| Citation: |
Anlin He, Gang Guo, Shuting Shi, Dongjun Shen, Jiancheng Liu, Li Cai, Hui Fan. Experimental research of heavy ion and proton induced single event effects for a Bi-CMOS technology DC/DC converter[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(11): 115010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/11/115010
****
A L He, G Guo, S T Shi, D J Shen, J C Liu, L Cai, H Fan. Experimental research of heavy ion and proton induced single event effects for a Bi-CMOS technology DC/DC converter[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(11): 115010. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/11/115010.
|
Experimental research of heavy ion and proton induced single event effects for a Bi-CMOS technology DC/DC converter
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/11/115010
More Information
-
Abstract
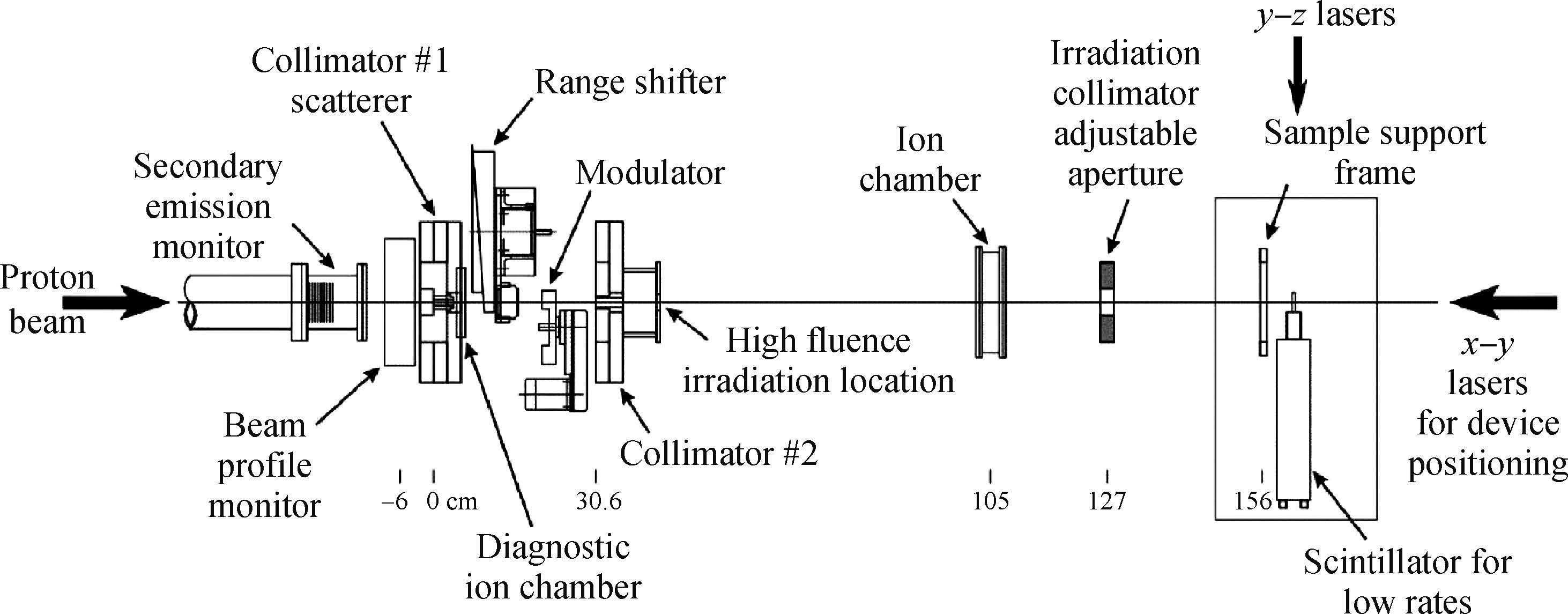
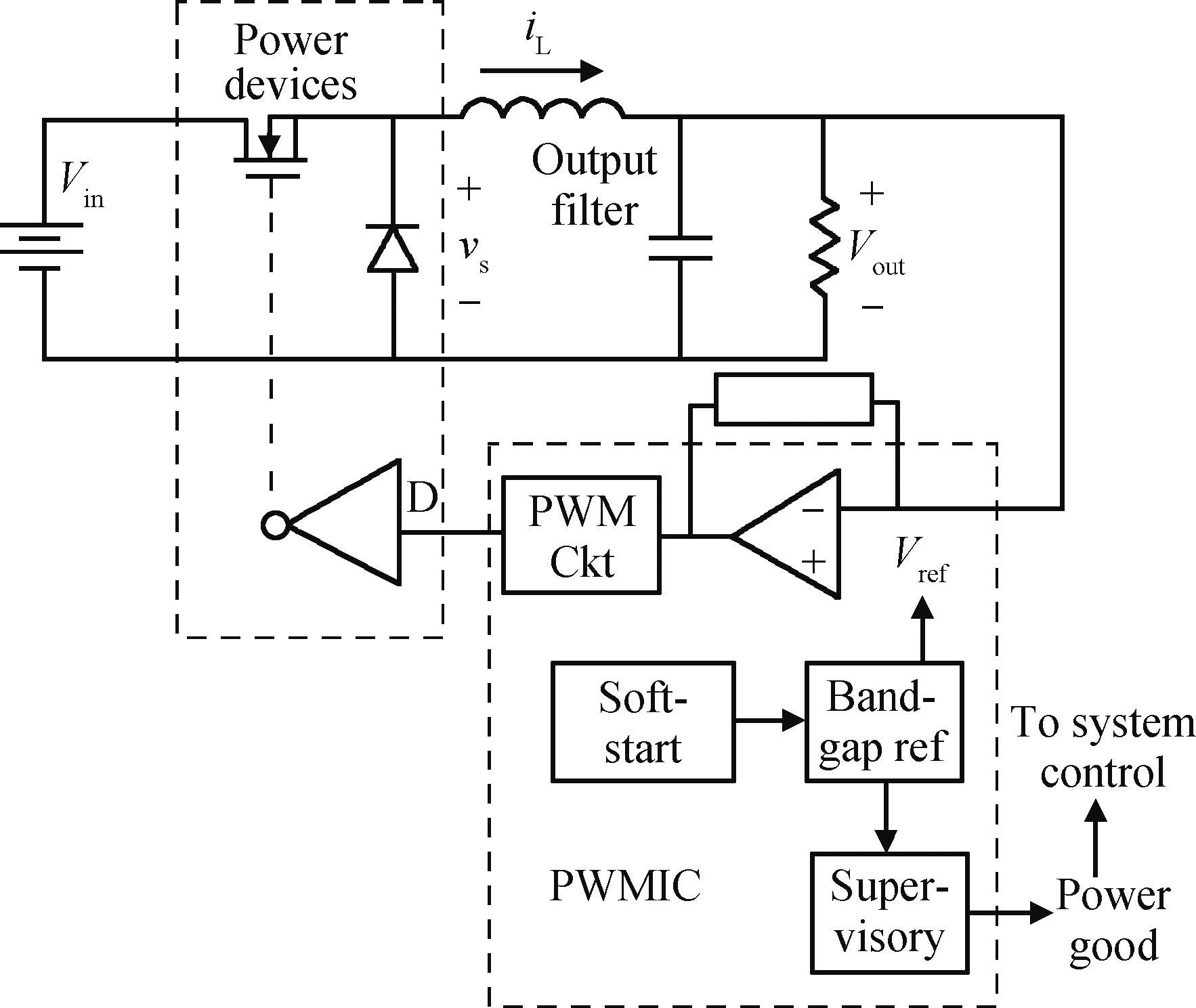
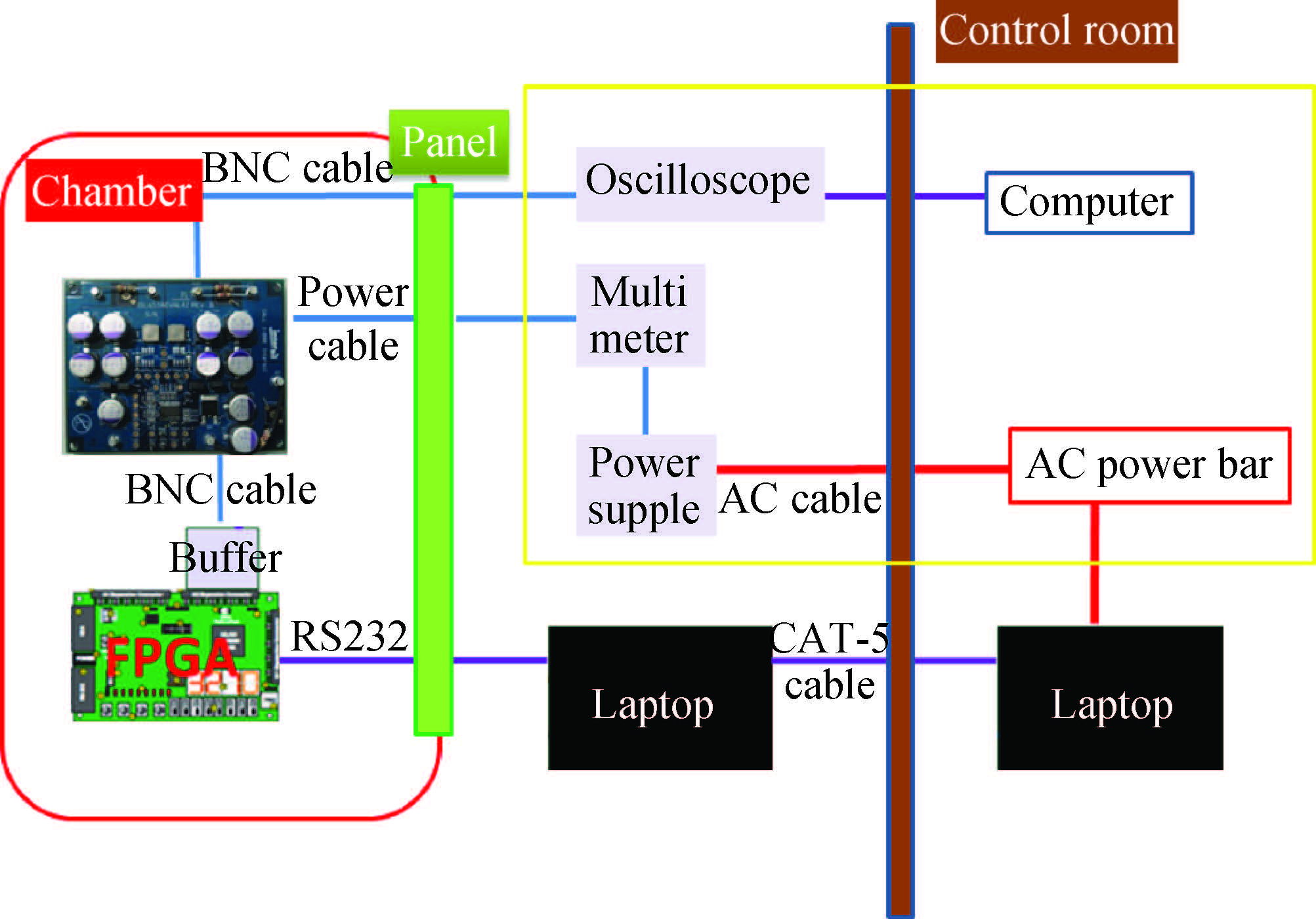
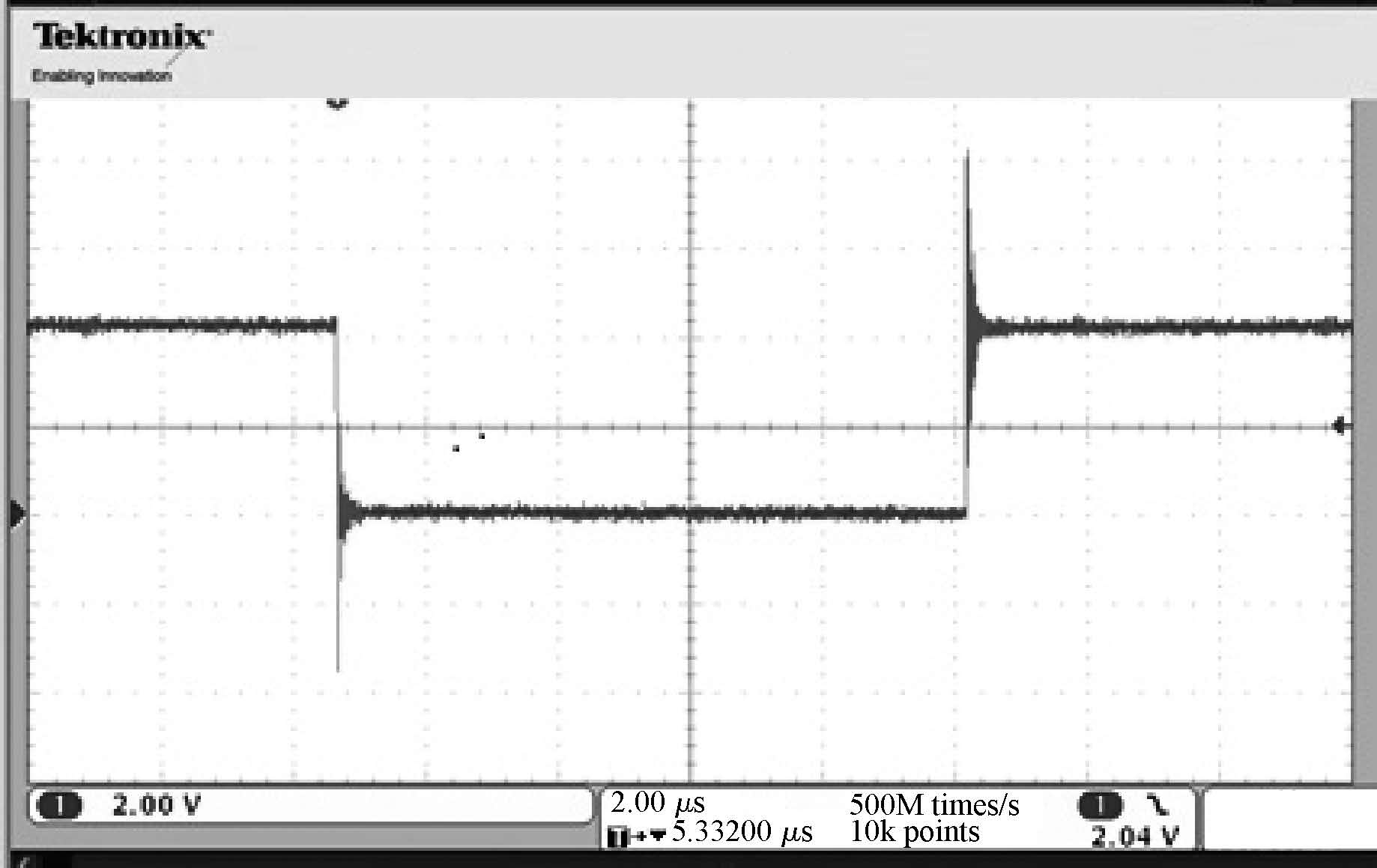
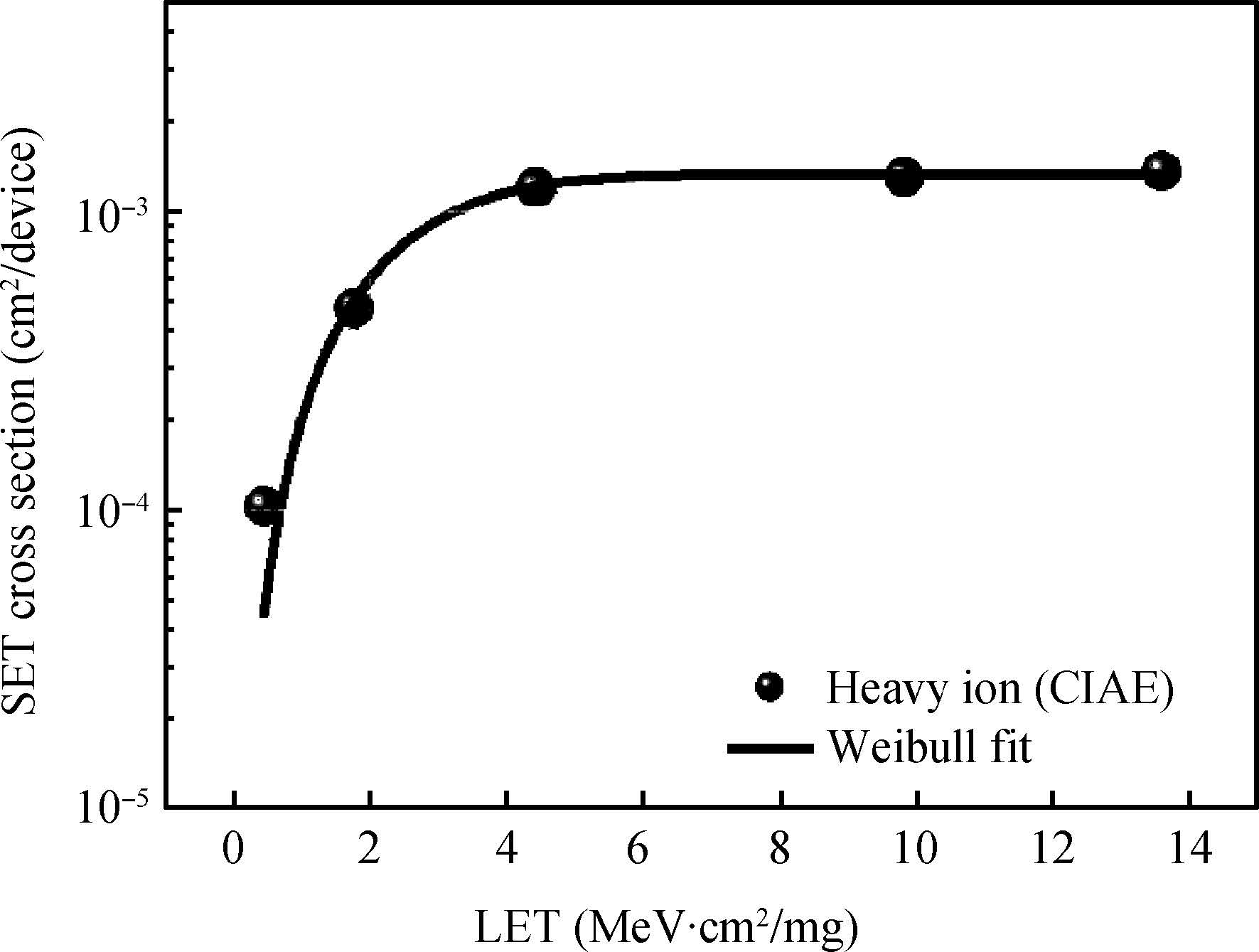
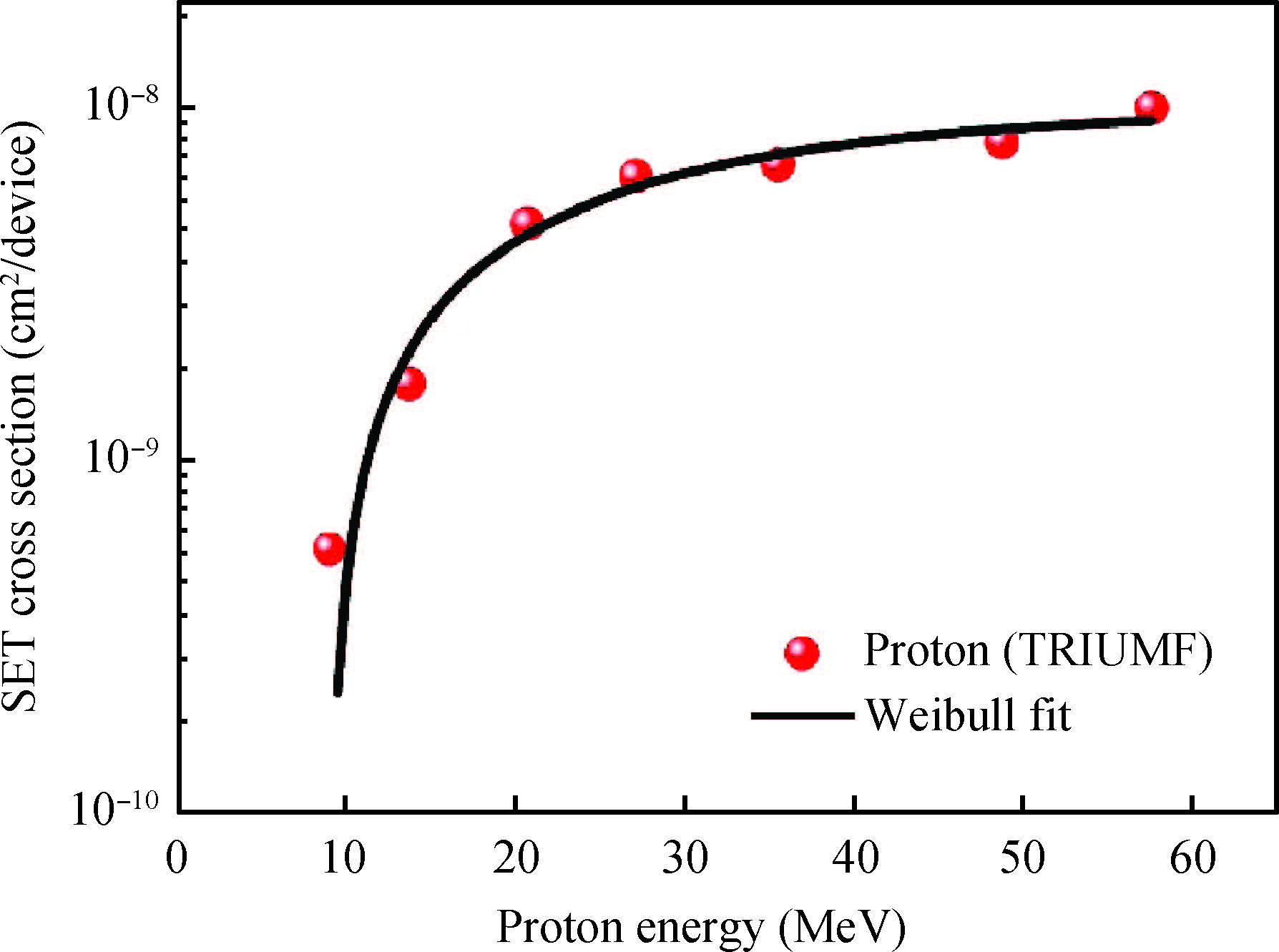
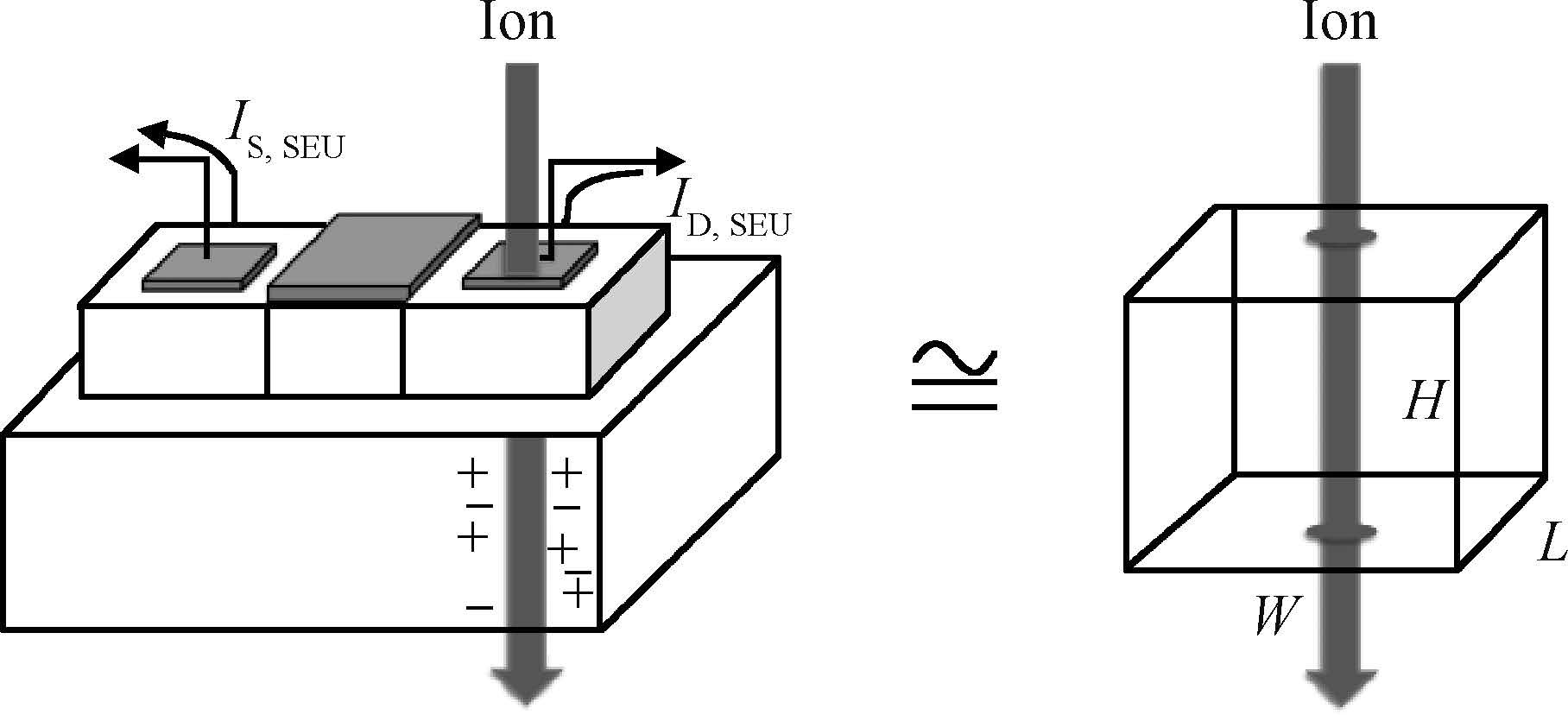
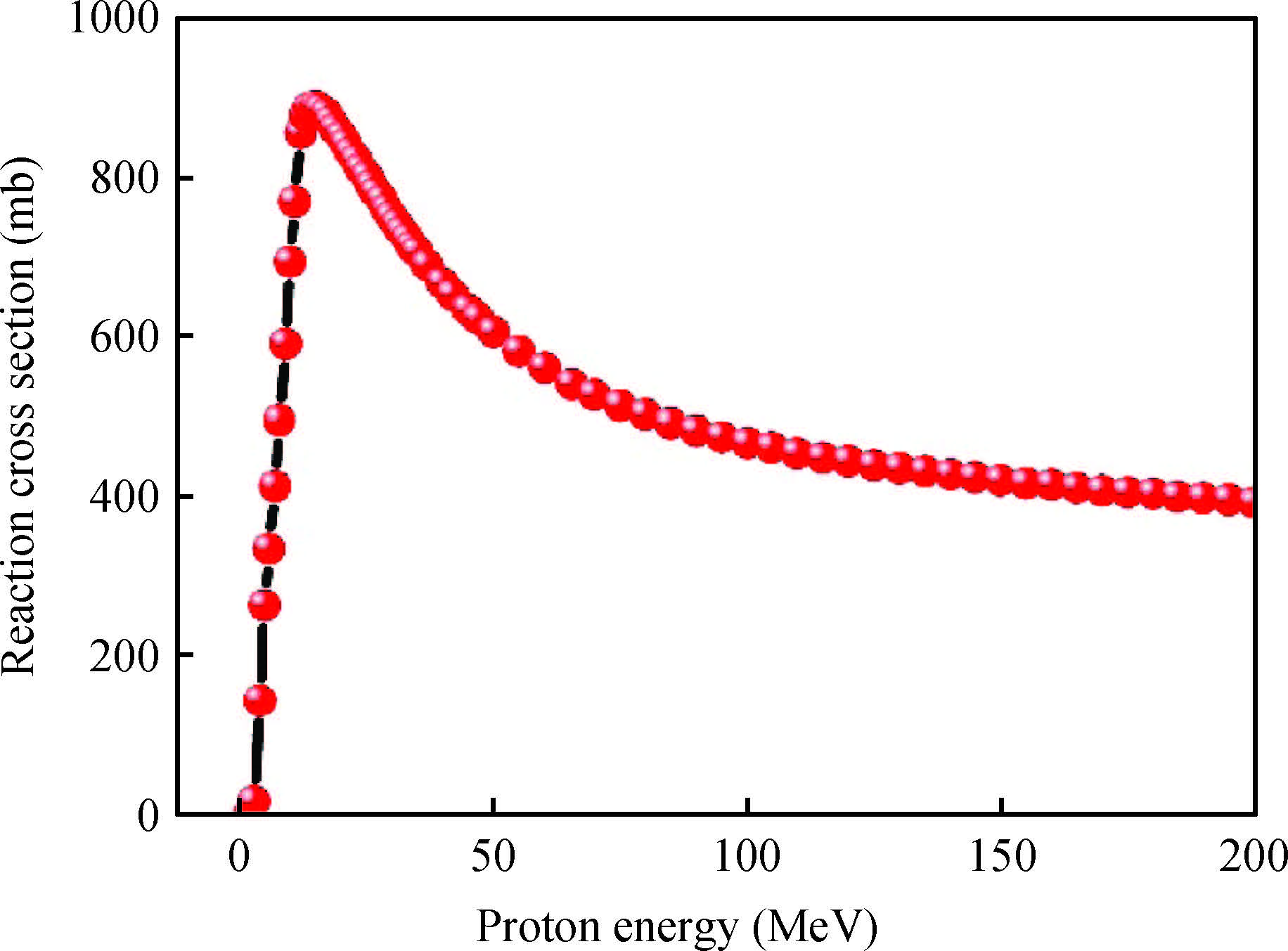
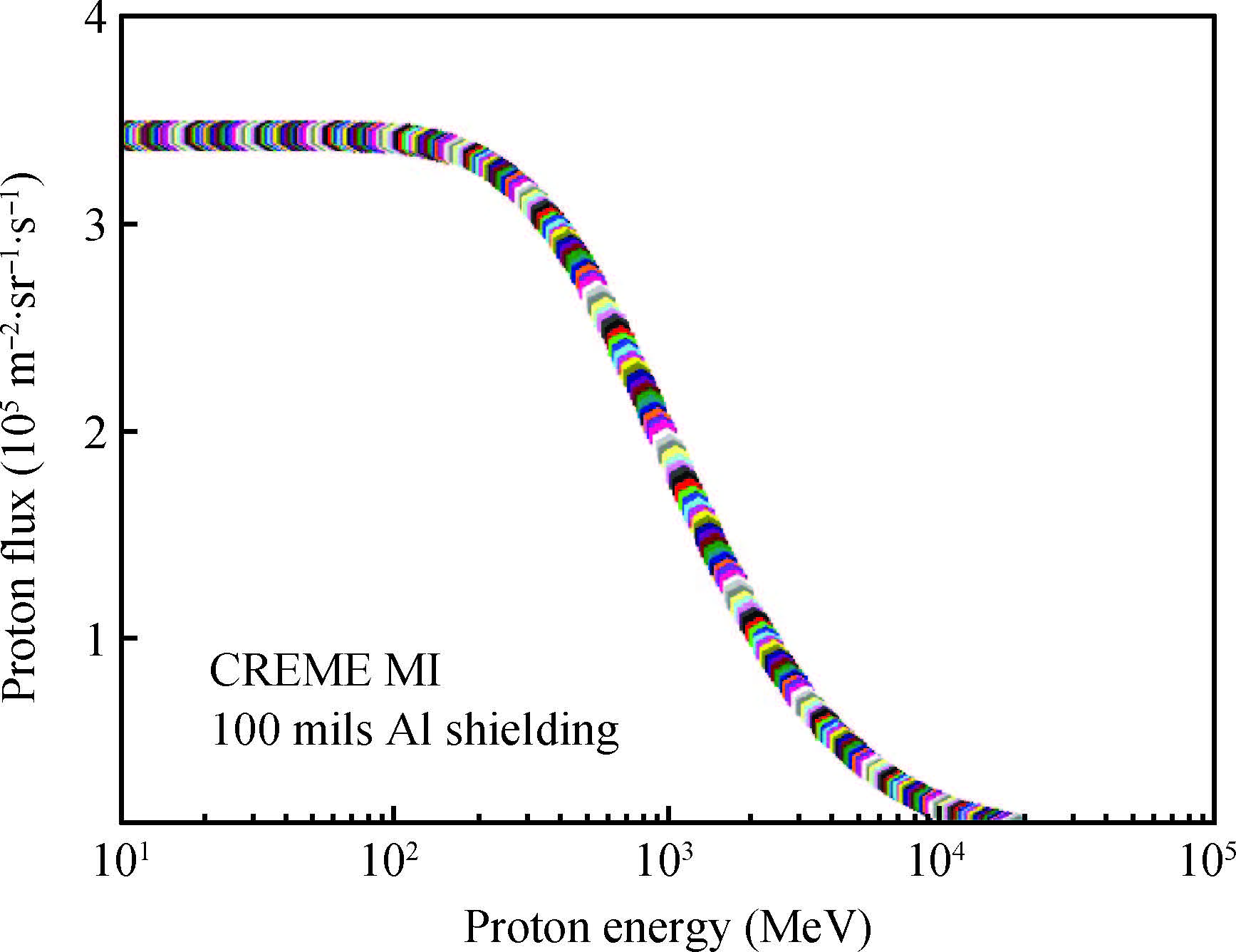
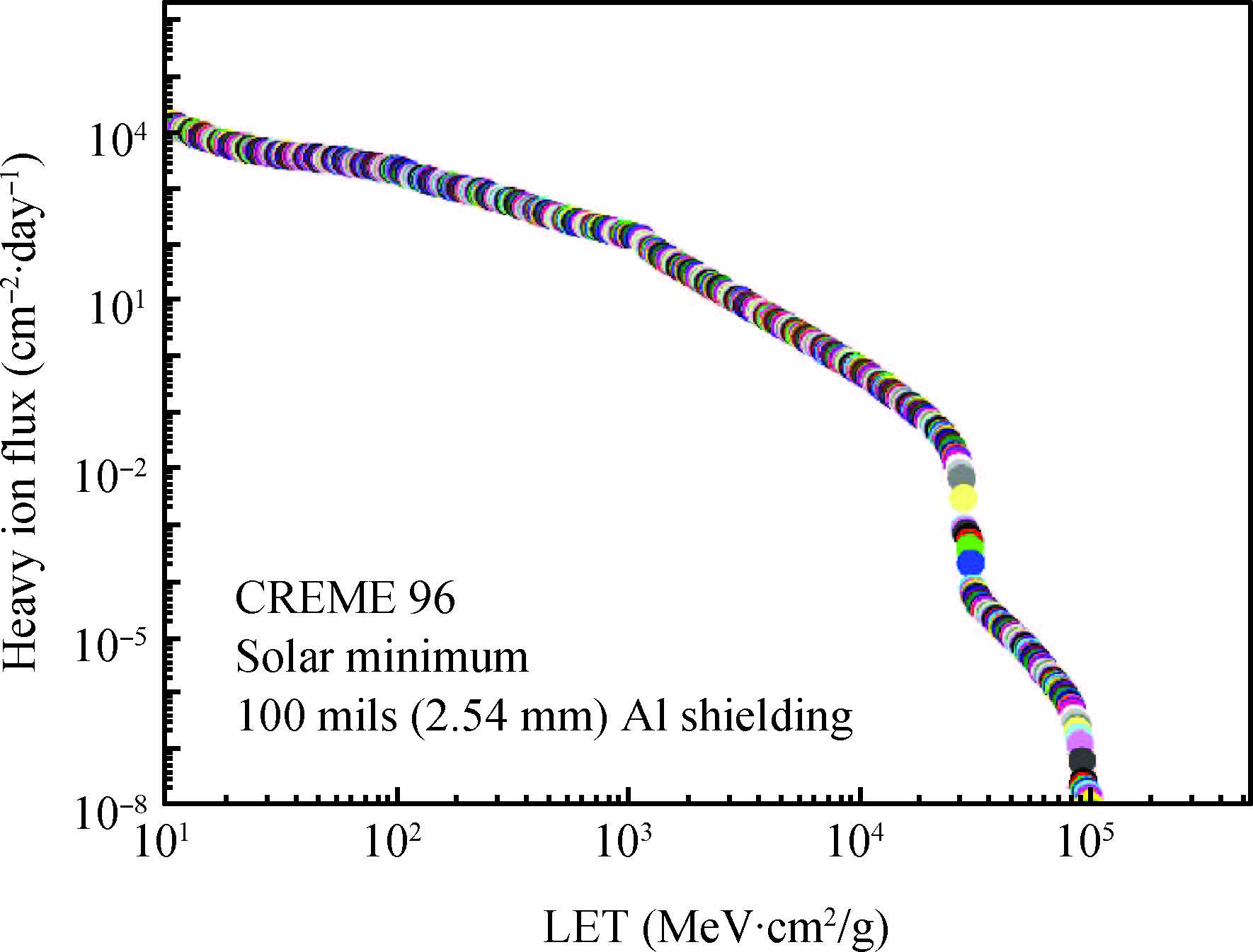
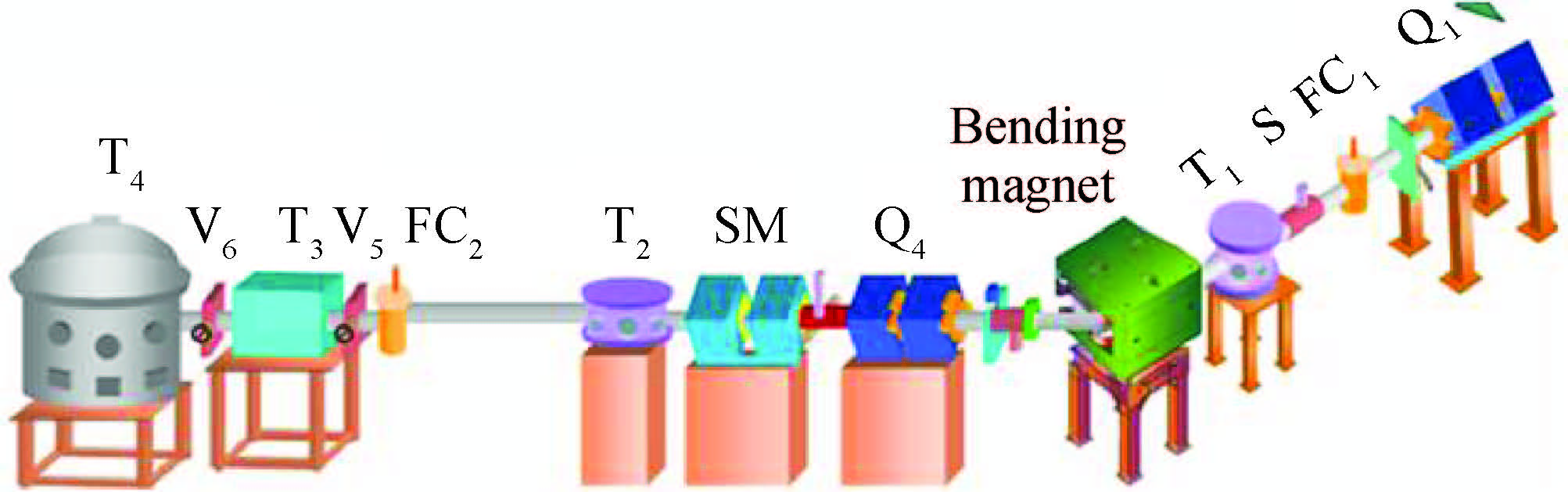
This paper tested and analyzed heavy ion and proton induced single event effects (SEE) of a commercial DC/DC converter based on a 600 nm Bi-CMOS technology. Heavy ion induced single event transients (SET) testing has been carried out by using the Beijing HI-13 tandem accelerator at China Institute of Atomic Energy. Proton test has been carried out by using the Canadian TRIUMF proton accelerator. Both SET cross section versus linear energy transfer (LET) and proton energy has been measured. The main study conclusions are: (1) the DC/DC is both sensitive to heavy ion and proton radiations although at a pretty large feature size (600 nm), and threshold LET is about 0.06 MeV·mg/cm2; (2) heavy ion SET saturation cross section is about 5 magnitudes order larger than proton SET saturation cross section, which is consistent with the theory calculation result deduced by the RPP model and the proton nuclear reaction model; (3) on-orbit soft error rate (SER) prediction showed, on GEO orbit, proton induced SERs calculated by the heavy ion derived model are 4-5 times larger than those calculated by proton test data.-
Keywords:
- heavy ion,
- proton,
- DC/DC converter,
- single event effects
-
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: