| Citation: |
Qian Xu, Jie Qiu, Mengyang Liu, Dongzi Yang, Tingpan Lan, Jie Cao, Yingfen Wei, Hao Jiang, Ming Wang. Back-gate-tuned organic electrochemical transistor with temporal dynamic modulation for reservoir computing[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2026, 47(1): 012802. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25090001
****
Q Xu, J Qiu, M Y Liu, D Z Yang, T P Lan, J Cao, Y F Wei, H Jiang, and M Wang, Back-gate-tuned organic electrochemical transistor with temporal dynamic modulation for reservoir computing[J]. J. Semicond., 2026, 47(1): 012802 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25090001
|
Back-gate-tuned organic electrochemical transistor with temporal dynamic modulation for reservoir computing
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/25090001
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.25090001
More Information-
Abstract
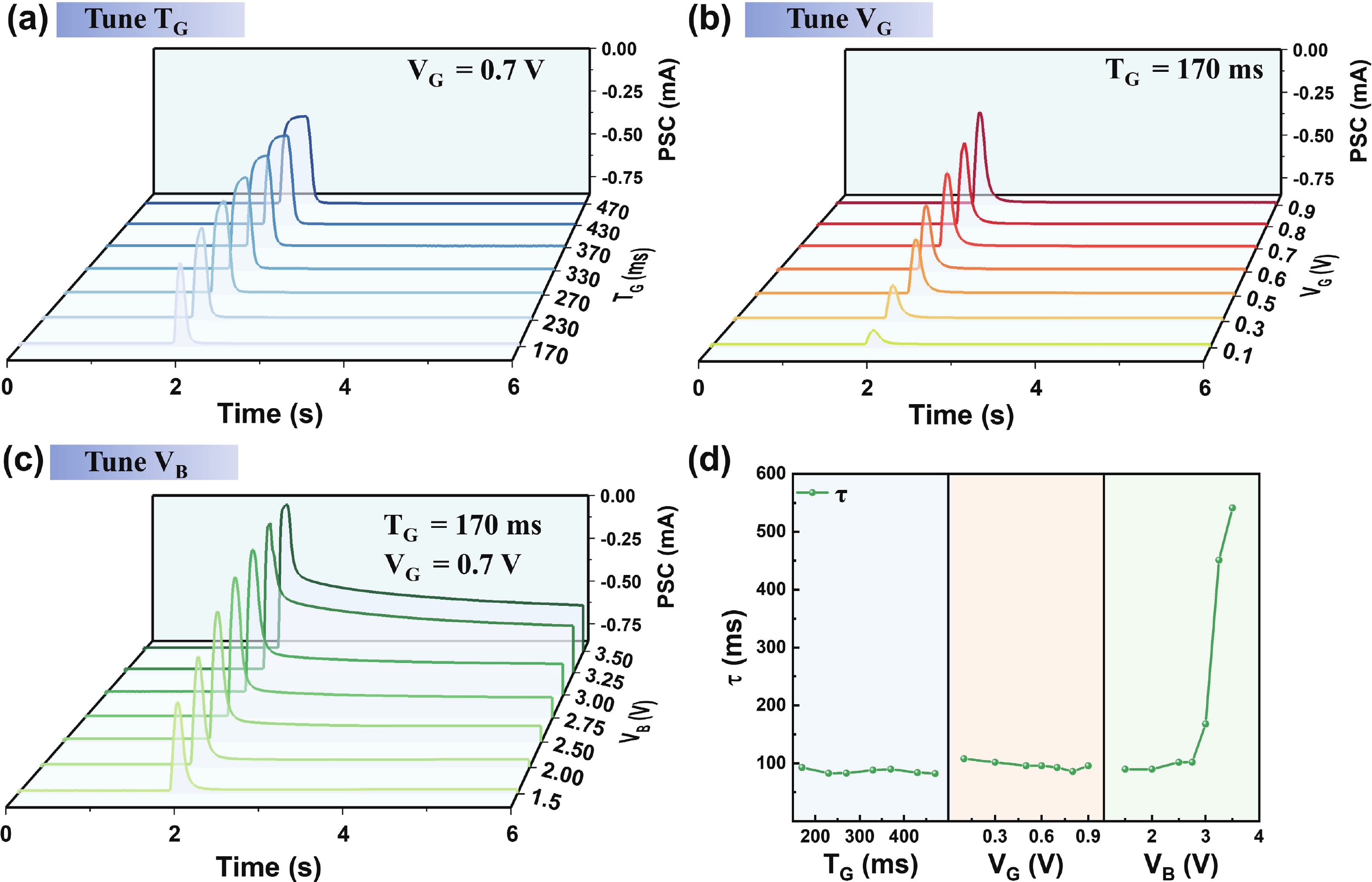
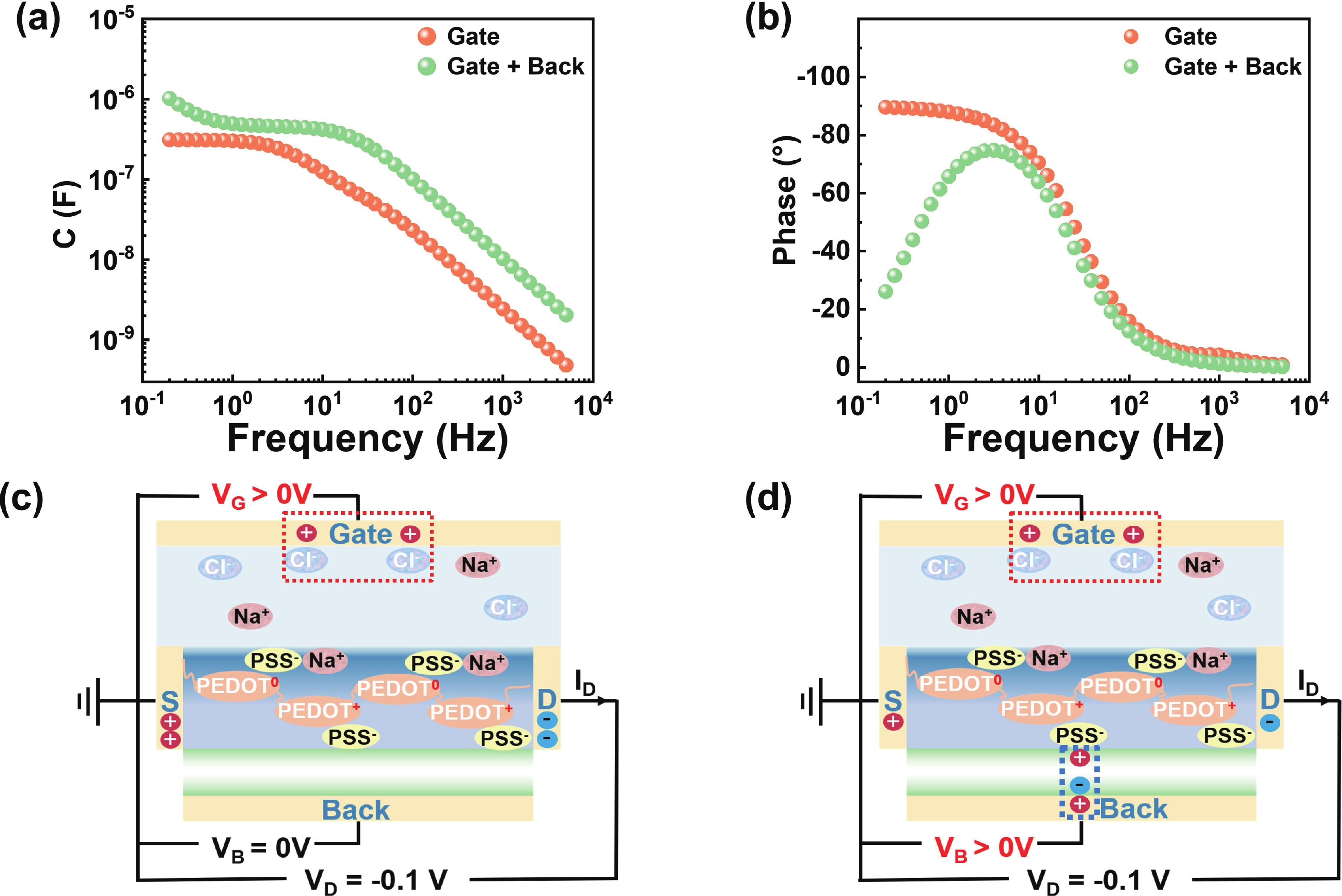
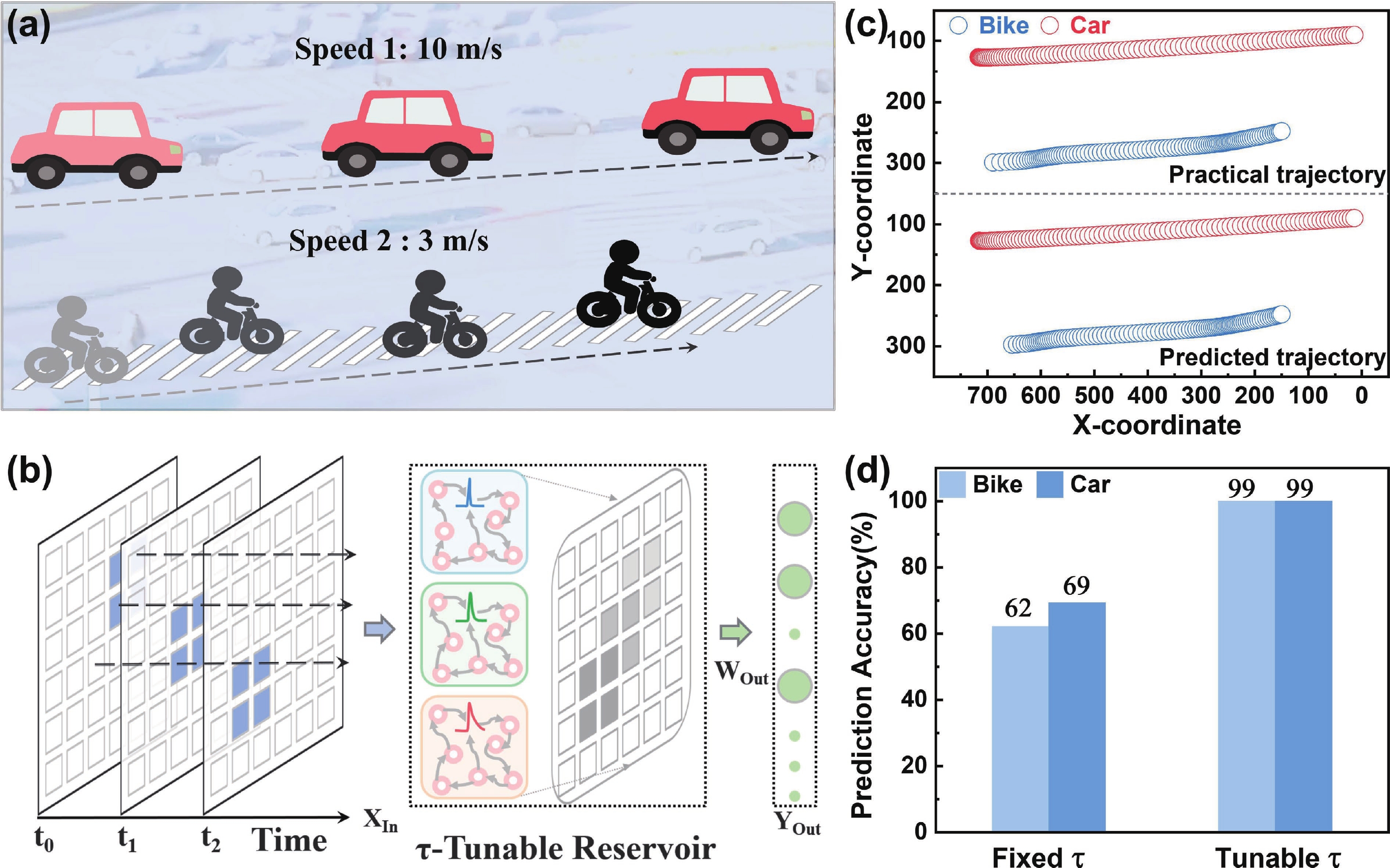
Organic electrochemical transistor (OECT) devices demonstrate great promising potential for reservoir computing (RC) systems, but their lack of tunable dynamic characteristics limits their application in multi-temporal scale tasks. In this study, we report an OECT-based neuromorphic device with tunable relaxation time (τ) by introducing an additional vertical back-gate electrode into a planar structure. The dual-gate design enables τ reconfiguration from 93 to 541 ms. The tunable relaxation behaviors can be attributed to the combined effects of planar-gate induced electrochemical doping and back-gate-induced electrostatic coupling, as verified by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis. Furthermore, we used the τ-tunable OECT devices as physical reservoirs in the RC system for intelligent driving trajectory prediction, achieving a significant improvement in prediction accuracy from below 69% to 99%. The results demonstrate that the τ-tunable OECT shows a promising candidate for multi-temporal scale neuromorphic computing applications. -
References
[1] Zhao M R, Gao B, Tang J S, et al. Reliability of analog resistive switching memory for neuromorphic computing. Appl Phys Rev, 2020, 7(1): 011301 doi: 10.1063/1.5124915[2] Zhang Y H, Qu P, Ji Y, et al. A system hierarchy for brain-inspired computing. Nature, 2020, 586(7829): 378 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2782-y[3] Chen R Q, Yang H Z, Li R Y, et al. Thin-film transistor for temporal self-adaptive reservoir computing with closed-loop architecture. Sci Adv, 2024, 10(7): eadl1299 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adl1299[4] Yan M, Huang C, Bienstman P, et al. Emerging opportunities and challenges for the future of reservoir computing. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 2056 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45187-1[5] Zhong Y N, Tang J S, Li X Y, et al. Dynamic memristor-based reservoir computing for high-efficiency temporal signal processing. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 408 doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20692-1[6] Liang X P, Tang J S, Zhong Y N, et al. Physical reservoir computing with emerging electronics. Nat Electron, 2024, 7(3): 193 doi: 10.1038/s41928-024-01133-z[7] Xiang S Y, Han Y N, Song Z W, et al. A review: Photonics devices, architectures, and algorithms for optical neural computing. J Semicond, 2021, 42(2): 023105 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/42/2/023105[8] Li Y, Cao J, Yu J, et al. Biomemristor reservoir computing with multi-value mask for improving recognition performance. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2024, 45(9): 1657 doi: 10.1109/LED.2024.3424781[9] Liu K Q, Zhang T, Dang B J, et al. An optoelectronic synapse based on α-In2Se3 with controllable temporal dynamics for multimode and multiscale reservoir computing. Nat Electron, 2022, 5(11): 761 doi: 10.1038/s41928-022-00847-2[10] Cucchi M, Gruener C, Petrauskas L, et al. Reservoir computing with biocompatible organic electrochemical networks for brain-inspired biosignal classification. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(34): eabh0693 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abh0693[11] Ghazal M, Kumar A, Garg N, et al. Neuromorphic signal classification using organic electrochemical transistor array and spiking neural simulations. IEEE Sens J, 2024, 24(6): 9104 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3353307[12] Rivnay J, Inal S, Salleo A, et al. Organic electrochemical transistors. Nat Rev Mater, 2018, 3(2): 17086 doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.86[13] Gkoupidenis P, Zhang Y, Kleemann H, et al. Organic mixed conductors for bioinspired electronics. Nat Rev Mater, 2023, 9(2): 134 doi: 10.1038/s41578-023-00622-5[14] Xu Q, Chen J W, Li Y, et al. Fully printed dual-gate organic electrochemical synaptic transistor with neurotransmitter-mediated plasticity. IEEE Electron Device Lett, 2024, 45(1): 104 doi: 10.1109/LED.2023.3335970[15] Cheng M, Xie Y F, Wang J Y, et al. Neurotransmitter-mediated artificial synapses based on organic electrochemical transistors for future biomimic and bioinspired neuromorphic systems. J Semicond, 2025, 46(1): 011604 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/24090013[16] Wang S J, Chen X, Zhao C, et al. An organic electrochemical transistor for multi-modal sensing, memory and processing. Nat Electron, 2023, 6(4): 281 doi: 10.1038/s41928-023-00950-y[17] Liu R P, He Y F, Zhu X Y, et al. Hardware-feasible and efficient N-type organic neuromorphic signal recognition via reservoir computing. Adv Mater, 2024, 37(3): 2409258 doi: 10.1002/adma.202409258[18] He Y F, Ge Z L, Li Z Y, et al. All-polymer organic electrochemical synaptic transistor with controlled ionic dynamics for high-performance wearable and sustainable reservoir computing. Adv Funct Materials, 2024, 35(8): 2415595 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202415595[19] Gao C S, Liu D, Xu C H, et al. Toward grouped-reservoir computing: Organic neuromorphic vertical transistor with distributed reservoir states for efficient recognition and prediction. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 740 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44942-8[20] Yin Y Y, Wang S C, Weng R H, et al. A dual-modal memory organic electrochemical transistor implementation for reservoir computing. Small Sci, 2024, 5(1): 2400451 doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400415[21] Han C G, Kim M Y, Park S J, et al. Reconfigurable organic electrochemical transistors with high dynamic ranges for fully integrated physical reservoir computing. Adv Funct Materials, 2025, 35(26): 2423814 doi: 10.1002/adfm.202423814[22] Yang Y, Cui H Y, Ke S, et al. Reservoir computing based on electric-double-layer coupled InGaZnO artificial synapse. Appl Phys Lett, 2023, 122(4): 043508 doi: 10.1063/5.0137647[23] Yang T Z, Wu Q, Dai F H, et al. Understanding, optimizing, and utilizing nonideal transistors based on organic or organic hybrid semiconductors. Adv Funct Materials, 2020, 30(20): 1903889 doi: 10.1002/adfm.201903889[24] Ohayon D, Druet V, Inal S. A guide for the characterization of organic electrochemical transistors and channel materials. Chem Soc Rev, 2023, 52(3): 1001 doi: 10.1039/D2CS00920J[25] Tjhe D H L, Ren X, Jacobs I E, et al. Non-equilibrium transport in polymer mixed ionic-electronic conductors at ultrahigh charge densities. Nat Mater, 2024, 23(12): 1712 doi: 10.1038/s41563-024-01953-6 -
Proportional views




 Qian Xu got her B.S. degree from Hangzhou Dianzi University in 2019 and M.S. degree from Xiamen University in 2022. Now she is a PhD candidate at Fudan University. Her research focuses on the fabrication and application of organic electrochemical transistor neuromorphic devices.
Qian Xu got her B.S. degree from Hangzhou Dianzi University in 2019 and M.S. degree from Xiamen University in 2022. Now she is a PhD candidate at Fudan University. Her research focuses on the fabrication and application of organic electrochemical transistor neuromorphic devices. Ming Wang is currently an Associate Professor at the College of Integrated Circuits and Micro-Nano Electronics, Fudan University, China. He received his Ph.D. degree in Microelectronics from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2015 and received his B.S. degree in Electronic Science and Technology from Jilin University (China) in 2009. His current research interests focus on memristors, neuromorphic computing, and flexible electronics.
Ming Wang is currently an Associate Professor at the College of Integrated Circuits and Micro-Nano Electronics, Fudan University, China. He received his Ph.D. degree in Microelectronics from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences in 2015 and received his B.S. degree in Electronic Science and Technology from Jilin University (China) in 2009. His current research interests focus on memristors, neuromorphic computing, and flexible electronics.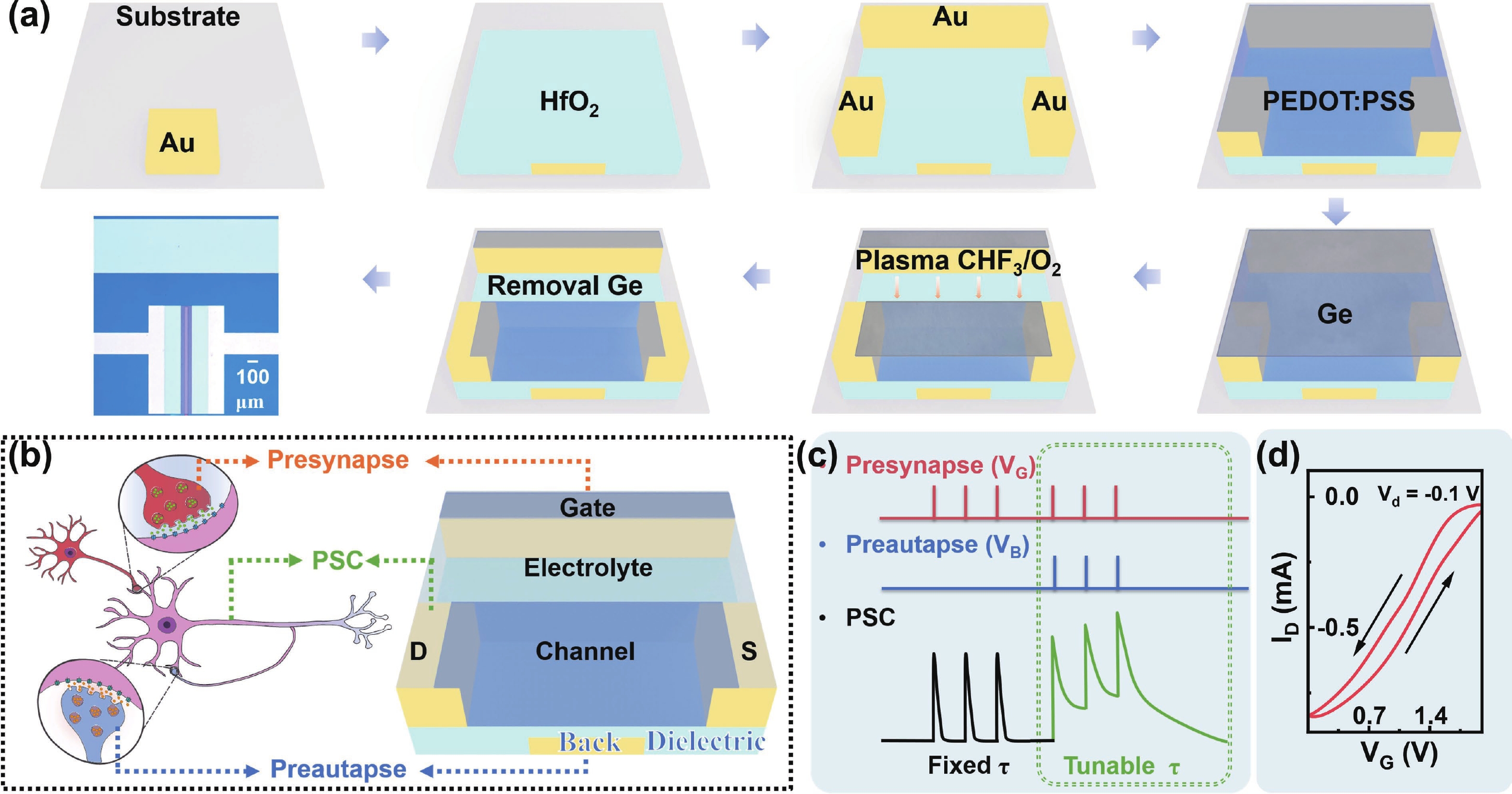
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: