| Citation: |
Yipeng Liang, Jianping Liu, Masao Ikeda, Aiqin Tian, Renlin Zhou, Shuming Zhang, Tong Liu, Deyao Li, Liqun Zhang, Hui Yang. Effect of inhomogeneous broadening on threshold current of GaN-based green laser diodes[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2019, 40(5): 052802. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/5/052802
****
Y P Liang, J P Liu, M Ikeda, A Q Tian, R L Zhou, S M Zhang, T Liu, D Y Li, L Q Zhang, H Yang, Effect of inhomogeneous broadening on threshold current of GaN-based green laser diodes[J]. J. Semicond., 2019, 40(5): 052802. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/5/052802.
|
Effect of inhomogeneous broadening on threshold current of GaN-based green laser diodes
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/5/052802
More Information
-
Abstract
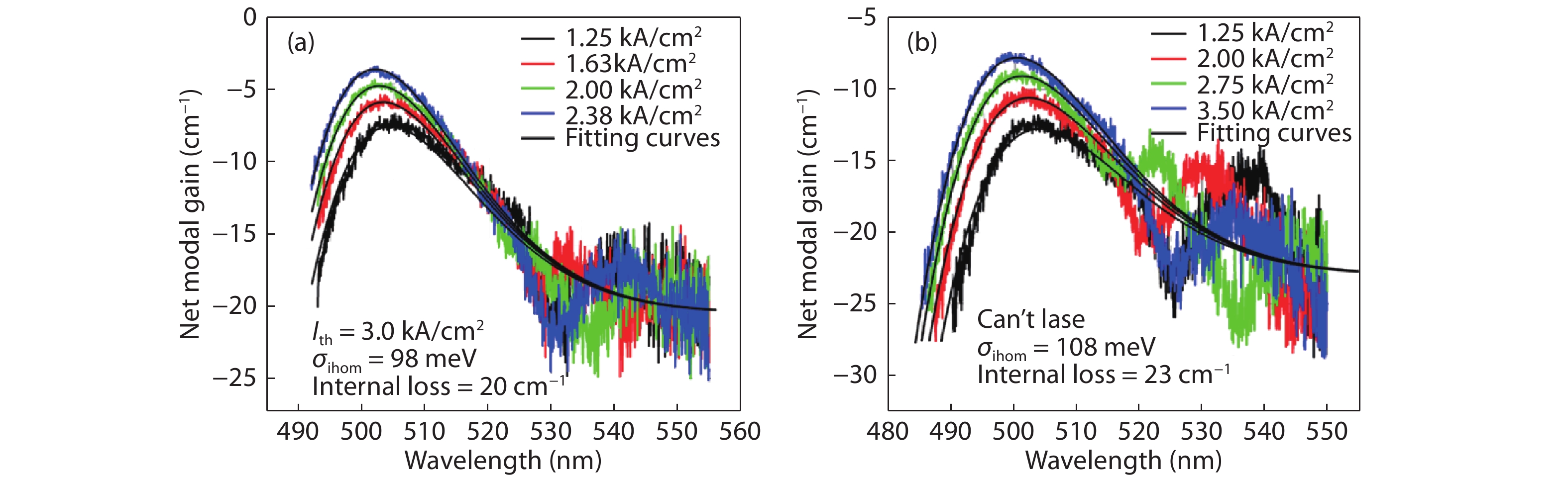
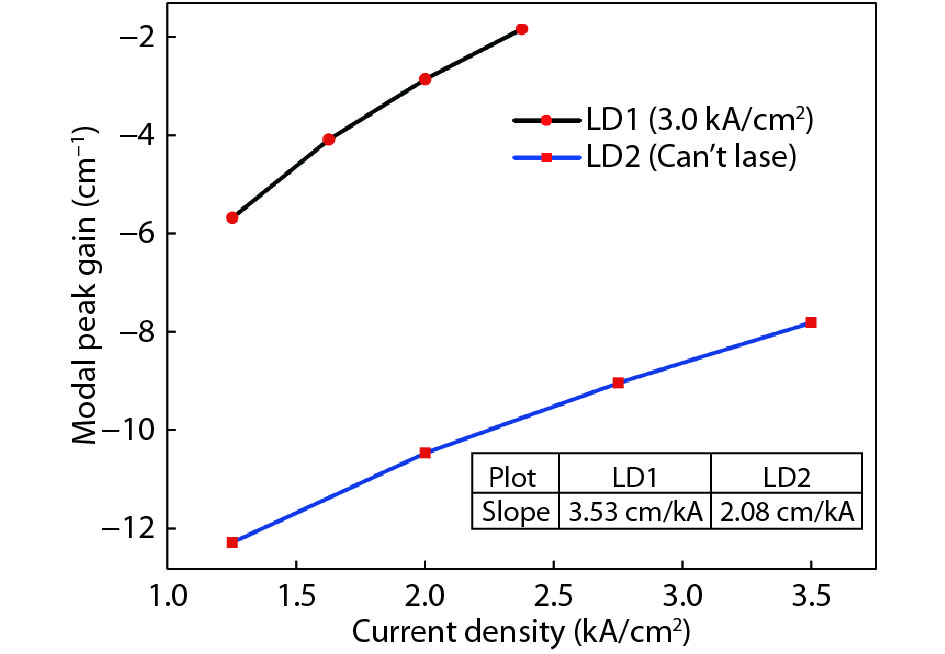
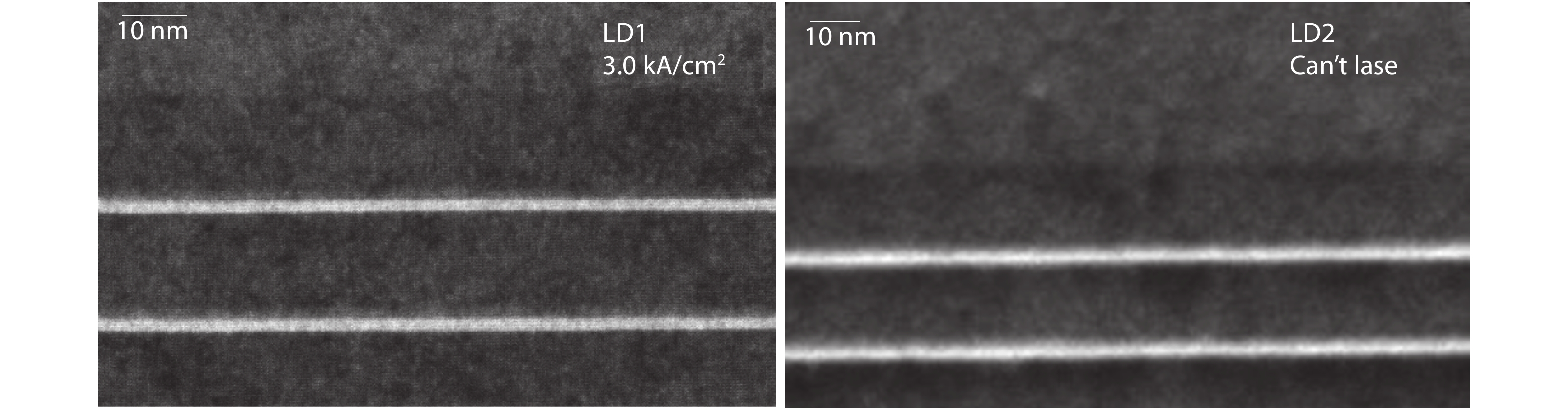
The inhomogeneous broadening parameter and the internal loss of green LDs are determined by experiments and theoretical fitting. It is found that the inhomogeneous broadening plays an important role on the threshold current density of green LDs. The green LD with large inhomogeneous broadening even cannot lase. Therefore, reducing inhomogeneous broadening is a key issue to improve the performance of green LDs. -
References
[1] Jiang L R, Liu J P, Tian A Q, et al. GaN-based green laser diodes. J Semicond, 2016, 37, 111001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/37/11/111001[2] Crump P, Erbert G, Wenzel H, et al. Efficient high-power laser diodes. J Sel Top Quantum Electron, 2013, 19, 1501211 doi: 10.1109/JSTQE.2013.2239961[3] Piprek J, States U. What limits the power conversion efficiency of GaN-based lasers. SPIE, 2017, 98, 3 doi: 10.1117/12.2256129[4] Miyoshi T, Masui S, Okada T, et al. 510–515 nm InGaN-based green laser diodes on c-plane GaN substrate. Appl Phys Express, 2009, 2(6), 062201 doi: 10.1143/APEX.2.062201[5] Yamaguchi A A, Kuramoto M, Nido M, et al. An alloy semiconductor system with a tailorable band-tail and its applications to high-performance laser operation: I. A band-states model for an alloy-fluctuated InGaN material system designed for quantum well laser operation. Semicond Sci Technol, 2001, 16, 763 doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/16/9/305[6] Chow W W, Wright A F, Girndt A, et al. Microscopic theory of gain for an InGaN/AlGaN quantum well laser. Appl Phys Lett, 1997, 71, 2608 doi: 10.1063/1.120155[7] Butté R, Lahourcade L, Uždavinys T K, et al. disorder and growth mode induced fluctuations optical absorption edge broadening in thick InGaN layers: Random alloy atomic disorder and growth mode induced fluctuations. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112, 032106 doi: 10.1063/1.5010879[8] Glauser M, Rossbach G, et al. Investigation of InGaN/GaN quantum wells for polariton laser diodes. Phys Status Solidi, 2012, 9(5), 1325 doi: 10.1002/pssc.v9.5[9] Schwarz U T. Investigation and comparison of optical gain spectra of (Al,In) GaN laser diodes emitting in the 375nm to 470 nm spectral range. Proc SPIE, 2007, 648506 doi: 10.1117/12.705867[10] Hakki B W, Paoli T L. cw degradation at 300 K of GaAs double-heterostructure junction laser. II. Electronic gain. J Appl Phys, 1973, 44, 4113 doi: 10.1063/1.1662905[11] Hakki B W, Paoli T L. Gain spectra in GaAs double-heterostructure injection lasers. J Appl Phys, 1974, 46, 1299 doi: 10.1063/1.321696[12] Chuang S L, Chang C S. k·p method for strained wurtzite semiconductors. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54, 2941 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.2491[13] Lew Yan Voon L C, Willatzen M. The k·p method : electronic properties of semiconductors. Springer, 2009[14] Chow W W, Koch S W. Semiconductor-laser fundamentals: physics of the gain materials. Spring, 1999, 12[15] Zhao H P, Arif R A, Tansu N. Self-consistent gain analysis of type-II self-consistent gain analysis of type-II ‘W’ InGaN - GaNAs quantum well. J Appl Phys, 2016, 104, 043104 doi: 10.1063/1.2970107[16] Piprek J. Optoelectronic devices: advanced simulation and analysis. New York: Springer, 2003, 304[17] Yariv A. Quantum electronics. New York: Wiley, 1967[18] Portis A. Inhomogeneous line-broadening in F centers. Phys Rev, 1971, 91, 1071[19] Li Q. A model for steady-state luminescence of localized-state ensemble. Europhys Lett, 2005, 71(6), 994 doi: 10.1209/epl/i2005-10170-7[20] Li Q. Thermal redistribution of localized excitons and its effect on the luminescence band in InGaN ternary alloys. Appl Phys Lett, 2001, 79, 1810 doi: 10.1063/1.1403655[21] Schwarz U T, Sturm E, Wegscheider W, et al. Gain spectra and current-induced change of refractive index in (In/Al) GaN diode lasers. Phys Status Solidi A, 2003, 200, 143 doi: 10.1002/pssa.200303340[22] Bergmann M J, Casey H C. Optical-field calculations for lossy multiple-layer Al xGa1-xN/InxGa1-xN laser diodes. J Appl Phys, 1998, 84(3), 1196 doi: 10.1063/1.368185[23] Lermer T, Schillgalies M, Breidenassel A, et al. Waveguide design of green InGaN laser diodes. Phys Status Solidi A, 2010, 207, 1328 doi: 10.1002/pssa.200983410[24] Zhang L, Jiang D, Zhu J, et al. Confinement factor and absorption loss of AlInGaN based laser diodes emitting from ultraviolet to green. J Appl Phys, 2009, 105, 023104 doi: 10.1063/1.3068182 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: