| Citation: |
Yiting Ye, Xiaoyun Huang, Yixian Song, Kai Xu. A novel split gate and contact-field-plate LDMOS with enhanced BV−Ron,sp trade-off and improved FOM[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2026, In Press. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25080033
****
Y T Ye, X Y Huang, Y X Song, and K Xu, A novel split gate and contact-field-plate LDMOS with enhanced BV−Ron,sp trade-off and improved FOM[J]. J. Semicond., 2026, accepted doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25080033
|
A novel split gate and contact-field-plate LDMOS with enhanced BV−Ron,sp trade-off and improved FOM
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/25080033
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.25080033
More Information-
Abstract
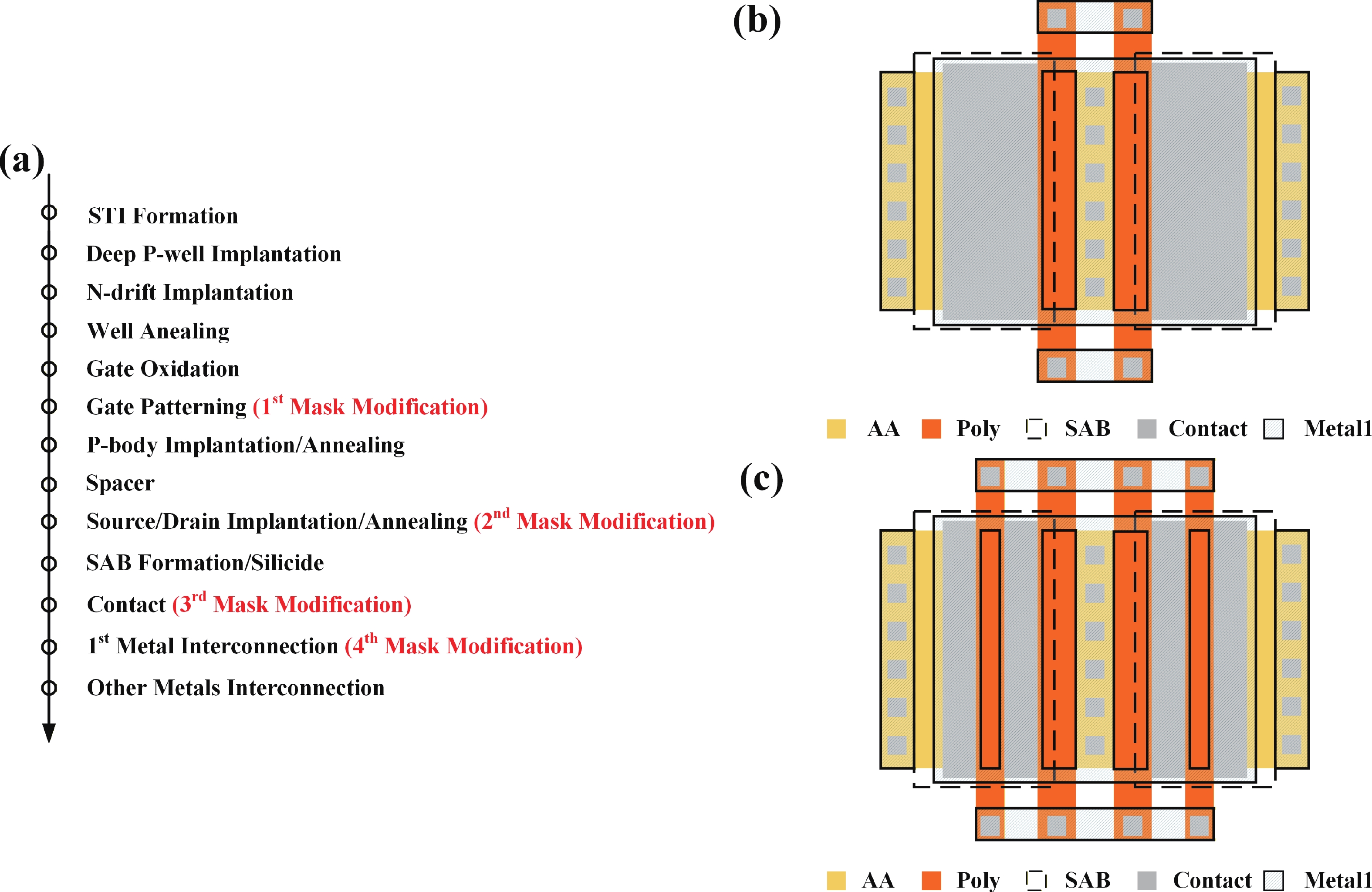
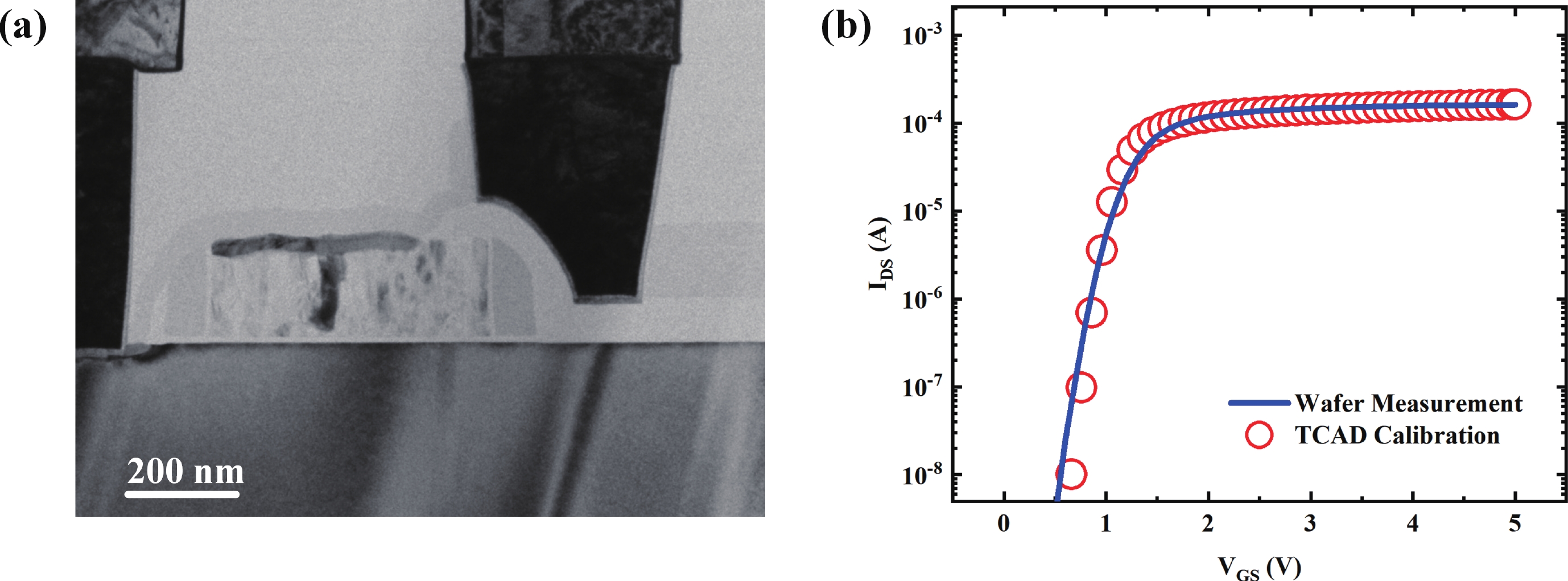
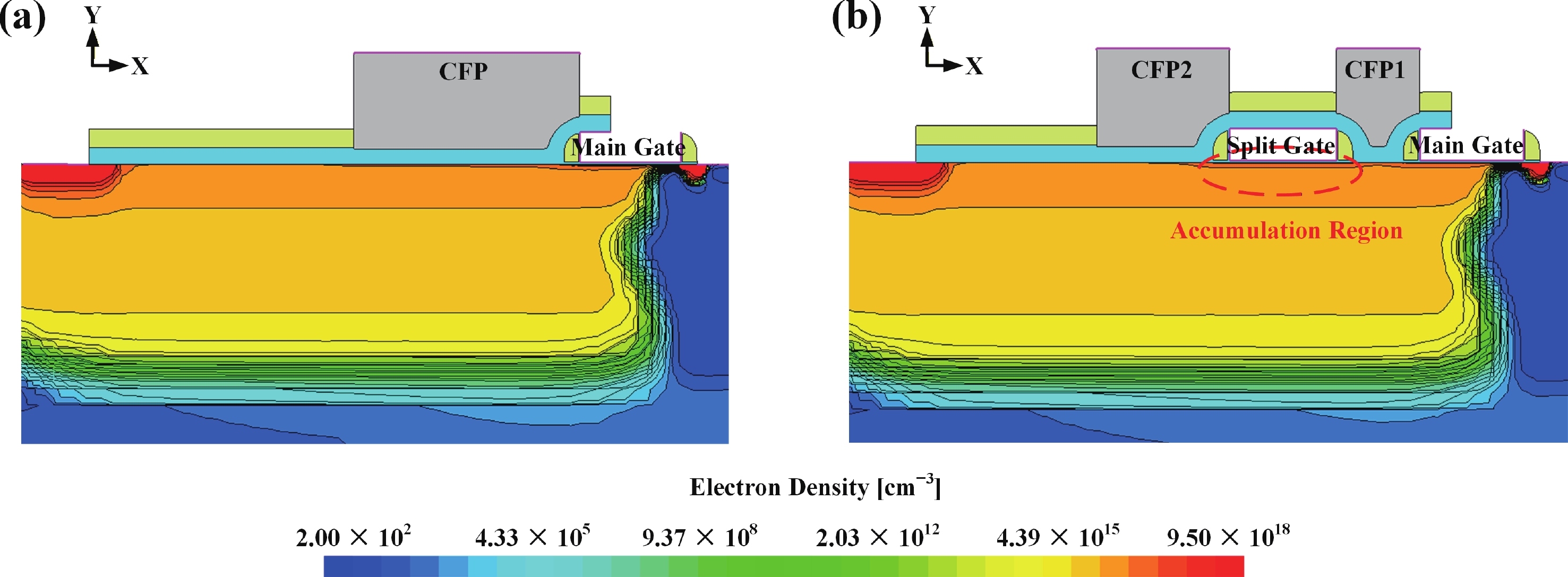
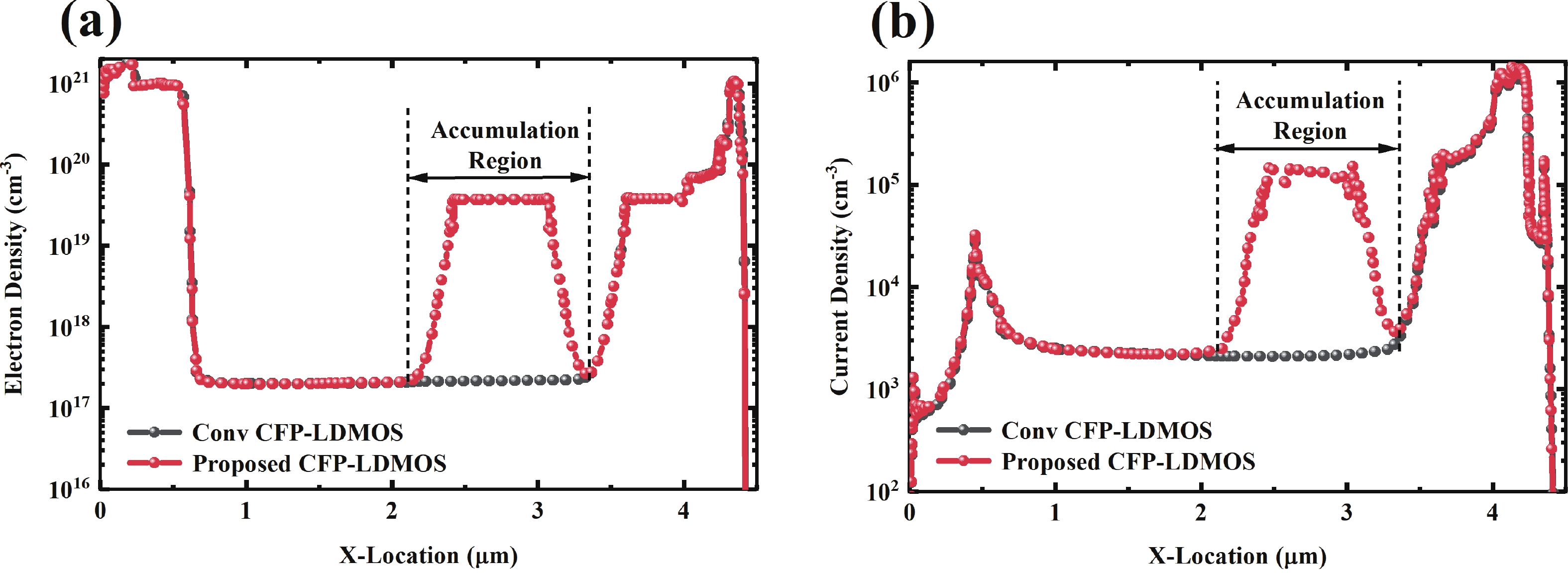
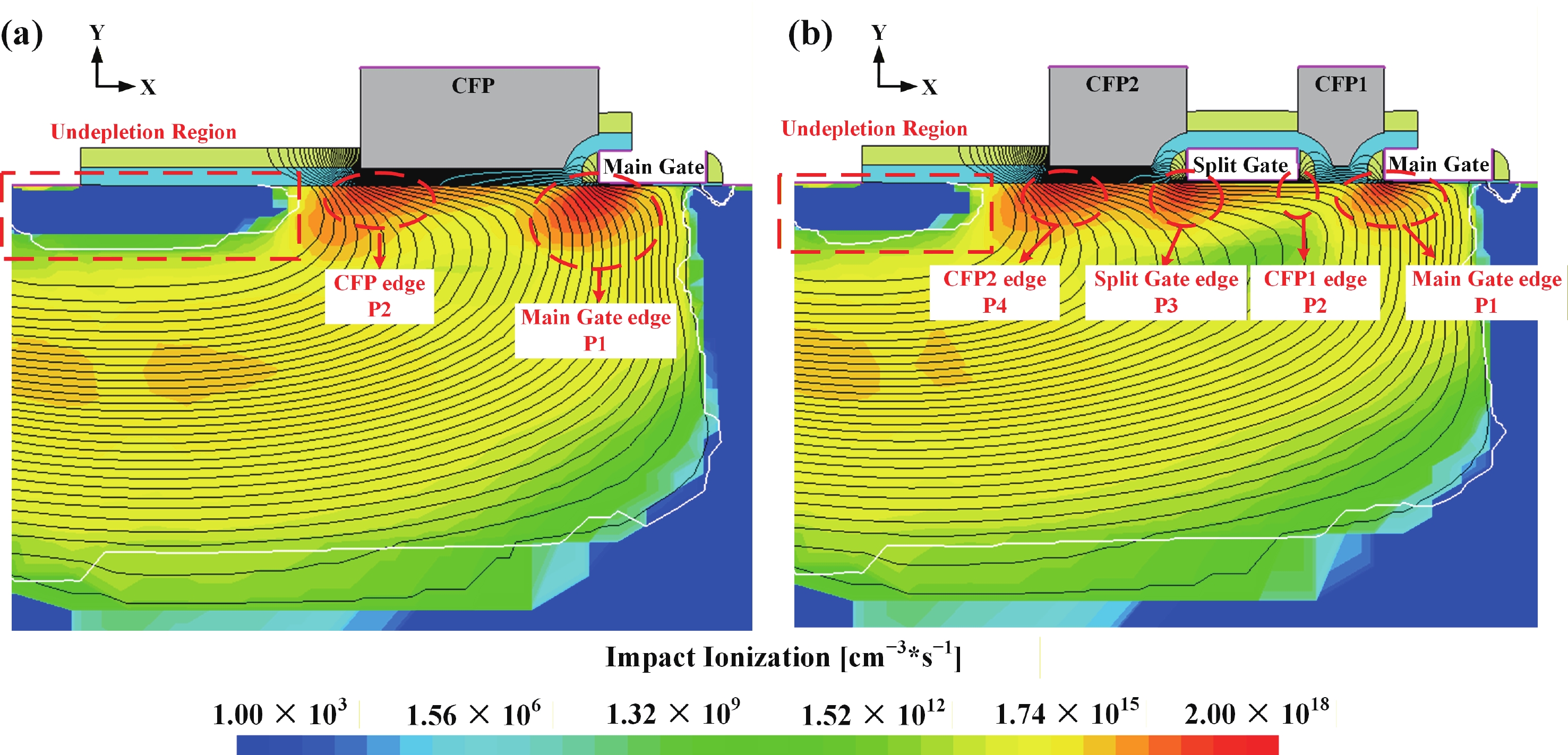
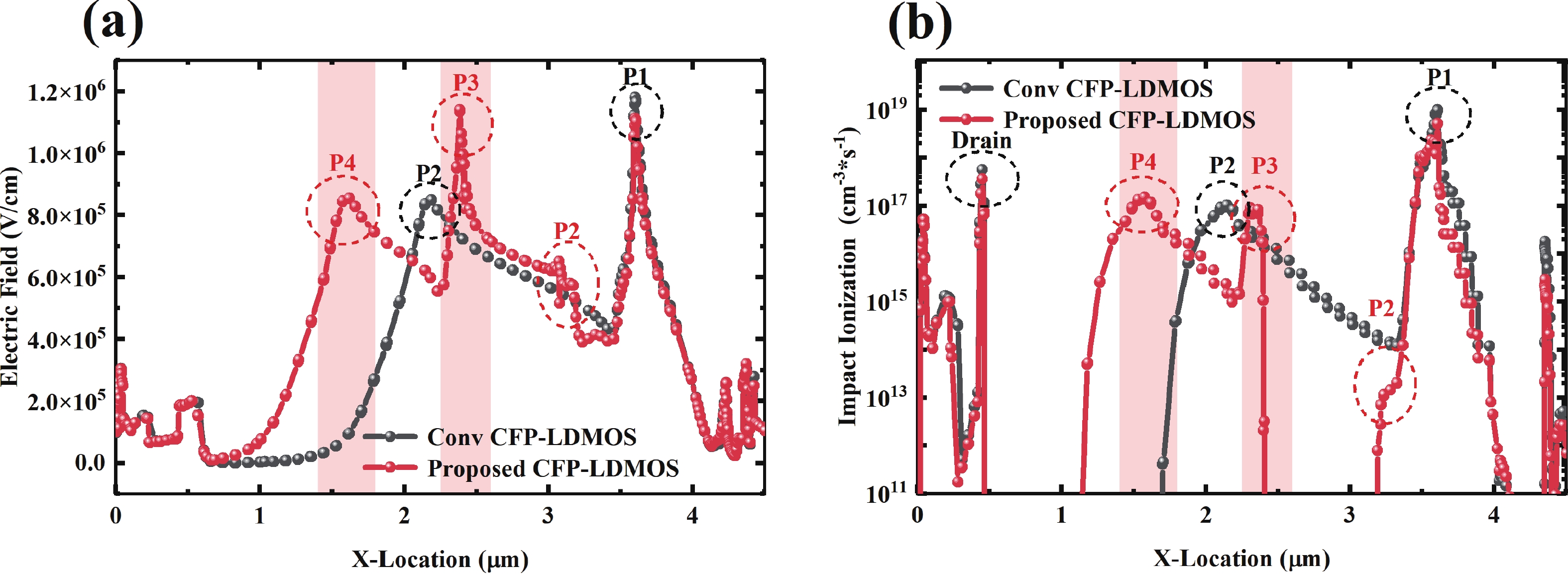
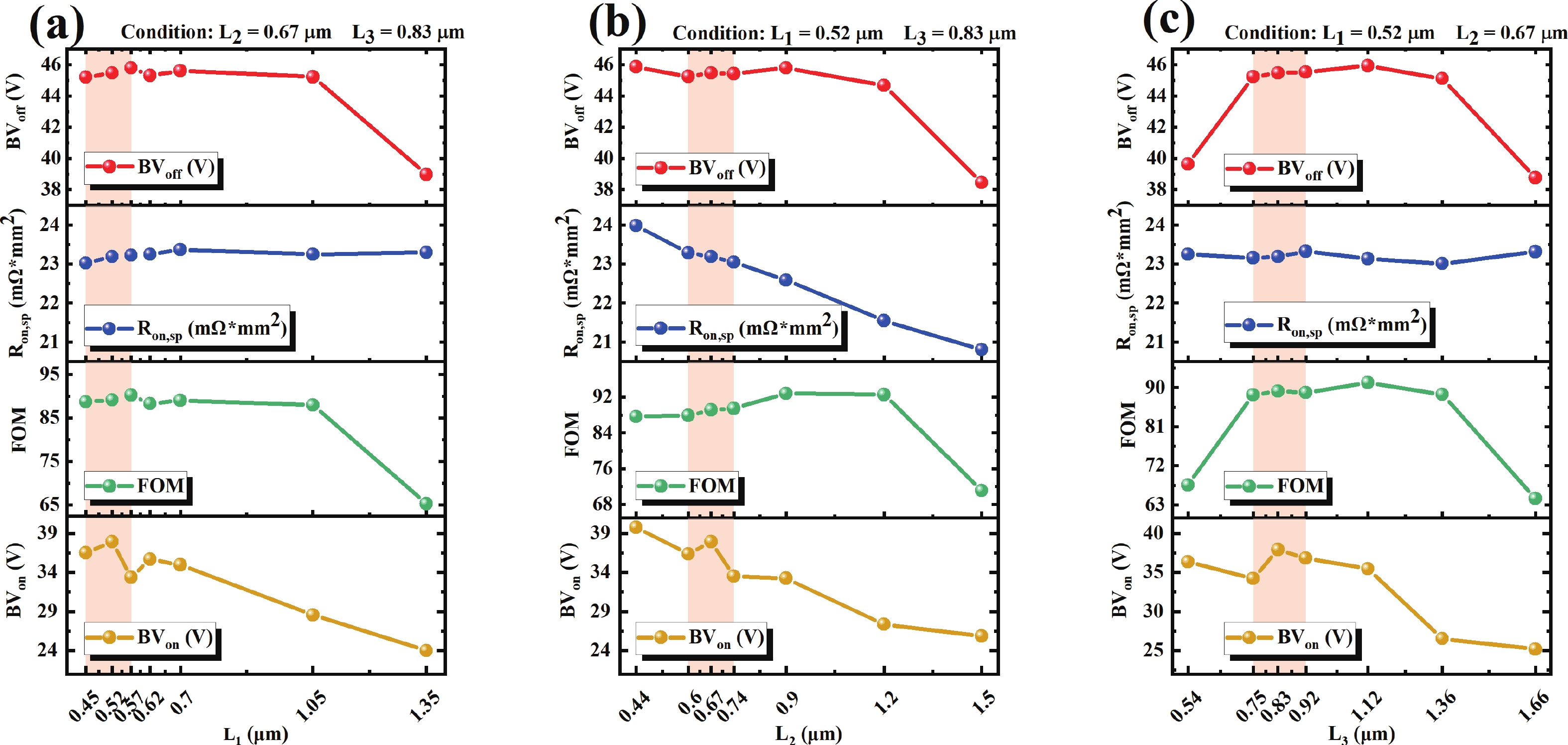
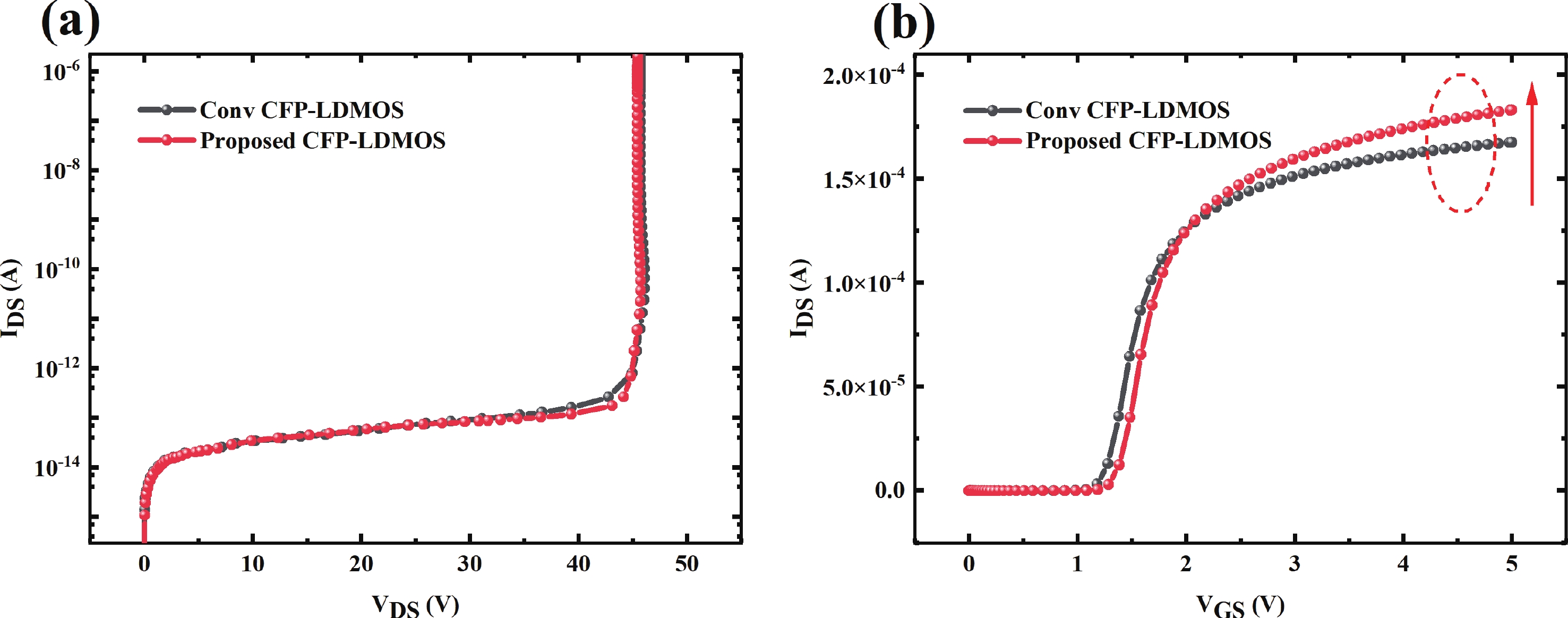
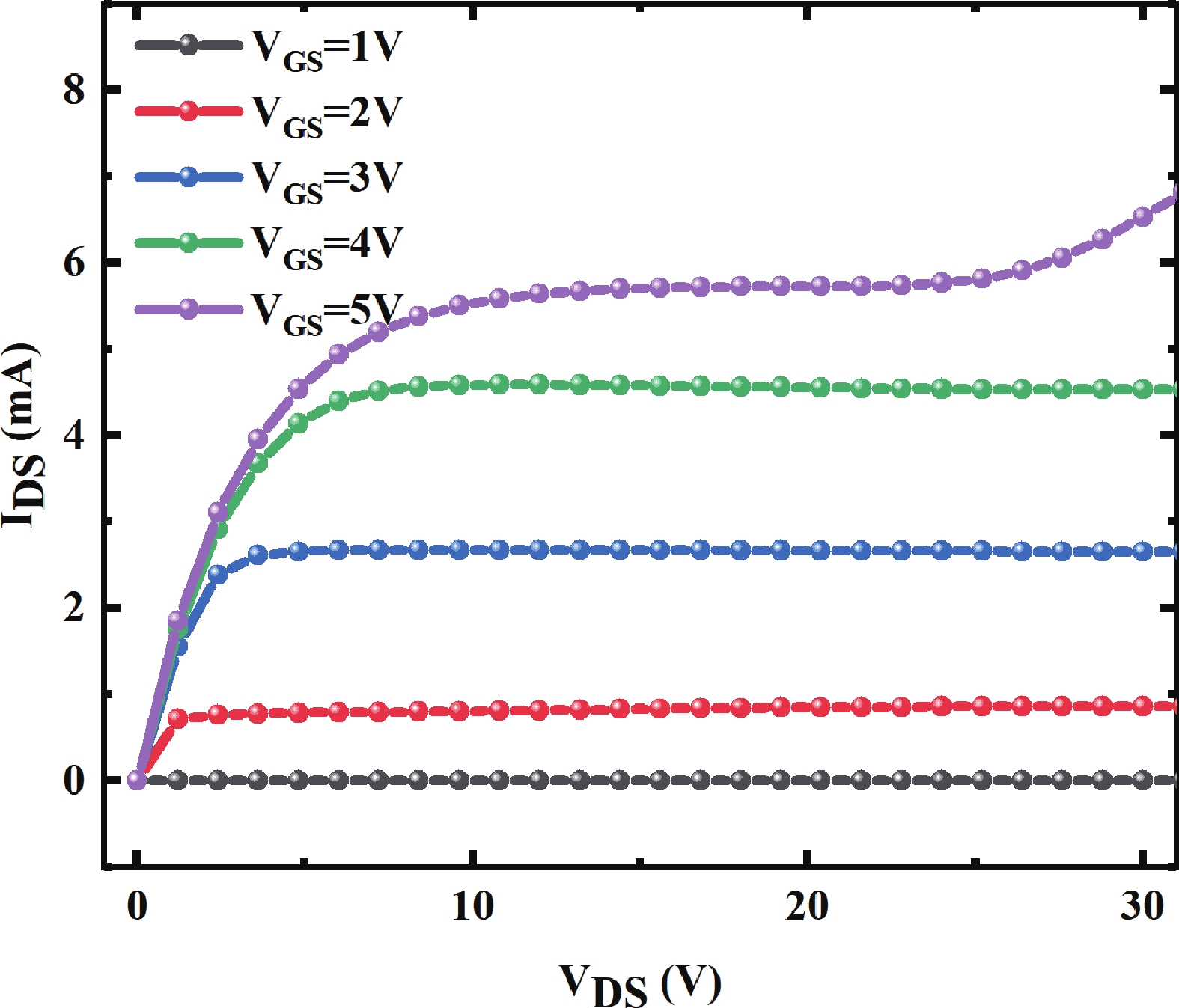
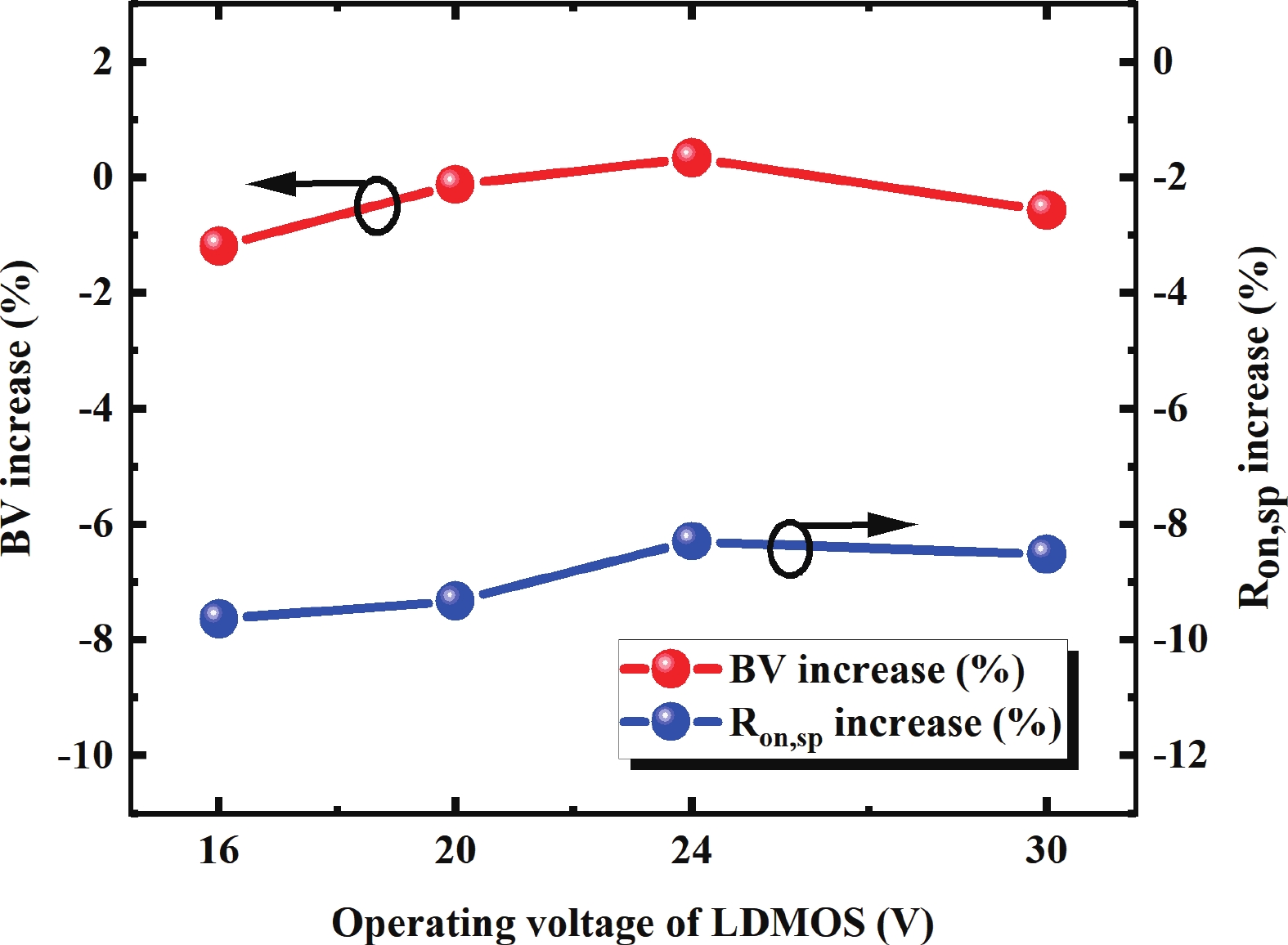
To improve the breakdown voltage (BV)−specific on-resistance (Ron,sp) trade-off and enhance manufacturability, this article proposes a novel lateral diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor (LDMOS) structure that features a split gate and split contact field plate (CFP). This novel structure requires no additional bias voltages, masks, or process steps, making it fully compatible with the bipolar-CMOS-DMOS (BCD) process flow. The physical mechanisms are elucidated through Technology computer-aided design (TCAD) simulations. In the on-state, the positively biased split gate forms an accumulation layer at the drift region surface, thereby reducing Ron,sp. In the off-state, both the split gate and split CFP introduce additional electric-field peaks that smooth the lateral electric field, thus preserving a high BV. Compared with the conventional CFP-LDMOS, the proposed CFP-LDMOS achieves an 8.52% reduction in Ron,sp without compromising BV, leading to an 8.07% improvement in the figure of merit (FOM). Notably, the proposed structure can be extended to LDMOS devices across different voltage levels within BCD platforms, demonstrating its broad applicability. -
References
[1] Duan B X, Cao Z, Yuan X, et al. New superjunction LDMOS breaking silicon limit by electric field modulation of buffered step doping. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2015, 36(1): 47 doi: 10.1109/LED.2014.2366298[2] Kaushal K N, Mohapatra N R. Unified theory of the capacitance behavior in LDMOS devices. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2022, 69(1): 39 doi: 10.1109/TED.2021.3131302[3] Chen S Y, Liao B, Dong J C, et al. Study on 20 V LDMOS with stepped-gate-oxide structure for PMIC applications: Design, fabrication, and characterization. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2022, 69(2): 878 doi: 10.1109/TED.2021.3131922[4] Ma J, Zhang L, Gu Y, et al. 200 V all-SiC floating gate driver process platform on 4H-SiC P-epi/N+ substate for high-temperature applications. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2024, 71(8): 5138 doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3418297[5] Williams R K, Darwish M N, Blanchard R A, et al. The trench power MOSFET: Part II: Application specific VDMOS, LDMOS, packaging, and reliability. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2017, 64(3): 692 doi: 10.1109/TED.2017.2655149[6] Chuang P J, Saadat A, Ghazvini S, et al. Determining the performance limits of LDMOS with three common types of field oxides. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2024, 71(4): 2315 doi: 10.1109/TED.2024.3370133[7] Disney D, Letavic T, Trajkovic T, et al. High-voltage integrated circuits: History, state of the art, and future prospects. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2017, 64(3): 659 doi: 10.1109/TED.2016.2631125[8] Kaushal K N, Mohapatra N R. A zero-cost technique to improve ON-state performance and reliability of power LDMOS transistors. IEEE J Electron Devices Soc, 2021, 9: 334 doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2021.3059854[9] Wei J, Dai K W, Luo X R, et al. Analyses and experiments of ultralow specific on-resistance LDMOS with integrated diodes. IEEE J Electron Devices Soc, 2021, 9: 1161 doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2021.3114738[10] Liu S Y, Ye R, Sun W F, et al. A novel lateral DMOS transistor with H-shape shallow-trench-isolation structure. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2018, 65(11): 5218 doi: 10.1109/TED.2018.2871501[11] Jin F, Liu D H, Xing J J, et al. Best-in-class LDMOS with ultra-shallow trench isolation and p-buried layer from 18V to 40V in 0.18μm BCD technology. 2017 29th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and IC’s (ISPSD), 2017: 295[12] Wei L, Chao C, Singh U, et al. A novel contact field plate application in drain-extended-MOSFET transistors. 2017 29th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and IC’s (ISPSD), 2017: 335[13] Hébert F, Parvarandeh P, Li M, et al. Building blocks of past, present and future BCD technologies. 2021 33rd International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs (ISPSD), 2021: 11[14] Yu S X, Shao W H, Chen R S, et al. Design and simulation optimization of an ultra-low specific on-resistance LDMOS device. IEEE J Electron Devices Soc, 2024, 12: 14 doi: 10.1109/JEDS.2023.3337341[15] Patel R, Mohapatra N R. Novel step field plate RF LDMOS transistor for improved BVDS-Ron tradeoff and RF performance. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2022, 69(8): 4401 doi: 10.1109/TED.2022.3182296[16] Hara K, Kakegawa T, Wada S, et al. Low on-resistance high voltage thin layer SOI LDMOS transistors with stepped field plates. 2017 29th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and IC’s (ISPSD), 2017: 307[17] Mori T, Fujii H, Kubo S, et al. Investigation into HCl improvement by a split-reeessed-gate structure in an STI-based nLDMOSFET. 2017 29th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and IC’s (ISPSD), 2017: 459[18] Ferrara A, Heringa A, Boksteen B K, et al. The boost transistor: A field plate controlled LDMOST. 2015 27th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices & IC’s (ISPSD), 2015: 165[19] Wei T. LDMOS of 34mΩ-cm2 on-resistance with 700V breakdown voltage. 2024 36th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs (ISPSD), 2024: 398[20] Hölke A. Field plate engineering for free metal routing over lateral HV devices. 2024 36th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs (ISPSD), 2024: 450[21] Zhang C W, Guo H J, Chen Z X, et al. Super field plate technique that can provide charge balance effect for lateral power devices without occupying drift region. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2020, 67(5): 2218 doi: 10.1109/TED.2020.2981264 -
Proportional views




 Yiting Ye got her BS degree from Central South University in 2024. Now she is a Master student at Zhejiang University under the supervision of Prof. Kai Xu. Her research focuses on lateral diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor (LDMOS) transistors.
Yiting Ye got her BS degree from Central South University in 2024. Now she is a Master student at Zhejiang University under the supervision of Prof. Kai Xu. Her research focuses on lateral diffused metal-oxide-semiconductor (LDMOS) transistors. Kai Xu got his PhD degree in 2017 at the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology. Then he went to University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign as a postdoc. In October 2021, he joined ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center as independent principal investigator. His research interests include semiconductor power devices and integration, intelligent manufacturing of integrated circuits and heterogeneous integration.
Kai Xu got his PhD degree in 2017 at the National Center for Nanoscience and Technology. Then he went to University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign as a postdoc. In October 2021, he joined ZJU-Hangzhou Global Scientific and Technological Innovation Center as independent principal investigator. His research interests include semiconductor power devices and integration, intelligent manufacturing of integrated circuits and heterogeneous integration.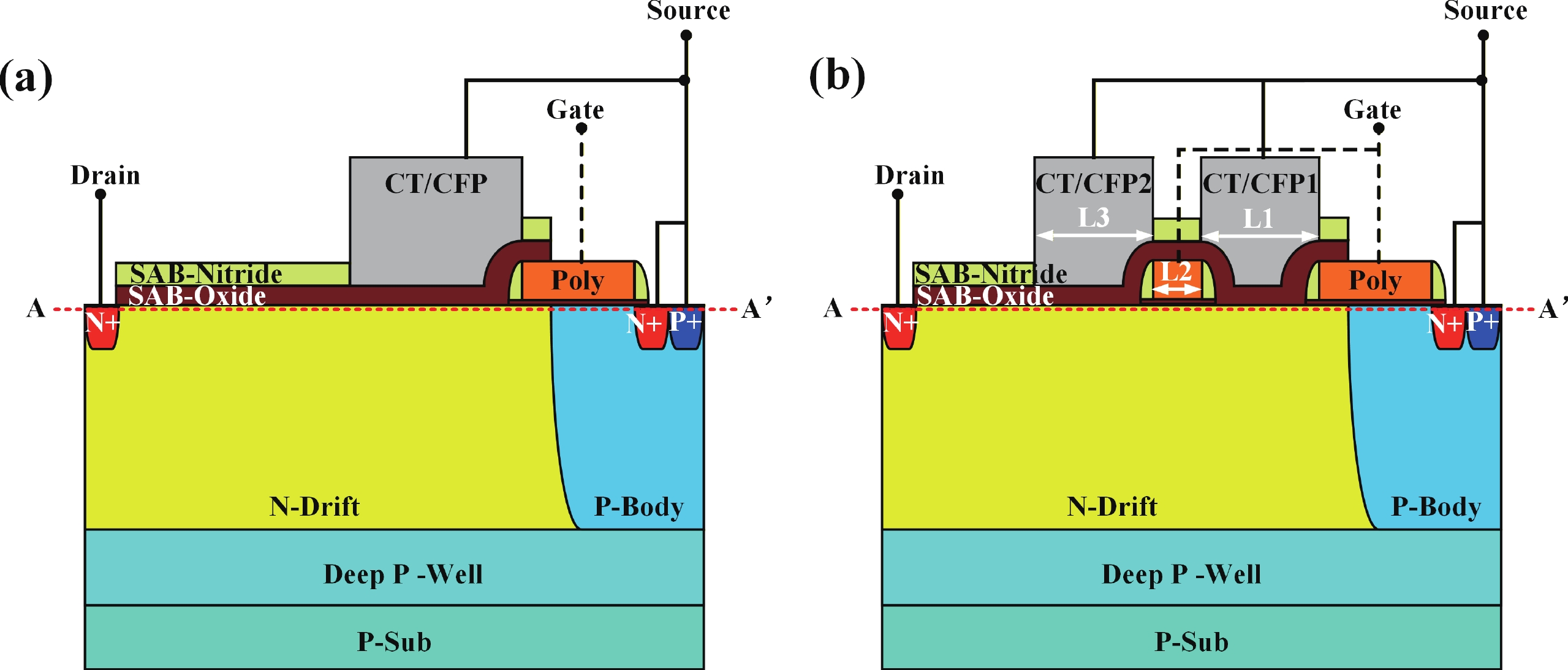
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: