo J, Yoon K S, Moon J, et al. Effects of physico-chemical properties between poly (ethyleneimine) and silica abrasive on copper chemical mechanical planarization. Microelectron Eng, 2014, 113:50 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2013.07.006[12] Liu X Y, Liu Y L, Liang Y, et al. Optimization of slurry components for a copper chemical mechanical polishing at low down pressure using response surface methodology. Microelectron Eng, 2011, 88:99 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2010.09.007[13] Wang C W, Liu Y L, Tian J Y, et al. A study on the comparison of CMP performance between a novel alkaline slurry and a commercial slurry for barrier removal. Microelectron Eng, 2012, 98:29 doi: 10.1016/j.mee.2012.05.028[14] Kwon T Y, Ramachandran M, Cho B J, et al. The impact of diamond conditioners on scratch formation during chemical mechanical planarization (CMP) of silicon dioxide. Tribology International, 2013, 67:272 doi: 10.1016/j.triboint.2013.08.008[15] Wei Wenhao, Liu Yuling, Wang Chenwei, et al. Study of a novel alkaline barrier slurry applied in copper chemical mechanical planarization. Journal of Functional Materials, 2012, 43(23):3333[16] Tan Baimei, Li Weiwei, Niu Xinhuan, et al. Effect of surfactant on removal of particle contamination on Si wafers in ULSI. Transaction of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2006, 16:195 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(06)60174-X -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: