| Citation: |
Hong Li, Hongbin Pu, Chunlei Zheng, Zhiming Chen. β-FeSi2 films prepared on 6H-SiC substrates by magnetron sputtering[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(6): 063005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/6/063005
****
H Li, H B Pu, C L Zheng, Z M Chen. β-FeSi2 films prepared on 6H-SiC substrates by magnetron sputtering[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(6): 063005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/6/063005.
|
β-FeSi2 films prepared on 6H-SiC substrates by magnetron sputtering
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/6/063005
More Information
-
Abstract
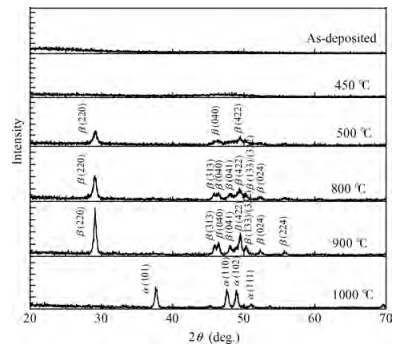
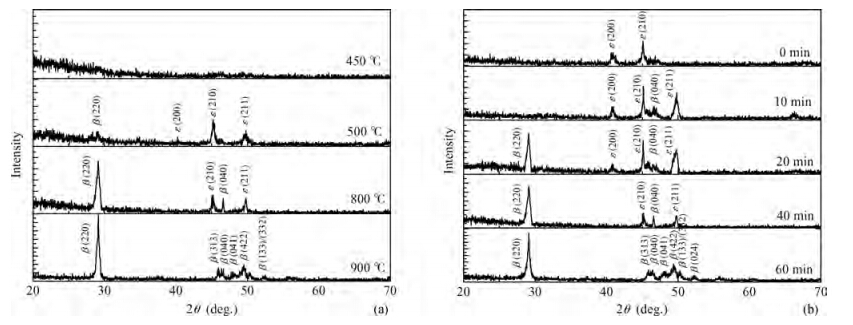
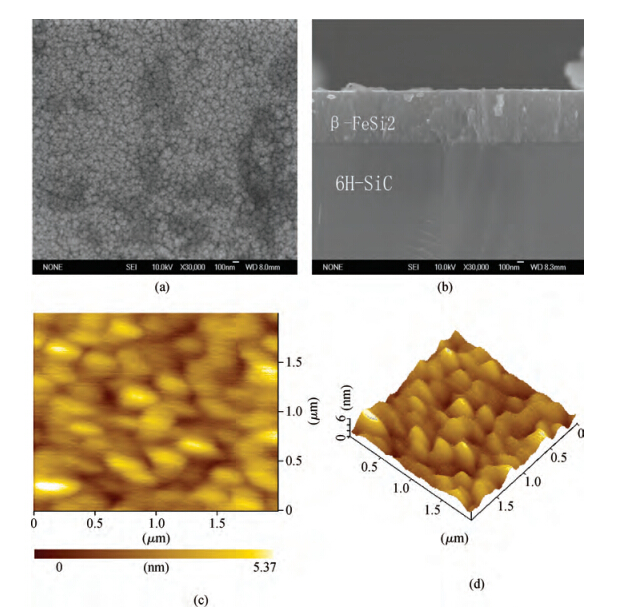
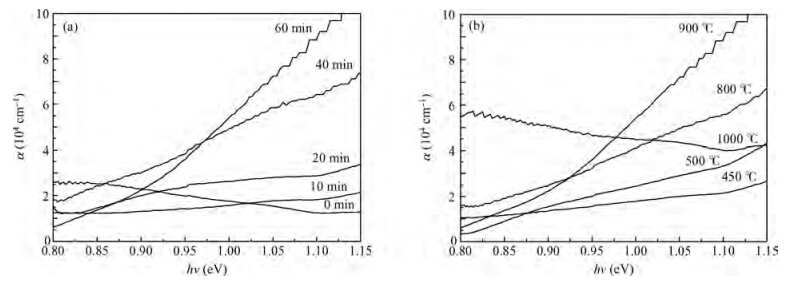
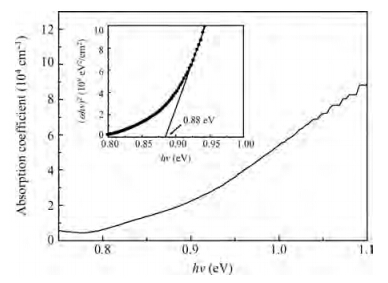
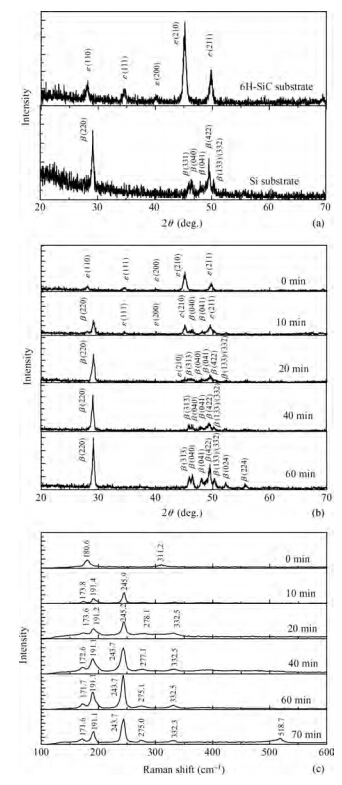
β-FeSi2 thin films have been successfully prepared by magnetron sputtering and post rapid thermal annealing method on 6H-SiC (0001) substrates using a FeSi2 target and a Si target. X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Raman spectroscopy are applied to analyze the formation of β-FeSi2 films. XRD spectra reveal that the amorphous FeSi2 films are transformed to β-FeSi2 phase as the annealing temperature is increased from 500 to 900 ℃ for 5 min and the optimal annealing temperature is 900 ℃. The formation of β-FeSi2 is also confirmed by Raman spectroscopy. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) observations indicate that the film is flat, relatively compact and the interface between β-FeSi2 and 6H-SiC is clear. Atomic force microscope (AFM) measurements demonstrate that the surface roughness confirmed by the root mean square (RMS) of the β-FeSi2 film is 0.87 nm. Near-infrared spectrophotometer observation shows that the absorption coefficient is of the order of 105cm-1 and the optical band-gap of the β-FeSi2 film is 0.88 eV. The β-FeSi2 film with high crystal quality is fabricated by co-sputtering a FeSi2 target and a Si target for 60 min and annealing at 900 ℃ for 5 min. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: