| Citation: |
Sudhansu Kumar Pati, Hemant Pardeshi, Godwin Raj, N Mohankumar, Chandan Kumar Sarkar. Flicker and thermal noise in an n-channel underlap DG FinFET in a weak inversion region[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2013, 34(2): 024002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/024002
****
S K Pati, H Pardeshi, G Raj, N Mohankumar, C K Sarkar. Flicker and thermal noise in an n-channel underlap DG FinFET in a weak inversion region[J]. J. Semicond., 2013, 34(2): 024002. doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/024002.
|
Flicker and thermal noise in an n-channel underlap DG FinFET in a weak inversion region
DOI: 10.1088/1674-4926/34/2/024002
More Information
-
Abstract
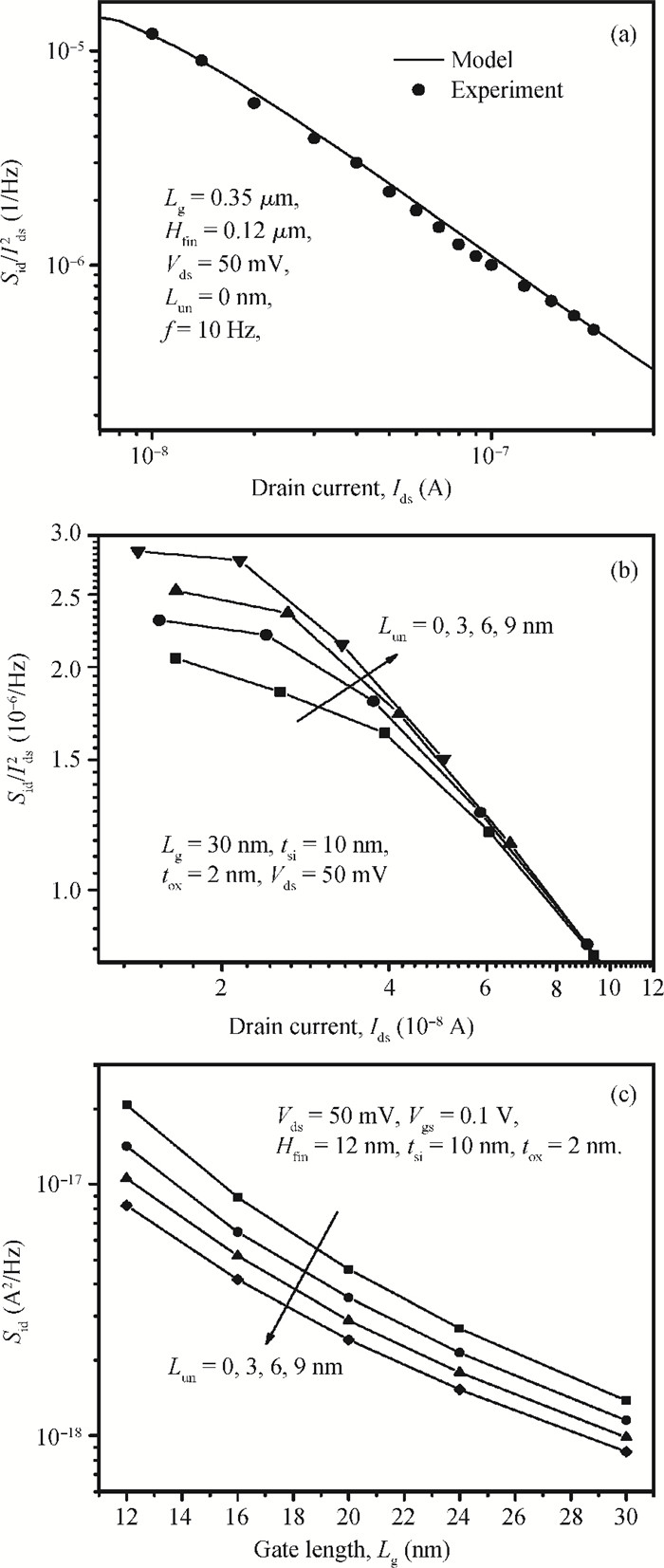
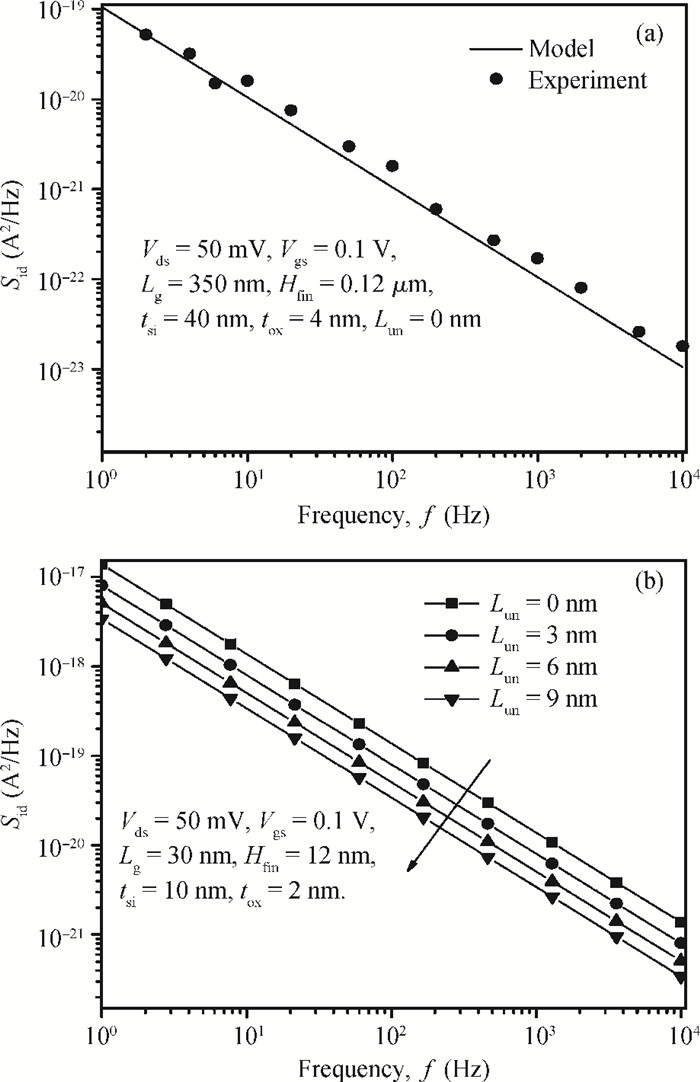
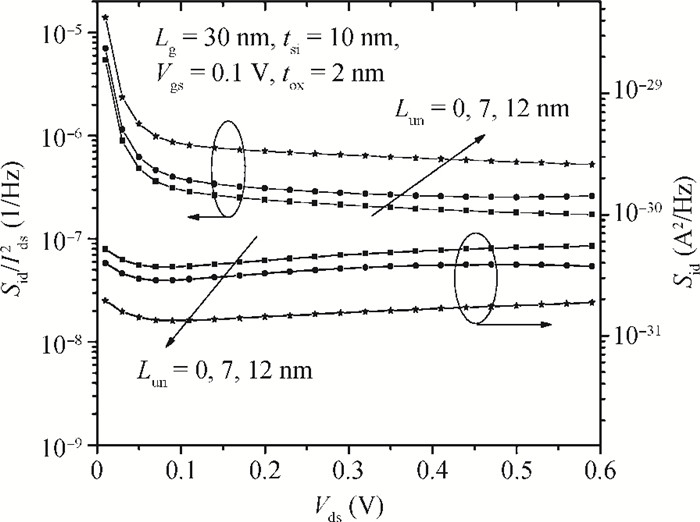
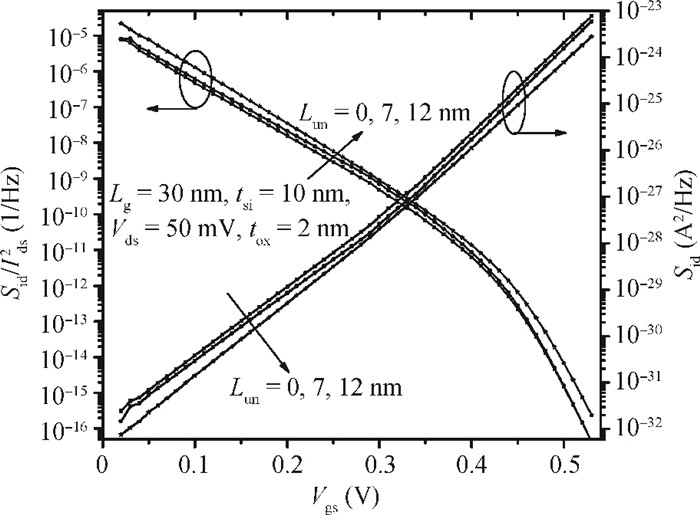
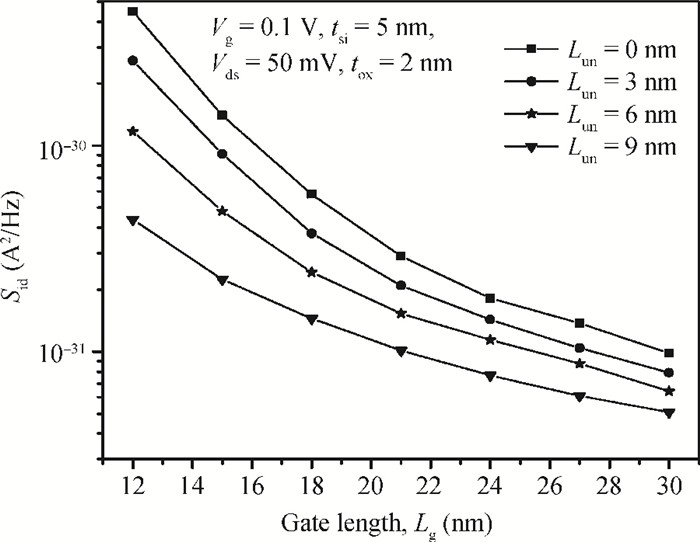
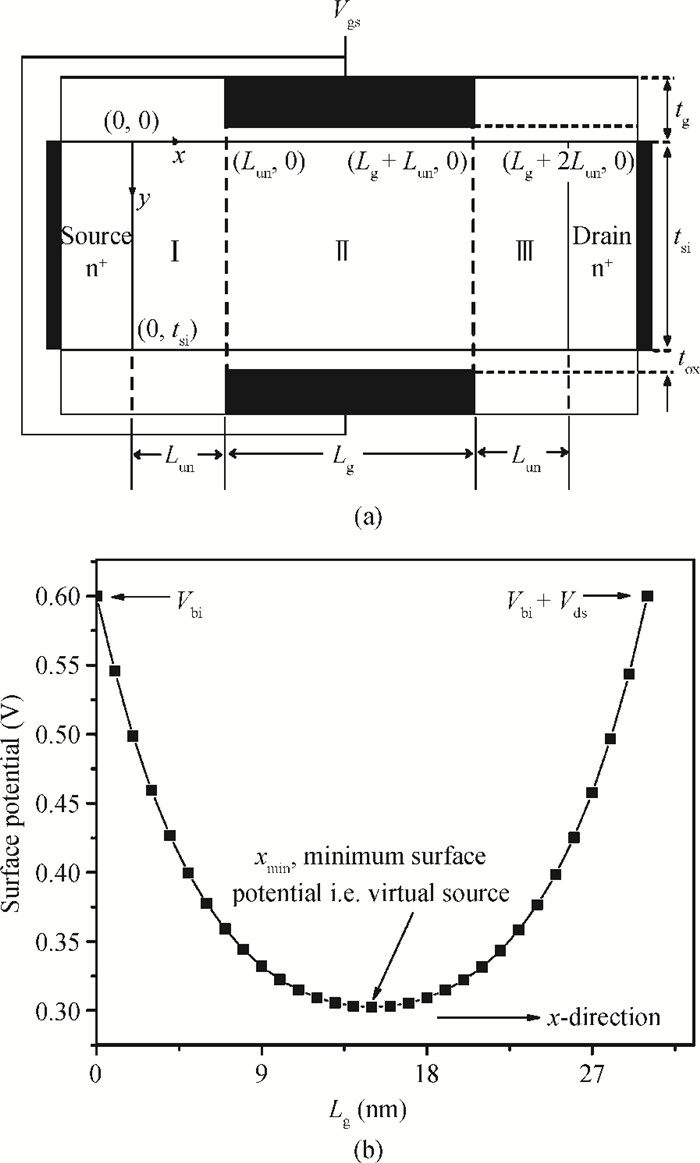
We propose an analytical model for drain current and inversion charge in the subthreshold region for an underlap DG FinFET by using the minimum channel potential method, i.e., the virtual source. The flicker and thermal noise spectral density models are also developed using these charge and current models expression. The model is validated with already published experimental results of flicker noise for DG FinFETs. For an ultrathin body, the degradation of effective mobility and variation of the scattering parameter are considered. The effect of device parameters like gate length Lg and underlap length Lun on both flicker and thermal noise spectral densities are also analyzed. Increasing Lg and Lun, increases the effective gate length, which reduces drain current, resulting in decreased flicker and thermal noise density. A decrease of flicker noise is observed for an increase of frequency, which indicates that the device can be used for wide range of frequency applications.-
Keywords:
- flicker noise,
- thermal noise,
- ultrathin body,
- virtual source,
- underlap DG FinFET
-
References
[1] Trivedi V, Fossum J G, Chowdhury M M, et al. Nanoscale FinFETs with gate source drain underlap. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52(1):56 doi: 10.1109/TED.2004.841333[2] Kim S, Fossum J G, Yang J, et al. Modeling and significance of fringe capacitance in nonclassical CMOS devices with G-S/drain underlap. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2006, 53(9):5 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1677847/[3] Yang J W, Zeitzoff P M, Tseng H H, et al. Highly manufacturable double-gate FinFET with G-S/drain underlap. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54(6):1464 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.896387[4] Pandit S, Syamal B, Sarkar C K, et al. Analytical modeling of flicker and thermal noise in n-channel DG FinFETs. Solid-State Electron, 2011, 63(1):177 doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2011.05.026[5] Hung K K, Ko P K, Hu C, et al. A unified model for the flicker noise in metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1990, 37(3):654 doi: 10.1109/16.47770[6] Vandamme E P, Lode K, Vandamme J, et al. Critical discussion on unified 1/$f$ noise models for MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2000, 47(11):2146 doi: 10.1109/16.877177[7] Li Z, Ma J, Ye Y, et al. Compact channel noise models for deep-submicron MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2009, 56(6):1300 doi: 10.1109/TED.2009.2018160[8] Van der Ziel A. Noise in solid state devices and circuits. New York:Wiley, 1986 http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA00909382[9] Sah C T, Wu S Y, Hielscher F H. The effects of fixed bulk charge on the thermal noise in MOS transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1966, 13(4):410 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1474293/[10] Shoji M. Analysis of high-frequency thermal noise of enhancement mode MOS FETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 1965, 13(6):520 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1474314/?arnumber=1474314[11] Knoblinger G, Klein P, Tiebout M, et al. A new model for thermal channel noise of deep-submicron MOSFETS and its application in RF-CMOS design. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 2001, 36(5):831 doi: 10.1109/4.918922[12] Chen C H, Deen M J. Channel noise modeling of deep submicron MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2002, 49(8):1484 doi: 10.1109/TED.2002.801229[13] Teng H F, Jang S L, Juang M H, et al. A unified model for high-frequency current noise of MOSFETs. Solid-State Electron, 2003, 47(11):2043 doi: 10.1016/S0038-1101(03)00248-X[14] Roy A S, Enz C C. Compact modeling of thermal noise in the MOS transistor. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2005, 52(4):611 doi: 10.1109/TED.2005.844735[15] Bansal A, Member S, Roy K, et al. Analytical subthreshold potential distribution model for gate underlap DG MOS transistors. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54(7):1793 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.898042[16] Vaddi R, Agarwal R P, Dasgupta S, et al. Analytical modeling of subthreshold current and subthreshold swing of an underlap DGMOSFET with tied-independent gate and symmetric-asymmetric options. Microelectron J, 2011, 42(5):798 doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2011.01.004[17] Liang X, Member S, Taur Y, et al. A 2-D analytical solution for SCEs in DG MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2004, 51(8):1385 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1325841/?isnumber=29334&arnumber=1325841&count=33&index=4[18] Dey A, Chakravorty A, Dasgupta N, et al. Analytical model of subthreshold current and slope for asymmetric 4-T and 3-T DG MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2008, 55(12):3442 doi: 10.1109/TED.2008.2006109[19] Moldovan O, Jiménez D, Guitart J R, et al. Explicit analytical charge and capacitance models of undoped DG MOSFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2007, 54(7):1718 doi: 10.1109/TED.2007.899402[20] Roy A S, Enz C C, Sallese J M, et al. Noise modeling methodologies in the presence of mobility degradation and their equivalence. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2006, 53(2):348 doi: 10.1109/TED.2005.862703[21] Wei C, Xiong Y Z, Zhou X. Investigation of low-frequency noise in N-channel FinFETs from weak to strong inversion. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2009, 56(11):2800 doi: 10.1109/TED.2009.2030972[22] Chowdhury M M, Fossum J G. Physical insights on electron mobility in contemporary FinFETs. IEEE Trans Electron Devices, 2006, 27(6):482 doi: 10.1109/LED.2006.874214 -
Proportional views





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: