| Citation: |
Shuai Feng, Lichuan Zhao, Qingzhu Zhang, Pengpeng Yang, Zhaoyun Tang, Cinan Wu, Jiang Yan. A simulation analysis of performance of both implanted doping and in situ doping ETSOI PMOSFETs[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(4): 046001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/046001
****
S Feng, L C Zhao, Q Z Zhang, P P Yang, Z Y Tang, C N Wu, J Yan. A simulation analysis of performance of both implanted doping and in situ doping ETSOI PMOSFETs[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(4): 046001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/046001.
|
A simulation analysis of performance of both implanted doping and in situ doping ETSOI PMOSFETs
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/4/046001
More Information
-
Abstract
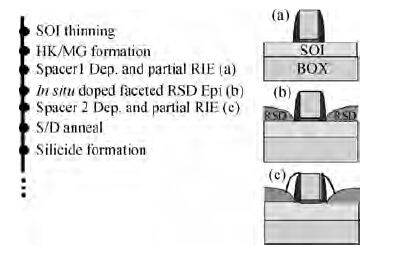
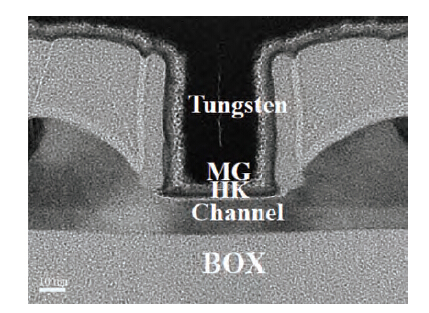
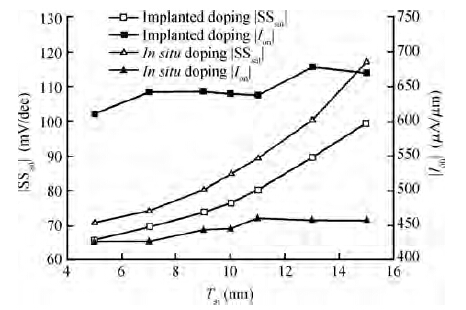
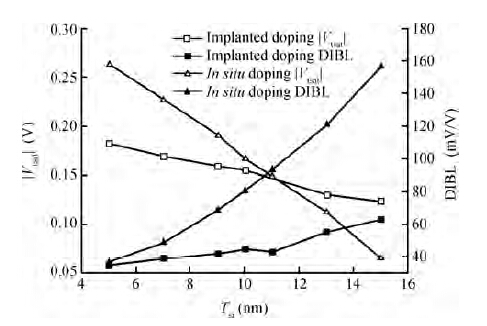
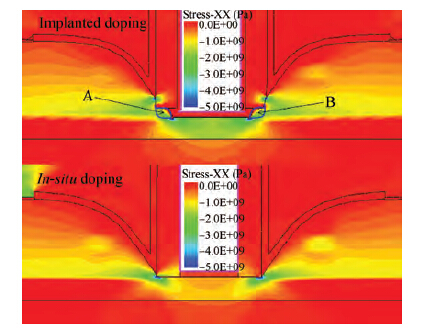
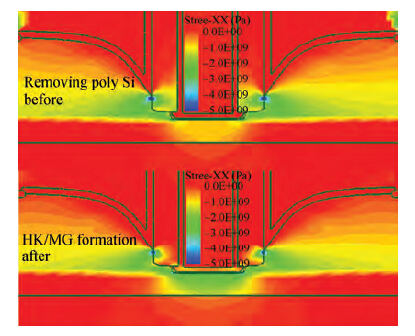
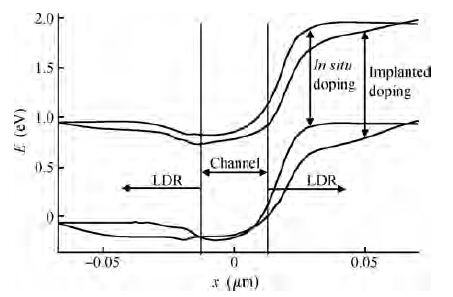
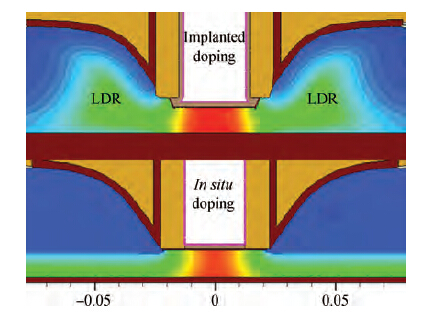
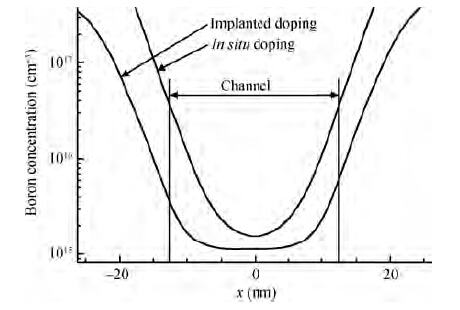
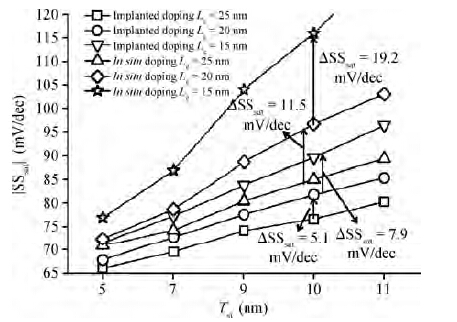
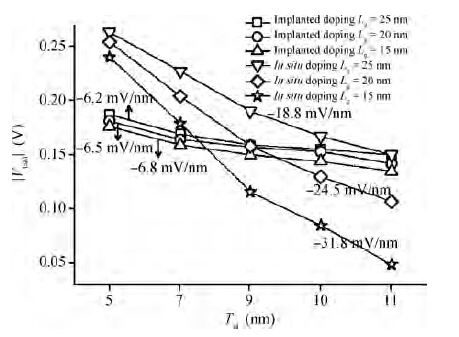
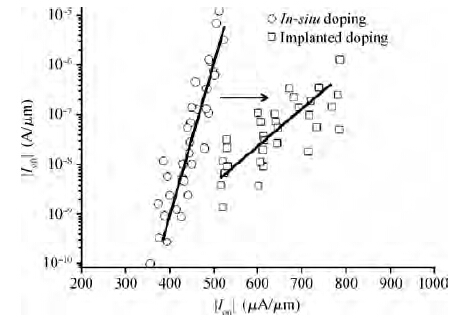
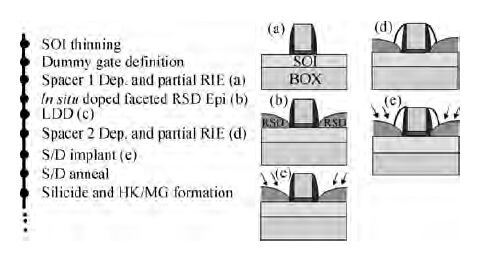
Extremely thin silicon on insulator p-channel metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (PMOSFETs) with implanted doping and in situ doping are analyzed by TCAD simulation. The critical characteristic parameters acquired by TCAD simulation are compared with each other to analyze their electrical performance. The saturated driven currents of implanted doping devices with a 25 nm gate length (Lg) are about 200 μA/μm bigger than the in situ doping devices at the same saturated threshold voltage (Vtsat). Meanwhile the drain-induced barrier lowering (DIBL) and saturated subthreshold swings for implanted doping devices are also 30-50 mV/V and 6.3-9.1 mV/dec smaller than those of in situ doping devices at 25 nm Lg and a 9-11 nm thickness of SOI (Tsi), respectively. The shift of Vtsat with Tsi for in situ doping devices with 15 nm Lg is -31.8 mV/nm, whereas that for in situ doping devices is only -6.8 mV/nm. These outcomes indicate that the devices with implanted doping can produce a more advanced and stable electrical performance.-
Keywords:
- implanted doping,
- in situ doping,
- TCAD simulation,
- PMOSFETs
-
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: