| Citation: |
Baoyong Chi, Zheng Song, Lixue Kuang, Haikun Jia, Xiangyu Meng, Zhihua Wang. CMOS mm-wave transceivers for Gbps wireless communication[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2016, 37(7): 071001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/7/071001
****
B Y Chi, Z Song, L X Kuang, H K Jia, X Y Meng, Z H Wang. CMOS mm-wave transceivers for Gbps wireless communication[J]. J. Semicond., 2016, 37(7): 071001. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/7/071001.
|
CMOS mm-wave transceivers for Gbps wireless communication
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/7/071001
More Information
-
Abstract
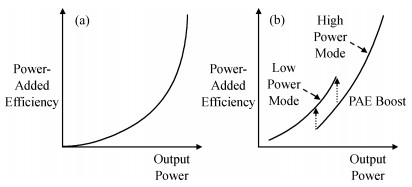
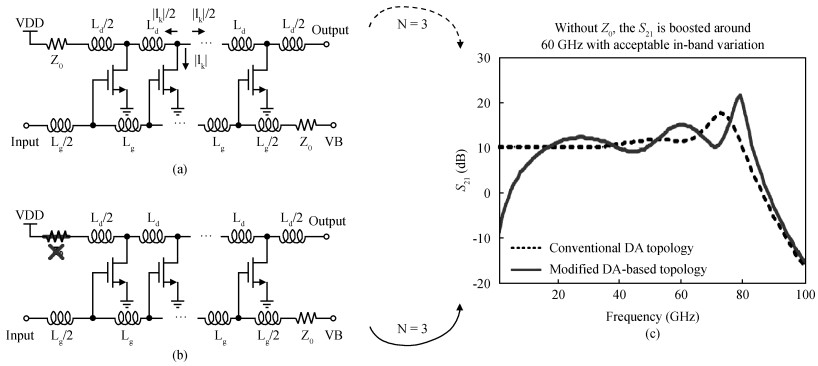
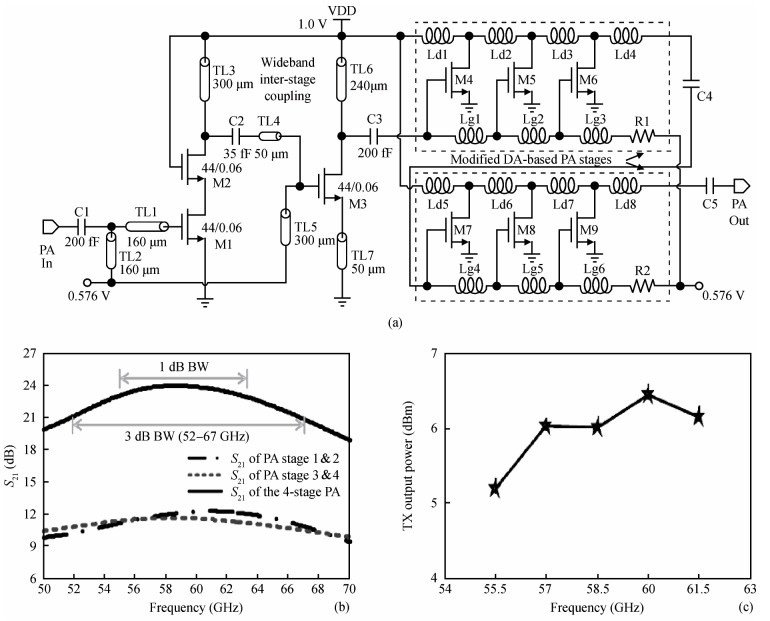
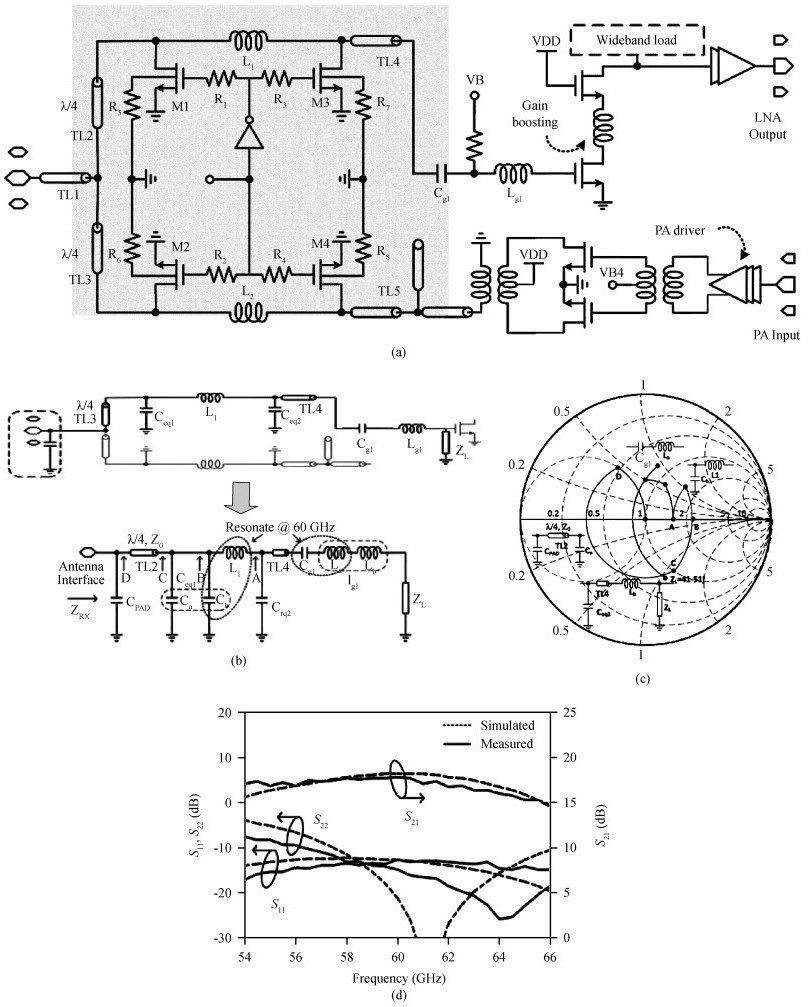
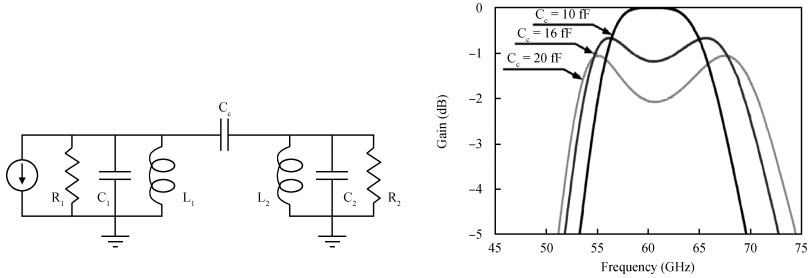
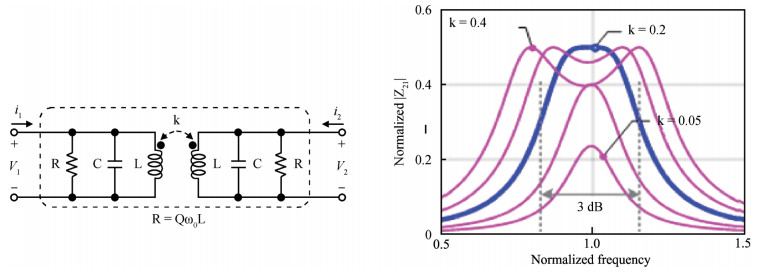
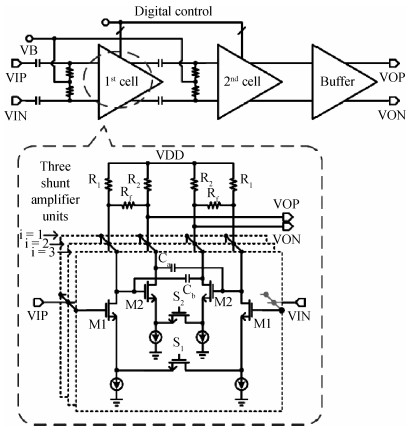
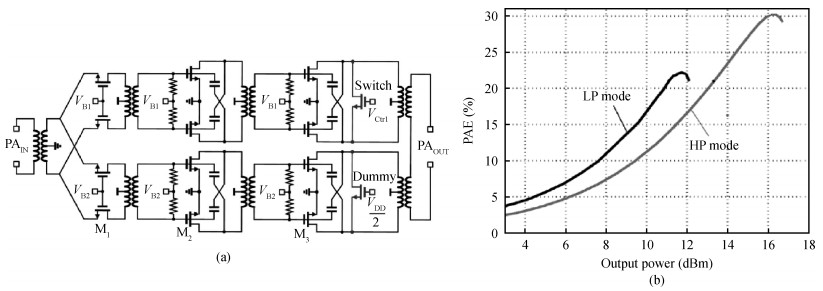
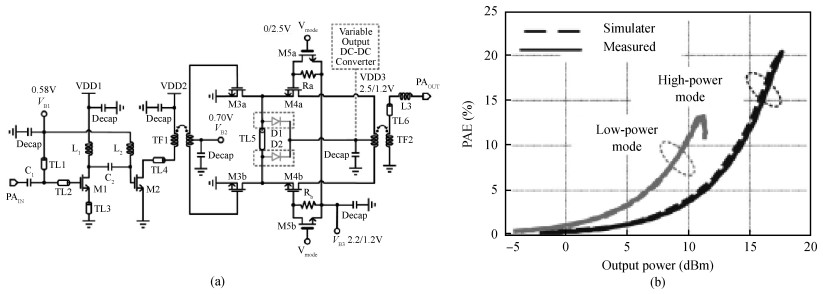
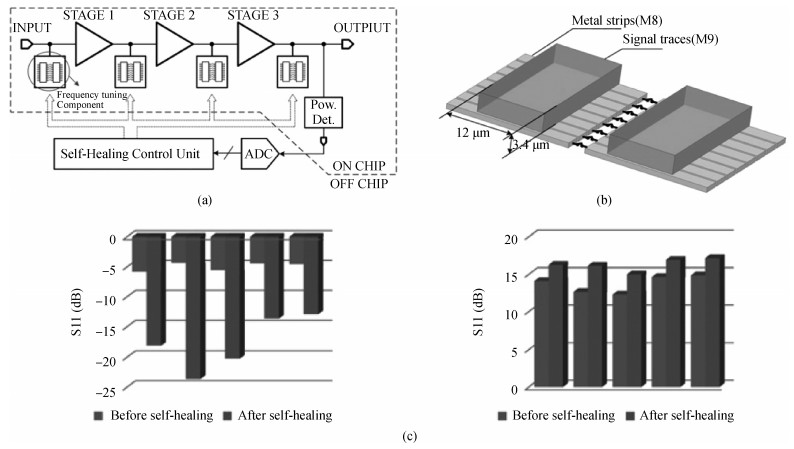
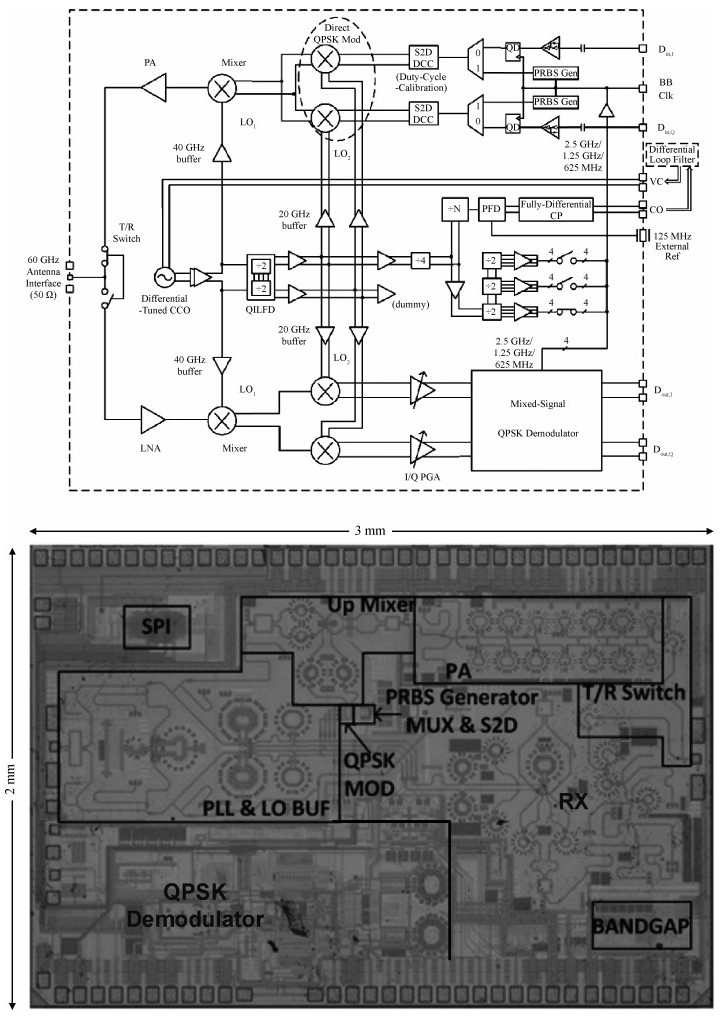
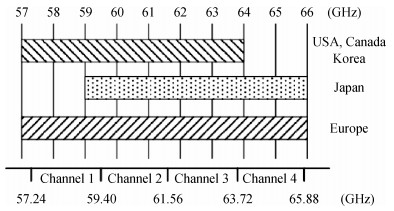
The challenges in the design of CMOS millimeter-wave (mm-wave) transceiver for Gbps wireless communication are discussed. To support the Gbps data rate, the link bandwidth of the receiver/transmitter must be wide enough, which puts a lot of pressure on the mm-wave front-end as well as on the baseband circuit. This paper discusses the effects of the limited link bandwidth on the transceiver system performance and overviews the bandwidth expansion techniques for mm-wave amplifiers and IF programmable gain amplifier. Furthermore, dual-mode power amplifier (PA) and self-healing technique are introduced to improve the PA's average efficiency and to deal with the process, voltage, and temperature variation issue, respectively. Several fully-integrated CMOS mm-wave transceivers are also presented to give a short overview on the state-of-the-art mm-wave transceivers. -
References
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21] [22] [23] [24] [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32] [33] [34] [35] -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: