| Citation: |
Madhavi Sharad Darekar, Praveen Beekanahalli Mokshanatha. Hyperfine splitting and ferromagnetism in CdS : Mn nanoparticles for optoelectronic device applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2023, 44(12): 122502. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/12/122502
****
M S Darekar, P Beekanahalli Mokshanatha. Hyperfine splitting and ferromagnetism in CdS : Mn nanoparticles for optoelectronic device applications[J]. J. Semicond, 2023, 44(12): 122502. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/12/122502
|
Hyperfine splitting and ferromagnetism in CdS : Mn nanoparticles for optoelectronic device applications
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/12/122502
More Information
-
Abstract
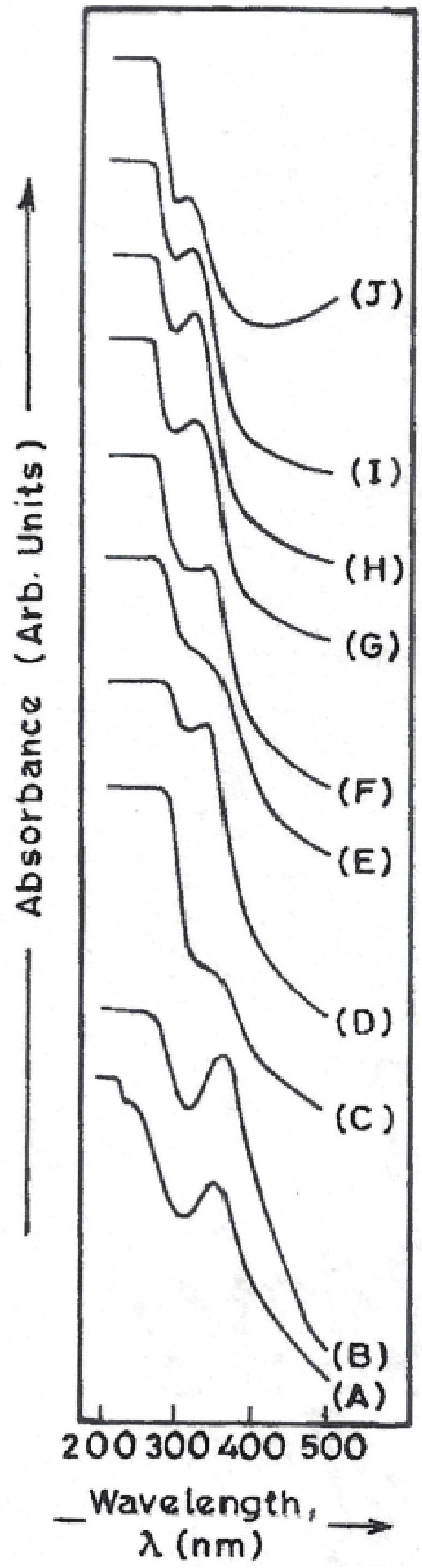
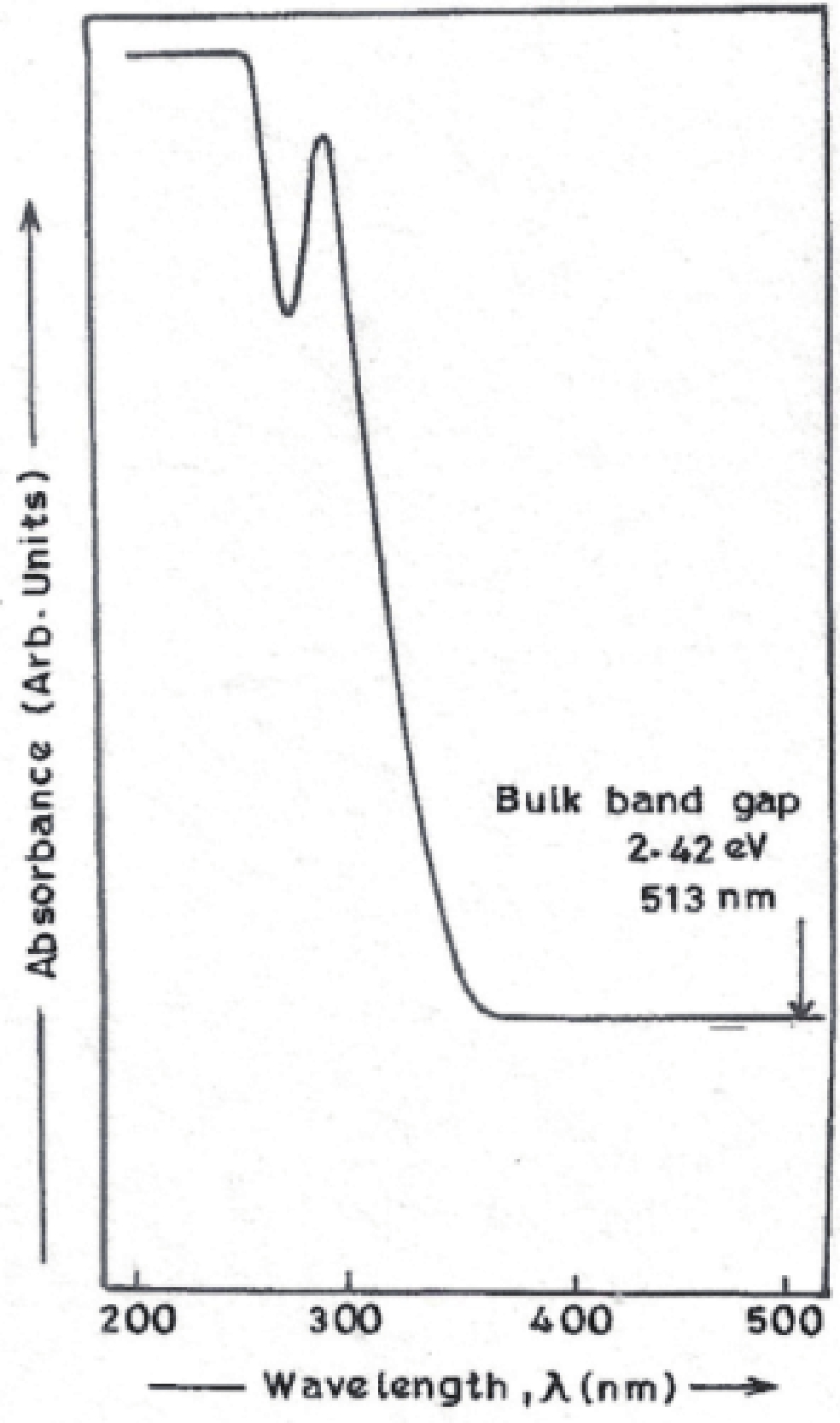
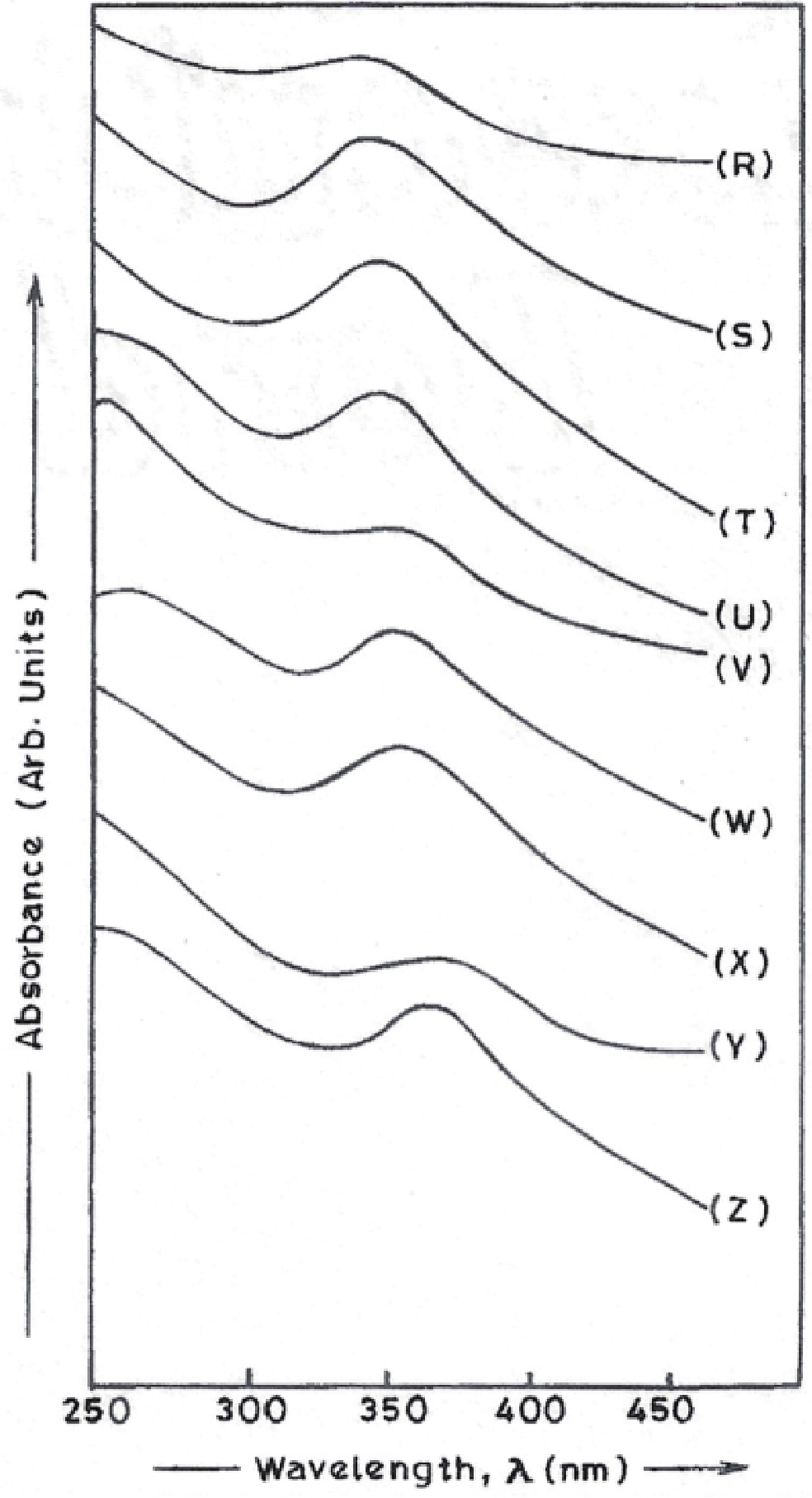
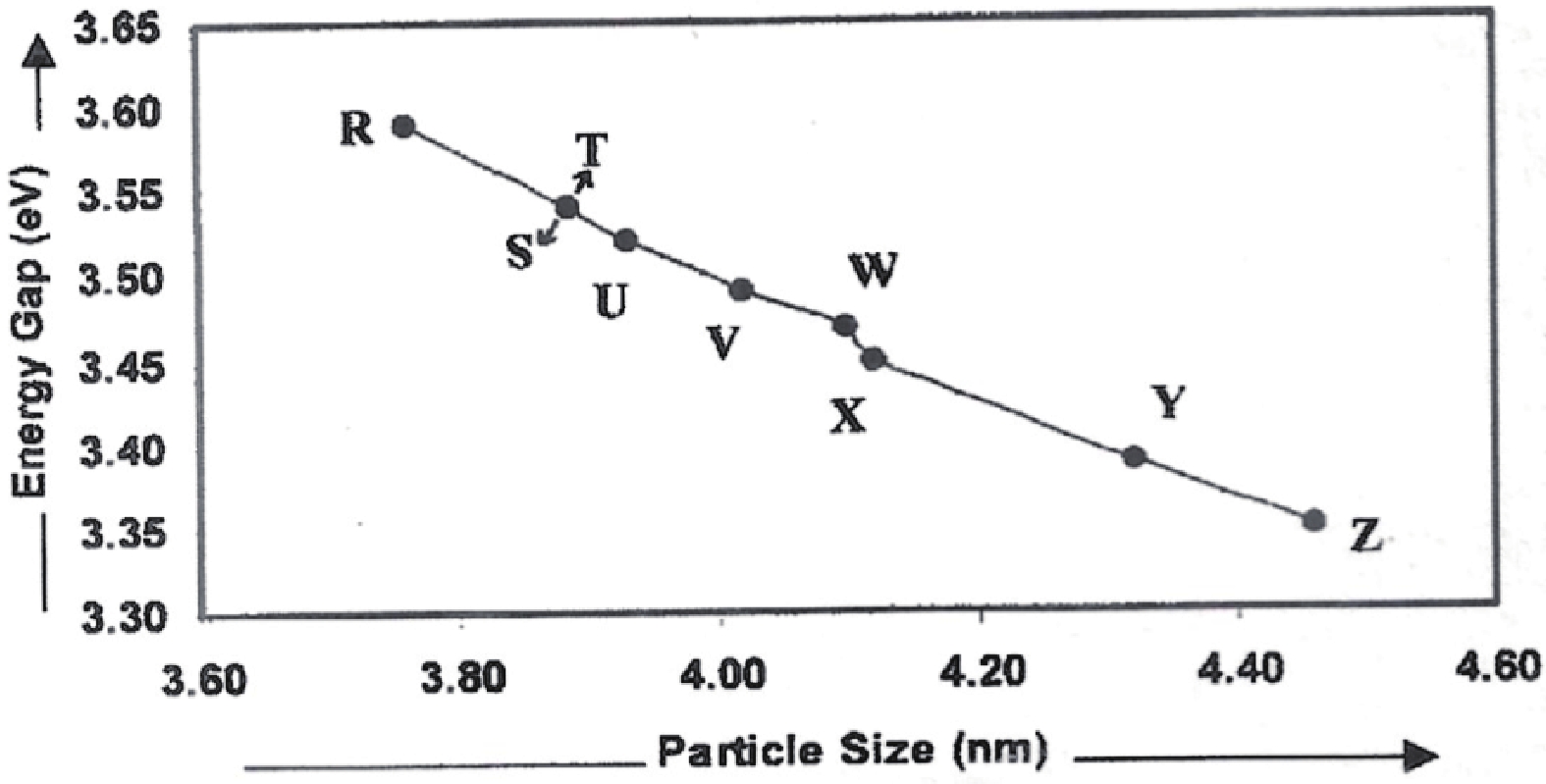
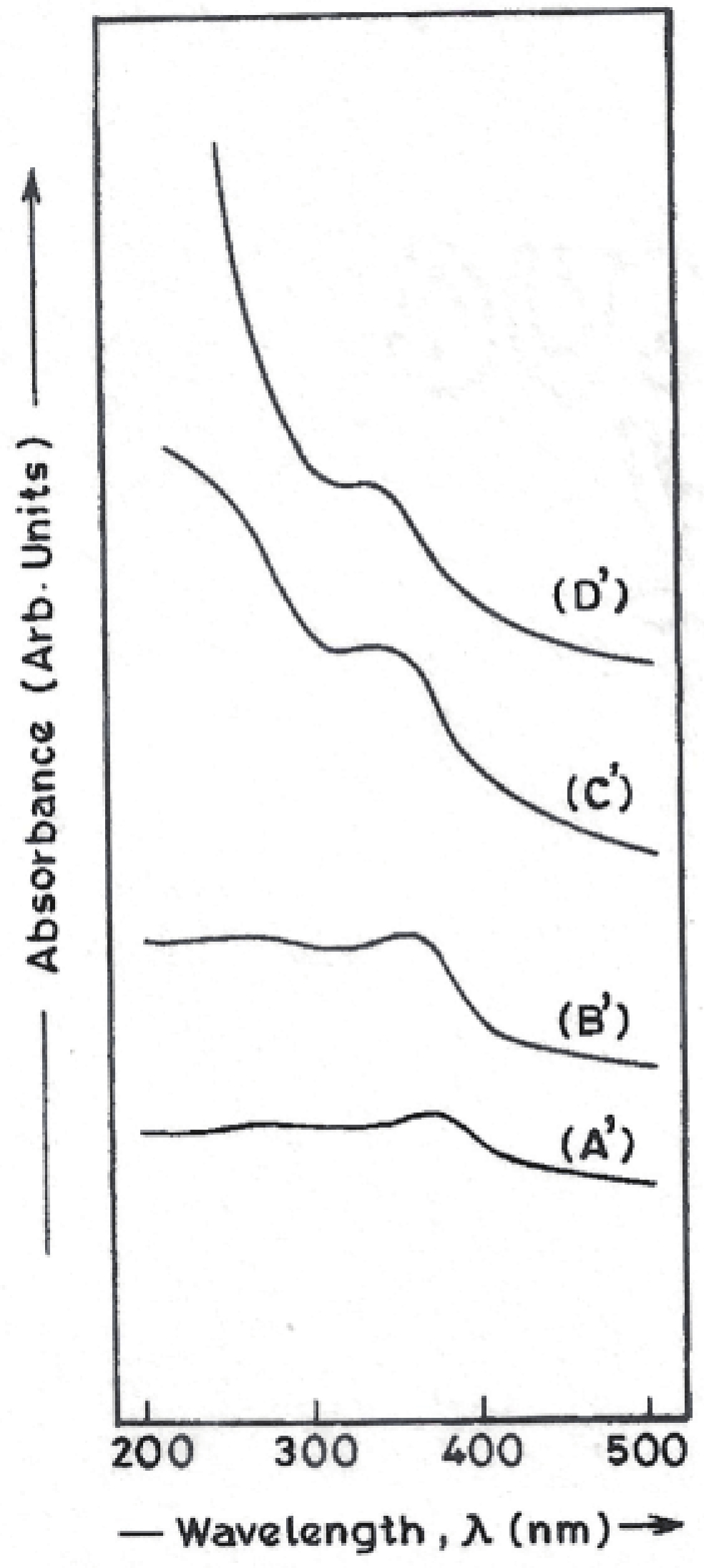
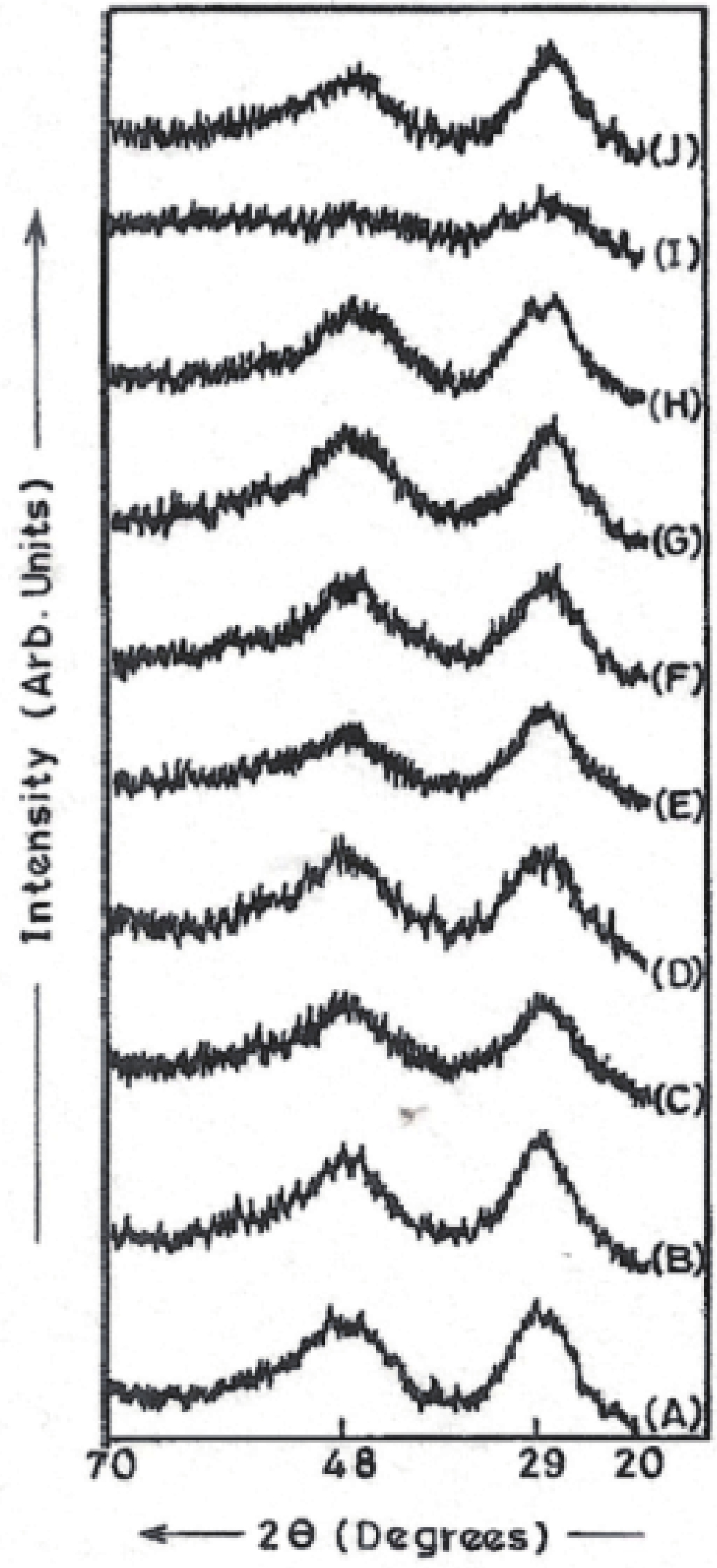
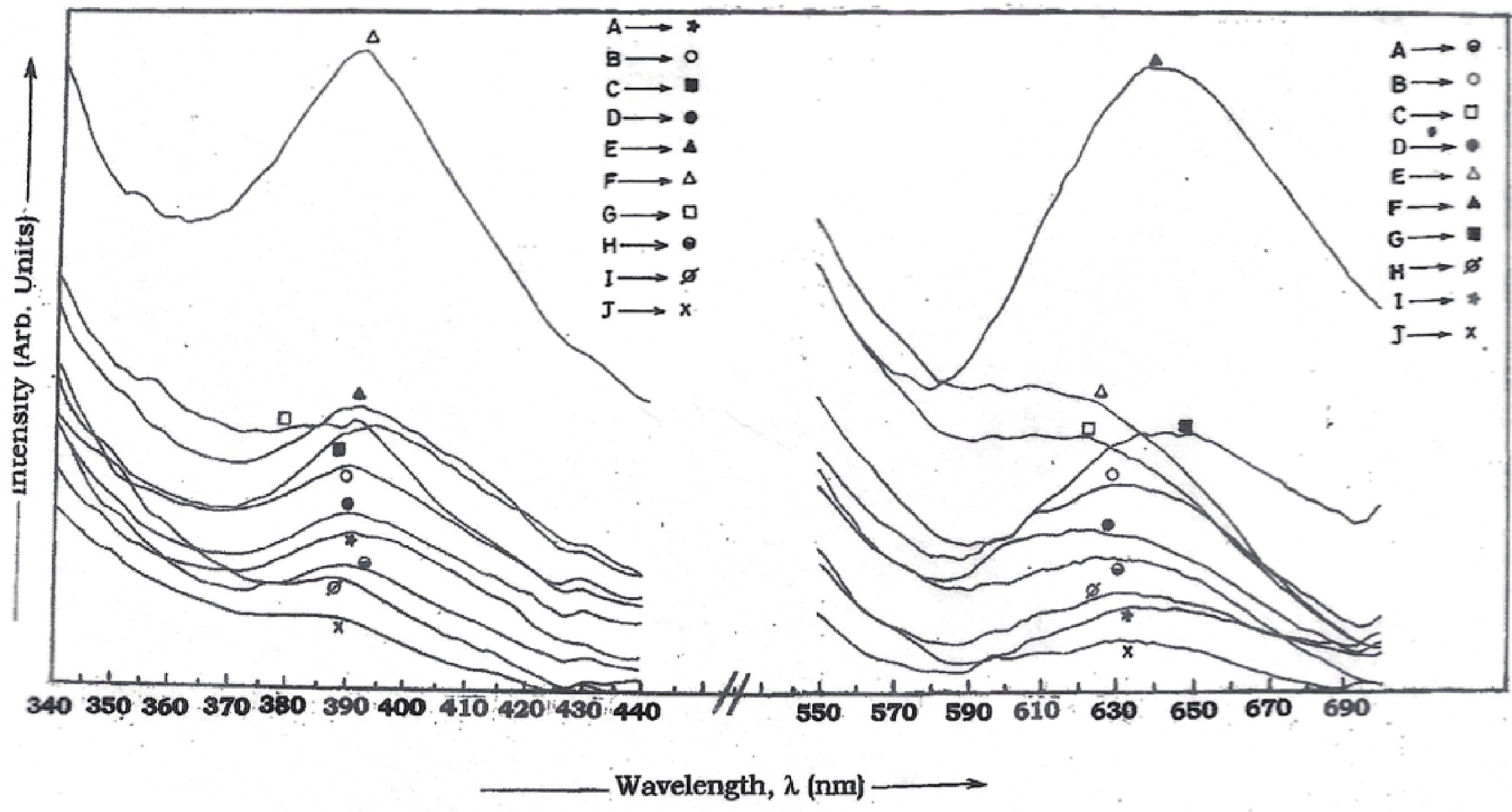
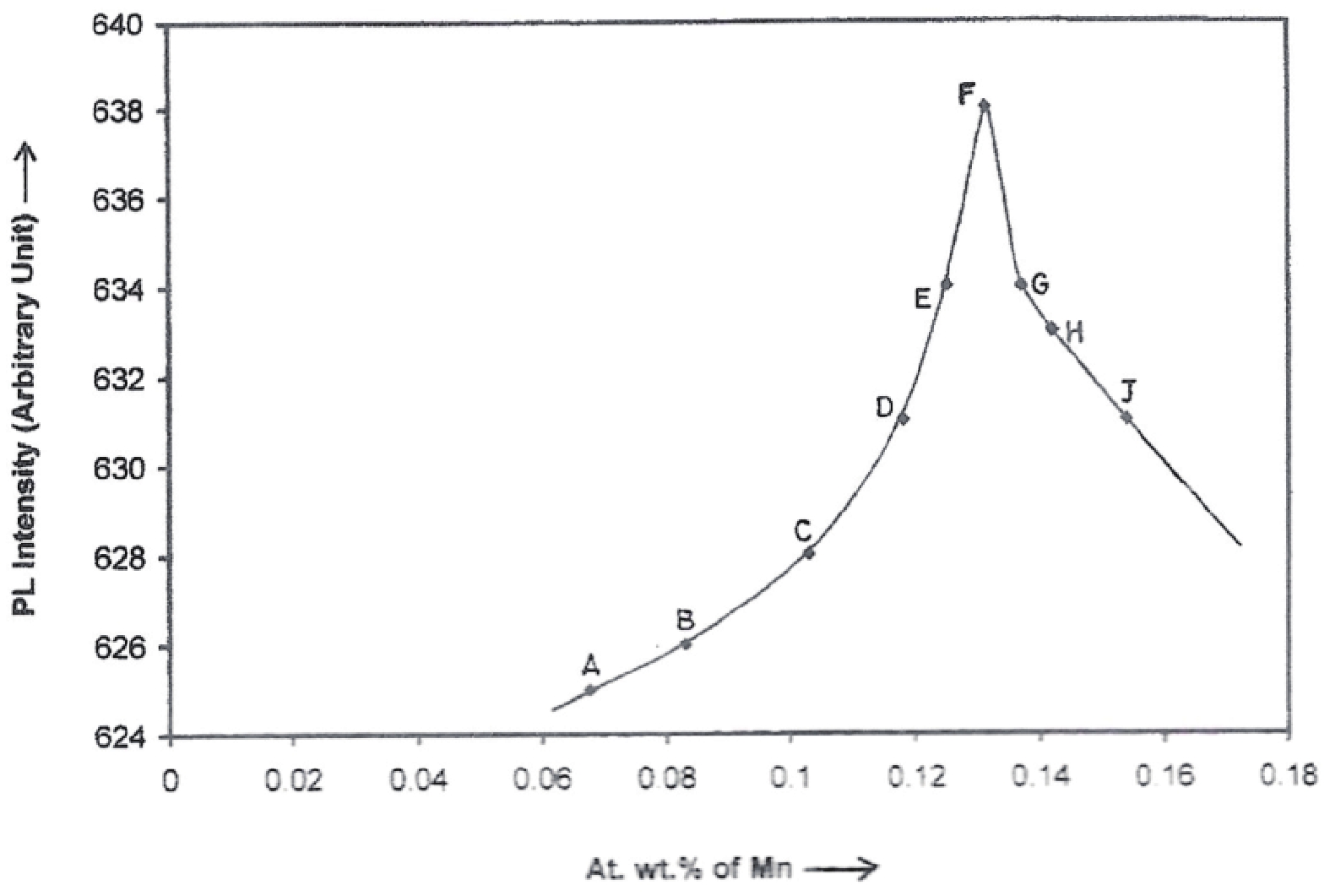
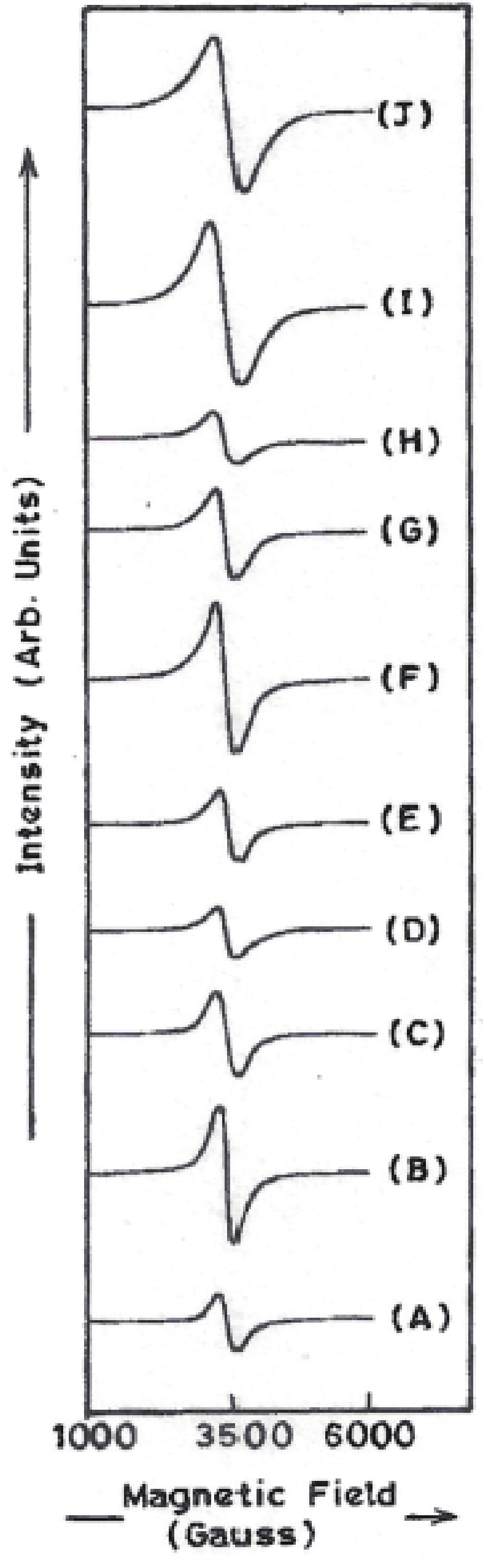
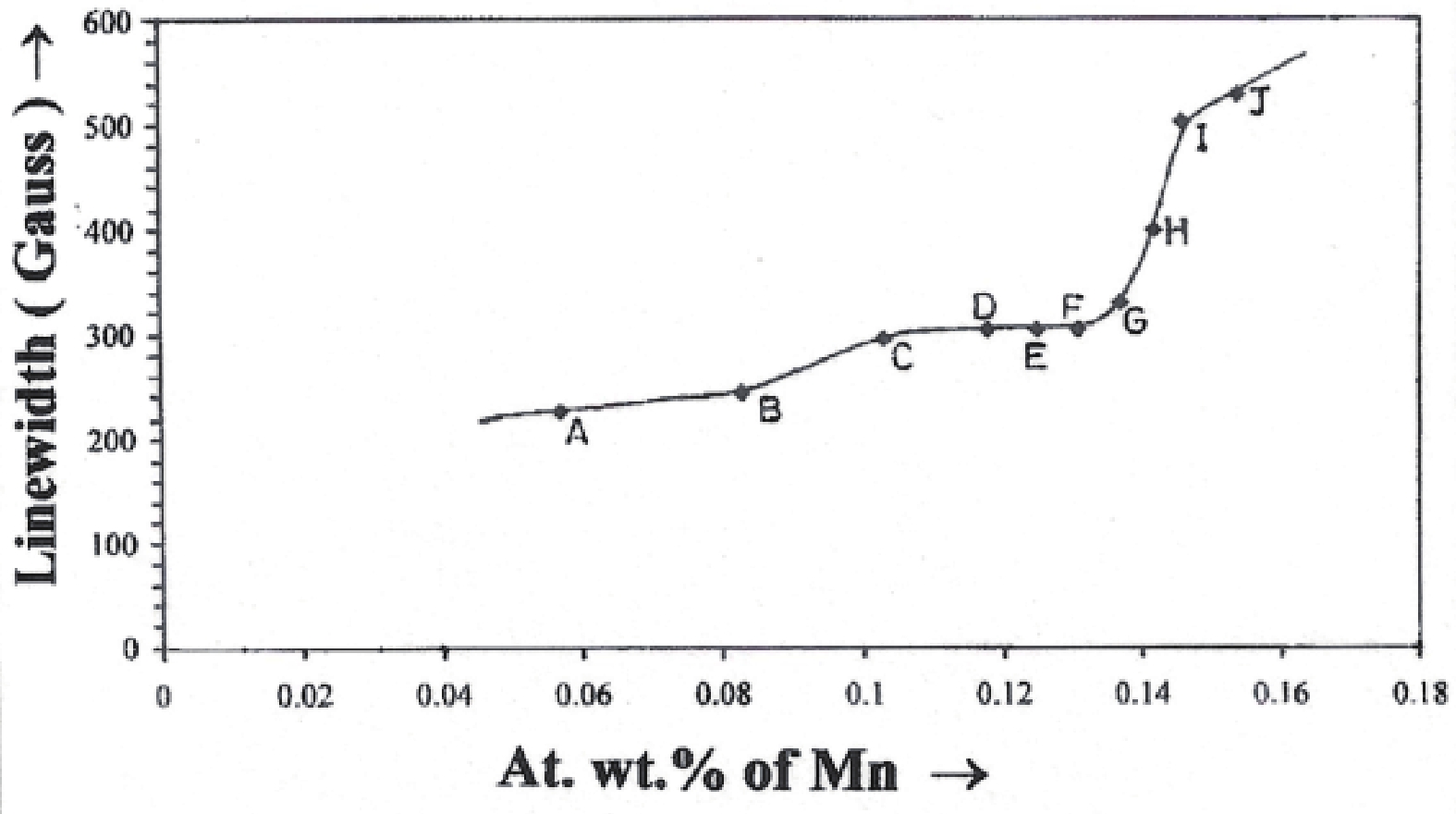
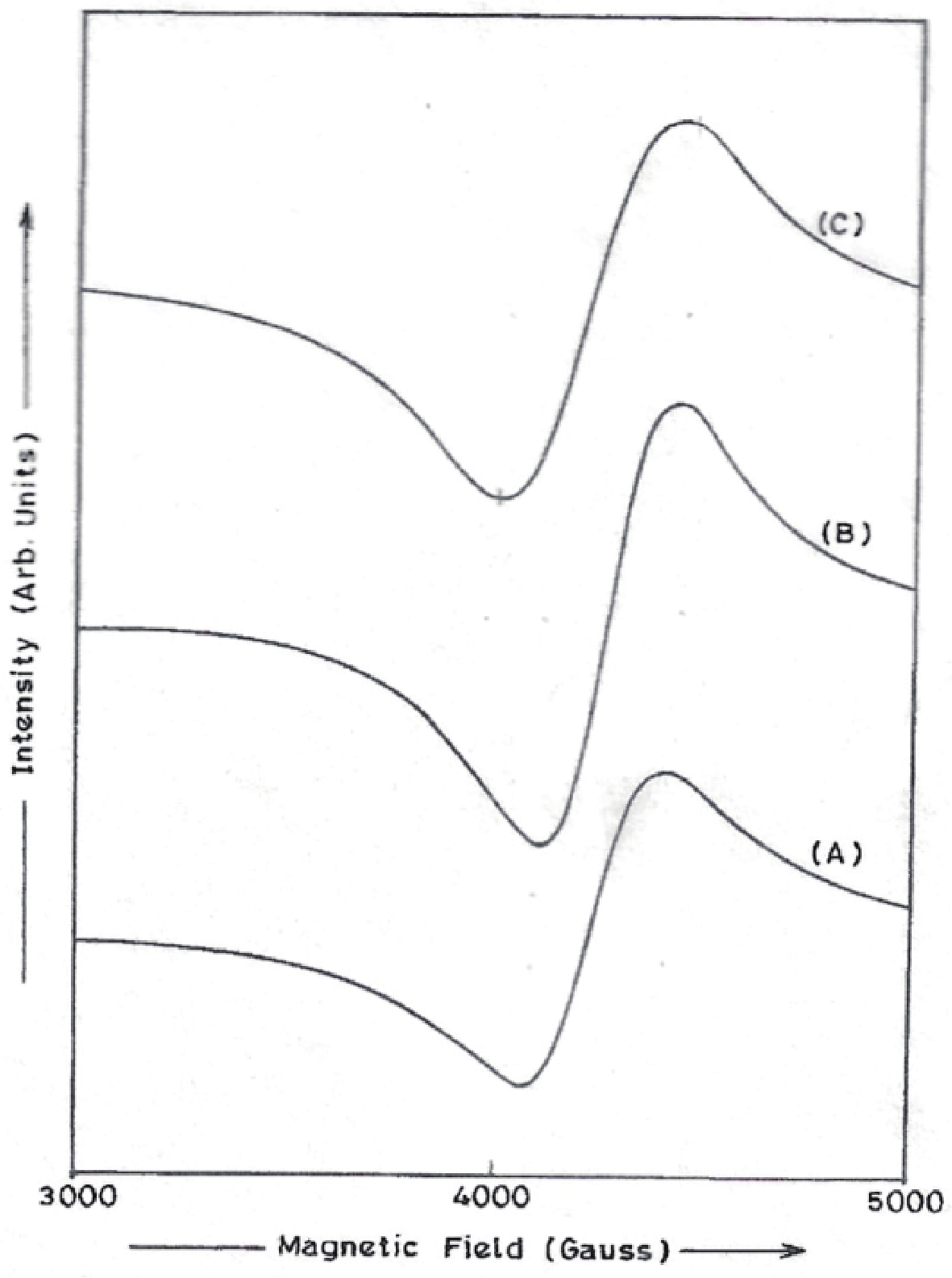
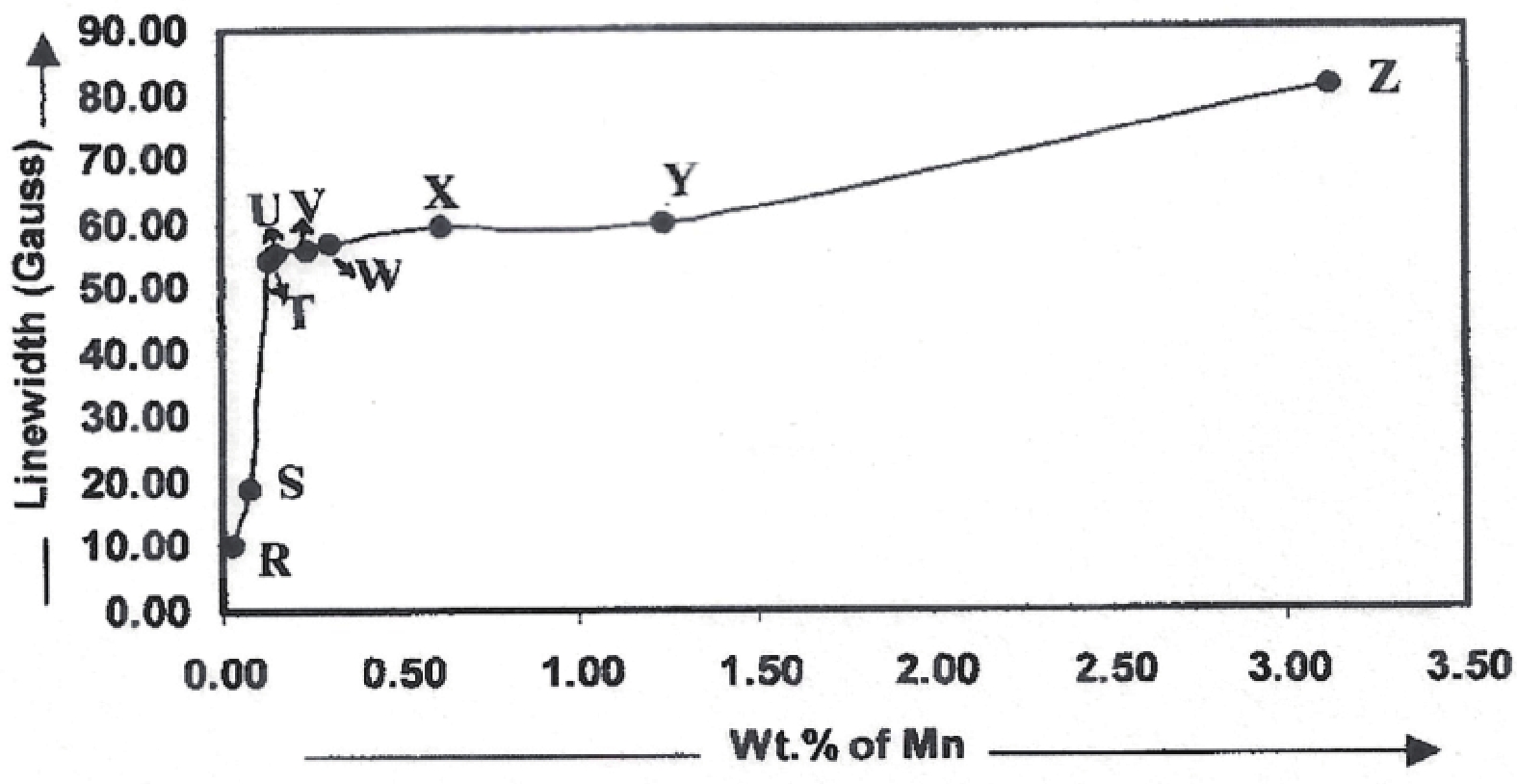
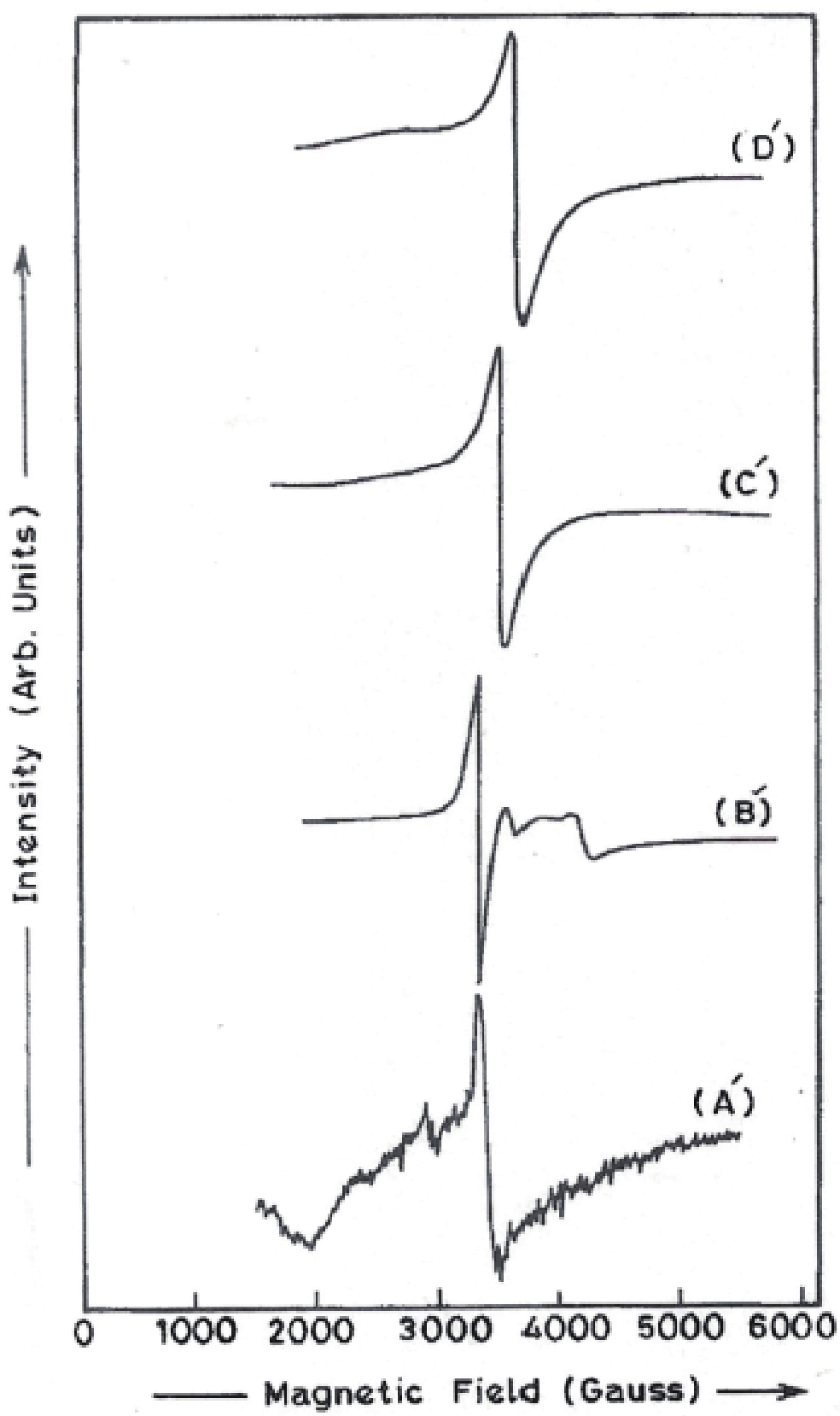
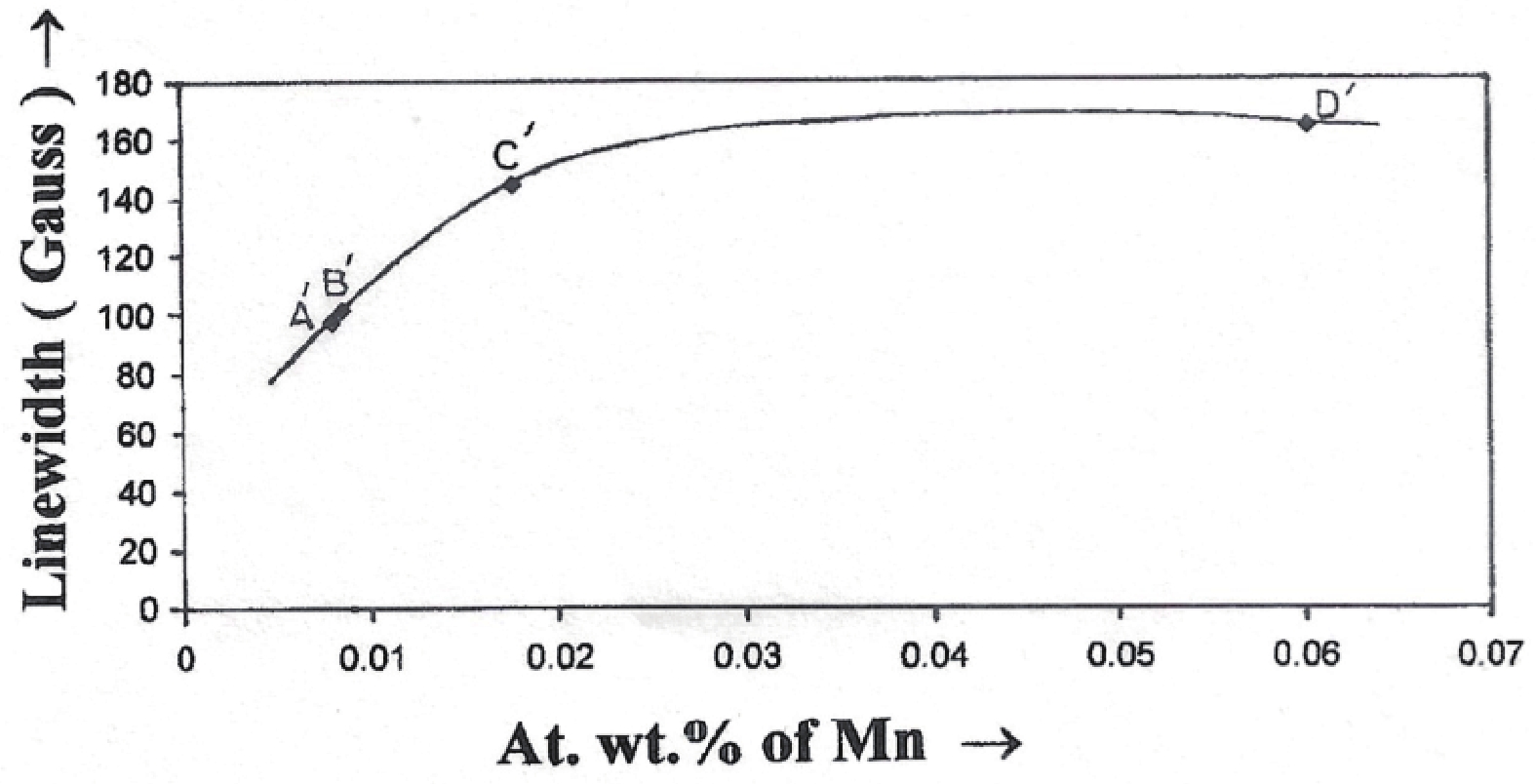
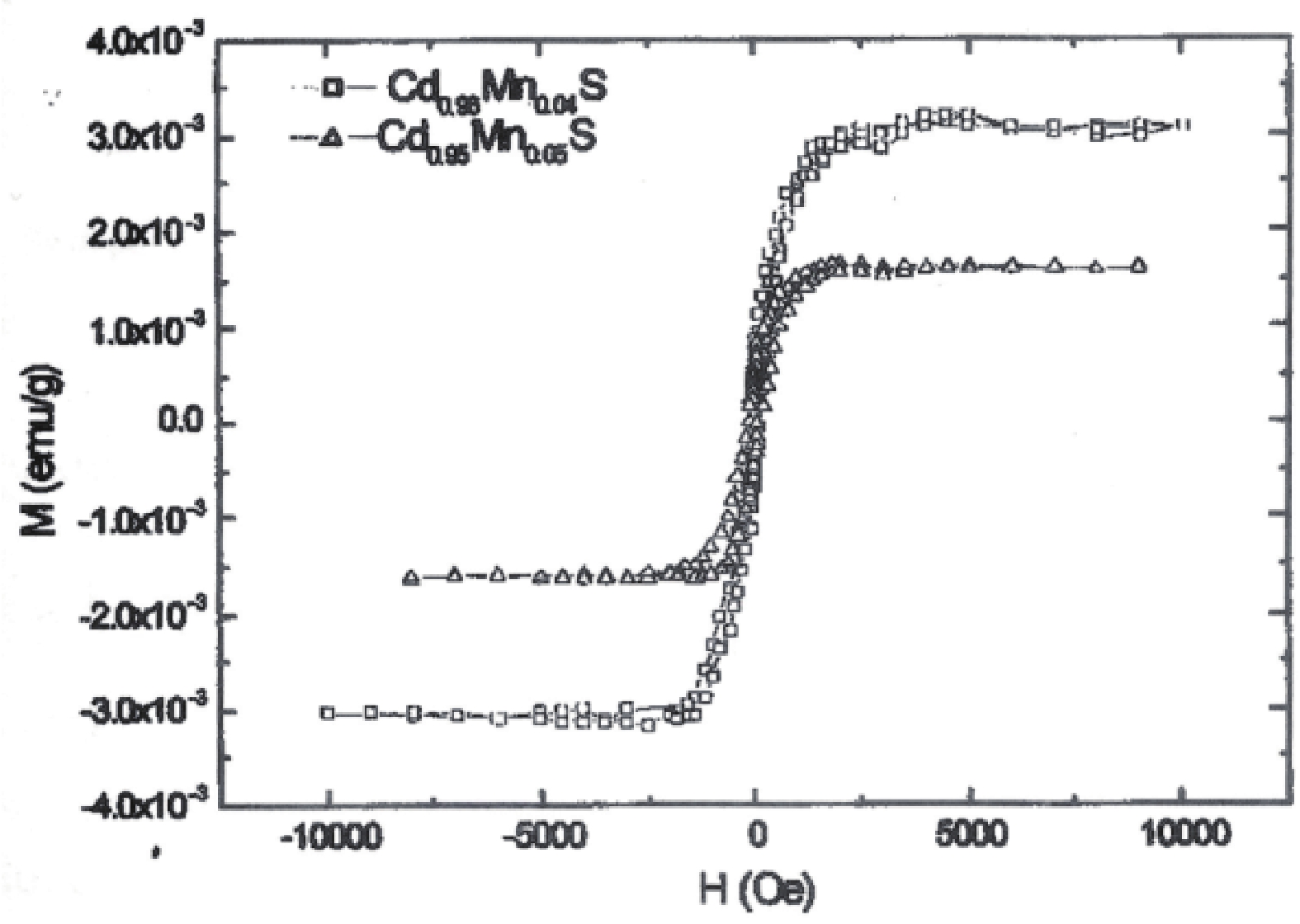
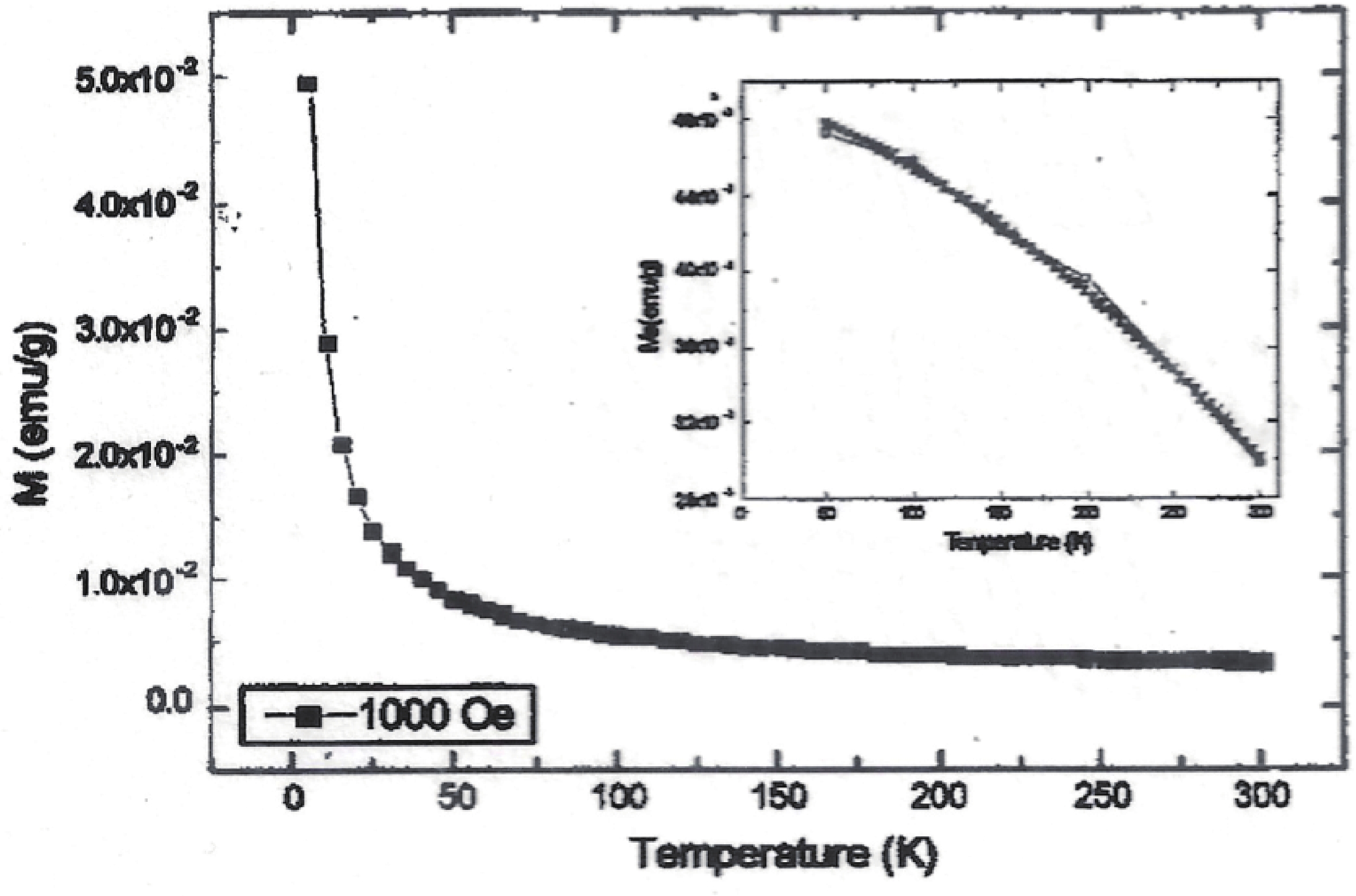
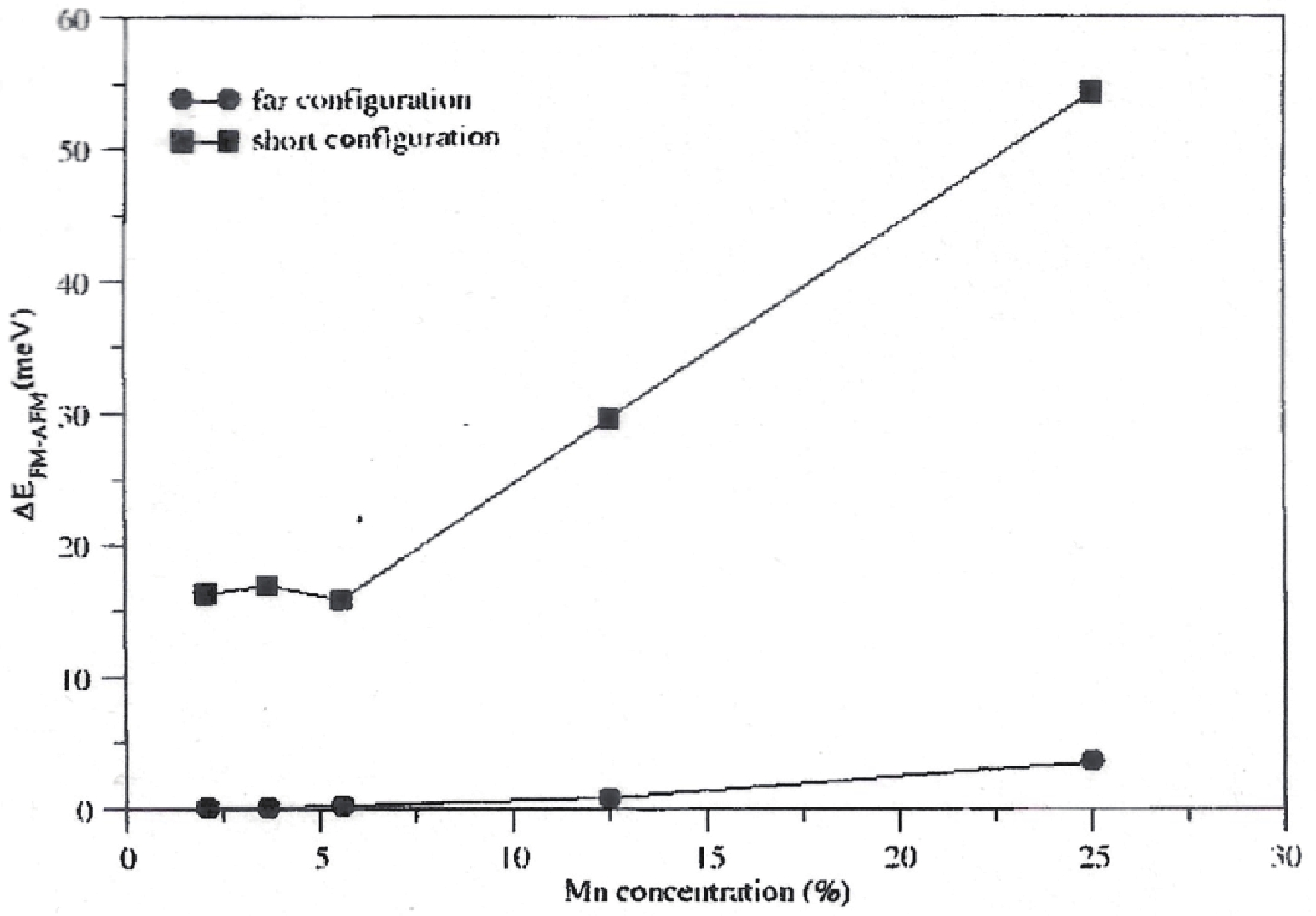
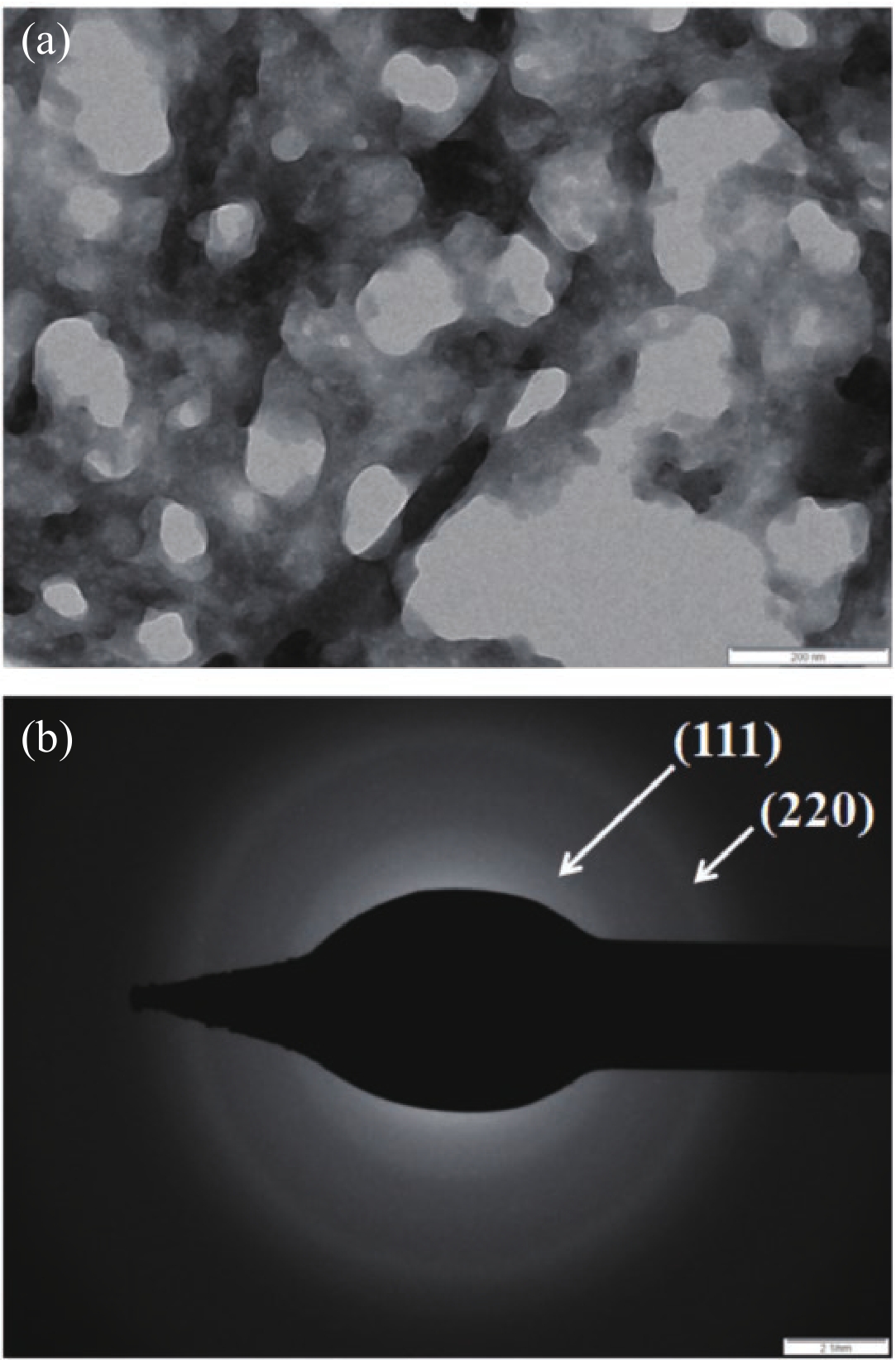
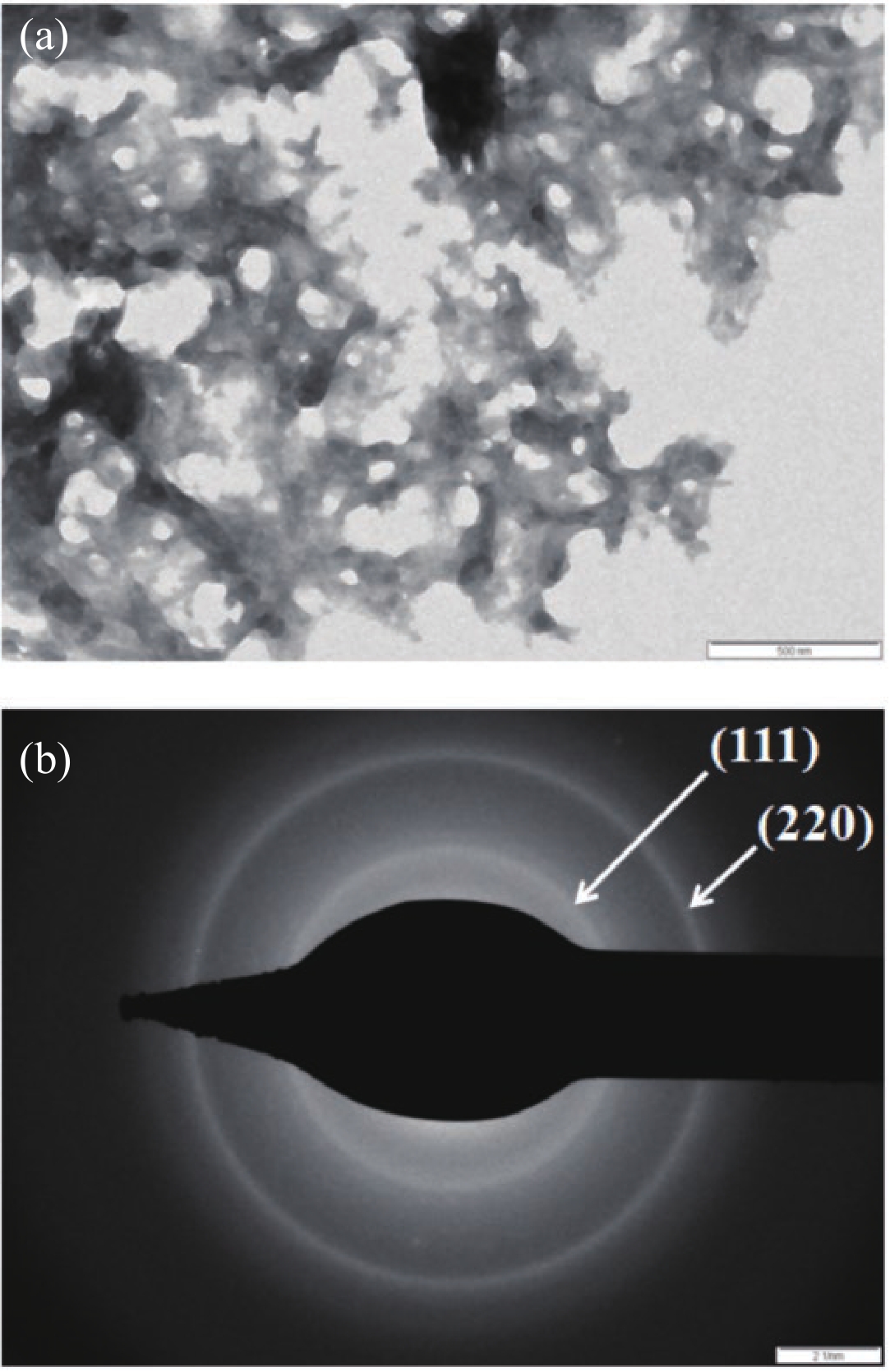
Manganese (Mn) doped cadmium sulphide (CdS) nanoparticles were synthesized using a chemical method. It was possible to decrease CdS : Mn particle size by increasing Mn concentration. Investigation techniques such as ultraviolet−visible (UV−Vis) absorption spectroscopy and photoluminescence (PL) spectroscopy were used to determine optical properties of CdS : Mn nanoparticles. Size quantization effect was observed in UV−Vis absorption spectra. Quantum efficiency for luminescence or the internal magnetic field strength was increased by doping CdS nanoparticles with Mn element. Orange emission was observed at wavelength ~630 nm due to 4T1 → 6A1 transition. Isolated Mn2+ ions arranged in tetrahedral coordination are mainly responsible for luminescence. Luminescence quenching and the effect of Mn doping on hyperfine interactions in the case of CdS nanoparticles were also discussed. The corresponding weight percentage of Mn element actually incorporated in doping process was determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS). Crystallinity was checked and the average size of nanoparticles was estimated using the X-ray diffraction (XRD) technique. CdS : Mn nanoparticles show ferromagnetism at room temperature. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images show spherical clusters of various sizes and selected area electron diffraction (SAED) patterns show the polycrystalline nature of the clusters. The electronic states of diluted magnetic semiconductors (DMS) of Ⅱ−Ⅵ group CdS nanoparticles give them great potential for applications due to quantum confinement. In this study, experimental results and discussions on these aspects have been given. -
References
[1] Gadalla A, Almokhtar M, Abouelkhir A N. Effect of Mn doping on structural, optical and magnetic properties of CdS diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. Chalcogenide Letters, 2018, 15, 207[2] Chaure S. Investigation of the effect of manganese doping in CdS nanocrystalline thin films. Mater Res Express, 2018, 6, 025912 doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/aad4e1[3] Venkatesan D, Deepan D, Ramkumar J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of sodium bis (2-ethylhexyl) sulfonsuccinate (AOT) capped pure and Mn-doped CdS nanoparticles. J Nanomater, 2012, 2012, 1 doi: 10.1155/2012/492573[4] Maity P, Kumar R, Jha S N, et al. Investigation of the Physical Properties of Mn-doped CdS Diluted Magnetic Semiconductor Quantum Dots: Non-linear Band Gap variation with Downwards Bowing. Available at SSRN 4066164[5] Levy L, Ingert D, Feltin N, et al. Cd1− yMn yS nanoparticles: Absorption and photoluminescence properties. J Cryst Growth, 1998, 184/185, 377 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(97)00780-X[6] Hofmann D M, Hofstaetter A, Leib U, et al. EPR and ENDOR investigations on CdS : Mn nanocrystals. J Cryst Growth, 1998, 184/185, 383 doi: 10.1016/S0022-0248(98)80081-X[7] Counio G, Esnouf S, Gacoin T, et al. CdS : Mn nanocrystals in transparent xerogel matrices: synthesis and luminescence properties. J Phys Chem, 1996, 100, 20021 doi: 10.1021/jp961937i[8] Bhargava R N, Gallagher D, Hong X, et al. Optical properties of manganese-doped nanocrystals of ZnS. Phys Rev Lett, 1994, 72, 416 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.72.416[9] Khosravi A A, Kundu M, Jatwa L, et al. Green luminescence from copper doped zinc sulphide quantum particles. Appl Phys Lett, 1995, 67, 2702 doi: 10.1063/1.114298[10] Khosravi A A, Kundu M, Kuruvilla B A, et al. Manganese doped zinc sulphide nanoparticles by aqueous method. Appl Phys Lett, 1995, 67, 2506 doi: 10.1063/1.114440[11] Bhargava R N, Gallagher D, Welker T, et al. Doped nanocrystals of semiconductors - a new class of luminescent materials. J Lumin, 1994, 60/61, 275 doi: 10.1016/0022-2313(94)90146-5[12] Bhargava R N. Nanoparticles and their use for multifunctional bioimaging. J Lumin, 1996, 70, 85 doi: 10.1016/0022-2313(96)00046-4[13] Norris D J, Yao N, Charnock F T, et al. High-quality manganese-doped ZnSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett, 2001, 1, 3 doi: 10.1021/nl005503h[14] Ochsenbein S T, Gamelin D R. Quantum oscillations in magnetically doped colloidal nanocrystals. Nat Nanotechnol, 2011, 6, 112 doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.252[15] Beaulac R, Ochsenbein S, Gamelin D, et al. Colloidal transition-metal-doped quantum dots. In nanocrystal quantum dots. CRC Press, 2010, 397[16] Yu J H, Liu X Y, Kweon K E, et al. Giant Zeeman splitting in nucleation-controlled doped CdSe : Mn2+ quantum nanoribbons. Nat Mater, 2010, 9, 47 doi: 10.1038/nmat2572[17] Wood V, Halpert J E, Panzer M J, et al. Alternating Current driven electroluminescence from ZnSe/ZnS : Mn/ZnS nanocrystals. Nano Lett, 2009, 9, 2367 doi: 10.1021/nl900898t[18] Levy L, Feltin N, Ingert D, et al. Three dimensionally diluted magnetic semiconductor clusters Cd1- yMn yS with a range of sizes and compositions: dependence of spectroscopic properties on the synthesis mode. J Phys Chem B, 1997, 101, 9153 doi: 10.1021/jp970978r[19] Liu S M, Liu F Q, Guo H Q, et al. Surface states induced photoluminescence from Mn2+ doped CdS nanoparticles. Solid State Commun, 2000, 115, 615 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1098(00)00254-4[20] McClure D S. Electronic spectra of molecules and ions in crystals part II. Solid State Physics, 1959, 9, 399 doi: 10.1016/S0081-1947(08)60569-X[21] Tanabe Y, Sugano S. On the absorption spectra of complex ions I, II. J Phys Soc Jpn, 1954, 9, 753 doi: 10.1143/JPSJ.9.753[22] Levy L, Hochepied J F, Pileni M P. Control of the size and composition of three dimensionally diluted magnetic semiconductor clusters. J Phys Chem, 1996, 100, 18322 doi: 10.1021/jp960824w[23] Romčević N, Kostic R, Romčević M, et al. Raman spectroscopy of Cd1− xMn xS quantum dots. J Phys D: Appl Phys, 2005, 38, 4321 doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/38/24/009[24] Patle U S, Ahirwar R K, Bhatt A, et al. Enhanced photoluminescence properties of Mn doped CdS nanocrystals. AIP Conf Proc, 2019, 2100, 020165-1 doi: 10.1063/1.5098719[25] Babi Stoji B, Milivojevi D, Comor M, et al. Optical and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy of Cd1- xMn xS quantum dots. J Phys: Condens Matter, 2004, 16, 4625 doi: 10.1088/0953-8984/16/25/020[26] Patel N H, Deshpande M P, Bhatt S V, et al. Structural and magnetic properties of undoped and Mn doped CdS nanoparticles prepared by chemical co-precipitation method. Adv Mater Lett, 2014, 5, 671 doi: 10.5185/amlett.2014.1574[27] Chauhan R, Kumar A, Chaudhary R P. Synthesis, structural and photocatalytic studies of Mn-doped CdS nanoparticles. Res Chem Intermed, 2013, 39, 645 doi: 10.1007/s11164-012-0586-x[28] Gadalla A A, Aboelkhir A N, Mahesha M G, et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE : Synthesis and characterization of Mn-doped CdS-diluted magnetic semiconductor nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron, 2020, 31, 10941 doi: 10.1007/s10854-020-03240-x[29] Venkatesu P. Doping effect of Mn on structural optical magnetic and electrical properties of CdS nanoparticles. International Conference on Advanced Nanomaterials & Emerging Engineering Technologies, 2013, 260 doi: 10.1109/ICANMEET.2013.6609255[30] Malik M A, O' Brien P, Revaprasadu N. Synthesis of TOPO-capped Mn-doped ZnS and CdS quantum dots. J Mater Chem, 2001, 11, 2382 doi: 10.1039/b102709n[31] Keerthana S, Yuvakkumar R, Ravi G, et al. PVP influence on Mn-CdS for efficient photocatalytic activity. Chemosphere, 2021, 277, 130346 doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130346[32] Patle U S. Synthesis and characterization of Mn doped CdS nanoparticles prepared by chemical bath deposition method. International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR), 2015, 4, 1945[33] Darekar M S, Praveen B M. Synthesis and characterization of nanoparticles of semiconducting metal suplhide and their application. Phys Scr, 2022, 97, 065805 doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/ac698f[34] Darekar M S, Praveen B M. High photosensitivity nanocrystalline p-Cu2S/n-FTO heterojunction photodetectors prepared by dip coating method. J Mod Nanotechnol, 2023, 3 doi: 10.53964/jmn.2023001[35] Dareka M S, Praveen B M. Effects of heat treatment in air atmosphere on dip coating deposited CdS thin films for photo sensor applications. J Mod Nanotechnol, 2023, 3 doi: 10.53964/jmn.2023002[36] Ikeda M, Itoh K, Sato H. Electrical and optical properties of CdS-MnS single crystals. J Phys Soc Jpn, 1968, 25, 455 doi: 10.1143/JPSJ.25.455[37] Tsai C T, Chen S H, Chuu D S, et al. Fabrication and physical properties of radio frequency sputtered Cd1– xMn xS thin films. Phys Rev B, 1996, 54, 11555 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.54.11555[38] Costa V C, Shen Y R, Bray K L. Luminescence properties of nanocrystalline CdS and CdS : Mn2+ doped silica-type glasses. J Non Cryst Solids, 2002, 304, 217 doi: 10.1016/S0022-3093(02)01026-8[39] Hoffman D M, Meyer B K, Ekimov A I, et al. Giant internal magnetic fields in Mn doped nanocrystal quantum dots. Solid State Commun, 2000, 114, 547 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1098(00)00089-2[40] Zhang Y N, Raman N, Bailey J K, et al. A new sol-gel route for the preparation of nanometer-scale semiconductor particles that exhibit quantum optical behavior. J Phys Chem, 1992, 96, 9098 doi: 10.1021/j100202a004[41] Oka Y, Yanata K. Excitonic properties of nanostructure semimagnetic semiconductors. J Lumin, 1996, 70, 35 doi: 10.1016/0022-2313(96)82859-6[42] de Mello Donegá C, Bol A A, Meijerink A. Time-resolved luminescence of ZnS : Mn2+ nanocrystals. J Lumin, 2002, 96, 87 doi: 10.1016/S0022-2313(01)00418-5[43] Ethiraj A S, Hebalkar N, Kulkarni S K, et al. Enhancement of photoluminescence in manganese-doped ZnS nanoparticles due to a silica shell. J Chem Phys, 2003, 118, 8945 doi: 10.1063/1.1566932[44] Samarth N, Furdyna J K. Electron paramagnetic resonance in Cd1- xMn xS, Cd1- xMn xSe, and Cd1- xMn xTe. Phys Rev B Condens Matter, 1988, 37, 9227 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.37.9227[45] Venkatesu P, Ravichandran K. Manganese doped cadmium sulphide (CdS : Mn) quantum particles: Topological, photoluminescence and magnetic studies. Adv Mater Lett, 2013, 4, 202 doi: 10.5185/amlett.2012.7379[46] Maaz K, Karim S, Lee K J, et al. Effect of temperature on the magnetic characteristics of Ni0.5Co0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys, 2012, 133, 1006 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.02.007[47] Feltin N, Levy L, Ingert D, et al. Magnetic properties of 4-nm Cd1- yMn yS nanoparticles differing by their compositions, y. J Phys Chem B, 1999, 103, 4 doi: 10.1021/jp981241k -
Proportional views






 DownLoad:
DownLoad:












 Madhavi Sharad Darekar received her Ph.D. (Physics) in the field of synthesis and characterization of undoped and doped semiconductor nanoparticles from the Department of Physics, Savitribai Phule Pune University, India, in 2006. She received a Post-Doctoral Fellow degree in Nanotechnology from the Department of Nanotechnology, Srinivas University, India, in 2023. At present, she is pursuing a Post-Doctoral Fellow course in Physics in the Department of Physics, Srinivas University, India. Her research involves synthesis of undoped and doped semiconductor nanoparticles by chemical method, thin film deposition by spin coating method, dip coating method, chemical bath deposition etc., their characterizations and applications
Madhavi Sharad Darekar received her Ph.D. (Physics) in the field of synthesis and characterization of undoped and doped semiconductor nanoparticles from the Department of Physics, Savitribai Phule Pune University, India, in 2006. She received a Post-Doctoral Fellow degree in Nanotechnology from the Department of Nanotechnology, Srinivas University, India, in 2023. At present, she is pursuing a Post-Doctoral Fellow course in Physics in the Department of Physics, Srinivas University, India. Her research involves synthesis of undoped and doped semiconductor nanoparticles by chemical method, thin film deposition by spin coating method, dip coating method, chemical bath deposition etc., their characterizations and applications



