| Citation: |
Jingjing Zhang, Jin Yang, Liangzhong Lin, JiaJi Zhu. An antiferromagnetic two-dimensional material: Chromium diiodides monolayer[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2020, 41(12): 122502. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/12/122502
****
J J Zhang, J Yang, L Z Lin, J J Zhu, An antiferromagnetic two-dimensional material: Chromium diiodides monolayer[J]. J. Semicond., 2020, 41(12): 122502. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/12/122502.
|
An antiferromagnetic two-dimensional material: Chromium diiodides monolayer
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/41/12/122502
More Information
-
Abstract
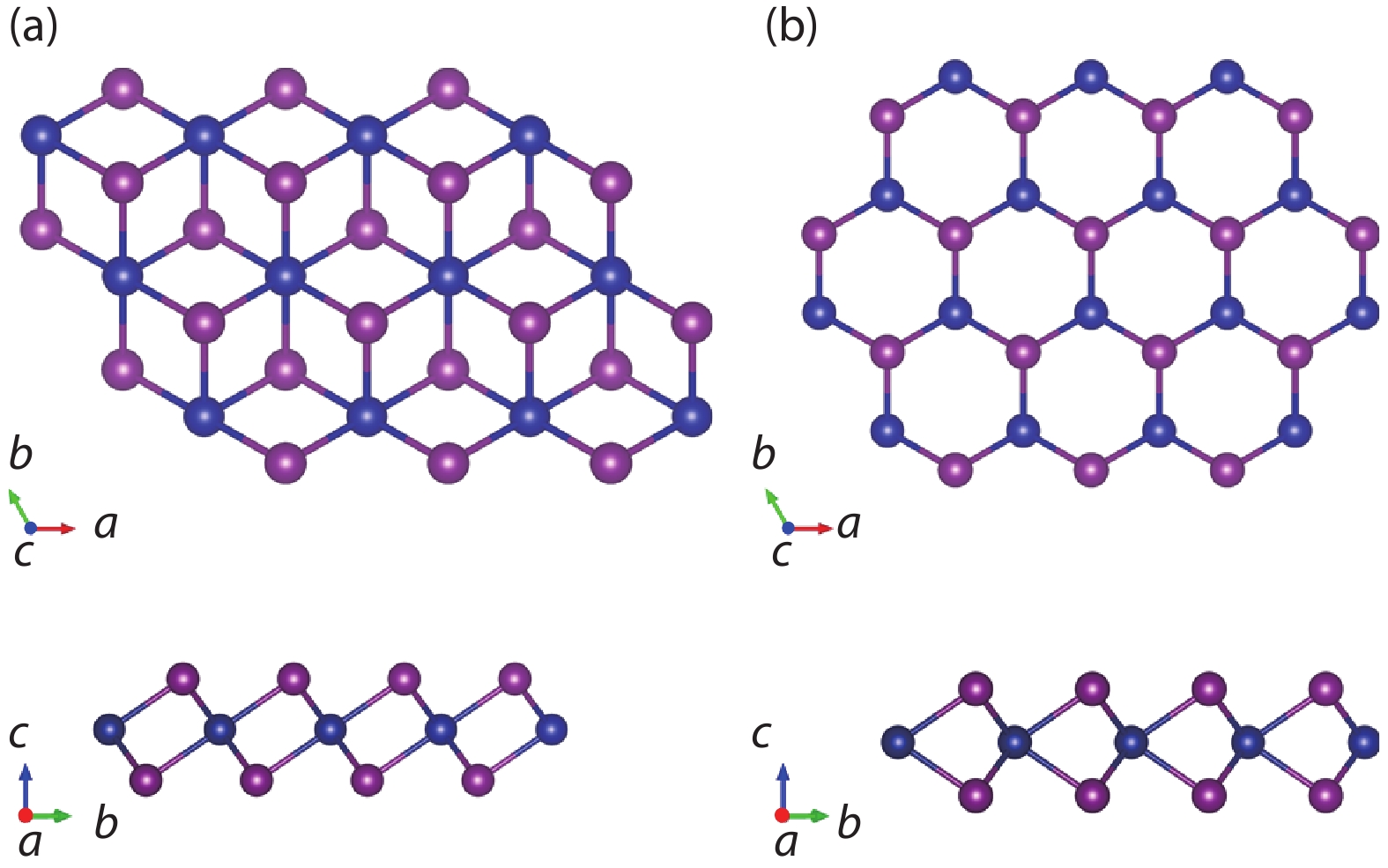
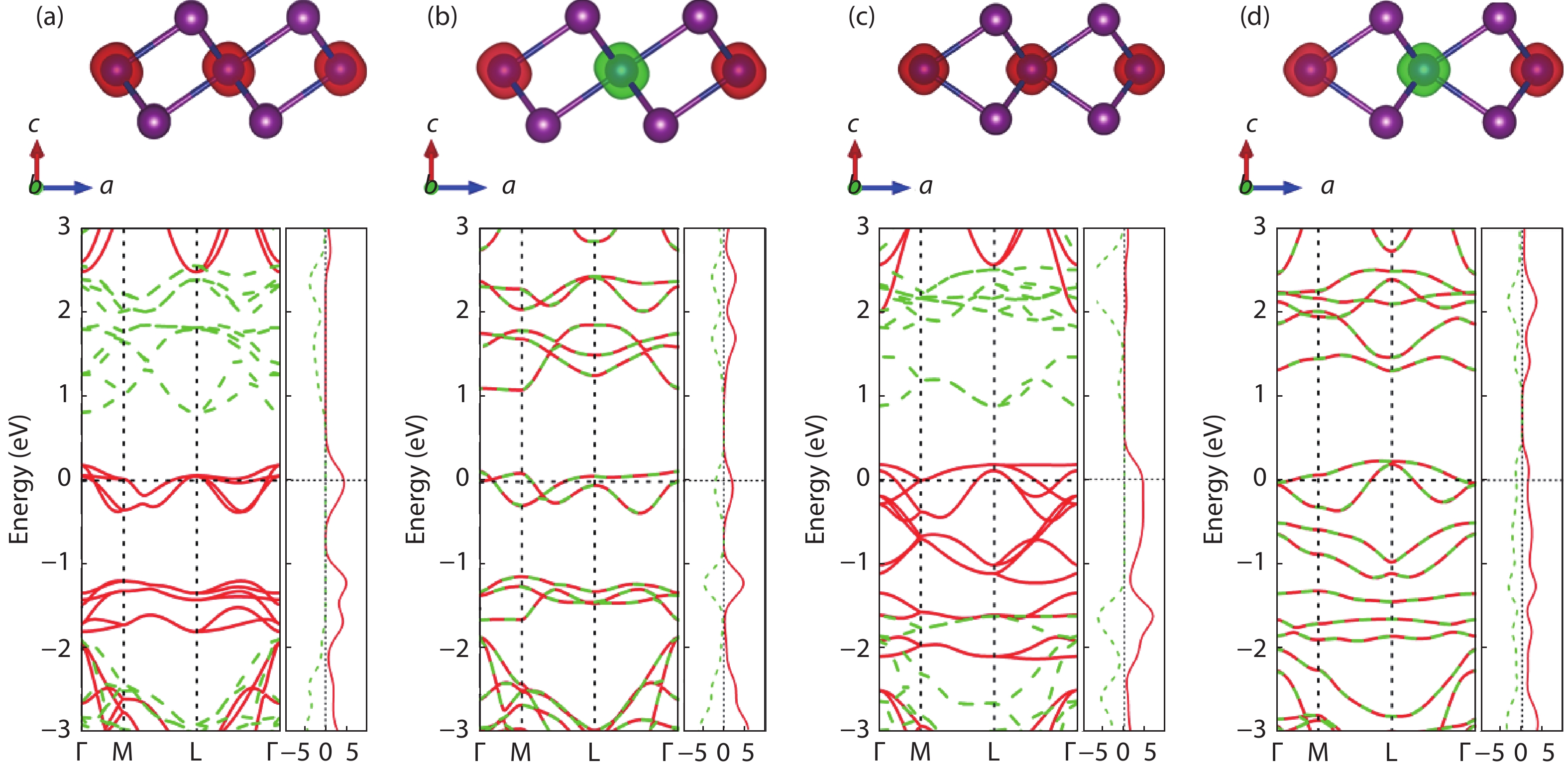
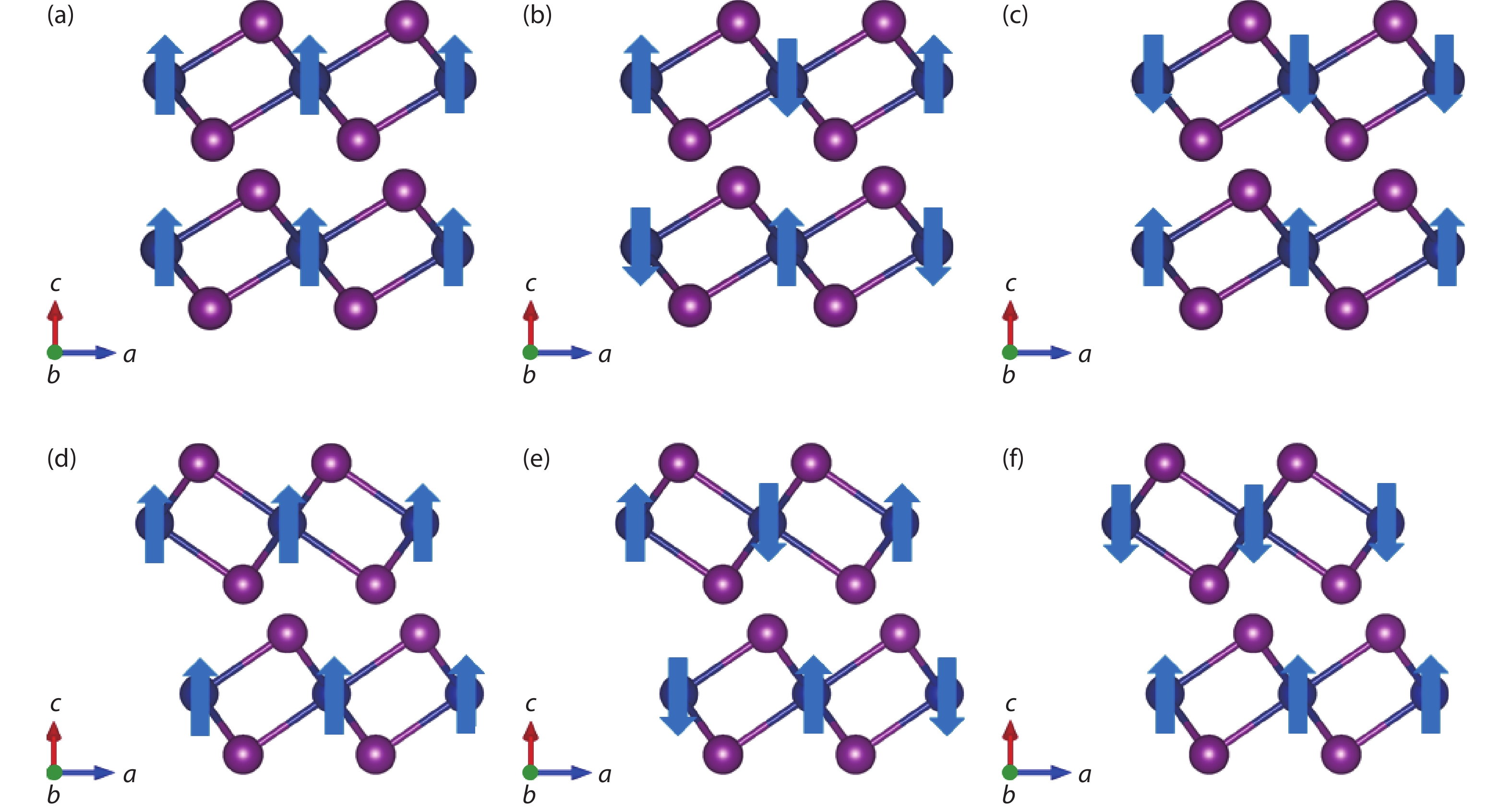
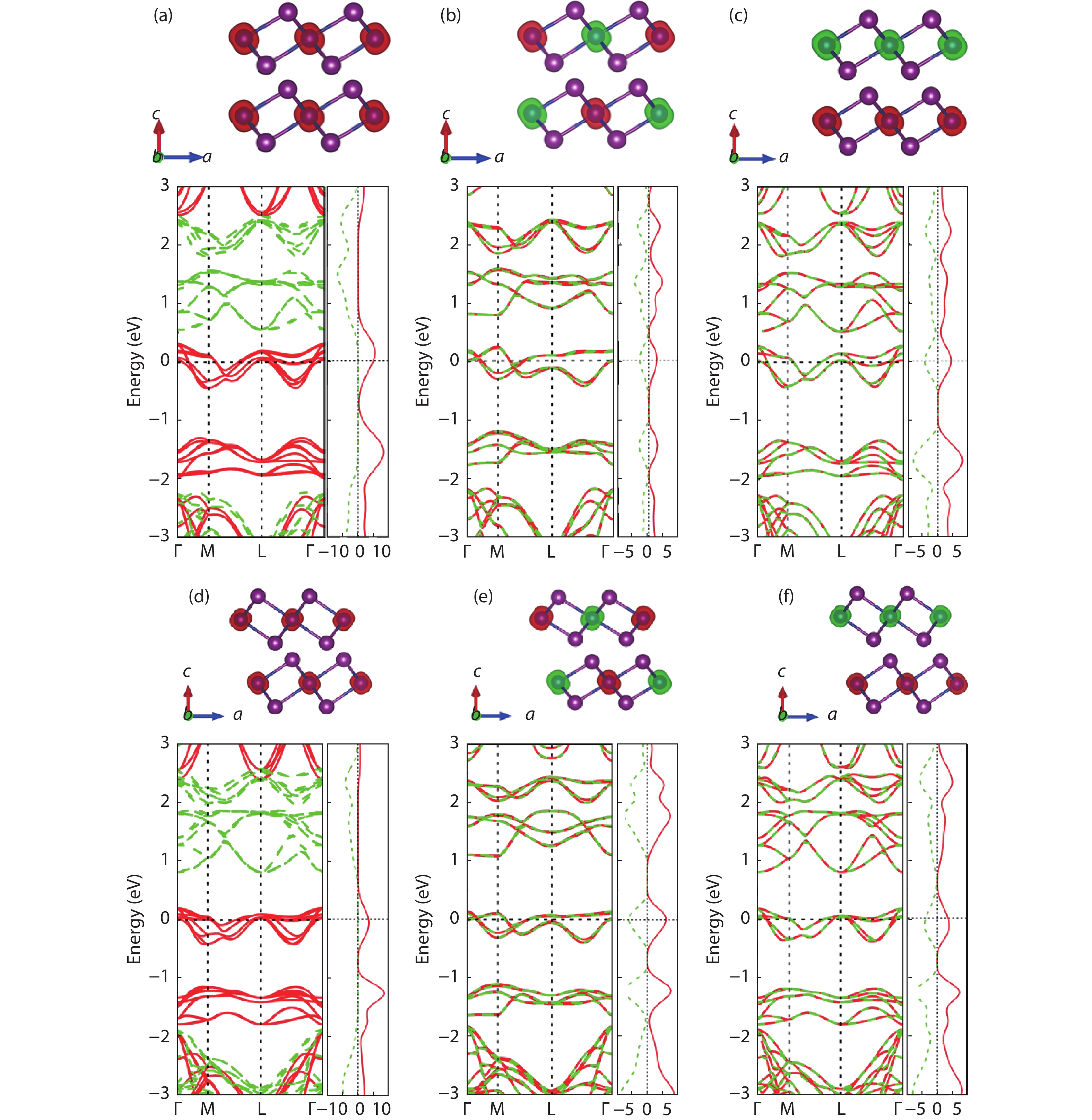
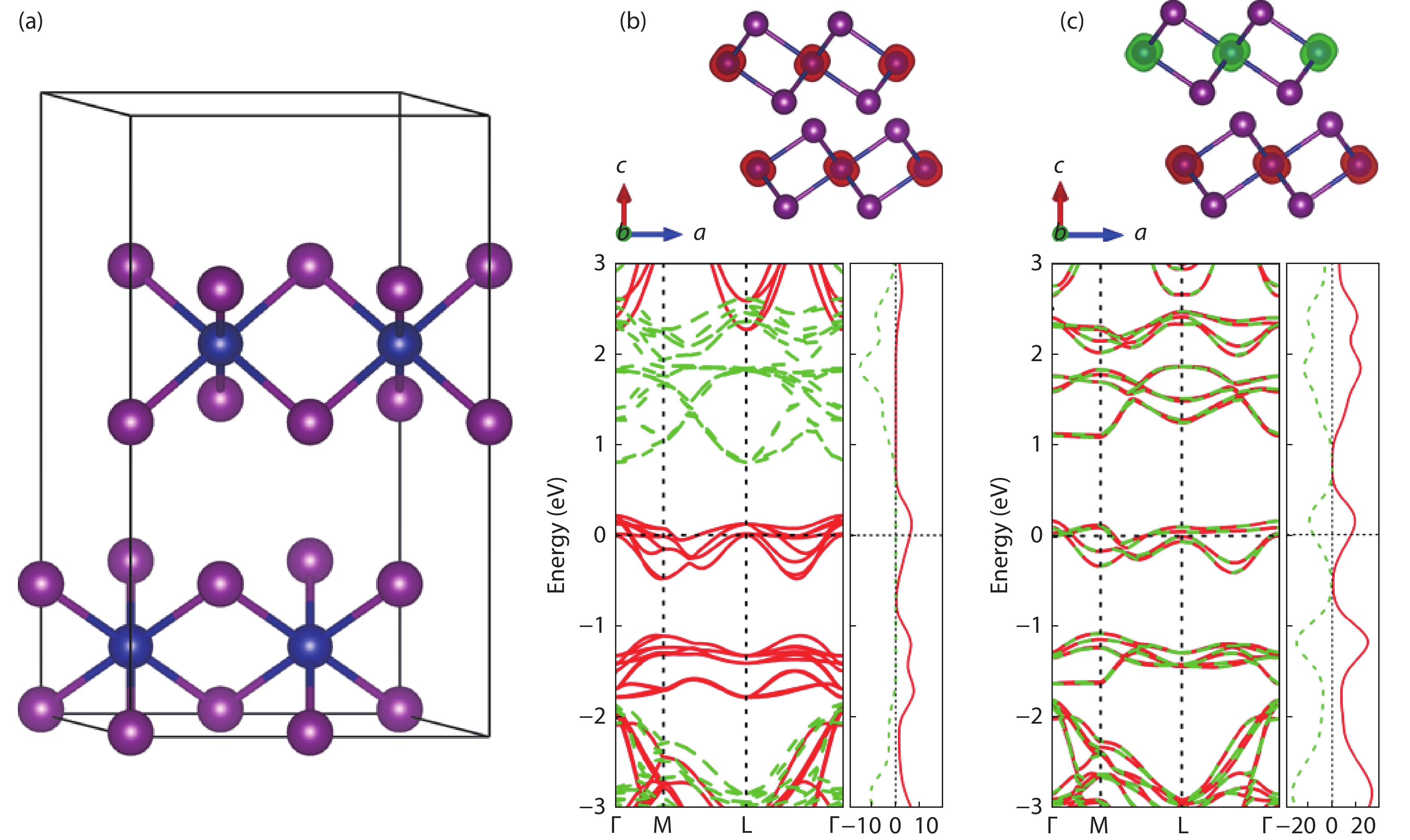
The two-dimensional (2D) ferromagnetic materials and the related van der Waals homostructures have attracted considerable interest, while the 2D antiferromagnetic material has not yet been reported. Based on first-principles calculations, we investigate both electronic structures and magnetic orderings of bulk and monolayer of chromium diiodides (CrI2). We demonstrate a counter-intuitive fact that the ground state of the free-standing monolayer of CrI2 is antiferromagnetic though the bulk possesses macroscopic ferromagnetic ordering. The interlayer interaction remains antiferromagnetic up to few-layer scenarios. The unique feature of CrI2 makes it an ideal workbench to investigate the relation between magnetic couplings and interlayer van der Waals interactions, and may offer an opportunity to 2D antiferromagnetic spintronic devices. -
References
[1] Tokmachev A M, Averyanov D V, Parfenov O E, et al. Emerging two-dimensional ferromagnetism in silicene materials. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 1672 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04012-2[2] Shi X Y, Huang Z J, Huttula M, et al. Introducing magnetism into 2D nonmagnetic inorganic layered crystals: A brief review from first-principles aspects. Crystals, 2018, 8, 24 doi: 10.3390/cryst8010024[3] Tao P, Guo H H, Yang T, et al. Strain-induced magnetism in MoS2 monolayer with defects. J Appl Phys, 2014, 115, 054305 doi: 10.1063/1.4864015[4] Kochat V, Apte A, Hachtel J A, et al. Re doping in 2D transition metal dichalcogenides as a new route to tailor structural phases and induced magnetism. Adv Mater, 2017, 29, 1703754 doi: 10.1002/adma.201703754[5] Hallal A, Ibrahim F, Yang H X, et al. Tailoring magnetic insulator proximity effects in graphene: First-principles calculations. 2D Mater, 2017, 4, 025074 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/aa6663[6] Mermin N D, Wagner H. Absence of ferromagnetism or antiferromagnetism in one- or two-dimensional isotropic Heisenberg models. Phys Rev Lett, 1966, 17, 1133 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.17.1133[7] Miao N H, Xu B, Zhu L G, et al. 2D intrinsic ferromagnets from van der Waals antiferromagnets. J Am Chem Soc, 2018, 140, 2417 doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b12976[8] Lin X, Yang W, Wang K L, et al. Two-dimensional spintronics for low-power electronics. Nat Electron, 2019, 2, 274 doi: 10.1038/s41928-019-0273-7[9] Huang B, Clark G, Navarro-Moratalla E, et al. Layer-dependent ferromagnetism in a van der Waals crystal down to the monolayer limit. Nature, 2017, 546, 270 doi: 10.1038/nature22391[10] Gong C, Li L, Li Z L, et al. Discovery of intrinsic ferromagnetism in two-dimensional van der Waals crystals. Nature, 2017, 546, 265 doi: 10.1038/nature22060[11] Sheng X L, Nikolić B K. Monolayer of the 5d transition metal trichloride OsCl3: A playground for two-dimensional magnetism, room-temperature quantum anomalous Hall effect, and topological phase transitions. Phys Rev B, 2017, 95, 201402 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.95.201402[12] Kuo C T, Neumann M, Balamurugan K, et al. Exfoliation and Raman spectroscopic fingerprint of few-layer NiPS3 van der waals crystals. Sci Rep, 2016, 6, 20904 doi: 10.1038/srep20904[13] Zhu W, Gan W, Muhammad Z, et al. Exfoliation of ultrathin FePS3 layers as a promising electrocatalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Chem Commun, 2018, 54, 4481 doi: 10.1039/C8CC01076E[14] Li X X, Yang J L. CrXTe3 (X = Si, Ge) nanosheets: Two dimensional intrinsic ferromagnetic semiconductors. J Mater Chem C, 2014, 2, 7071 doi: 10.1039/C4TC01193G[15] Zhuang H L, Kent P R C, Hennig R G. Strong anisotropy and magnetostriction in the two-dimensional Stoner ferromagnet Fe3GeTe2. Phys Rev B, 2016, 93, 134407 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.93.134407[16] Yadav C S, Rastogi A K. Transport and magnetic properties of FexVSe2 (x = 0–0.33). J Phys: Condens Matter, 2008, 20, 465219 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/20/46/465219[17] Sun J J, Li C, Chen D, et al. Controlled synthesis of ferromagnetic MnSex particles. Chin Phys B, 2016, 25, 107405 doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/25/10/107405[18] Lado J L, Fernández-Rossier J. On the origin of magnetic anisotropy in two dimensional CrI3. 2D Mater, 2017, 4, 035002 doi: 10.1088/2053-1583/aa75ed[19] Abramchuk M, Jaszewski S, Metz K R, et al. Controlling magnetic and optical properties of the van der waals crystal CrCl3− xBrx via mixed halide chemistry. Adv Mater, 2018, 30, 1801325 doi: 10.1002/adma.201801325[20] Gibertini M, Koperski M, Morpurgo A F, et al. Magnetic 2D materials and heterostructures. Nat Nanotechnol, 2019, 14, 408 doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0438-6[21] Gong S J, Gong C, Sun Y Y, et al. Electrically induced 2D half-metallic antiferromagnets and spin field effect transistors. PNAS, 2018, 115, 8511 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1715465115[22] Hohenberg P, Kohn W. Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys Rev, 1964, 136, b864 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.136.B864[23] Kohn W, Sham L J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys Rev, 1965, 140, a1133 doi: 10.1103/PhysRev.140.A1133[24] Kresse G, Hafner J. Ab initio molecular-dynamics simulation of the liquid-metal-amorphous-semiconductor transition in germanium. Phys Rev B, 1994, 49, 14251 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.49.14251[25] Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput Mater Sci, 1996, 6, 15 doi: 10.1016/0927-0256(96)00008-0[26] Kresse G, Furthmüller J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54, 11169 doi: 10.1103/physrevb.54.11169[27] Blöchl P E. Projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B, 1994, 50, 17953 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.50.17953[28] Kresse G, Joubert D. From ultrasoft pseudopotentials to the projector augmented-wave method. Phys Rev B, 1999, 59, 1758 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.59.1758 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: