| Citation: |
Jinrong Huang, Yuchen Guo, Yongchang Jiang, Feiyu Wang, Lijia Pan, Yi Shi. Recent advances and future prospects in tactile sensors for normal and shear force detection, decoupling, and applications[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45(12): 121601. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24080006
****
J R Huang, Y C Guo, Y C Jiang, F Y Wang, L J Pan, and Y Shi, Recent advances and future prospects in tactile sensors for normal and shear force detection, decoupling, and applications[J]. J. Semicond., 2024, 45(12), 121601 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24080006
|
Recent advances and future prospects in tactile sensors for normal and shear force detection, decoupling, and applications
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/24080006
More Information
-
Abstract
Human skin, through its complex mechanoreceptor system, possesses the exceptional ability to finely perceive and differentiate multimodal mechanical stimuli, forming the biological foundation for dexterous manipulation, environmental exploration, and tactile perception. Tactile sensors that emulate this sensory capability, particularly in the detection, decoupling, and application of normal and shear forces, have made significant strides in recent years. This review comprehensively examines the latest research advancements in tactile sensors for normal and shear force sensing, delving into the design and decoupling methods of multi-unit structures, multilayer encapsulation structures, and bionic structures. It analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of various sensing principles, including piezoresistive, capacitive, and self-powered mechanisms, and evaluates their application potential in health monitoring, robotics, wearable devices, smart prosthetics, and human-machine interaction. By systematically summarizing current research progress and technical challenges, this review aims to provide forward-looking insights into future research directions, driving the development of electronic skin technology to ultimately achieve tactile perception capabilities comparable to human skin.-
Keywords:
- tactile sensors,
- shear force,
- force decoupling,
- e-skin
-
References
[1] Shao B Y, Zhang S, Hu Y F, et al. Color-shifting iontronic skin for on-site, nonpixelated pressure mapping visualization. Nano Lett, 2024, 24, 4741 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c04755[2] Liu Z, Hu X N, Bo R H, et al. A three-dimensionally architected electronic skin mimicking human mechanosensation. Science, 2024, 384, 987 doi: 10.1126/science.adk5556[3] Kim Y R, Lim G, Cho H, et al. Bilayer piezoionic sensors for enhanced detection of dynamic, static, and directional forces with self-healing capabilities. Nano Energy, 2024, 127, 109749 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.109749[4] Zhang L, Wang S H, Wang Z M, et al. A sweat-pH-enabled strongly adhesive hydrogel for self-powered e-skin applications. Mater Horiz, 2023, 10, 2271 doi: 10.1039/D3MH00174A[5] Wang Z Y, Bu T Z, Li Y Y, et al. Multidimensional force sensors based on triboelectric nanogenerators for electronic skin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13, 56320 doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c17506[6] Boutry C M, Negre M, Jorda M, et al. A hierarchically patterned, bioinspired e-skin able to detect the direction of applied pressure for robotics. Sci Robot, 2018, 3, eaau6914 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.aau6914[7] de Wert L A, Schoonhoven L, Stegen J H C H, et al. Improving the effect of shear on skin viability with wound dressings. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2016, 60, 505 doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2016.03.006[8] Amoli V, Kim J S, Kim S Y, et al. Ionic tactile sensors for emerging human-interactive technologies: A review of recent progress. Adv Funct Mater, 2020, 30, 1904532 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201904532[9] Chun S, Son W, Choi C, et al. Bioinspired hairy skin electronics for detecting the direction and incident angle of airflow. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11, 13608 doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b01427[10] Shang C, Xu Q H, Liang N M, et al. Multi-parameter e-skin based on biomimetic mechanoreceptors and stress field sensing. NPJ Flex Electron, 2023, 7, 19 doi: 10.1038/s41528-023-00252-5[11] Waseem A, Abdullah A, Bagal I V, et al. Self-powered and flexible piezo-sensors based on conductivity-controlled GaN nanowire-arrays for mimicking rapid- and slow-adapting mechanoreceptors. NPJ Flex Electron, 2022, 6, 58 doi: 10.1038/s41528-022-00197-1[12] Yan Y C, Hu Z, Yang Z B, et al. Soft magnetic skin for super-resolution tactile sensing with force self-decoupling. Sci Robot, 2021, 6, eabc8801 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.abc8801[13] Choi D, Jang S, Kim J S, et al. A highly sensitive tactile sensor using a pyramid-plug structure for detecting pressure, shear force, and torsion. Adv Mater Technol, 2019, 4, 1800284 doi: 10.1002/admt.201800284[14] Huynh H Q, Trung T Q, Bag A, et al. Bio-inspired artificial fast-adaptive and slow-adaptive mechanoreceptors with synapse-like functions. Adv Funct Mater, 2023, 33, 2303535 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202303535[15] Ji B, Zhou Q, Chen G, et al. In situ assembly of a wearable capacitive sensor with a spine-shaped dielectric for shear-pressure monitoring. J Mater Chem C, 2020, 8, 15634 doi: 10.1039/D0TC03110K[16] Jung Y, Jung K K, Kim D H, et al. Flexible and highly sensitive three-axis pressure sensors based on carbon nanotube/polydimethylsiloxane composite pyramid arrays. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2021, 331, 113034 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2021.113034[17] Yin J Z, Aspinall P, Santos V J, et al. Measuring dynamic shear force and vibration with a bioinspired tactile sensor skin. IEEE Sens J, 2018, 18, 3544 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2811407[18] Hu C F, Su W S, Fang W. Development of patterned carbon nanotubes on a 3D polymer substrate for the flexible tactile sensor application. J Micromech Microeng, 2011, 21, 115012 doi: 10.1088/0960-1317/21/11/115012[19] Jin M L, Park S, Lee Y, et al. An ultrasensitive, visco-poroelastic artificial mechanotransducer skin inspired by Piezo2 protein in mammalian merkel cells. Adv Mater, 2017, 29, 1605973 doi: 10.1002/adma.201605973[20] Li S, Chen X L, Li X M, et al. Bioinspired robot skin with mechanically gated electron channels for sliding tactile perception. Sci Adv, 2022, 8, eade0720 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.ade0720[21] Mohagheghian E, Luo J Y, Chen J J, et al. Quantifying compressive forces between living cell layers and within tissues using elastic round microgels. Nat Commun, 2018, 9, 1878 doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04245-1[22] Noda K, Matsumoto K, Shimoyama I. Stretchable tri-axis force sensor using conductive liquid. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2014, 215, 123 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2013.09.031[23] Chen J, Zhu Y, Chang X, et al. Recent progress in essential functions of soft electronic skin. Adv Funct Mater, 2021, 31, 2104686 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202104686[24] Zhang Y X, Zeng J T, Wang Y, et al. Flexible three-dimensional force tactile sensor based on velostat piezoresistive films. Micromachines, 2024, 15, 486 doi: 10.3390/mi15040486[25] Zhu Y, Li Y H, Xie D D, et al. High-performance flexible tactile sensor enabled by multi-contact mechanism for normal and shear force measurement. Nano Energy, 2023, 117, 108862 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108862[26] Aksoy B, Digumarti K M, Shea H. Soft monolithic shielded sensors to measure shear and normal forces for local slip detection. Adv Mater Technol, 2024, 9, 2400486 doi: 10.1002/admt.202400486[27] Xu D C, Hu B, Zheng G Q, et al. Sandwich-like flexible tactile sensor based on bioinspired honeycomb dielectric layer for three-axis force detection and robotic application. J Mater Sci Mater Electron, 2023, 34, 942 doi: 10.1007/s10854-023-10336-7[28] Zhang C Y, Zhang X T, Zhang Q, et al. A BTO/PVDF/PDMS piezoelectric tangential and normal force sensor inspired by a wind chime. Micromachines, 2023, 14, 1848 doi: 10.3390/mi14101848[29] Han C C, Cao Z, Hu Y R, et al. Flexible tactile sensors for 3D force detection. Nano Lett, 2024, 24, 5277 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c00894[30] Zhang W Y, Xi Y, Wang E G, et al. Self-powered force sensors for multidimensional tactile sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2022, 14, 20122 doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c03812[31] Cao D Q, Hu J, Li Y, et al. Polymer-based optical waveguide triaxial tactile sensing for 3-dimensional curved shell. IEEE Robot Autom Lett, 2022, 7, 3443 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3146596[32] Jin K Z, Li Z R, Nan P Y, et al. Fiber Bragg grating-based fingertip tactile sensors for normal/shear forces and temperature detection. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2023, 357, 114368 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2023.114368[33] Yousry Y M, Wong V K, Ji R, et al. Shear mode ultrasonic transducers from flexible piezoelectric PLLA fibers for structural health monitoring. Adv Funct Mater, 2023, 33, 2213582 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202213582[34] Liu C, Tan Q, Deng Y Q, et al. Highly sensitive and stable 3D flexible pressure sensor based on carbon black and multi-walled carbon nanotubes prepared by hydrothermal method. Compos Commun, 2022, 32, 101178 doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2022.101178[35] Yu Z, Mao Y H, Wu Z X, et al. Fully-printed bionic tactile E-skin with coupling enhancement effect to recognize object assisted by machine learning. Adv Funct Mater, 2024, 34, 2307503 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202307503[36] Roy S, Deo K A, Lee H P, et al. 3D printed electronic skin for strain, pressure and temperature sensing. Adv Funct Mater, 2024, 34, 2313575 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202313575[37] Zhang M P, Gao X P, Lu C, et al. Ultrathin superhydrophobic flexible tactile sensors for normal and shear force discrimination. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2021, 13, 55735 doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c17391[38] Yang X L, Gan T S, Zhong D L, et al. Rapid self-assembly of self-healable and transferable liquid metal epidermis. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2024, 658, 148 doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2023.12.070[39] Tian C H, Khan S A, Zhang Z Y, et al. Thermoelectric hydrogel electronic skin for passive multimodal physiological perception. ACS Sens, 2024, 9, 840 doi: 10.1021/acssensors.3c02172[40] Yang C, Wang H Y, Cao Z L, et al. Memristor-based bionic tactile devices: Opening the door for next-generation artificial intelligence. Small, 2024, 20, 2308918 doi: 10.1002/smll.202308918[41] Yu P, Chen F N, Long J Q. A three-dimensional force/temperature composite flexible sensor. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2024, 365, 114891 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2023.114891[42] Bai N N, Xue Y H, Chen S Q, et al. A robotic sensory system with high spatiotemporal resolution for texture recognition. Nat Commun, 2023, 14, 7121 doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42722-4[43] Park J, Lee Y, Hong J, et al. Tactile-direction-sensitive and stretchable electronic skins based on human-skin-inspired interlocked microstructures. ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 12020 doi: 10.1021/nn505953t[44] Zhu Y C, Zhou R, Su S L, et al. Flexible three-axis tactile sensor based on double-layer electrospun polyimide nanofiber membrane. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2023, 357, 114369 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2023.114369[45] Zhang X, Li Z K, Du W W, et al. Self-powered triboelectric-mechanoluminescent electronic skin for detecting and differentiating multiple mechanical stimuli. Nano Energy, 2022, 96, 107115 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107115[46] Xiong W N, Feng H, Liwang H S, et al. Multifunctional tactile feedbacks towards compliant robot manipulations via 3D-shaped electronic skin. IEEE Sens J, 2022, 22, 9046 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3162914[47] Mu C H, Song Y Q, Huang W T, et al. Flexible normal-tangential force sensor with opposite resistance responding for highly sensitive artificial skin. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 28, 1707503 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201707503[48] Chong Y S, Yeoh K H, Leow P L, et al. Piezoresistive strain sensor array using polydimethylsiloxane-based conducting nanocomposites for electronic skin application. Sens Rev, 2018, 38, 494 doi: 10.1108/SR-11-2017-0238[49] Huang J J, Liu Y, Chi X, et al. Programming electronic skin with diverse skin-like properties. J Mater Chem A, 2021, 9, 963 doi: 10.1039/D0TA09101D[50] Kim D, Yoon J. Water-borne fabrication of stretchable and durable microfibers for high-performance underwater strain sensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2020, 12, 20965 doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c04013[51] Wang J C, Yang S N, Ding P T, et al. Omnidirectional printing of soft elastomer for liquid-state stretchable electronics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11, 18590 doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b04730[52] Kim K, Lee K R, Kim Y K, et al. 3-axes flexible tactile sensor fabricated by Si micromachining and packaging technology. 19th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, 2006, 678 doi: 10.1109/MEMSYS.2006.1627890[53] Hammond F L, Kramer R K, Wan Q, et al. Soft tactile sensor arrays for force feedback in micromanipulation. IEEE Sens J, 2014, 14, 1443 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2013.2297380[54] Wang L, Beebe D J. A silicon-based shear force sensor: development and characterization. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2000, 84, 33 doi: 10.1016/S0924-4247(99)00342-8[55] Yang J Y, Li X P, Lü X Z, et al. Three-dimensional interfacial stress sensor based on graphene foam. IEEE Sens J, 2018, 18, 7956 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2855691[56] Chen S Y, Bai C, Zhang C Y, et al. Flexible piezoresistive three-dimensional force sensor based on interlocked structures. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2021, 330, 112857 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2021.112857[57] Gu Y D, Zhang T, Li J, et al. A new force-decoupling triaxial tactile sensor based on elastic microcones for accurately grasping feedback. Adv Intell Syst, 2023, 5, 2200321 doi: 10.1002/aisy.202200321[58] Xu K C, Fujita Y, Lu Y Y, et al. A wearable body condition sensor system with wireless feedback alarm functions. Adv Mater, 2021, 33, 2008701 doi: 10.1002/adma.202008701[59] Wang Y C, Ding W, Mei D Q. Development of flexible tactile sensor for the envelop of curved robotic hand finger in grasping force sensing. Measurement, 2021, 180, 109524 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109524[60] Zhang L, Wu Z Y, Li H Y, et al. Force sensing and feedback system based on novel triaxial force capacitive sensor for minimally invasive surgical robot. Adv Sens Res, 2023, 2, 2300033 doi: 10.1002/adsr.202300033[61] Wang D R, Zhao N J, Yang Z K, et al. Iontronic capacitance-enhanced flexible three-dimensional force sensor with ultrahigh sensitivity for machine-sensing interface. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2023, 44, 2023 doi: 10.1109/LED.2023.3324086[62] Morton K, Ishizaki R, Chen Z, et al. Soft three-axis capacitive force sensor for robotic E-skin on curved surfaces. IEEE Sens Lett, 2023, 7, 2503404 doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2023.3303082[63] Liu Y, Weng L, Li Z L, et al. Design and characterization of large-range 3-D force tactile sensor based on Fe-Ga alloy. IEEE Sens J, 2023, 23, 30249 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3324846[64] Zhu Y L, Chen X, Chu K M, et al. Carbon black/PDMS based flexible capacitive tactile sensor for multi-directional force sensing. Sensors, 2022, 22, 628 doi: 10.3390/s22020628[65] Xu T P, Zhu H, Dai S P, et al. High-sensitivity flexible tri-axial capacitive tactile sensor for object grab sensing. Measurement, 2022, 202, 111876 doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111876[66] Wu D Z, Cheng X S, Chen Z, et al. A flexible tactile sensor that uses polyimide/graphene oxide nanofiber as dielectric membrane for vertical and lateral force detection. Nanotechnology, 2022, 33, 405205 doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ac73a4[67] Wang Y F, Ruan X Y, Xing C W, et al. Highly sensitive and flexible three-dimensional force tactile sensor based on inverted pyramidal structure. Smart Mater Struct, 2022, 31, 095013 doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/ac7dcf[68] Subad R A S I, Saikot M M H, Park K. Soft multi-directional force sensor for underwater robotic application. Sensors, 2022, 22, 3850 doi: 10.3390/s22103850[69] Meng H L, Zhu W H, Zhou L X, et al. A 3-D force sensor based on combination of magnetic and piezoresistive transduction. IEEE Sens J, 2022, 22, 3595 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3141126[70] Wu Z Y, Huang T, Hou C, et al. A flexible triaxial force capacitive sensor with microstructure electrode and orthogonal microstructure. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), 2021, 319 doi: 10.1109/3M-NANO49087.2021.9599733[71] Wang S, Wang C Y, Lin Q J, et al. Flexible three-dimensional force sensor of high sensing stability with bonding and supporting composite structure for smart devices. Smart Mater Struct, 2021, 30, 105004 doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/ac1bf0[72] Nie B Q, Geng J L, Yao T, et al. Sensing arbitrary contact forces with a flexible porous dielectric elastomer. Mater Horiz, 2021, 8, 962 doi: 10.1039/D0MH01359E[73] Albrecht A, Trautmann M, Becherer M, et al. Shear-force sensors on flexible substrates using inkjet printing. J Sens, 2019, 2019, 1864239 doi: 10.1155/2019/1864239[74] Won S M, Wang H L, Kim B H, et al. Multimodal sensing with a three-dimensional piezoresistive structure. ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 10972 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b02030[75] Jin J, Wang S H, Mei D Q, et al. A novel flexible centralized force sensor based on tri-axis force refactoring method for arbitrary force components measurement. Adv Intell Syst, 2024, 6, 2300213 doi: 10.1002/aisy.202300213[76] Zeng X W, Liu Y D, Liu F M, et al. A bioinspired three-dimensional integrated e-skin for multiple mechanical stimuli recognition. Nano Energy, 2022, 92, 106777 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106777[77] Miura R, Sekine T, Wang Y F, et al. Printed soft sensor with passivation layers for the detection of object slippage by a robotic gripper. Micromachines, 2020, 11, 927 doi: 10.3390/mi11100927[78] Guo H C, Tan Y J, Chen G, et al. Artificially innervated self-healing foams as synthetic piezo-impedance sensor skins. Nat Commun, 2020, 11, 5747 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19531-0[79] Holgado A C, Tomo T P, Somlor S, et al. A multimodal, adjustable sensitivity, digital 3-axis skin sensor module. Sensors, 2020, 20, 3128 doi: 10.3390/s20113128[80] Zhang Y, Sezen A S, Rajamani R. A low-profile supercapacitor-based normal and shear force sensor. IEEE Sens J, 2021, 21, 239 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3014174[81] Cao Y D, Li T, Gu Y, et al. Fingerprint-inspired flexible tactile sensor for accurately discerning surface texture. Small, 2018, 14, 1703902 doi: 10.1002/smll.201703902[82] Chun S, Kim Y, Jung H, et al. A flexible graphene touch sensor in the general human touch range. Appl Phys Lett, 2014, 105, 4 doi: 10.1063/1.4892062[83] Huang X, Guo W, Liu S Y, et al. Flexible mechanical metamaterials enabled electronic skin for real-time detection of unstable grasping in robotic manipulation. Adv Funct Mater, 2022, 32, 2109109 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202109109[84] Shan J H, Mei T, Sun L, et al. The design and fabrication of a flexible three-dimensional force sensor skin. 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2005, 1818 doi: 10.1109/IROS.2005.1545265[85] Yin R Y, Li L L, Wang L L, et al. Self-healing Au/PVDF-HFP composite ionic gel for flexible underwater pressure sensor. J Semicond, 2023, 44, 032602 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/3/032602[86] Wu X Z, Li Z P, Wang H G, et al. Stretchable and self-healable electrical sensors with fingertip-like perception capability for surface texture discerning and biosignal monitoring. J Mater Chem C, 2019, 7, 9008 doi: 10.1039/C9TC02575H[87] Sun X G, Sun J H, Li T, et al. Flexible tactile electronic skin sensor with 3D force detection based on porous CNTs/PDMS nanocomposites. Nanomicro Lett, 2019, 11, 57 doi: 10.1007/s40820-019-0288-7[88] Cheng X Y, Gong Y, Liu Y S, et al. Flexible tactile sensors for dynamic triaxial force measurement based on piezoelectric elastomer. Smart Mater Struct, 2020, 29, 075007 doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/ab8748[89] Viry L, Levi A, Totaro M, et al. Flexible three-axial force sensor for soft and highly sensitive artificial touch. Adv Mater, 2014, 26, 2659 doi: 10.1002/adma.201305064[90] Joo Y, Byun J, Seong N, et al. Silver nanowire-embedded PDMS with a multiscale structure for a highly sensitive and robust flexible pressure sensor. Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 6208 doi: 10.1039/C5NR00313J[91] Chen X L, Parida K, Wang J X, et al. A stretchable and transparent nanocomposite nanogenerator for self-powered physiological monitoring. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9, 42200 doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b13767[92] Park J, Kim M, Lee Y, et al. Fingertip skin-inspired microstructured ferroelectric skins discriminate static/dynamic pressure and temperature stimuli. Sci Adv, 2015, 1, e1500661 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500661[93] Al-Mai O, Albert J, Ahmadi M. Development and characterization of compliant FBG-based, shear and normal force sensing elements for biomechanical applications. IEEE Sens J, 2020, 20, 5176 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2969866[94] Cirillo A, Cirillo P, De Maria G, et al. An artificial skin based on optoelectronic technology. Sens Actuat A Phys, 2014, 212, 110 doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2014.03.030[95] Saen M, Ito K, Osada K. Action-intention-based grasp control with fine finger-force adjustment using combined optical-mechanical tactile sensor. IEEE Sens J, 2014, 14, 4026 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2331689[96] Zhang Y Q, Khan S A, Luo D X, et al. Flexible perovskite light-emitting diodes for display applications and beyond. J Semicond, 2024, 45, 051601 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/5/051601[97] Alfadhel A, Kosel J. Magnetic nanocomposite cilia tactile sensor. Adv Mater, 2015, 27, 7888 doi: 10.1002/adma.201504015[98] Koda H, Okada Y, Fukumoto T, et al. Effect of tilt-in-space and reclining angles of wheelchairs on normal force and shear force in the gluteal region. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2022, 19, 5299 doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095299[99] Luo H, Jin T H, Zhang Y, et al. A skin-integrated device for neck posture monitoring and correction. Microsyst Nanoeng, 2023, 9, 150 doi: 10.1038/s41378-023-00613-0[100] Guan K D, Chen D, Hua Q L, et al. Sweat-permeable electronic patches by designing three-dimensional liquid diodes. J Semicond, 2024, 45, 070401 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24040035[101] Wang L F, Jones D, Jones A, et al. A portable insole system to simultaneously measure plantar pressure and shear stress. IEEE Sens J, 2022, 22, 9104 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3162713[102] Li G Z, Liu S Q, Wang L Q, et al. Skin-inspired quadruple tactile sensors integrated on a robot hand enable object recognition. Sci Robot, 2020, 5, eabc8134 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.abc8134[103] Liang G H, Wang Y C, Mei D Q, et al. Flexible capacitive tactile sensor array with truncated Pyramids as dielectric layer for three-axis force measurement. J Microelectromech Syst, 2015, 24, 1510 doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2015.2418095[104] Zhang J P, Wei S, Liu C C, et al. Porous nanocomposites with enhanced intrinsic piezoresistive sensitivity for bioinspired multimodal tactile sensors. Microsyst Nanoeng, 2024, 10, 19 doi: 10.1038/s41378-023-00630-z[105] Wolterink G, Sanders R, Krijnen G. A flexible three material, 3D-printed, shear force sensor for use on finger tips. 2019 IEEE Sensors, 2019, 1 doi: 10.1109/SENSORS43011.2019.8956757 -
Proportional views





 Jinrong Huang got his B.S. degree from the University of Science and Technology Beijing in 2017, and completed his M.S. degree from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2020. He is currently pursuing his Ph.D. in Electronic Science and Engineering at Nanjing University. His research interests are primarily in human-robot interaction and deep learning.
Jinrong Huang got his B.S. degree from the University of Science and Technology Beijing in 2017, and completed his M.S. degree from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2020. He is currently pursuing his Ph.D. in Electronic Science and Engineering at Nanjing University. His research interests are primarily in human-robot interaction and deep learning. Lijia Pan is a Full Professor of the School of Electronic Engineering, Nanjing University. He obtained his Ph.D. in polymer physics from University of Science and Technology of China. He was a visiting scholar to Prof. Zhenan Bao’s group at Stanford University. He obtained the National Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (2019−2023). His research interests include conducting polymers and skin-inspired electronic devices.
Lijia Pan is a Full Professor of the School of Electronic Engineering, Nanjing University. He obtained his Ph.D. in polymer physics from University of Science and Technology of China. He was a visiting scholar to Prof. Zhenan Bao’s group at Stanford University. He obtained the National Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (2019−2023). His research interests include conducting polymers and skin-inspired electronic devices.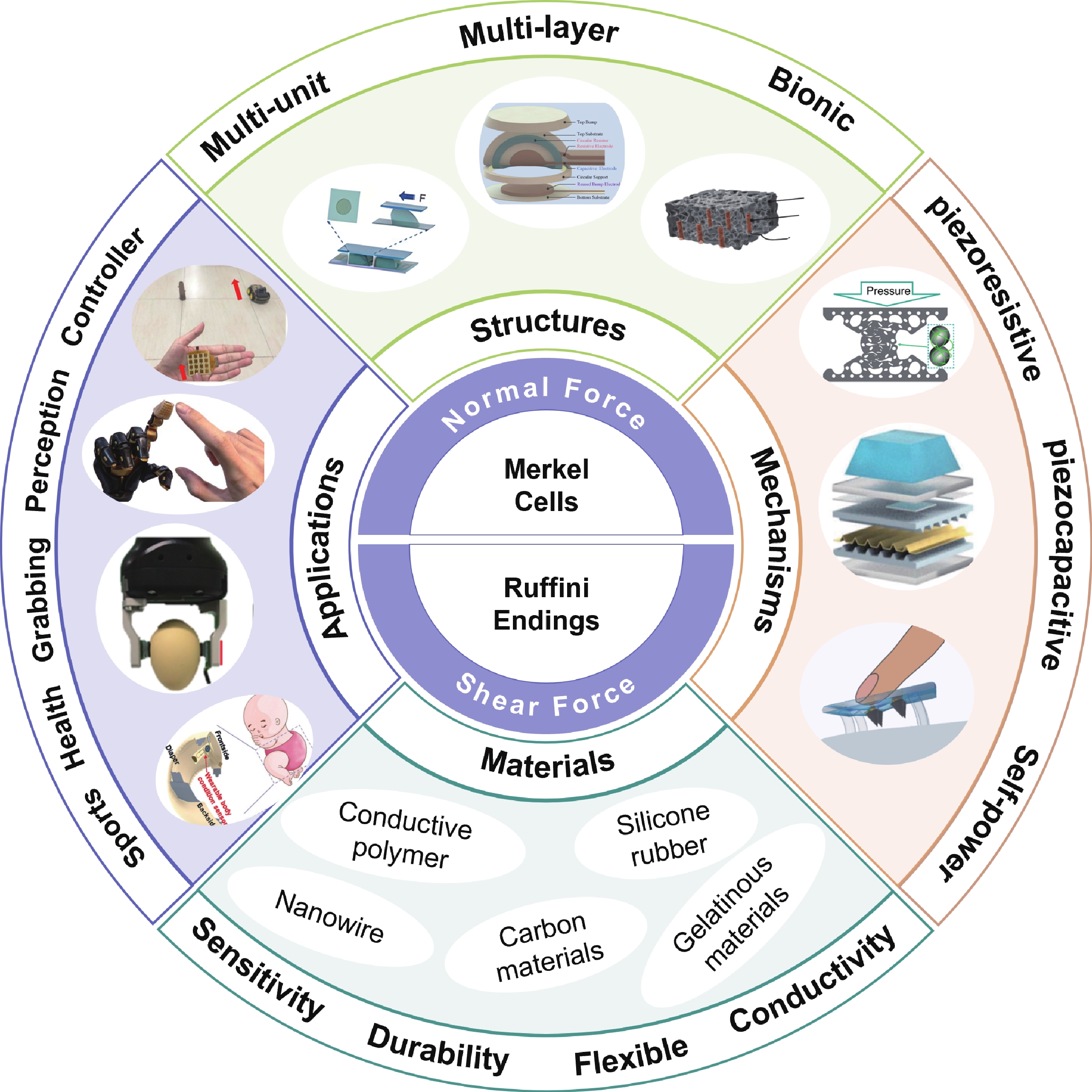
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: