| Citation: |
Dongyan Tao, Yu Cheng, Jingming Liu, Jie Su, Tong Liu, Fengyun Yang, Fenghua Wang, Kewei Cao, Zhiyuan Dong, Youwen Zhao. Chemical and electrical properties of (NH4)2S passivated GaSb surface[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2015, 36(7): 073006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/7/073006
****
D Y Tao, Y Cheng, J M Liu, J Su, T Liu, F Y Yang, F H Wang, K W Cao, Z Y Dong, Y W Zhao. Chemical and electrical properties of (NH4)2S passivated GaSb surface[J]. J. Semicond., 2015, 36(7): 073006. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/7/073006.
|
Chemical and electrical properties of (NH4)2S passivated GaSb surface
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/36/7/073006
More Information
-
Abstract
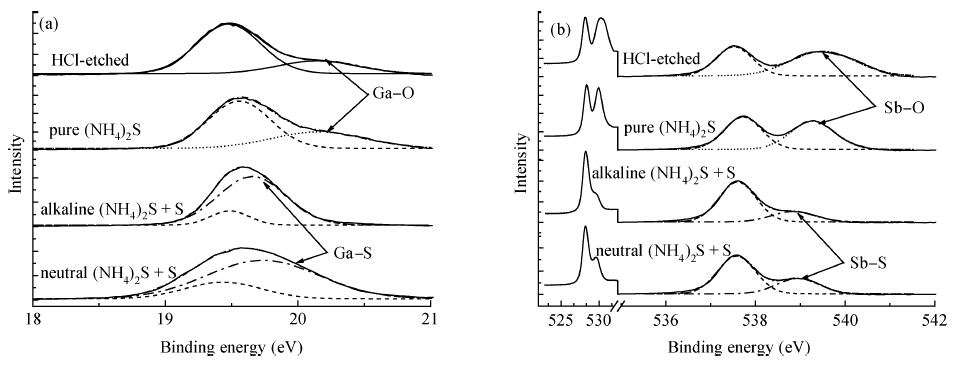
The surface chemical properties of gallium antimonide (GaSb) after ammonium sulfide ((NH4)2S) solution passivation have been studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), time of flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy (TOF-SIMS) and I-V measurement. An advantage of neutral (NH4)2S + S solution over pure (NH4)2S solution and alkaline (NH4)2S + S solution has been found in the ability to passivate the GaSb surface by contrast and comparison. It has been found that alkaline (NH4)2S + S solution passivation effectively removes oxides of the GaSb surface and forms sulfide products to improve device performance. TOF-SIMS complementally demonstrates that pure (NH4)2S passivation did form sulfide products, which are too soluble to really exist. The lowest roughness determined using a 3D optical profilometer and the highest improved SBD quality proved that neutral (NH4)2S + S solution passivation worked much better in improving the surface properties of GaSb.-
Keywords:
- surface passivation,
- GaSb,
- XPS,
- TOF-SIMS
-
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad:


















