| Citation: |
Xusheng Tang, Fengyi Huang, Youming Zhang, Xin Tang. Reconfigurable dual-band low noise amplifier design and realization[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2014, 35(5): 055004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/055004
****
X S Tang, F Y Huang, Y M Zhang, X Tang. Reconfigurable dual-band low noise amplifier design and realization[J]. J. Semicond., 2014, 35(5): 055004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/055004.
|
Reconfigurable dual-band low noise amplifier design and realization
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/35/5/055004
More Information
-
Abstract
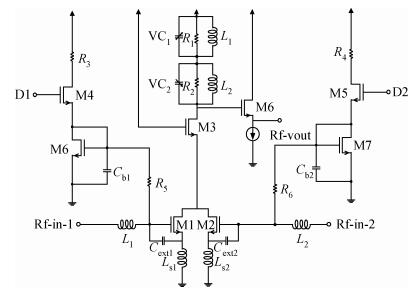
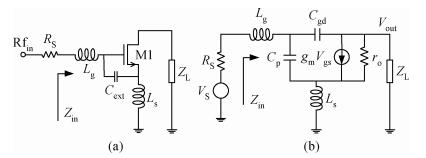
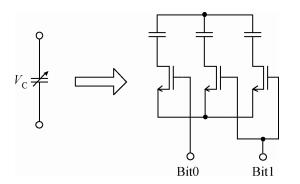
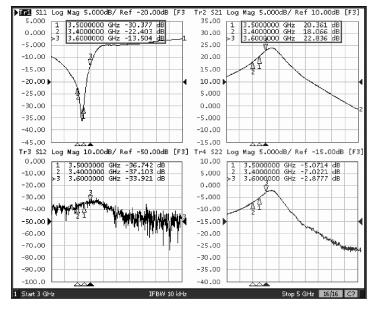
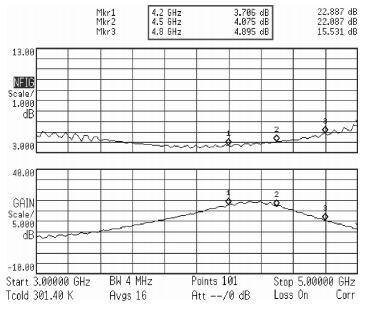
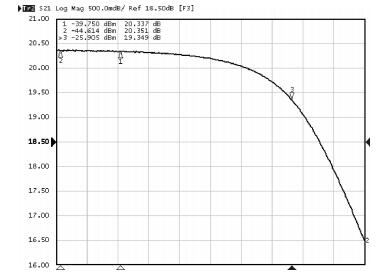
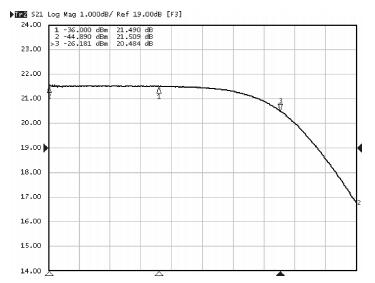
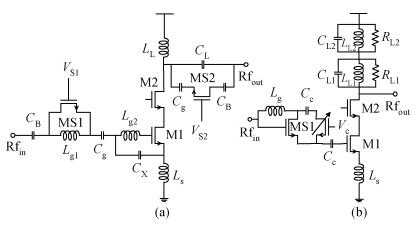
A reconfigurable dual-band LNA is presented. The LNA employs switching capacitors and circuit in to realize the dual-band operation. These methodologies are used to design and implement a reconfigurable LNA for IMT-A and UWB application. The LNA is implemented using TSMC-0.13 μm CMOS technology. Measured performance shows an input matching of better than -13.5 dB, a voltage gain of 18-22.8 dB, with an NF of 4.3-4.7 dB in the band of 3.4-3.6 GHz, and an input matching of better than -9.7 dB, a voltage gain of 14.7-22.4 dB, and with an NF of 3.7-4.9 dB in the band of 4.2-4.8 GHz. According to the measure results, the proposed LNA achieves dual-band operation, and it proves the feasibility of the proposed topology. -
References
[1] Lin Y J, Hsu S S H, Jin J D, et al. A 3.1-10.6 GHz ultra-wideband CMOS low noise amplifier with current-reused technique. IEEE Microw Wireless Compon Lett, 2007, 17(3):232 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2006.890503[2] Ismail A, Abidi A A. A 3-10-GHz low-noise amplifier with wideband LC-ladder matching network. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2004, 39(12):2269 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2004.836344[3] Wu S, Razavi B. A 900-MHz/1.8-GHz CMOS receiver for dual-band applications. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 1998, 33(12):2178 doi: 10.1109/4.735702[4] Dao V K, Choi B G, Park C S. A dual-band CMOS RF front-end for 2.4/5.2 GHz applications. IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, 2007:145 http://www.jpier.org/PIERC/pier.php?paper=11032705[5] Yoo S S, Yoo H J. A compact dualband LNA using self-matched capacitor. RFIT2007-IEEE International Workshop on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology, Singapore, 2007:227 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/articleDetails.jsp?arnumber=4450162[6] Balemarthy D. Process variations and noise analysis on a miller capacitance. Advances in Computing, Control, and Telecommunication Technologies, 2009:414 doi: 10.1007/s10470-013-0206-8[7] El-Nozahi M, Sánchez-Sinencio E, Entesari K. A CMOS low-noise amplifier with reconfigurable input matching network. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2009, 7(5):1054 http://www.jpier.org/PIER/pier.php?paper=13012303[8] Khurram M, Rezaul H S M. A 3-5 GHz current-reuse gm-boosted CG LNA for ultrawideband in 130 nm CMOS. IEEE Trans Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Syst, 2012, 20(3):400 doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2011.2106229[9] Hashemi H, Hajimiri A. Concurrent multiband low-noise amplifiers-theory, design, and applications. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2002, 50(1):228 http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/showciting?cid=3327994[10] Lee T H. The design of CMOS radio-frequency integrated circuits. 2nd ed. USA Cambridge University Press, 2004[11] Nguyen T K, Kim C H, Ihm G J, et al. CMOS low-noise amplifier design optimization techniques. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2004, 52(5):1433 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2004.827014[12] Neihart N M, Brown J, Yu X H. A dual-band 2.45/6 GHz CMOS LNA utilizing a dual-resonant transformer-based matching network. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I:Regular Papers, 2012, 59(8):1743 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2011.2180436 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: