| Citation: |
Limeng Zhang, Dan Lu, Zhaosong Li, Biwei Pan, Lingjuan Zhao. C-band fundamental/first-order mode converter based on multimode interference coupler on InP substrate[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(12): 124005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/12/124005
****
L M Zhang, D Lu, Z S Li, B W Pan, L J Zhao. C-band fundamental/first-order mode converter based on multimode interference coupler on InP substrate[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(12): 124005. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/12/124005.
|
C-band fundamental/first-order mode converter based on multimode interference coupler on InP substrate
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/12/124005
More Information
-
Abstract
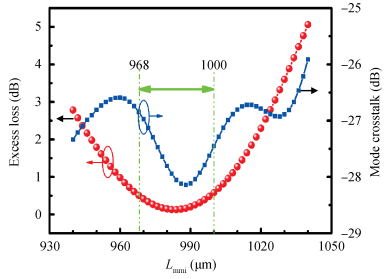
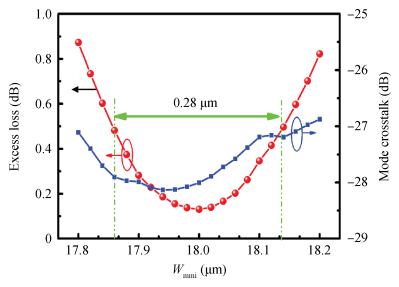
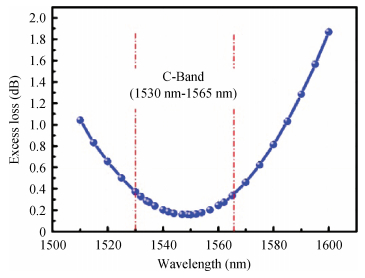
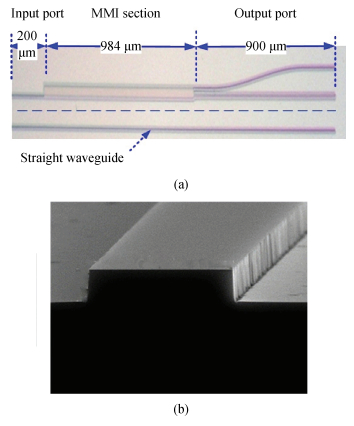
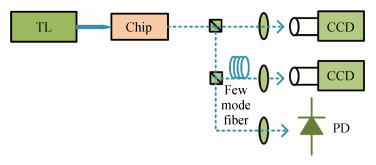
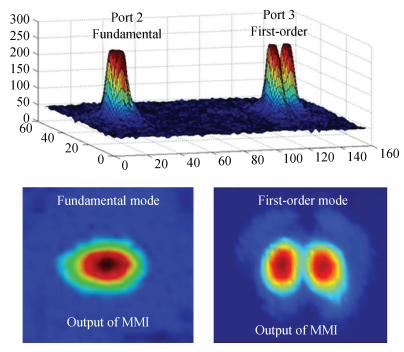
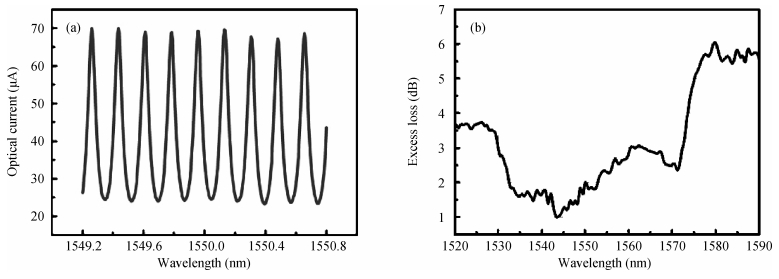
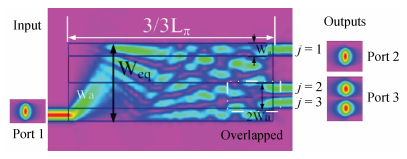
The design, fabrication and characterization of a fundamental/first-order mode converter based on multimode interference coupler on InP substrate were reported. Detailed optimization of the device parameters were investigated using 3D beam propagation method. In the experiments, the fabricated mode converter realized mode conversion from the fundamental mode to the first-order mode in the wavelength range of 1530-1565 nm with excess loss less than 3 dB. Moreover, LP01 and LP11 fiber modes were successfully excited from a few-mode fiber by using the device. This InP-based mode converter can be a possible candidate for integrated transceivers for future mode-division multiplexing system. -
References
[1] Qian D, Huang M, Ip E, et al. 101.7-Tb/s (370×294-Gb/s) PDM-128QAM-OFDM transmission over 3×55-km SSMF using pilot-based phase noise mitigation. Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Optical Society of America, 2011: PDPB5[2] Sano A, Kobayashi T, Yamanak S, et al. 102.3-Tb/s (224×548-Gb/s) C-and extended L-band all-Raman transmission over 240 km using PDM-64QAM single carrier FDM with digital pilot tone. Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Optical Society of America, 2012: PDP5C.3[3] Mitra P, Stark J. Nonlinear limits of the information capacity of optical fiber communication. Nature, 2011, 411: 1027 http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v411/n6841/abs/4111027a0.html[4] Essiambre J, Foschini G, Karmer G, et al. Capacity limits of information transport in fiber-optic networks. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 101: 163901 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.163901[5] Sakaguchi J, Puttnam B, Klaus W, et al. 19-core fiber transmission of 19×100×172-Gb/s SDM-WDM-PDM-QPSK signals at 305 Tb/s. Proceedings of National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference Optical Society of America, 2012: PDP5C.1[6] Ryf R, Randel S, Gnauck A, et al. Space-division multiplexing over 10 km of three-mode fiber using coherent 6×6 MIMO. Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Optical Society of America, 2011: PDPB10[7] Sleiffer V, Jung Y, Veljanovski V, et al. 73.7 Tb/s (96×3×256-Gb/s) mode-division-multiplexed DP-16QAM transmission with inline MM-EDFA. Opt Express, 2012, 20 (26): 428 doi: 10.1364/OE.20.00B428[8] Giles I, Obeysekara A, Chen R, et al. Fiber LPG mode converters and mode selection technique for multimode SDM. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 2012, 24(21): 1922 doi: 10.1109/LPT.2012.2219044[9] Hanzawa N, Saitoh K, Sakamoto T, et al. Mode-division multiplexed transmission with fiber mode couplers. Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Optical Society of America, 2012: OW1D.4[10] Saitoh F, Saitoh K, Koshiba M. A design method of a fiber-based mode multi/demultiplexer for mode-division multiplexing. Opt Express, 2010, 18(5): 4709 doi: 10.1364/OE.18.004709[11] Hanzawa N, Saitoh K, Sakamoto T, et al. Two-mode PLC-based mode multi/demultiplexer for mode and wavelength division multiplexed transmission. Opt Express, 2013, 21(22): 25752 doi: 10.1364/OE.21.025752[12] Chan Waiying, Chan Hauping. Reconfigurable two-mode mux/demux device. Opt Express, 2014, 22(8): 9282 doi: 10.1364/OE.22.009282[13] Hanzawa N, Saitoh K, Sakamoto T, et al. Three-mode PLC-type multi/demultiplexer for mode-division multiplexing transmission. Proceedings of European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication, 2013: 183 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261020891_Three-mode_PLC-type_multidemultiplexer_for_mode-division_multiplexing_transmission[14] Chang Yuxin, Hu Guijun, Bai Song, et al. Research of asymmetric planar waveguide type mode division multiplexer/demultiplexer. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2014, 12: 125 http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ201412023.htm[15] Hanzawa N, Saitoh K, Sakamoto T, et al. Asymmetric parallel waveguide with mode conversion for mode and wavelength division multiplexing transmission. Proceedings of Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Optical Society of America, 2012: OTu1l.4[16] Leuthold J, Eckner J, Gamper E, et al. Multimode interference couplers for the conversion and combining of zero-and first-order modes. J Lightwave Technol, 1998, 16(7): 1228 doi: 10.1109/50.701401[17] Bachmann M, Besse P, General H. Self-imaging properties in N×N multimode interference couplers including phase relations. Appl Opt, 1994, 33(18): 3905 doi: 10.1364/AO.33.003905[18] Bachmann M, Besse P, Melchior H. Overlapping Imagemultimode interference couplers with reduced number of self-imagesfor uniform and nonuniform power splitting. Appl Opt, 1995, 34(30): 6898 doi: 10.1364/AO.34.006898[19] Feuchter T, Thirstrup C. High precision planar waveguide propagation loss measurement technique using a Fabry-Perot cavity. IEEE Photon Technol Lett, 1994, 6(10): 1244 doi: 10.1109/68.329652 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: