| Citation: |
Jinpeng Shen, Xin'an Wang, Shan Liu, Shoucheng Li, Zhengkun Ruan. A voltage regulator system with dynamic bandwidth boosting for passive UHF RFID transponders[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(10): 105004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/10/105004
****
J P Shen, X A Wang, S Liu, S C Li, Z K Ruan. A voltage regulator system with dynamic bandwidth boosting for passive UHF RFID transponders[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(10): 105004. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/10/105004.
|
A voltage regulator system with dynamic bandwidth boosting for passive UHF RFID transponders
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/10/105004
More Information
-
Abstract
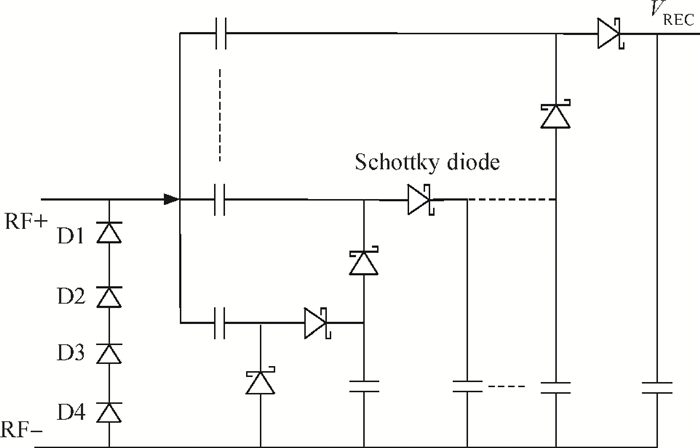
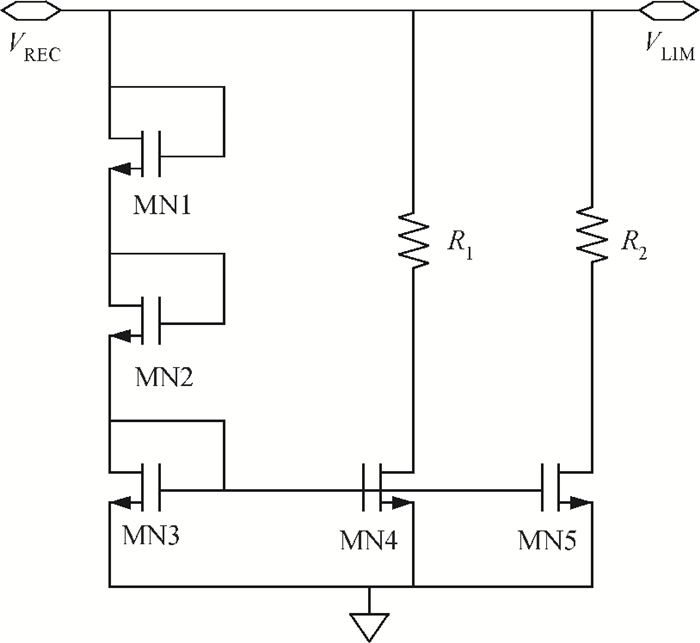
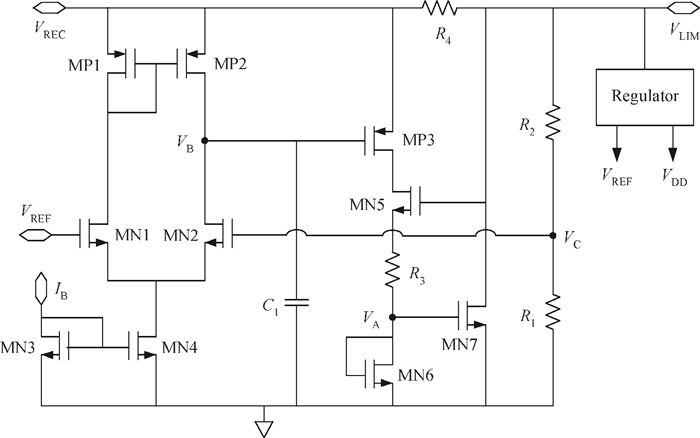
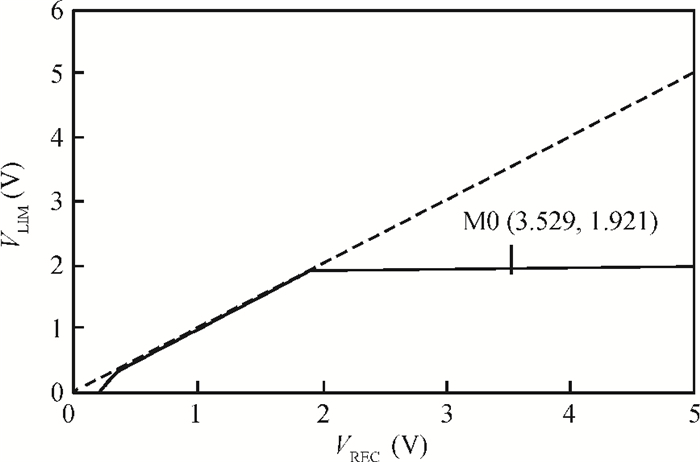
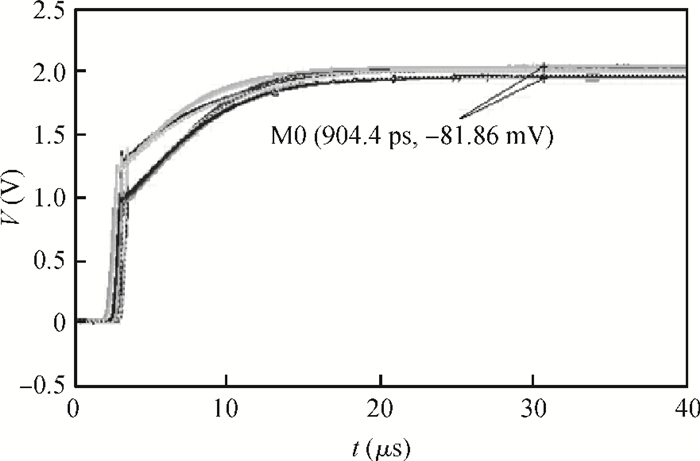
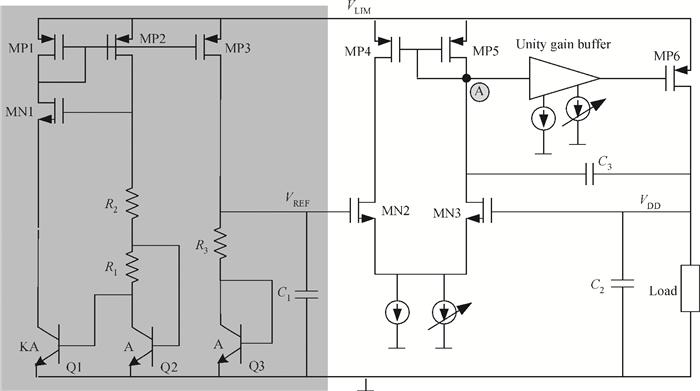
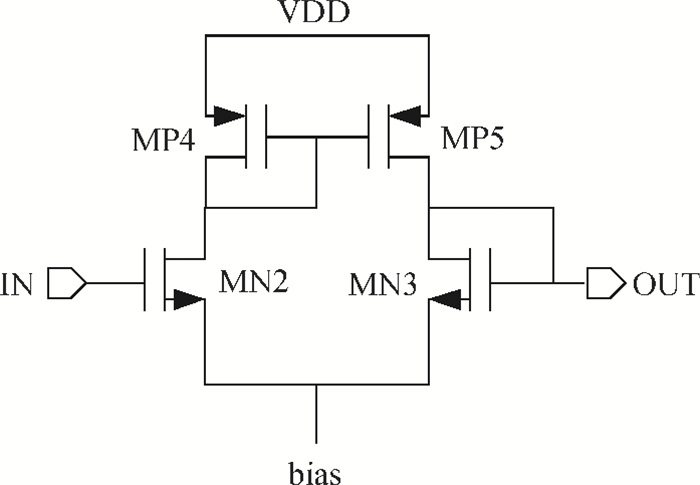
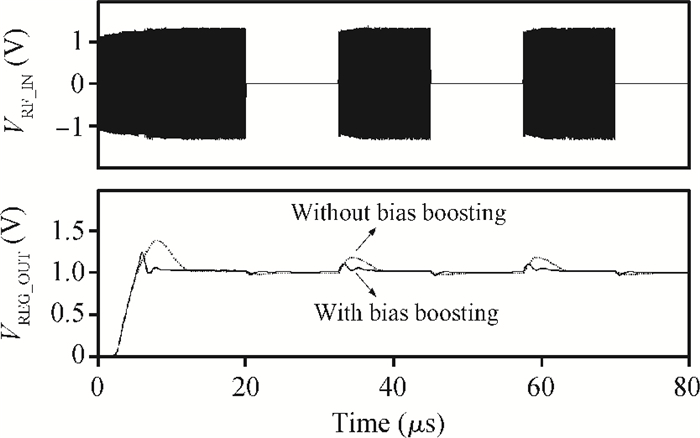
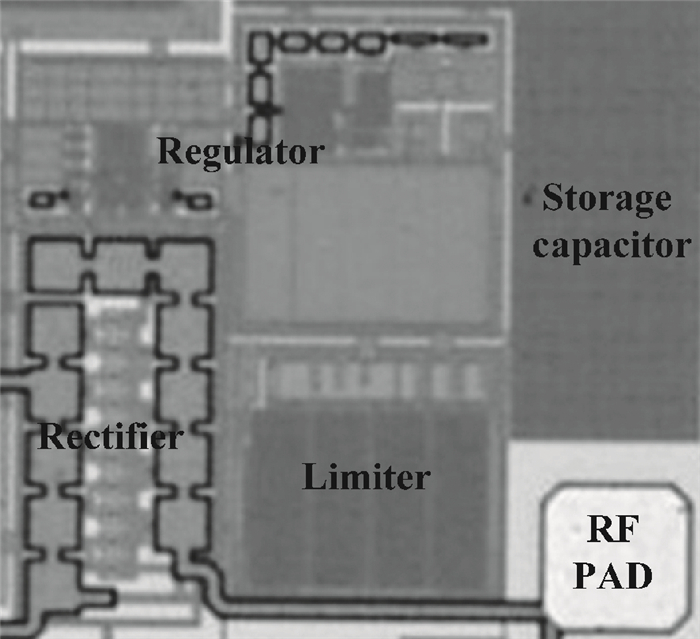
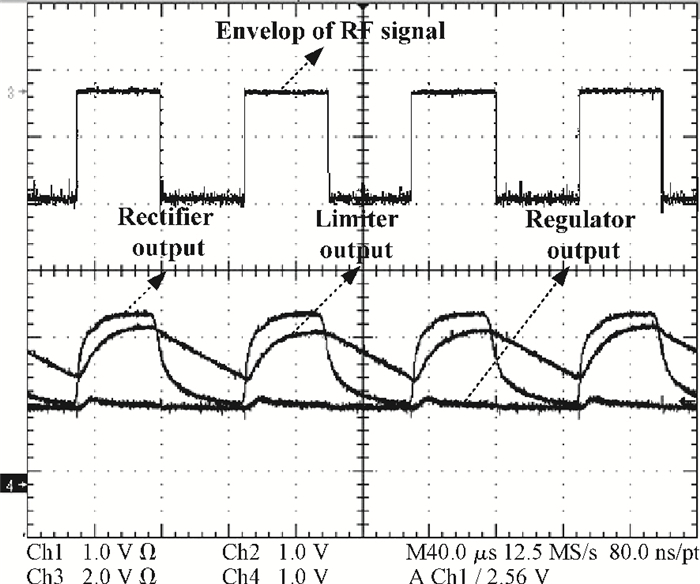
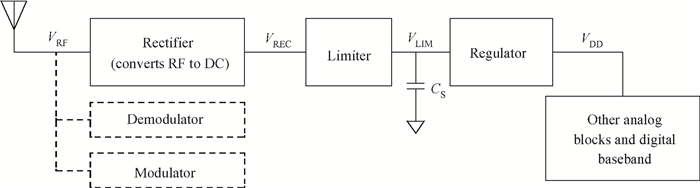
This paper presents a voltage regulator system for passive UHF RFID transponders, which contains a rectifier, a limiter, and a regulator. The rectifier achieves power by rectifying the incoming RF energy. Due to the huge variation of the rectified voltage, a limiter at the rectifier output is used to clamp the rectified voltage. In this paper, the design of a limiter circuit is discussed in detail, which can provide a stable limiting voltage with low sensitivity to temperature variation and process dispersion. The key aspect of the voltage regulator system is the dynamic bandwidth boosting in the regulator. By sensing the excess current that is bypassed in the limiter during periods of excess energy, the bias current as well as the bandwidth of the regulator are increased, the output supply voltage can recover quickly from line transients during the periods of no RF energy to a full blast of RF energy. This voltage regulator system is implemented in a 0.18 μm CMOS process. -
References
[1] Nakamoto H, Yamazaki D, Yamamoto T, et al. A passive UHF RF identification CMOS tag IC using ferroelectric RAM in 0.35μm technology. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2007, 42(1):101 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2006.886523[2] Karthaus U, Fischer M. Fully integrated passive UHF RFID transponder IC with 16.7μ W minimum RF input power. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2003, 38(10):1602 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2003.817249[3] Dobkin D M. The RF in RFID:passive UHF RFID in practice. USA:Newnes, 2007 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA87276886?l=en[4] Finkenzeller K. RFID handbook:fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards and identification. 2nd ed. Hoboken, NJ:Wiley, 2003 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA6360268X[5] Barnett R E, Liu J, Lazar S. A RF to DC voltage conversion model for multi-stage rectifiers in UHF RFID transponders. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2009, 44(2):354 doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2008.2010991[6] Zong H Q, Shen J P, Liu S, et al. An ultra low power ASK demodulator for passive UHF RFID tag. IEEE 9th International Conference on ASIC (ASICON), 2011:637 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6157286/?arnumber=6157286&punumber%3D6153219[7] Lee J W, Vo D H T, Huynh Q H, et al. A fully integrated HF-band passive RFID tag IC using 0.18-μm CMOS technology for low-cost security applications. IEEE Trans Industrial Electron, 2011, 58:2531 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2060460[8] Duong Q T, Vo D H T, Huynh Q H, et al. High dynamic range power regulator design for UHF band near-field passive RFID tag chips. International SOC Design, 2009:112[9] Chung C, Kim Y H, Ki T H, et al. Fully integrated ultra-low-power passive UHF RFID transponder IC. IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), 2011:77 https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.ieee-art-000006141789[10] Tran N, Lee B, Lee J W. Development of long-range UHF-band RFID tag chip using Schottky diodes in standard CMOS technology. IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, 2007:281 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4266431/[11] Shen J P, Wang X A, Liu S, et al. Design and implementation of an ultra-low power passive UHF RFID tag. Journal of Semiconductors, 2012, 33(11):115011 doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/33/11/115011 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: