| Citation: |
Yanlong Li, Hao Sun, Zhao Zhao, Yingli Shi, Guozhen Shen. Experimental and simulated studies on thin-film thermoelectric generator insensitive to tensile strain[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2026, In Press. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25110021
****
Y L Li, H Sun, Z Zhao, Y L Shi, and G Z Shen, Experimental and simulated studies on thin-film thermoelectric generator insensitive to tensile strain[J]. J. Semicond., 2026, accepted doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25110021
|
Experimental and simulated studies on thin-film thermoelectric generator insensitive to tensile strain
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/25110021
CSTR: 32376.14.1674-4926.25110021
More Information-
Abstract
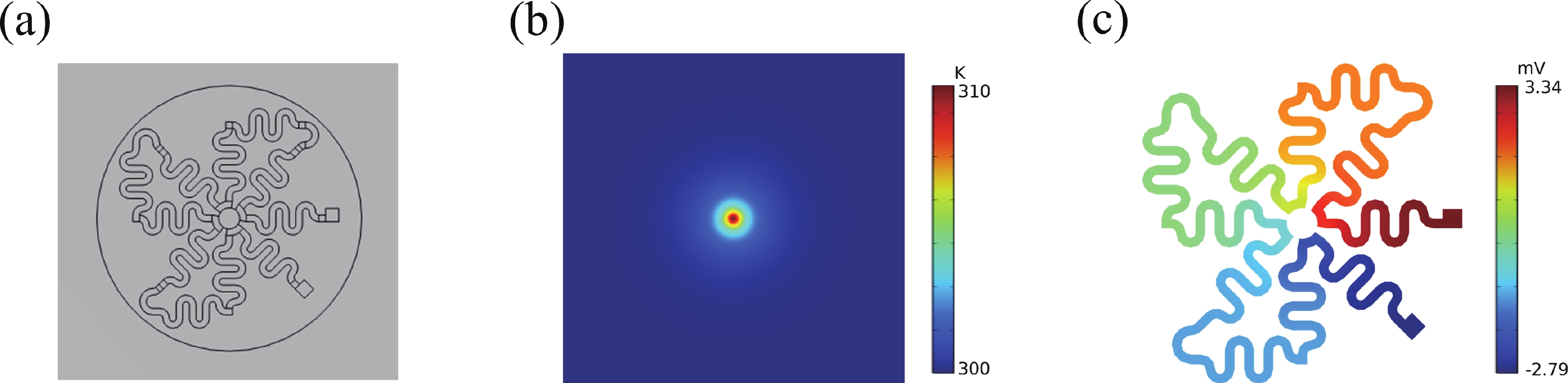
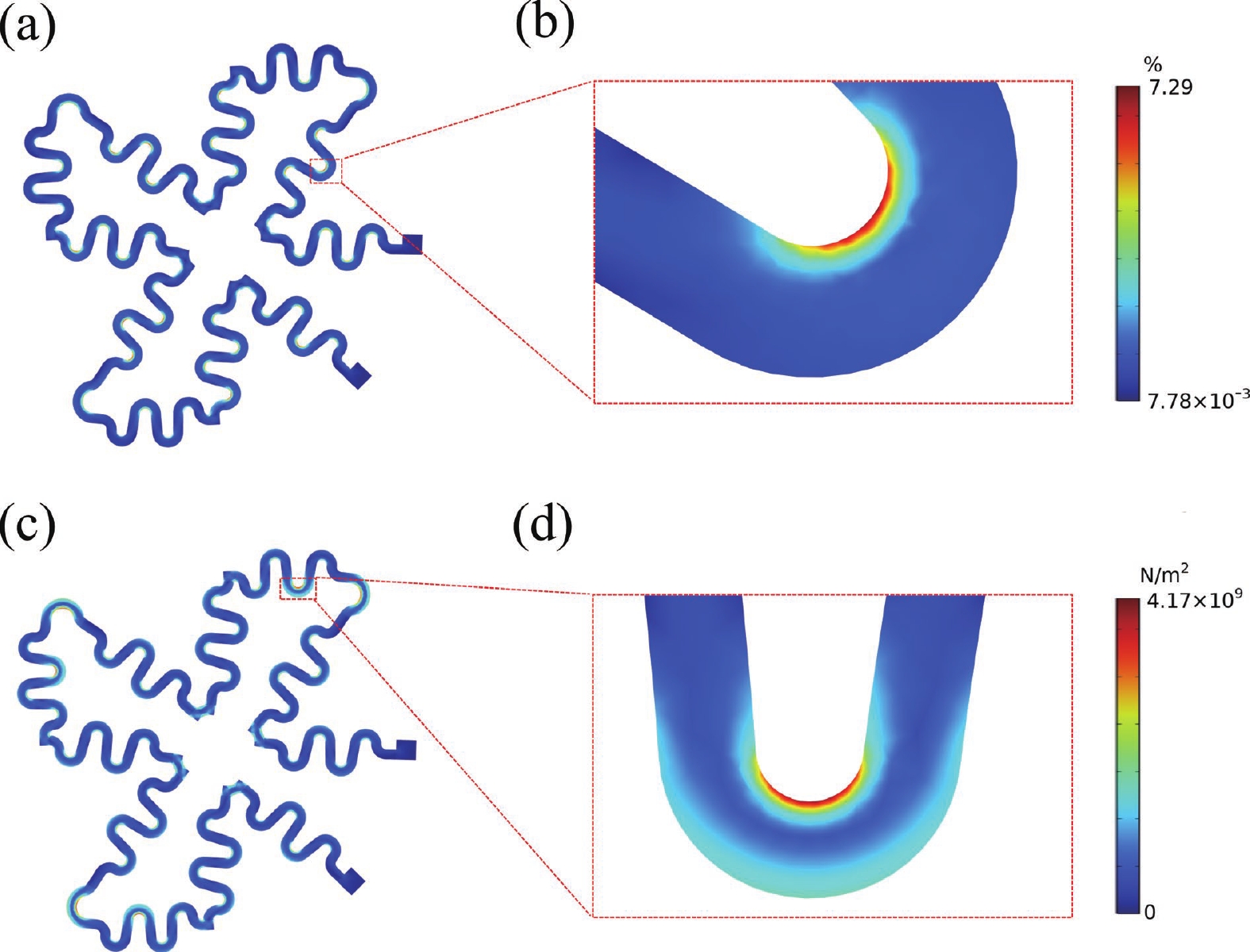
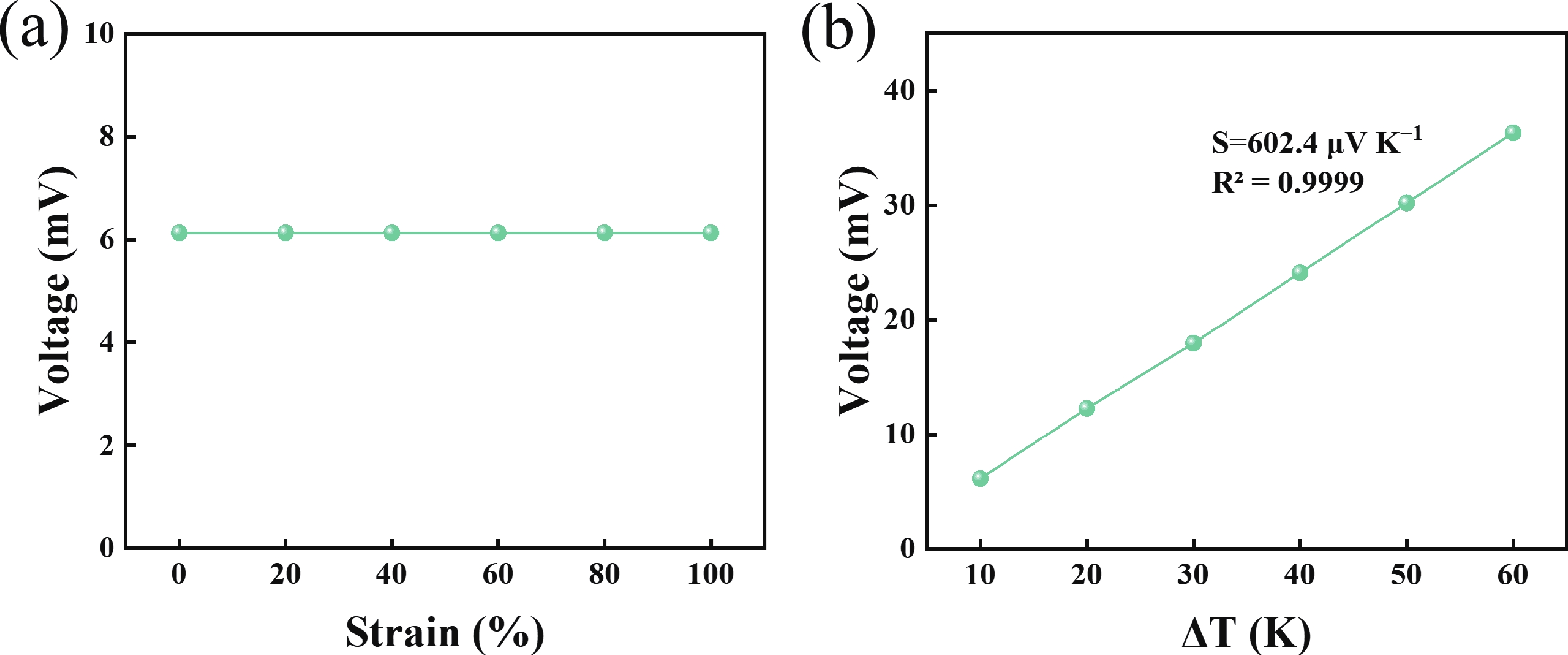
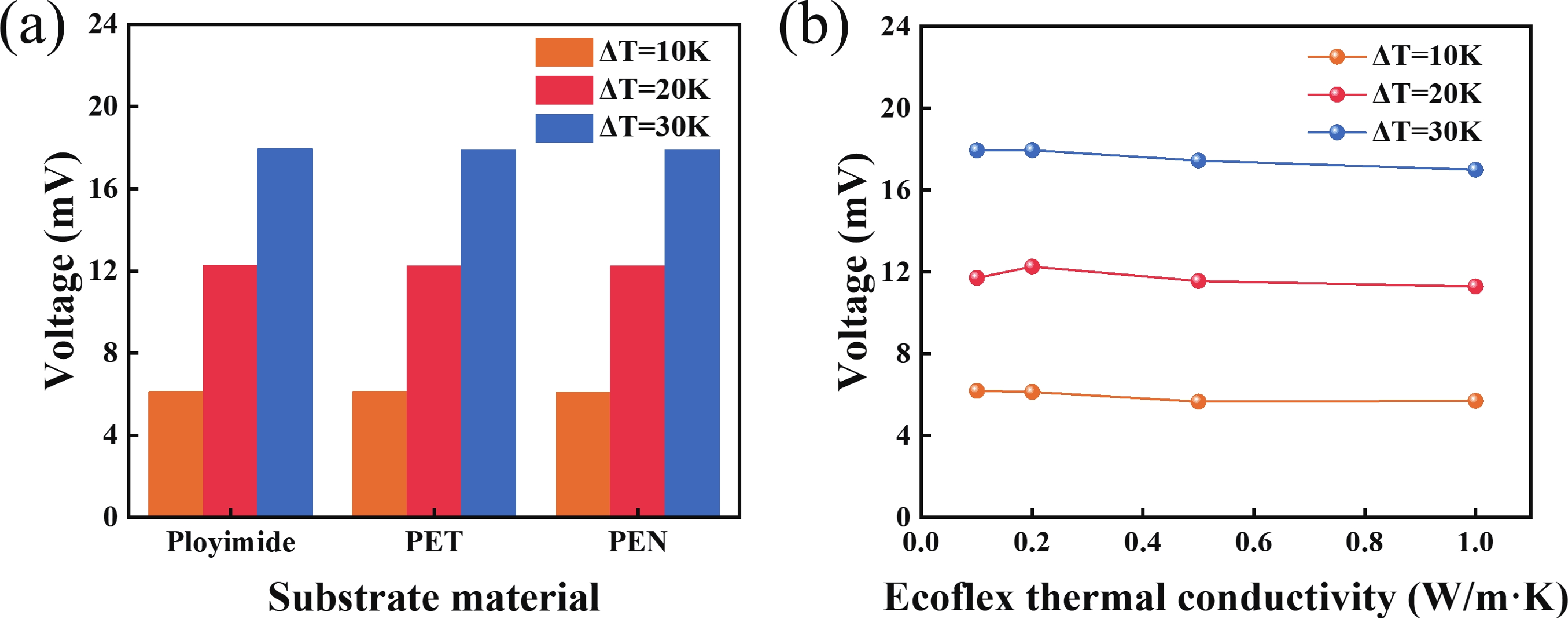
Thermoelectric power generation has attracted significant interest for its capability to directly convert thermal energy into electricity. Among various configurations, thin-film thermoelectric generators (TEGs) stand out due to their lightweight nature and facile integration, offering promising applications in waste heat recovery and wearable electronics. However, the performance of such devices under complex mechanical conditions, particularly under biaxial tensile strain, remains underexplored. In this work, we designed and fabricated a thin-film TEG insensitive to tensile strain and performed a parametric analysis using validated 3D numerical simulations to evaluate the effects of environmental conditions, material properties, and geometric parameters. Notably, the designed device maintained stable electrical performance under various biaxial tensile strains. Owing to its miniature and thin profile, variations in any component of the generator significantly affected its electrical performance. The results indicated that reduced thermal conductivity of the substrate and Ecoflex layer, as well as a thinner substrate, enhance the output voltage. Furthermore, longer thermoelectric legs within a certain range contributed to higher output voltage. Higher output voltage was more readily achieved when the inner radius length was close to the radius of the heat source. This work provides valuable insights for the development of high-performance compliant TEGs applicable in dynamic mechanical environments, such as complex stretching in the back and shoulder–elbow regions induced by human motion. -
References
[1] Pan X Z, Shao T M, Zheng X Z, et al. Energy and sustainable development nexus: A review. Energy Strategy Rev, 2023, 47: 101078 doi: 10.1016/j.esr.2023.101078[2] Duggan J E. Recent progress in sustainable energy systems development: Investment, operations, and decarbonization. Curr Sustain Energy Rep, 2025, 12(1): 1 doi: 10.1007/s40518-024-00248-3[3] Nama Manjunatha K, Paul S, Sahu S, et al. Introduction to advances in emerging thermoelectric materials and devices. Mater Adv, 2025, 6(9): 2714 doi: 10.1039/D5MA90026C[4] Miao L, Zhu S J, Liu C Y, et al. Comfortable wearable thermoelectric generator with high output power. Nat Commun, 2024, 15: 8516 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52841-1[5] Zhang S, Liu Z K, Wu Z H, et al. Boosting self-powered wearable thermoelectric generator with solar absorber and radiative cooler. Nano Energy, 2024, 132: 110381 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2024.110381[6] Fan W S, An Z J, Liu F, et al. High-performance stretchable thermoelectric generator for self-powered wearable electronics. Adv Sci, 2023, 10(12): 2206397[7] Liu J, Liu Q T, Lin S P, et al. Wearable thermoelectric generators: Materials, structures, fabrications, and applications. Phys Status Solidi RRL, 2023, 17(7): 2200502 doi: 10.1002/pssr.202200502[8] Zhang J, Zhang W H, Wei H X, et al. Flexible micro thermoelectric generators with high power density and light weight. Nano Energy, 2023, 105: 108023 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.108023[9] Tao H Y, Wang T L, Li D Y, et al. Preparation, properties, and applications of Bi2O2Se thin films: A review. J Semicond, 2023, 44(3): 031001 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/44/3/031001[10] Guo J, Feng Y R, Zhang J J, et al. Investigating the doping performance of an ionic dopant for organic semiconductors and thermoelectric applications. J Semicond, 2025, 46(8): 082801 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/25010027[11] Jiang Q H, Yu Z X, Zhang X Y, et al. Flexible polyvinylidene fluoride/multiwall carbon nanotube-based thermoelectric composite films with excellent environmental stability and enhanced power factor from ferroelectric polarization. Sci China Mater, 2025, 68(4): 1240 doi: 10.1007/s40843-024-3240-9[12] Kim S J, Lee H E, Choi H, et al. High-performance flexible thermoelectric power generator using laser multiscanning lift-off process. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(12): 10851 doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b05004[13] Zhang X, He D, Chen L, et al. Enhanced performance of n-type Ag2Se thin films via texture engineering. Sci China Mater, 2025, 68(5): 1630 doi: 10.1007/s40843-025-3294-1[14] Zhang Z L, Yang W Y, Wu B, et al. A Zn-doped Sb2Te3 flexible thin film with decoupled Seebeck coefficient and electrical conductivity via band engineering. Chem Sci, 2025, 16(8): 3638 doi: 10.1039/D4SC07793H[15] Yang D, Shi X L, Li M, et al. Flexible power generators by Ag2Se thin films with record-high thermoelectric performance. Nat Commun, 2024, 15: 923 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45092-7[16] Qiu G J, Li J, Ling Y F, et al. Carrier concentration and orientation optimization for high performance (Sb, Bi)2Te3 thermoelectric films via magnetron co-sputtering. J Alloys Compd, 2023, 950: 169916 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169916[17] Tao X D, Zheng Q F, Zeng C Y, et al. Cu- or Ag-containing Bi-Sb-Te for in-line roll-to-roll patterned thin-film thermoelectrics. Nat Commun, 2025, 16: 196 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55279-7[18] Song Y J, Yu H L, Ran Y J, et al. High-performance flexible wavy-structure thermoelectric generator based on (Bi, Sb)2Te3 films for energy harvesting. J Power Sources, 2024, 600: 234260 doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2024.234260[19] Guo Z P, Yu Y D, Zhu W, et al. Kirigami-based stretchable, deformable, ultralight thin-film thermoelectric generator for BodyNET application. Adv Energy Mater, 2022, 12(5): 2102993[20] Ren W, Sun Y, Zhao D L, et al. High-performance wearable thermoelectric generator with self-healing, recycling, and Lego-like reconfiguring capabilities. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(7): eabe0586 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abe0586[21] Yang Y, Hu H J, Chen Z Y, et al. Stretchable nanolayered thermoelectric energy harvester on complex and dynamic surfaces. Nano Lett, 2020, 20(6): 4445 doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c01225[22] Liu Y J, Wang X D, Hou S H, et al. Scalable-produced 3D elastic thermoelectric network for body heat harvesting. Nat Commun, 2023, 14: 3058 doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38852-4[23] Lv H C, Liang L R, Zhang Y C, et al. A flexible spring-shaped architecture with optimized thermal design for wearable thermoelectric energy harvesting. Nano Energy, 2021, 88: 106260 doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2021.106260[24] Ding W J, Shen X Y, Jin M, et al. Robust bendable thermoelectric generators enabled by elasticity strengthening. Nat Commun, 2024, 15: 9767 doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54084-6[25] Hu B X, Shi X L, Cao T Y, et al. High-performing flexible Mg3Bi2 thin-film thermoelectrics. Adv Sci, 2024, 11(44): 2409788[26] Shi X L, Cao T Y, Chen W Y, et al. Advances in flexible inorganic thermoelectrics. EcoEnergy, 2023, 1(2): 296 doi: 10.1002/ece2.17[27] Chen M R, Mao Z D, Ji Y R, et al. Bi2Te3-based flexible thermoelectrics. Mater Today Energy, 2024, 44: 101643 doi: 10.1016/j.mtener.2024.101643 -
Proportional views




 Yanlong Li got his Bs from Anhui University in 2024. Now he is a postgraduate student at Beijing Institute of Technology. His research focuses on flexible sensing and thermal control.
Yanlong Li got his Bs from Anhui University in 2024. Now he is a postgraduate student at Beijing Institute of Technology. His research focuses on flexible sensing and thermal control. Hao Sun got his Bs from Dalian University of Technology in 2025. Now he is a postgraduate student at Beijing Institute of Technology. His research focuses on flexible sensing and thermal control.
Hao Sun got his Bs from Dalian University of Technology in 2025. Now he is a postgraduate student at Beijing Institute of Technology. His research focuses on flexible sensing and thermal control. Zhao Zhao got his Ph.D. degree from Beihang University in 2022 and his Master degree in 2018 from Beijing University of Technology, and he obtained his B.S. degree in 2015 from Ocean University of China. He is now working at the China Special Equipment Inspection and Research Institute. His current research interests focus on flexible electronics, heat conduction and vibration analysis.
Zhao Zhao got his Ph.D. degree from Beihang University in 2022 and his Master degree in 2018 from Beijing University of Technology, and he obtained his B.S. degree in 2015 from Ocean University of China. He is now working at the China Special Equipment Inspection and Research Institute. His current research interests focus on flexible electronics, heat conduction and vibration analysis. Yingli Shi got his Ph.D. degree from Beihang University in 2020. He is currently an associate researcher / assistant professor at the School of Integrated Circuits and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT). His current research focuses on flexible integrated sensing and communication, and thermal management devices.
Yingli Shi got his Ph.D. degree from Beihang University in 2020. He is currently an associate researcher / assistant professor at the School of Integrated Circuits and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT). His current research focuses on flexible integrated sensing and communication, and thermal management devices. Guozhen Shen received his PhD degree in Chemistry from the University of Science and Technology of China. He is currently a professor at the School of Integrated Circuits and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), and the director of the Institute of Flexible Electronics and Intelligent Manufacturing. Before joining BIT, he worked at Hanyang University (Korea), National Institute for Materials Science (Japan), University of Southern California (US), and Huazhong University of Science and Technology (China), the Institute of Semiconductors, CAS (China). His current research focuses on flexible electronic devices for artificial intelligence and healthcare monitoring.
Guozhen Shen received his PhD degree in Chemistry from the University of Science and Technology of China. He is currently a professor at the School of Integrated Circuits and Electronics, Beijing Institute of Technology (BIT), and the director of the Institute of Flexible Electronics and Intelligent Manufacturing. Before joining BIT, he worked at Hanyang University (Korea), National Institute for Materials Science (Japan), University of Southern California (US), and Huazhong University of Science and Technology (China), the Institute of Semiconductors, CAS (China). His current research focuses on flexible electronic devices for artificial intelligence and healthcare monitoring.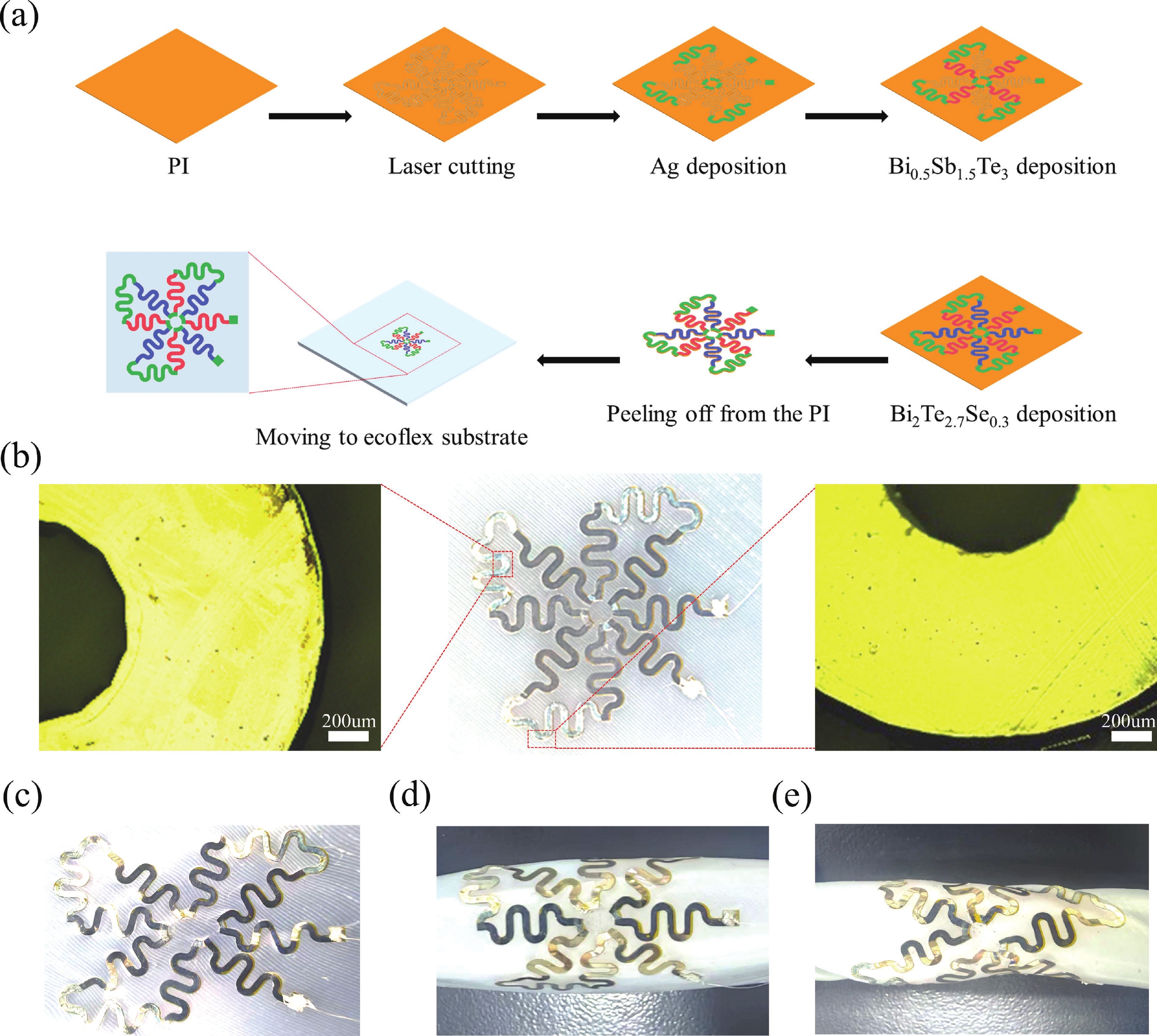
 DownLoad:
DownLoad: