| Citation: |
Hao Zhang, Qiangsheng Cui, Xu Yan, Jiahui Shi, Fujiang Lin. A 0.5–3.0 GHz SP4T RF switch with improved body self-biasing technique in 130-nm SOI CMOS[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2020, 41(10): 102404. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/10/102404
****
H Zhang, Q S Cui, X Yan, J H Shi, F J Lin. A 0.5–3.0 GHz SP4T RF switch with improved body self-biasing technique in 130-nm SOI CMOS[J]. J. Semicond, 2020, 41(10): 102404. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/10/102404
|
A 0.5–3.0 GHz SP4T RF switch with improved body self-biasing technique in 130-nm SOI CMOS
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/10/102404
More Information
-
Abstract
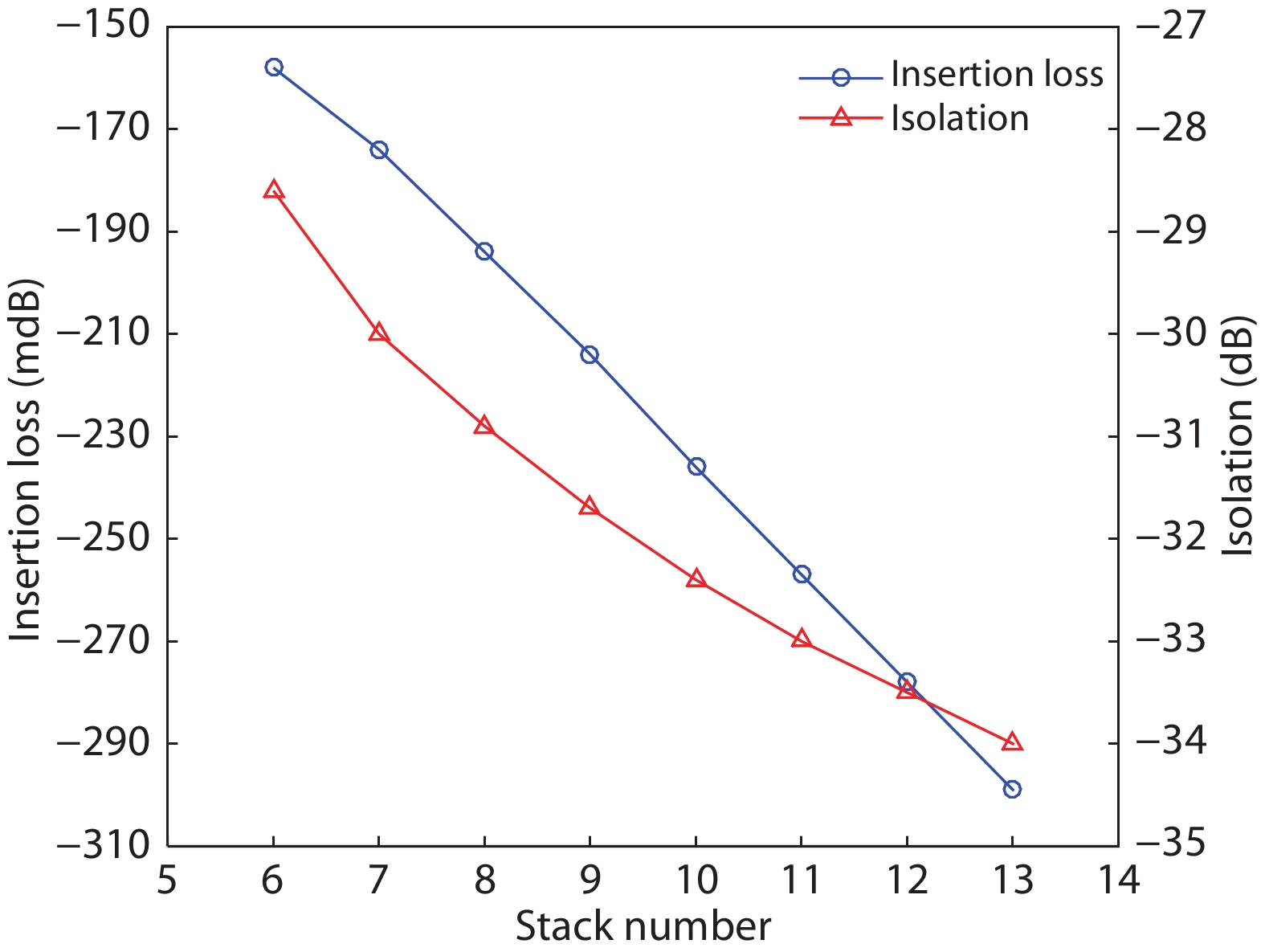
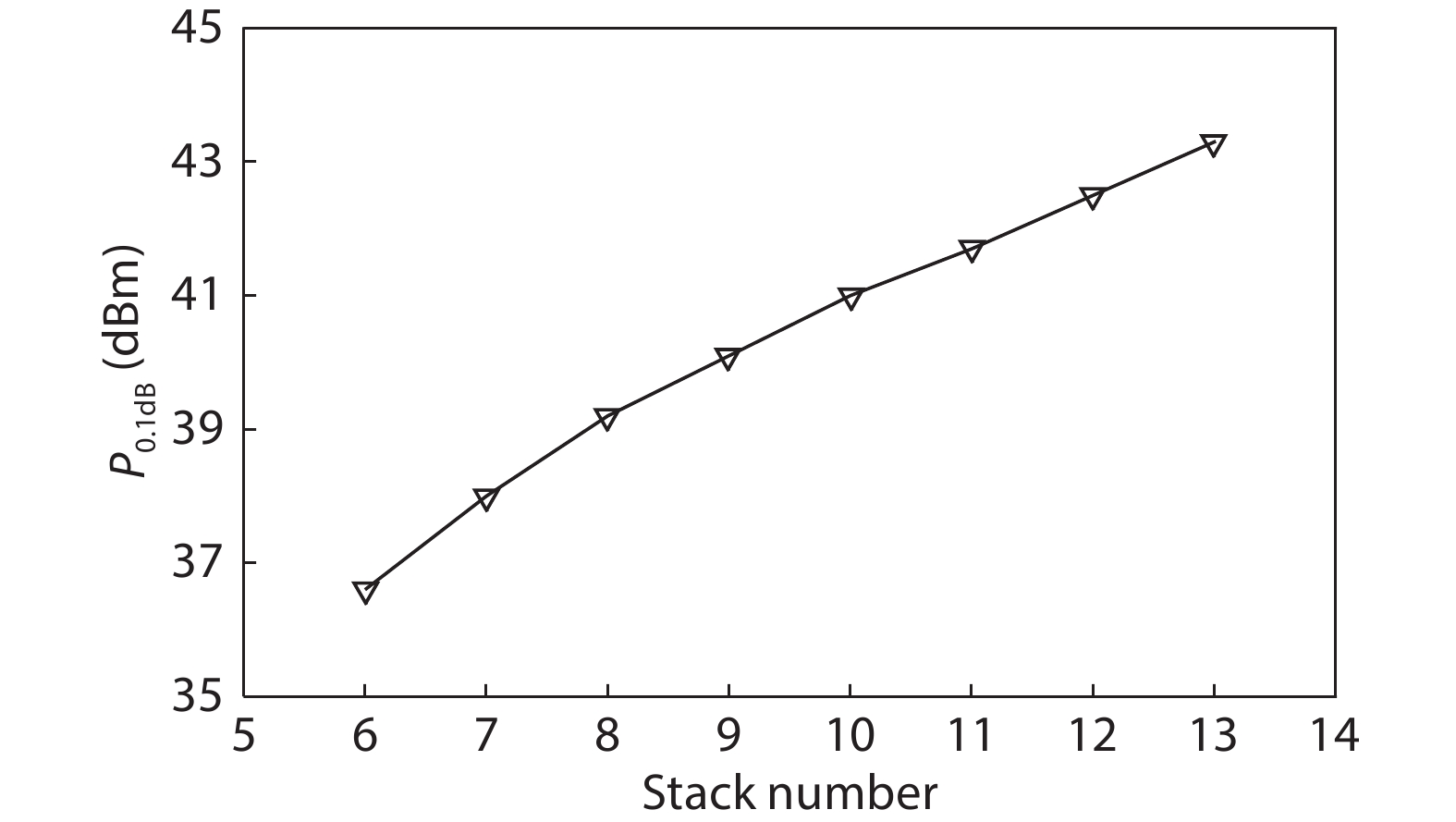
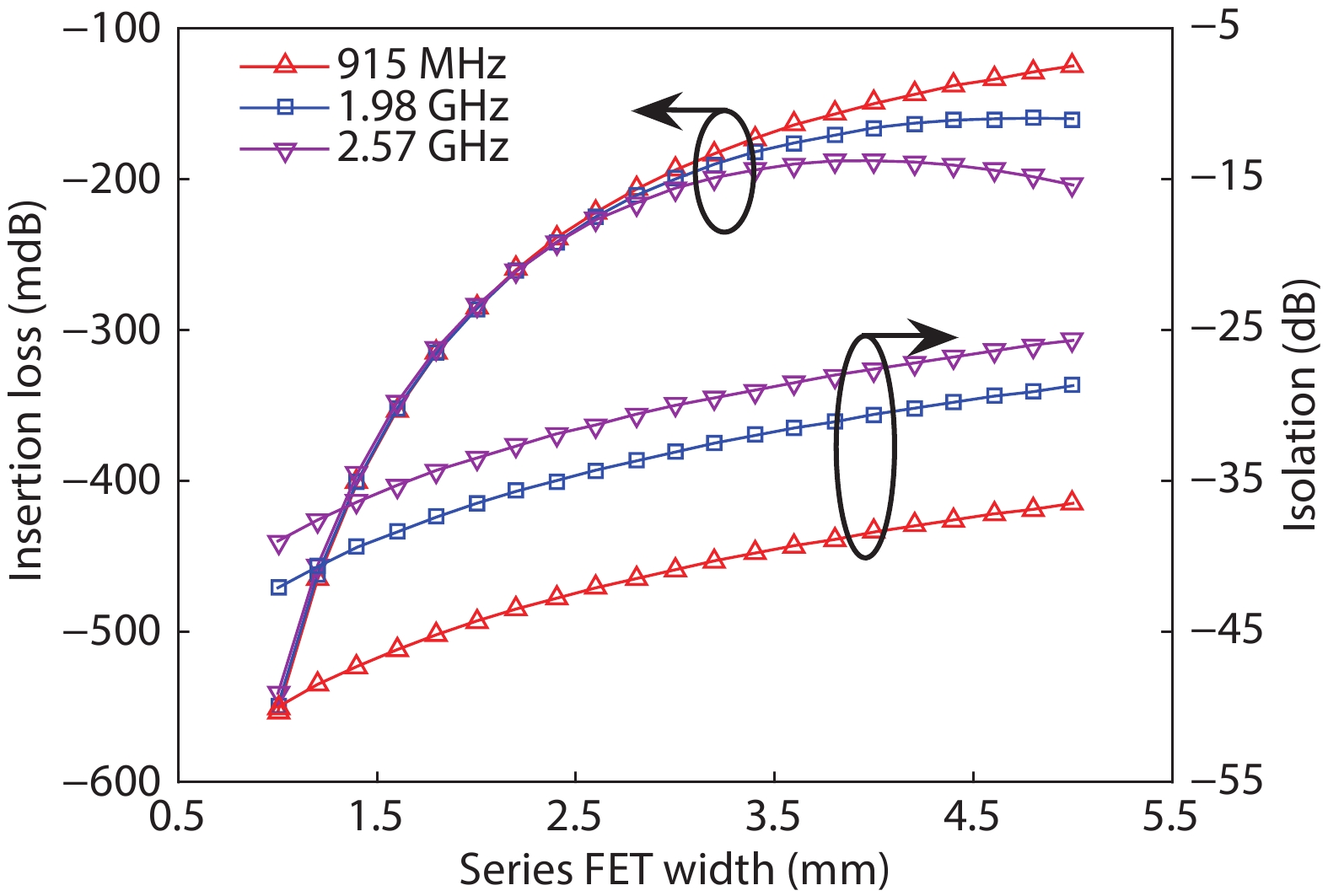
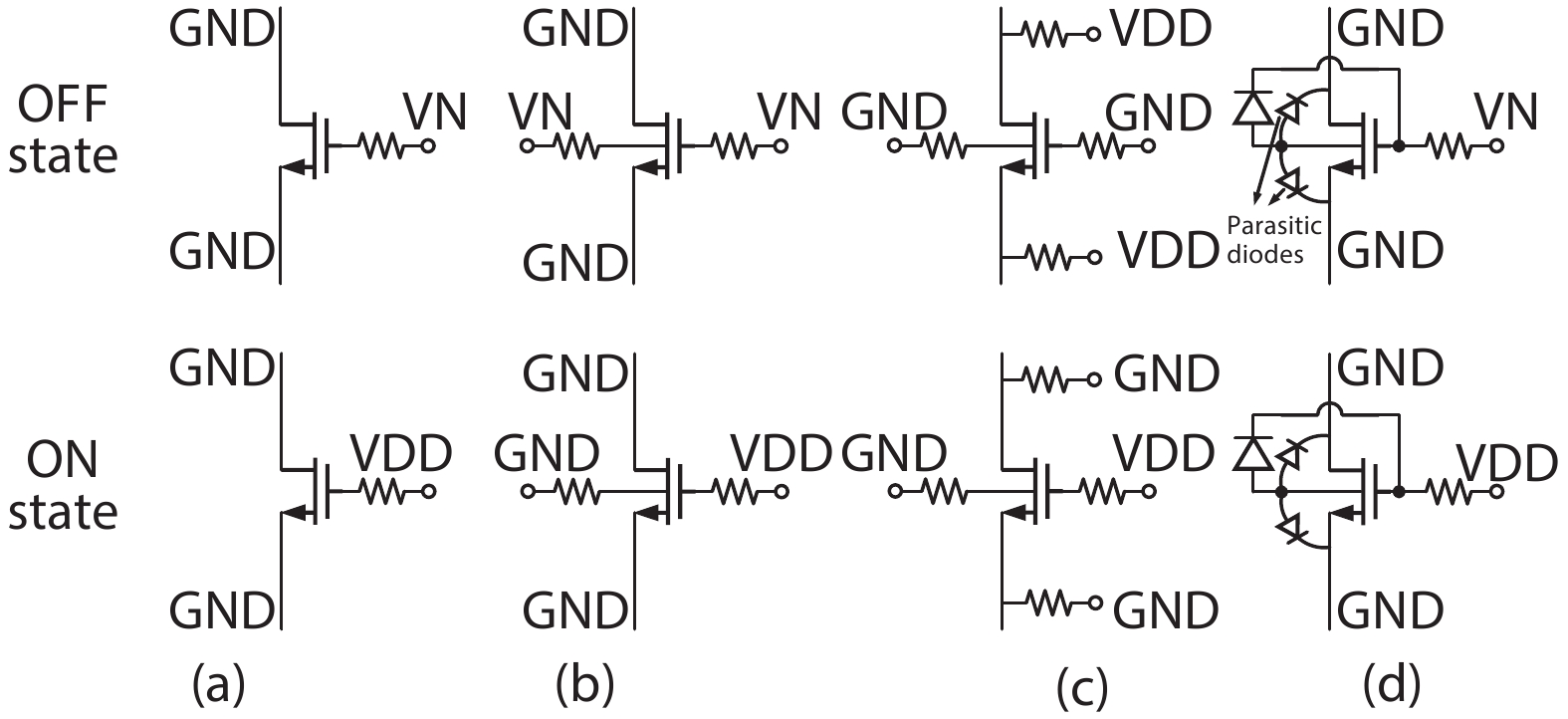
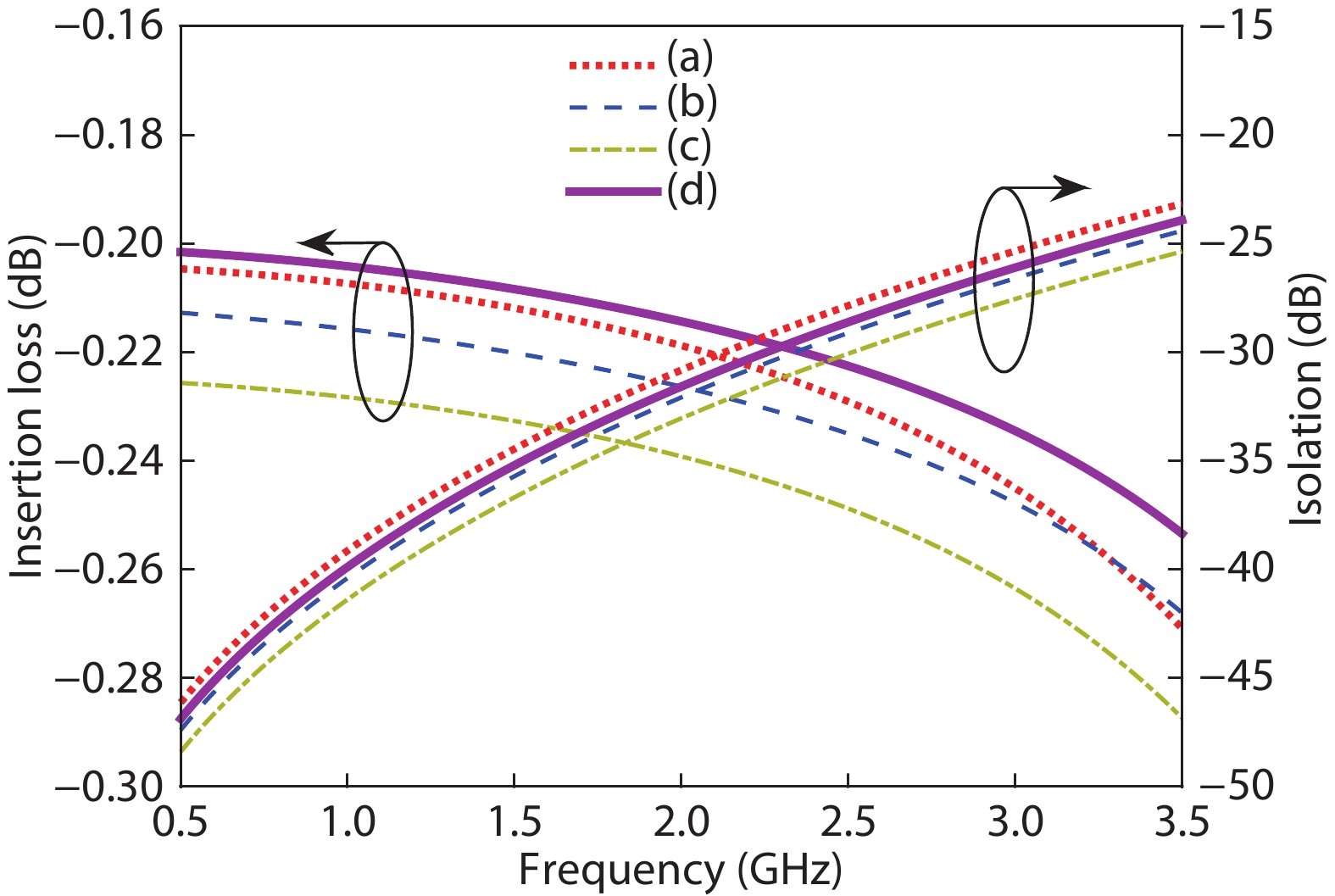
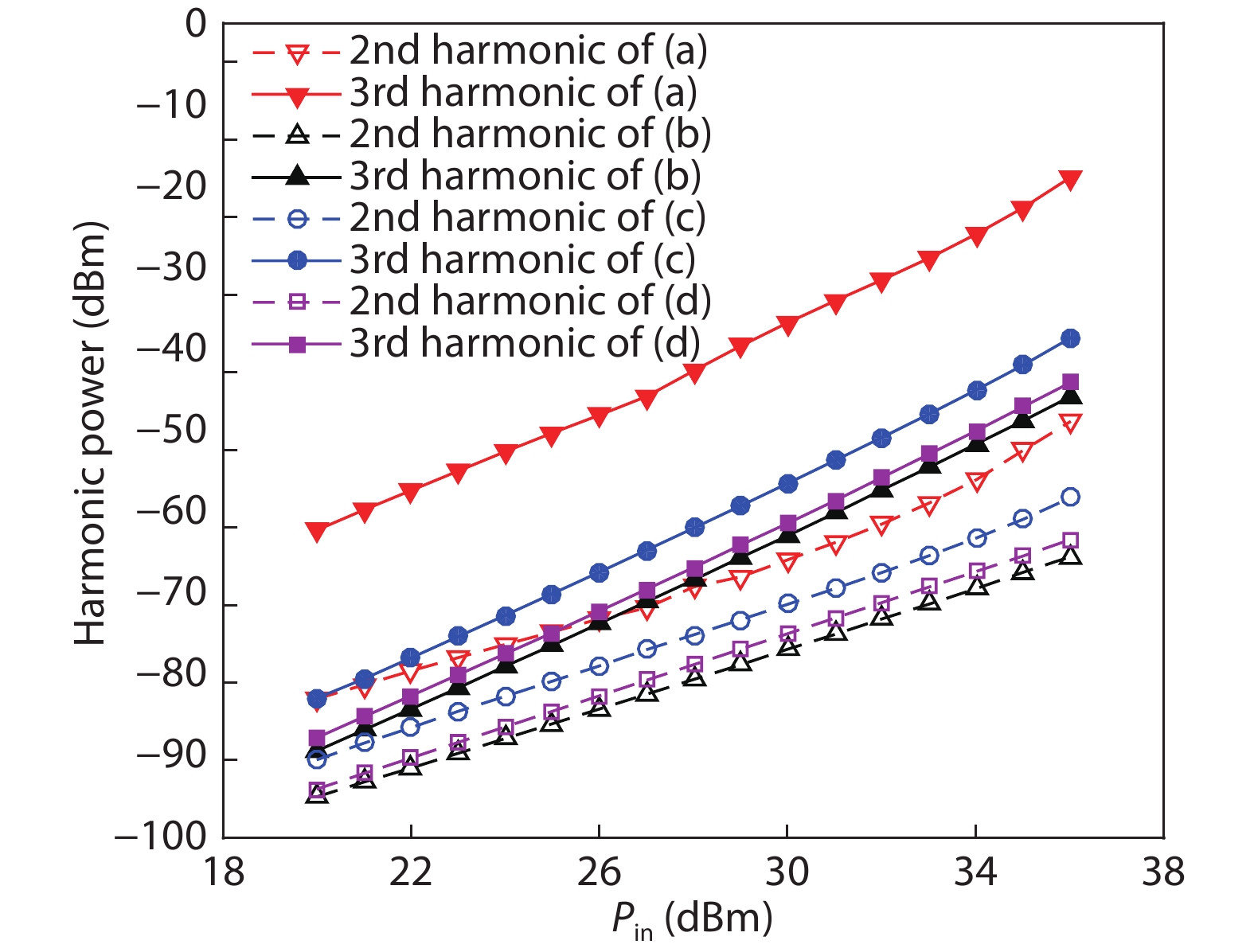
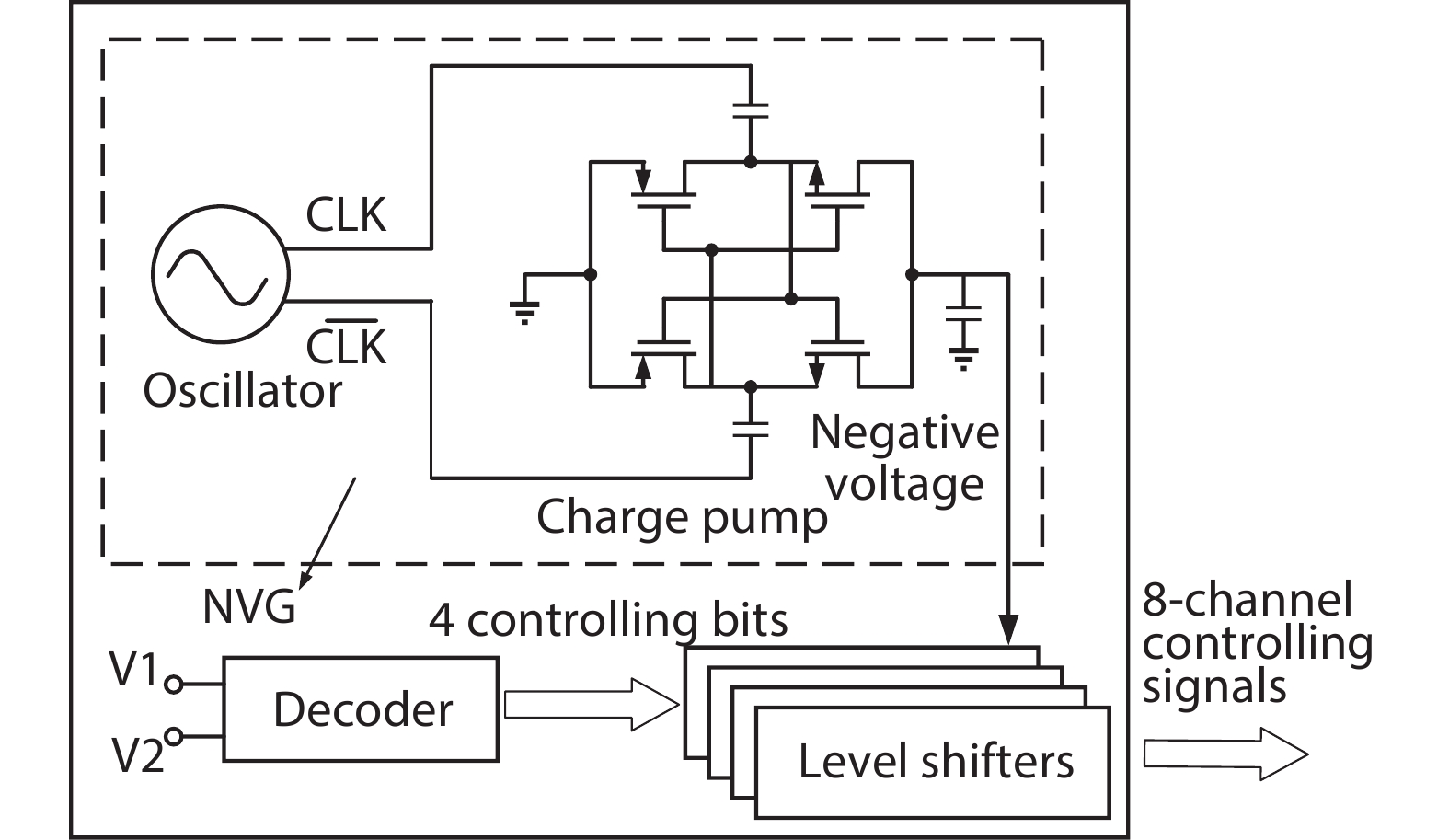
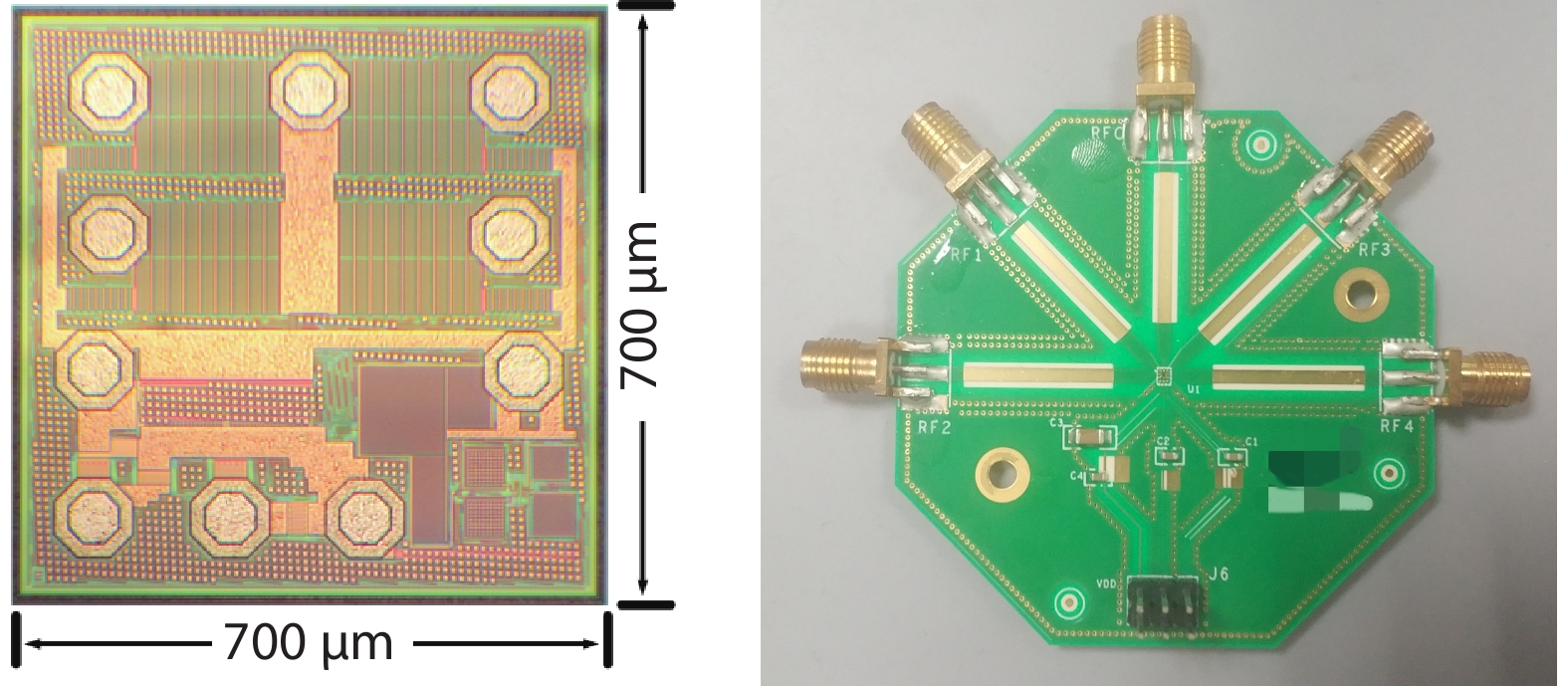
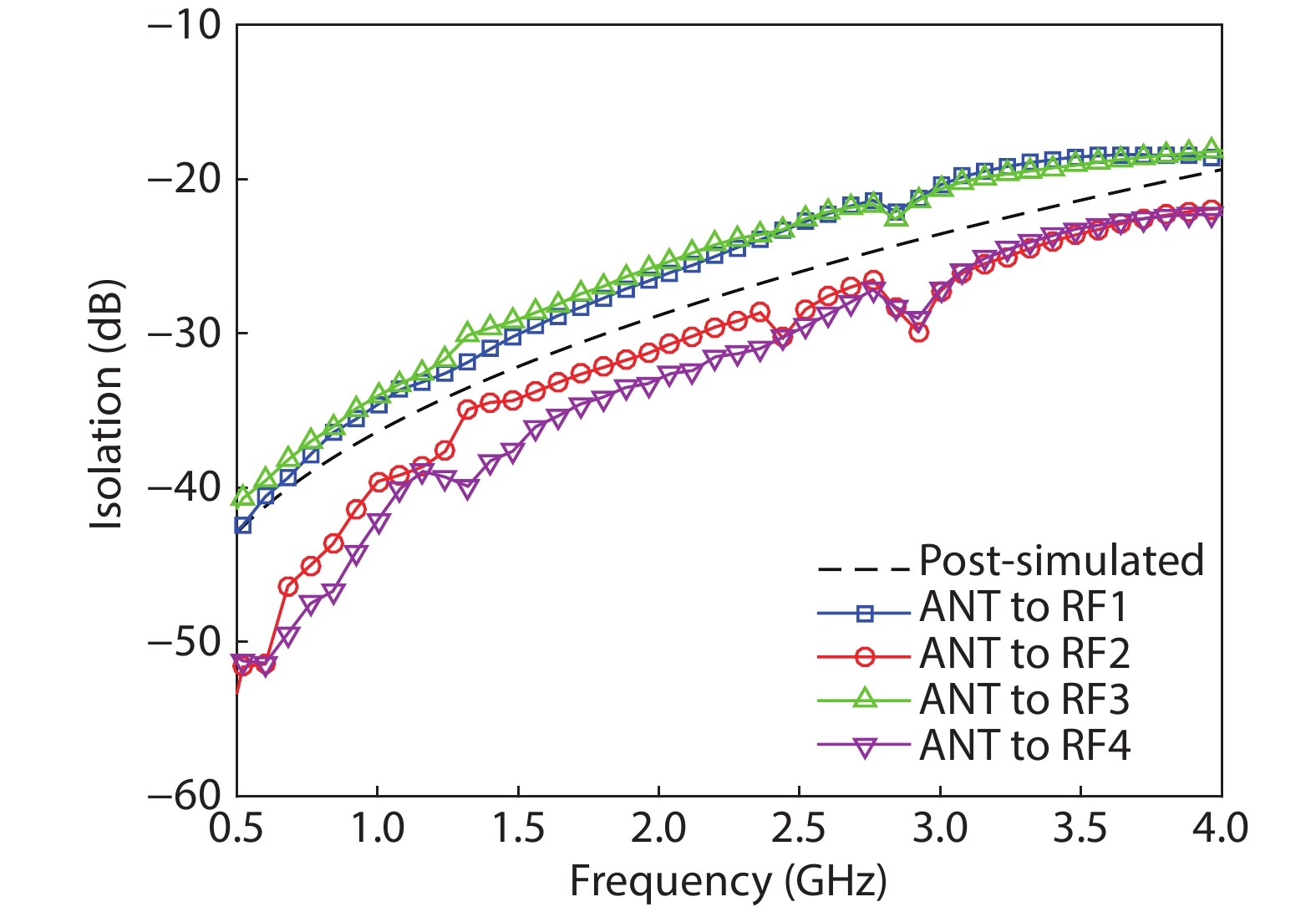
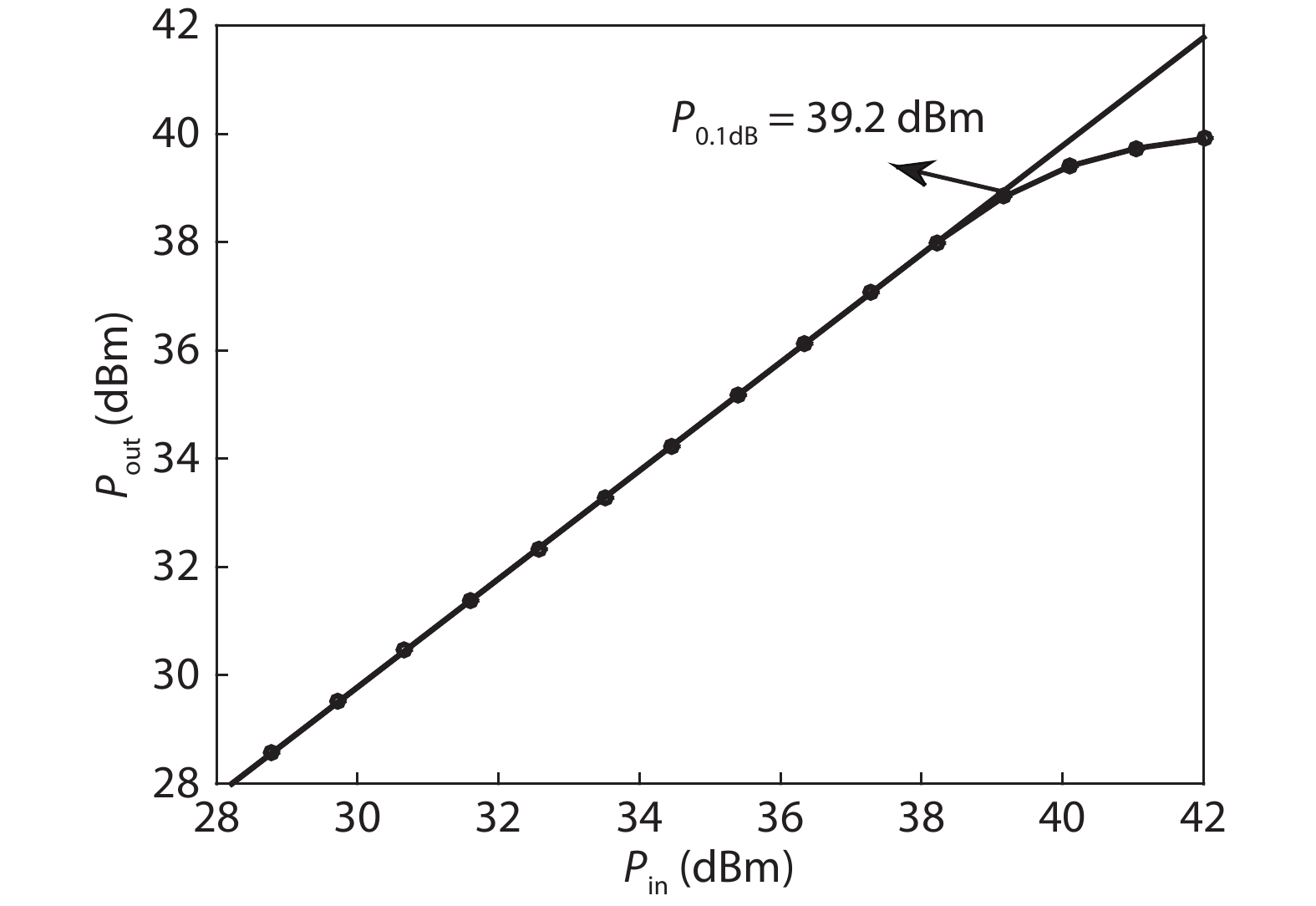
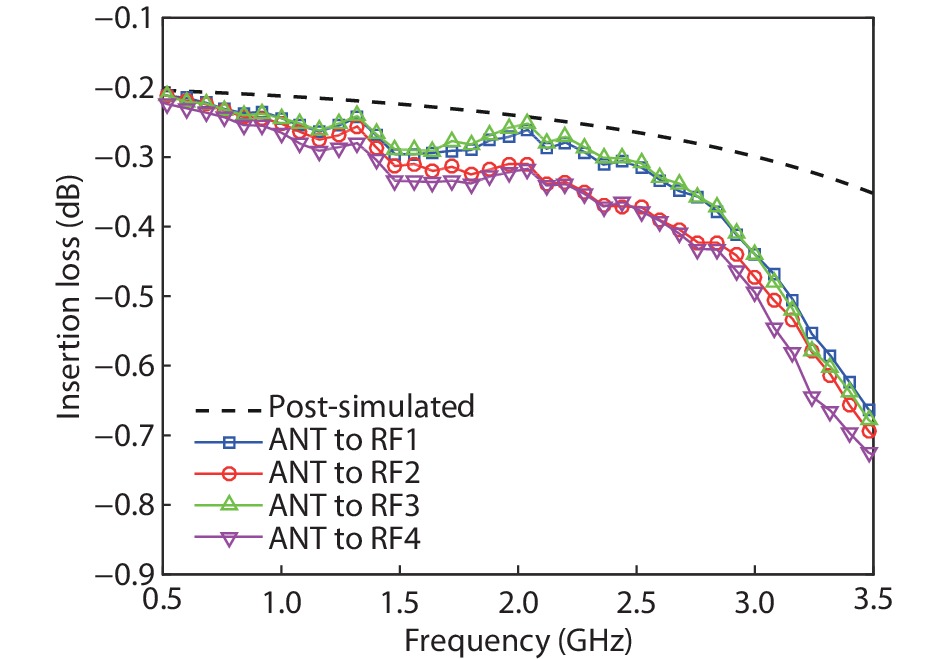
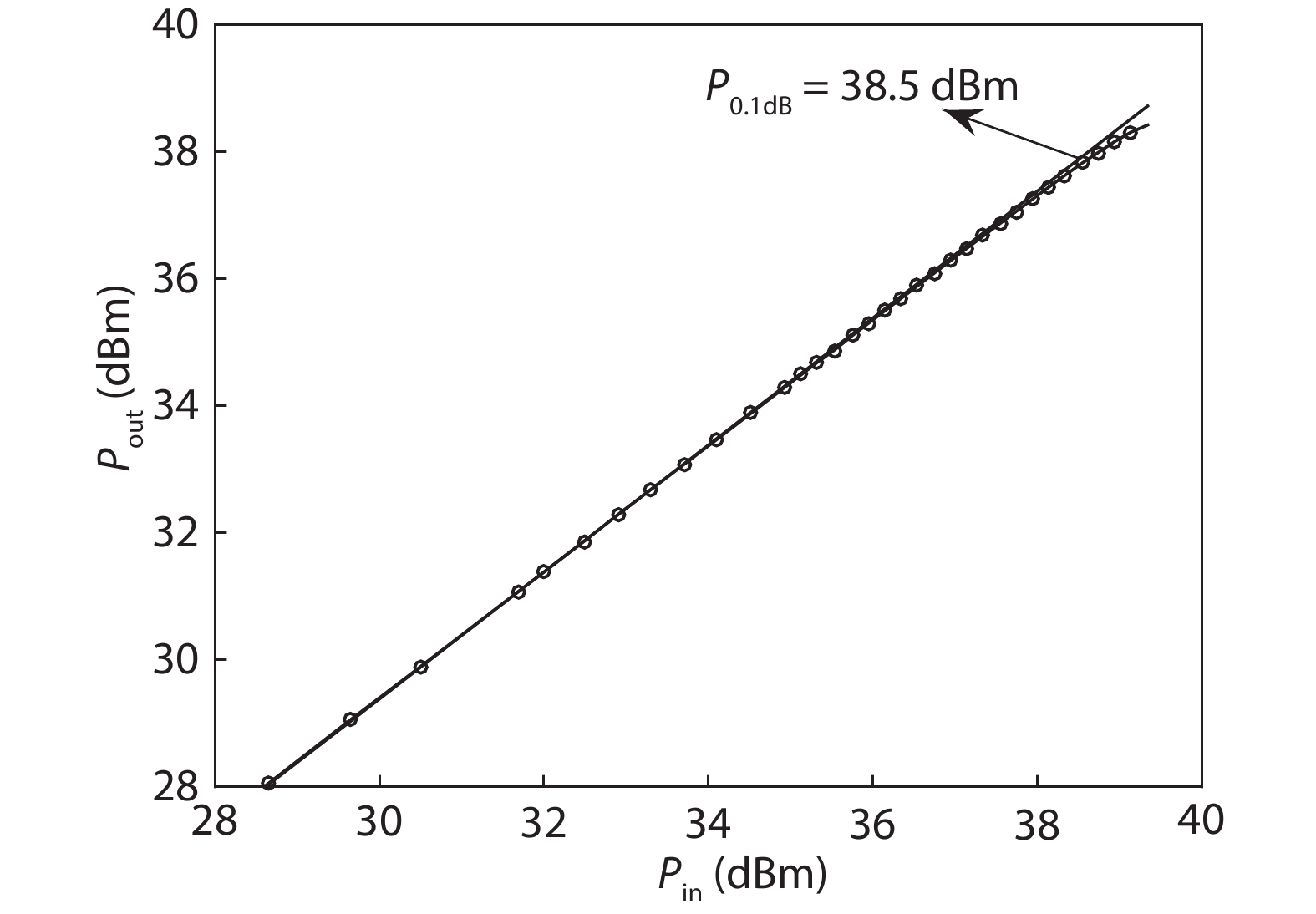
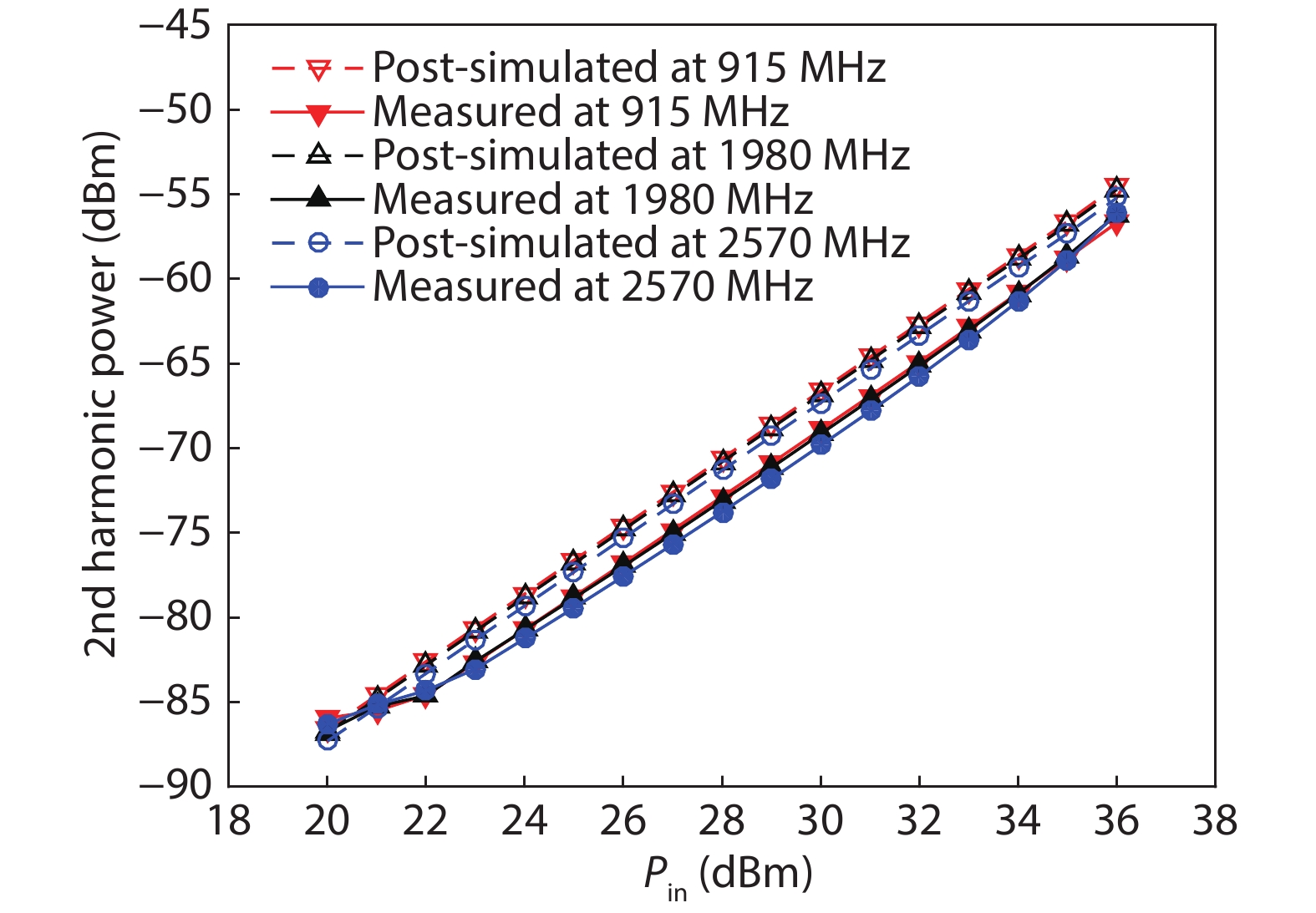
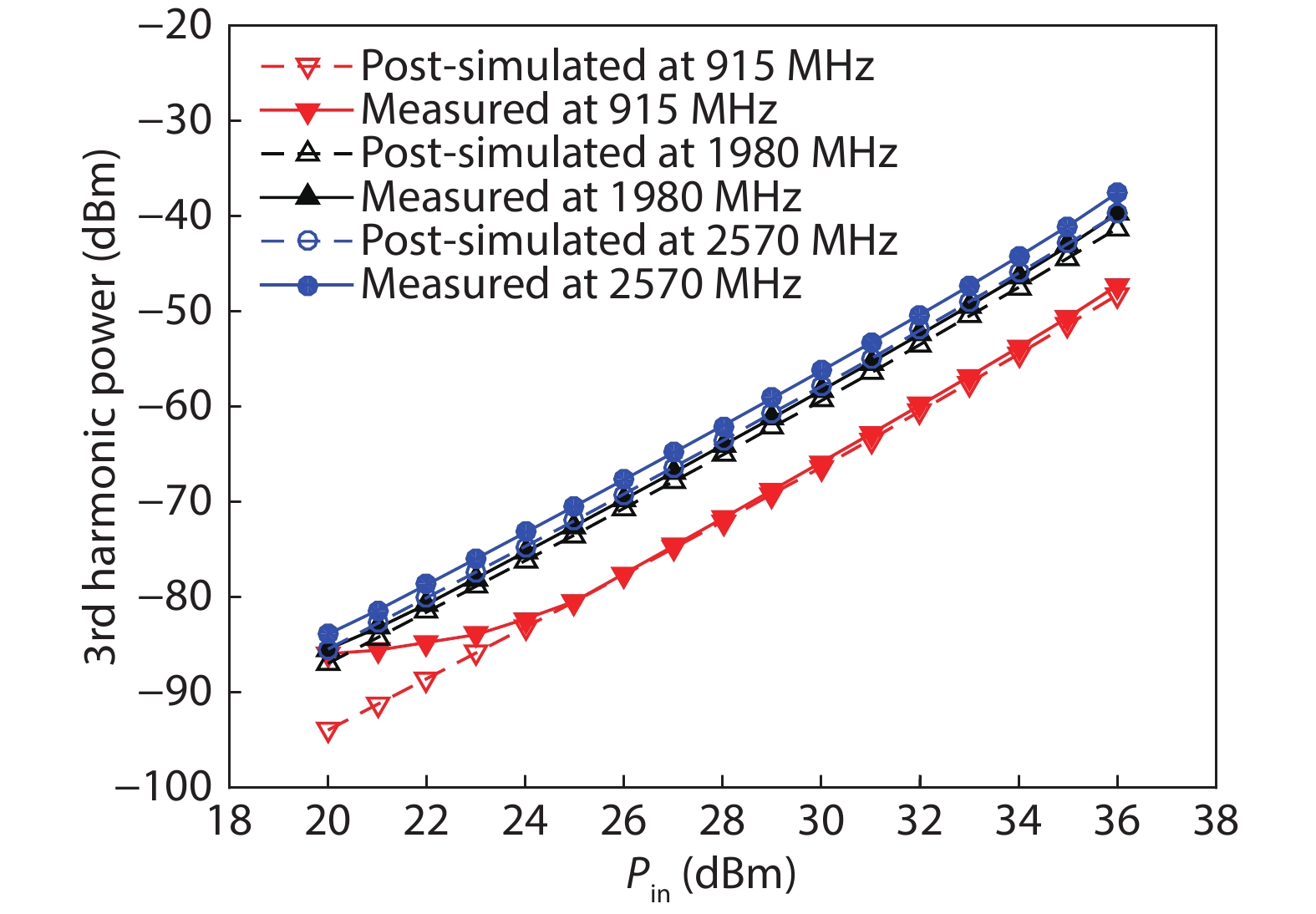
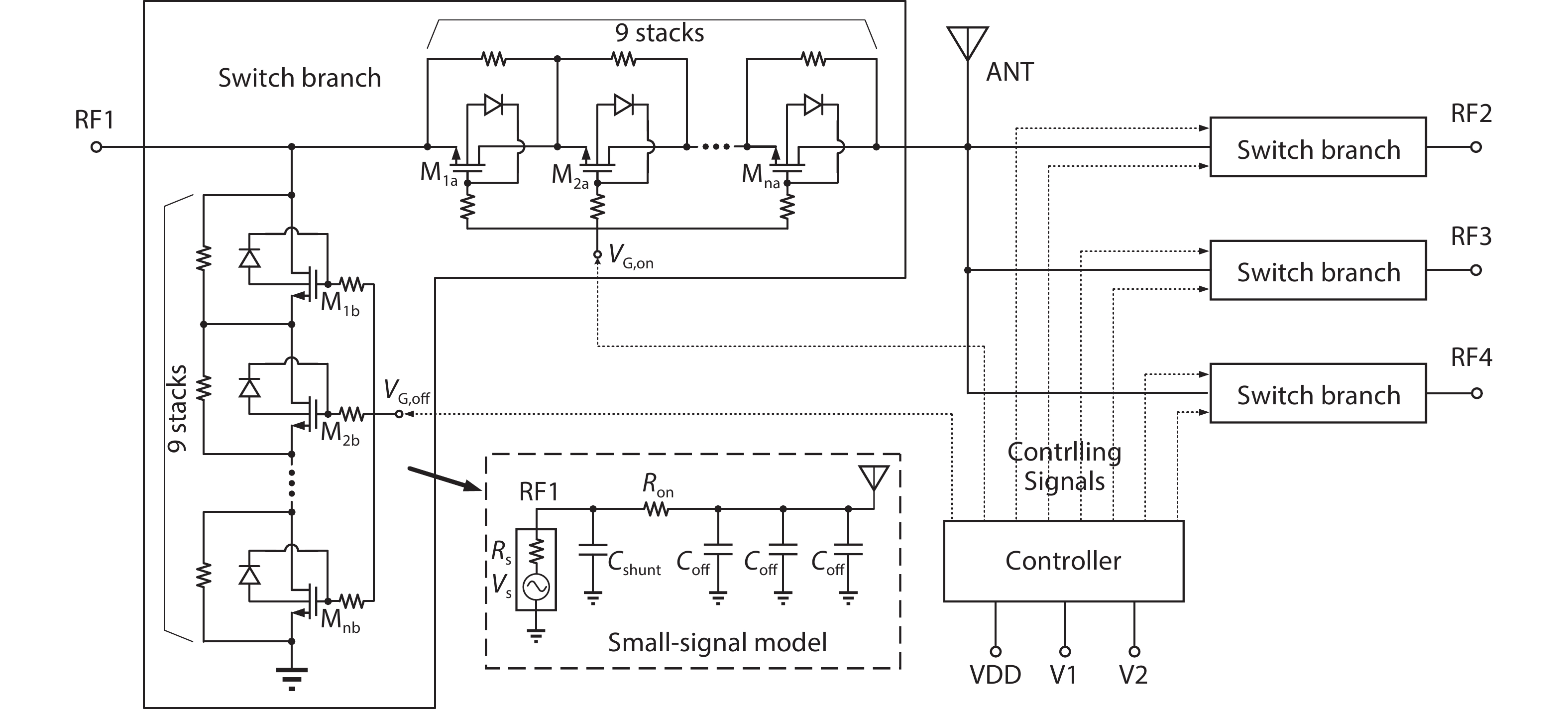
A single-pole four-throw (SP4T) RF switch with charge-pump-based controller is designed and implemented in a commercial 130-nm silicon-on-insulator (SOI) CMOS process. An improved body self-biasing technique based on diodes is utilized to simplify the controlling circuitry and improve the linearity. A multistack field-effect-transistor (FET) structure with body floating technique is employed to provide good power-handling capability. The proposed design demonstrates a measured input 0.1-dB compression point of 38.5 dBm at 1.9 GHz, an insertion loss of 0.27 dB/0.33 dB and an isolation of 35 dB/27 dB at 900 MHz/1.9 GHz, respectively. The overall chip area is only 0.49 mm2. This RF switch can be used in GSM/WCDMA/LTE front-end modules. -
References
[1] Yan X, Li Y, Chen Y, et al. A LNA-merged RF front-end with digitally assisted technique for gain flatness and input-match compensation. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process, 2019, 101, 219 doi: 10.1007/s10470-019-01539-2[2] Zhang H, Yan X, Shi J H, et al. A 0.5–5.6 GHz inductorless wideband LNA with local active feedback. 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Microsystems (ICICM), 2018, 164[3] Yan X, Chen C, Yang L, et al. A 0.1–1.1 GHz inductorless differential LNA with double gm -boosting and positive feedback. Analog Integr Circuits Signal Process, 2017, 93, 205 doi: 10.1007/s10470-017-1043-y[4] Huang C W P, Christainsen K, Nabokin S, et al. A highly integrated single chip 5–6 GHz front-end IC based on SiGe BiCMOS that enhances 802.11ac WLAN radio front-end designs. 2015 IEEE Radio Freq Integr Circuits Symp RFIC, 2015, 227[5] Im D, Kim B K, Im D K, et al. A stacked-FET linear SOI CMOS cellular antenna switch with an extremely low-power biasing strategy. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2015, 63, 1964 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2427801[6] Ahn M, Cha J, Cho C, et al. Ultra low loss and high linearity SPMT antenna switch using SOI CMOS process. 40th Eur Microw Conf, 2010, 652[7] Joshi A B, Lee S, Chen Y Y, et al. Optimized CMOS-SOI process for high performance RF switches. 2012 IEEE Int SOI Conf SOI, 2012, 1[8] Ben Ali K, Roda Neve C, Gharsallah A, et al. Ultrawide frequency range crosstalk into standard and trap-rich high resistivity silicon substrates. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2011, 58, 4258 doi: 10.1109/TED.2011.2170074[9] Wang X S, Yue C P. A dual-band SP6T t/r switch in SOI CMOS with 37-dBm P–0.1 dB for GSM/W-CDMA handsets. IEEE Trans Theory Technol, 2014, 62, 861 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2014.2308306[10] Ohnakado T, Yamakawa S, Murakami T, et al. 21.5 dBm power-handling 5 GHz transmit/receive CMOS switch realized by voltage division effect of stacked transistor configuration with depletion-layer-extended transistors (DETs). 2003 Symp VLSI Circuits Dig Tech Pap, 2003, 1152, 25[11] Ahn M, Lee C H, Kim B S, et al. A high-power CMOS switch using A novel adaptive voltage swing distribution method in multistack FETs. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2008, 56, 849 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2008.919047[12] Ahn M, Kim H W, Lee C H, et al. A 1.8-GHz 33-dBm P0.1-dB CMOS T/R switch using stacked FETs with feed-forward capacitors in a floated well structure. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2009, 57, 2661 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2009.2031928[13] Cui J, Chen L, Liu Y. Monolithic single-pole sixteen-throw T/R switch for next-generation front-end module. IEEE Microw Wirel Compon Lett, 2014, 24, 345 doi: 10.1109/LMWC.2014.2309082[14] Yeh M C, Tsai Z M, Liu R C, et al. Design and analysis for a miniature CMOS SPDT switch using body-floating technique to improve power performance. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech, 2006, 54, 31 doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2005.860894[15] Tinella C, Richard O, Cathelin A, et al. 0.13 μm CMOS SOI SP6T antenna switch for multi-standard handsets. 2006 Topical Meeting on Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems, 2006, 4[16] Zhang Z H, Huang L, Yu K, et al. A novel body self-biased technique for enhanced RF performance of a SP8T antenna switch in partially depleted CMOS-SOI technology. 2014 12th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), 2014, 1[17] Xu H F, Kenneth K O. A 31.3-dBm bulk CMOS T/R switch using stacked transistors with sub-design-rule channel length in floated p-wells. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42, 2528 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2007.907201[18] Tseng Y C, Huang W M, Monk D J, et al. AC floating body effects and the resultant analog circuit issues in submicron floating body and body-grounded SOI MOSFET's. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1999, 46, 1685 doi: 10.1109/16.777157[19] Cha J, Ahn M, Cho C, et al. Analysis and design techniques of CMOS charge-pump-based radio-frequency antenna-switch controllers. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, 2009, 56, 1053 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2009.2016129[20] Zhu H W, Li Q L, Sun H, et al. Ultra low loss and high linearity RF switch using 130 nm SOI CMOS process. 2017 IEEE 12th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), 2017, 698[21] Guan H, Sun H, Bao J L, et al. High-performance RF switch in 0.13 μm RF SOI process. J Semicond, 2019, 40, 022401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/40/2/022401 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: