| Citation: |
Donghua Cao, Hui Wang, Hongjun Wei, Weiqiang Yang. Preparation, electronic structure, and photoluminescent properties of Eu2+ activated BaSi2O5 powder phosphors for solid-state lighting[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(12): 123008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/12/123008
****
D H Cao, H Wang, H J Wei, W Q Yang. Preparation, electronic structure, and photoluminescent properties of Eu2+ activated BaSi2O5 powder phosphors for solid-state lighting[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(12): 123008. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/12/123008.
|
Preparation, electronic structure, and photoluminescent properties of Eu2+ activated BaSi2O5 powder phosphors for solid-state lighting
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/12/123008
More Information
-
Abstract
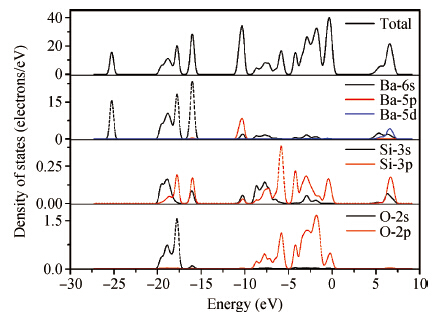
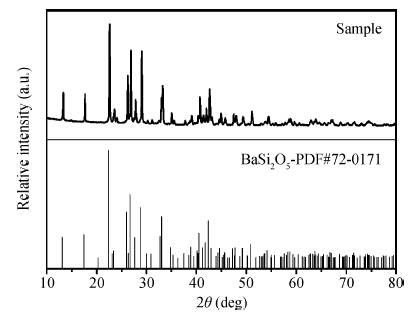
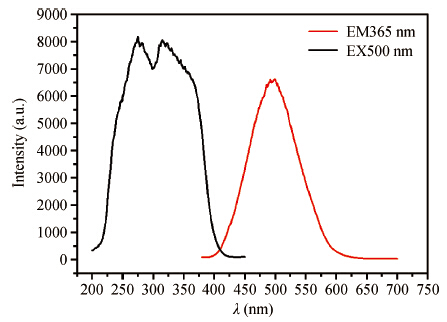
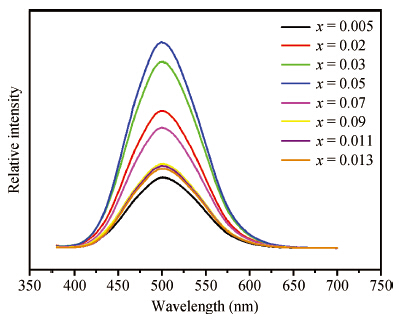
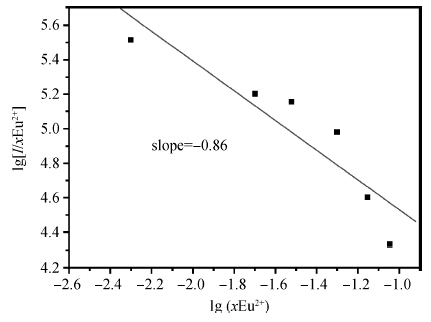
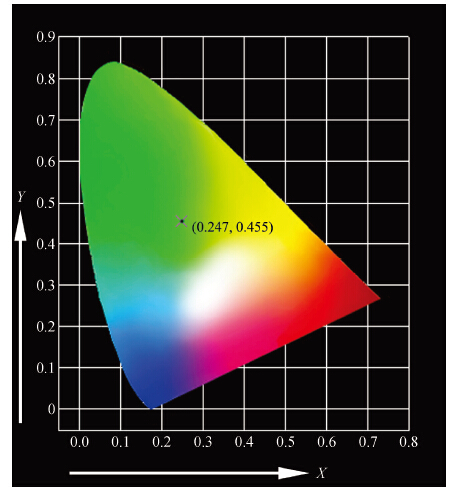
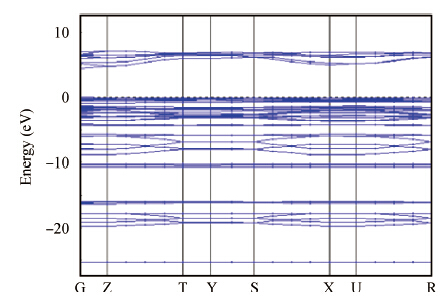
The green-emitting phosphor BaSi2O5:Eu2+ was synthesized by the conventional solid state reaction. Using the CASTEP code, BaSi2O5 is calculated to be an intermediate band gap semiconductor with an indirect energy gap of about 3. 2 eV. As expected, the calculated optical band gap of BaSi2O5 is lower compared to the experimentally determined values. Eu2+-activated BaSi2O5 phosphor can be excited efficiently over a broad spectral range between 200 and 400 nm, and has an emission peak at 500 nm with a full width at half maximum of 95 nm. The study of concentration-dependent emission intensity shows the optimal concentration of the Eu2+ is 0.05 mol, and that concentration quenching occurs when the Eu2+ content is beyond the critical value. The external quantum efficiency of the optimized BaSi2O5:Eu2+ is 96. 1%, 70. 2% and 62. 1% under excitation at 315, 350 and 365 nm, respectively. The superior optical properties of the sample show the potential as an ultraviolet converting green-emitting phosphor for white light emitting diodes. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] [36] [37] [38] [39] [40] [41] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: