| Citation: |
Xiangye Chen, Li Cai, Qiang Zeng, Xinqiao Wang. Impact of stray charge on interconnect wire via probability model of double-dot system[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(2): 022002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/2/022002
****
X Y Chen, L Cai, Q Zeng, X Q Wang. Impact of stray charge on interconnect wire via probability model of double-dot system[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(2): 022002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/2/022002.
|
Impact of stray charge on interconnect wire via probability model of double-dot system
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/2/022002
More Information
-
Abstract
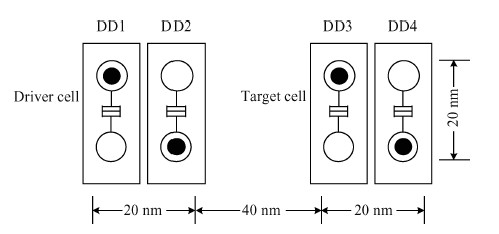
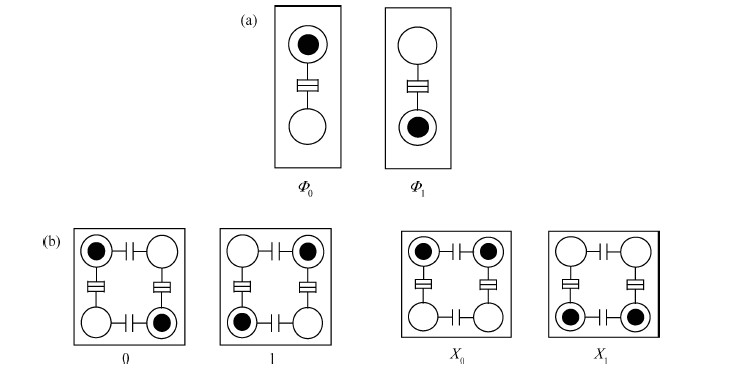
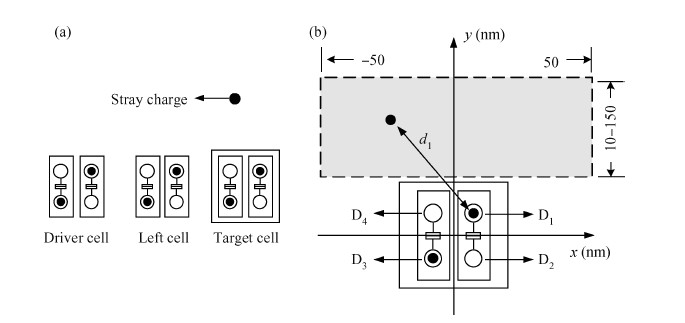
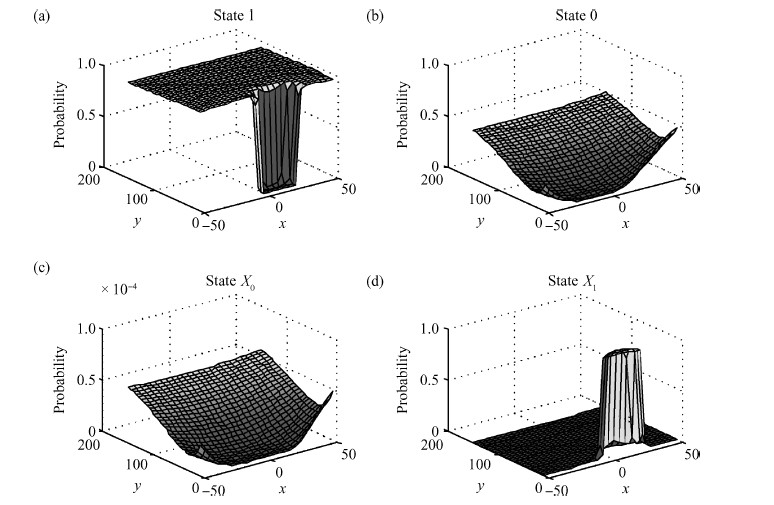
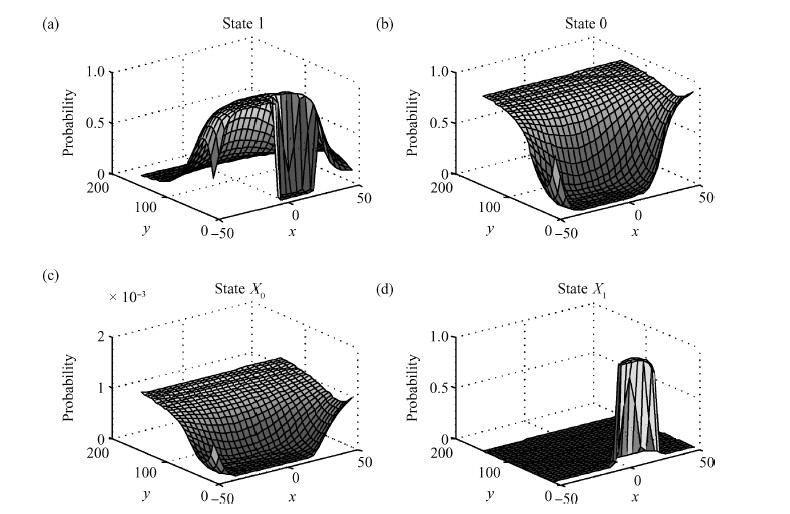
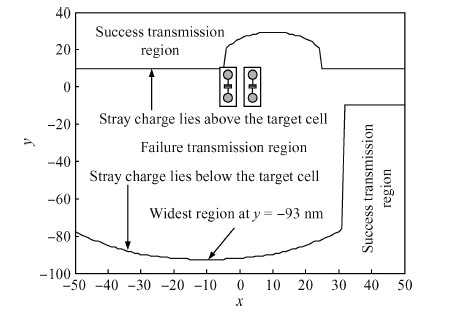
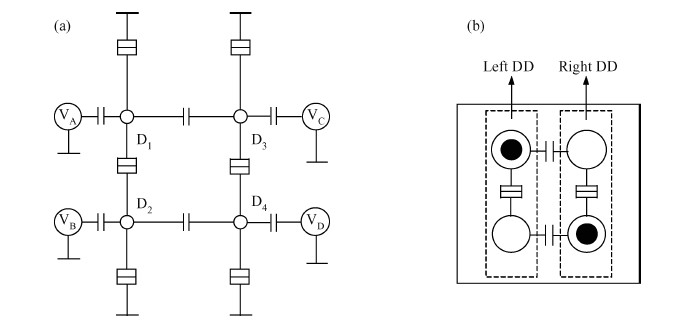
The behavior of quantum cellular automata (QCA) under the influence of a stray charge is quantified. A new time-independent switching paradigm, a probability model of the double-dot system, is developed. Superiority in releasing the calculation operation is presented by the probability model compared to previous stray charge analysis utilizing ICHA or full-basis calculation. Simulation results illustrate that there is a 186-nm-wide region surrounding a QCA wire where a stray charge will cause the target cell to switch unsuccessfully. The failure is exhibited by two new states' dominating the target cell. Therefore, a bistable saturation model is no longer applicable for stray charge analysis. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: